Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 viewsCH 07
CH 07
Uploaded by
Mohammed Abdul MajidThis document contains multiple physics problems and their solutions. It addresses topics like work, energy, springs, vectors, relativity, and more. The problems involve calculating things like the work done by forces, kinetic energies of objects, speeds and distances traveled, spring constants, and more. The solutions provide quantitative answers to the calculation questions posed in each problem.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Thesis of Sieve Machine 2010Document36 pagesThesis of Sieve Machine 2010nigus gereziher50% (2)
- Examples MomentumDocument9 pagesExamples Momentumettypasewang0% (1)
- Pisiks 71 Prob SetsDocument8 pagesPisiks 71 Prob SetsAndroNo ratings yet
- 004 Problem Sheet 4 - Energy Methods For Particles DEN5108 PS4-2Document4 pages004 Problem Sheet 4 - Energy Methods For Particles DEN5108 PS4-2JoséRobertoNo ratings yet
- P6 TonetDocument12 pagesP6 TonetAlyssa Fermin0% (1)
- PhyDocument56 pagesPhyJohn Ray CuevasNo ratings yet
- Physics I ProblemsDocument1 pagePhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNo ratings yet
- 8 CE199L-1 Physics2Document3 pages8 CE199L-1 Physics2IwaNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Physics Problem SetDocument3 pagesPhysics Problem SetLilian GauiranNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document4 pagesTutorial 5Cheryl LowNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Force and MotionDocument4 pagesChapter 3 - Force and MotionJerico LlovidoNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1 FinalsDocument2 pagesProblem Set 1 FinalsJaysel PamittanNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document4 pagesCH 10Mohammed Abdul MajidNo ratings yet
- CH 05Document6 pagesCH 05Mohammed Abdul MajidNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM - SOLVING - Friction and 2nd Law UstDocument34 pagesPROBLEM - SOLVING - Friction and 2nd Law UstMarj Ladica MangaNo ratings yet
- Extra Problem Phys 1 CH 3Document2 pagesExtra Problem Phys 1 CH 3Tú NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Extra Problem Phys 1 CH 3Document2 pagesExtra Problem Phys 1 CH 3Quỳnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Grav and Energy Practice AP: Multiple ChoiceDocument11 pagesGrav and Energy Practice AP: Multiple ChoiceJohnNo ratings yet
- Extra Problem Phys 1 CH 3Document2 pagesExtra Problem Phys 1 CH 311Sinh1-16-Nguyễn Phúc QuangNo ratings yet
- Extra Problem Phys 1 CH 3Document2 pagesExtra Problem Phys 1 CH 3Thu HòaNo ratings yet
- Standard of Excellence Work Energy ProblemsDocument2 pagesStandard of Excellence Work Energy ProblemsNamhey MaanNo ratings yet
- PHYS1020 Practice Test 2 SolutionsDocument10 pagesPHYS1020 Practice Test 2 SolutionsAaisha SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Examples 2 MeasurementDocument43 pagesExamples 2 Measurementmoon starNo ratings yet
- Work Energy Worksheet 1Document5 pagesWork Energy Worksheet 1TheOnesNo ratings yet
- HowDocument43 pagesHowAudrey Ruth V. SirunoNo ratings yet
- FHSC1014 Mechanics Tutorial 5Document3 pagesFHSC1014 Mechanics Tutorial 5许敬霖No ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet - 5Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet - 5chewe chewe100% (1)
- Rev2, ENGR 62, StanfordDocument40 pagesRev2, ENGR 62, StanfordsuudsfiinNo ratings yet
- CH 06Document3 pagesCH 06Mohammed Abdul MajidNo ratings yet
- Laboratory No. 2 F DynamicsDocument2 pagesLaboratory No. 2 F Dynamicsjutr ruyluNo ratings yet
- Problems On DynamicsDocument3 pagesProblems On DynamicsPablo AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Work, Energy and PowerDocument5 pagesTutorial Work, Energy and PowerAimeenul AzfarNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems 11 - Dynamics Part 2Document1 pagePractice Problems 11 - Dynamics Part 2Jayve BasconNo ratings yet
- Recitation CH 4 1 CompressDocument6 pagesRecitation CH 4 1 Compressallan zenarosaNo ratings yet
- Physics 11Document12 pagesPhysics 11Jane100% (1)
- Physics I ProblemsDocument1 pagePhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- 221HCh04 PDFDocument25 pages221HCh04 PDFisele1977No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - DynamicsDocument8 pagesChapter 2 - DynamicsTHIÊN LÊ TRẦN THUẬNNo ratings yet
- Extra Problem Phys 1 CH 2Document2 pagesExtra Problem Phys 1 CH 2Quỳnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- 2022 - Tutorial - 5 - Work - Energy - PowerDocument3 pages2022 - Tutorial - 5 - Work - Energy - PowerBEN CHILUFYANo ratings yet
- Quiz 2Document5 pagesQuiz 2Nurul AinNo ratings yet
- Practice Test2 ps150Document3 pagesPractice Test2 ps150Antoine S. NdiayeNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document2 pagesTutorial 2Clinton DebrahNo ratings yet
- Tut Test 4 MemoDocument8 pagesTut Test 4 MemoVogelNo ratings yet
- Physics - Textbook - Cambridge 6th Edition 2014.pdf - ExtractDocument2 pagesPhysics - Textbook - Cambridge 6th Edition 2014.pdf - ExtractTheodore KimNo ratings yet
- 1st Yr Hy 09Document4 pages1st Yr Hy 09Grezzju CauchiNo ratings yet
- Topic 7: Kinetics: Momentum: The Quantity of Motion Possessed by A Moving BodyDocument3 pagesTopic 7: Kinetics: Momentum: The Quantity of Motion Possessed by A Moving BodyTom ManNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-Dynamics-Kinematics-KineticsDocument36 pagesChapter 6-Dynamics-Kinematics-Kineticsعمر صرانNo ratings yet
- All AnswersDocument22 pagesAll AnswersNadiatul JannahNo ratings yet
- Work Energy Power 1Document4 pagesWork Energy Power 1Gaming baseNo ratings yet
- Unit-Two INSTRUCTION - Work Out The Following ProblemsDocument3 pagesUnit-Two INSTRUCTION - Work Out The Following ProblemsKhalid A.No ratings yet
- Unit-Two INSTRUCTION - Work Out The Following ProblemsDocument3 pagesUnit-Two INSTRUCTION - Work Out The Following ProblemsKhalid A.No ratings yet
- Tutorial Das14103 - Chapter 6Document4 pagesTutorial Das14103 - Chapter 6Najiha SufianNo ratings yet
- Assignment PHY12Document7 pagesAssignment PHY12Nadine FrisnediNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- CH 13Document4 pagesCH 13Mohammed Abdul MajidNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document4 pagesCH 10Mohammed Abdul MajidNo ratings yet
- CH 04Document3 pagesCH 04Mohammed Abdul MajidNo ratings yet
- CH 06Document3 pagesCH 06Mohammed Abdul MajidNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document3 pagesCH 02Mohammed Abdul MajidNo ratings yet
- CH 05Document6 pagesCH 05Mohammed Abdul MajidNo ratings yet
- What Is The Meaning of The Wave Function?Document20 pagesWhat Is The Meaning of The Wave Function?nNo ratings yet
- Ch.4 Elastic Collisions in 1DDocument1 pageCh.4 Elastic Collisions in 1D17latifaNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 2 NotesDocument35 pagesPhysics Form 2 NotesLeon MzarabaniNo ratings yet
- Forces and Motion1Document29 pagesForces and Motion1DesNo ratings yet
- GRFP01 CRU Gr12 Ch01 ALLDocument20 pagesGRFP01 CRU Gr12 Ch01 ALLNyiNo ratings yet
- CHM02 - CO1 - LESSON2 - Intermolecular ForceDocument20 pagesCHM02 - CO1 - LESSON2 - Intermolecular ForceMeg IglianeNo ratings yet
- FE-based Multiscale Modelling of Soft Acoustic MetamaterialsDocument8 pagesFE-based Multiscale Modelling of Soft Acoustic MetamaterialsDonald ZekaNo ratings yet
- PMC Mock Test 1 by WisegotDocument17 pagesPMC Mock Test 1 by WisegotblahNo ratings yet
- Unit I-D - Defects in SolidsDocument16 pagesUnit I-D - Defects in Solidsjyoti kumariNo ratings yet
- Planck Units - WikipediaDocument24 pagesPlanck Units - WikipediaSrujan SubashNo ratings yet
- Pptu-5 Oscillation 1Document19 pagesPptu-5 Oscillation 1Abraham DamtewNo ratings yet
- Franco Ivaldi - Concept of Energy Seen in The Light of Resonance PhysicsDocument10 pagesFranco Ivaldi - Concept of Energy Seen in The Light of Resonance PhysicsJoel Gallardo ParamoNo ratings yet
- Graduation Project PV English VersionDocument56 pagesGraduation Project PV English VersionabidineNo ratings yet
- String Theory Research ContentDocument7 pagesString Theory Research ContentAround the WorldNo ratings yet
- Session 16 - Newton's LawsDocument35 pagesSession 16 - Newton's LawsClemence Marie FuentesNo ratings yet
- 16 - Clicker - Question SolutionsDocument9 pages16 - Clicker - Question SolutionsFati AzNo ratings yet
- Conducting MaterialsDocument9 pagesConducting MaterialsGauri Deshmukh KaranjgaokarNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Week 16Document6 pagesScience 10 - Week 16Mira VeranoNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure TheoryDocument36 pagesAtomic Structure TheoryDhritismita KalitaNo ratings yet
- Tugas TTT A - 1910953009 - Muhammad Fajar Ruhud ManurungDocument8 pagesTugas TTT A - 1910953009 - Muhammad Fajar Ruhud ManurungFajar AsheqafNo ratings yet
- Modern PhysicsDocument37 pagesModern Physicsgambo_dcNo ratings yet
- Algebra Assignment 7 TransformationDocument14 pagesAlgebra Assignment 7 TransformationĐỗ ĐạtNo ratings yet
- Physics DPP XDocument15 pagesPhysics DPP XAlok RanjanNo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual For Fluid Mechanics 5th PDFDocument20 pagesSolutions Manual For Fluid Mechanics 5th PDFchala nigussieNo ratings yet
- Recombination of Electrons in SemiconductorDocument6 pagesRecombination of Electrons in SemiconductorAnkit ThalorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Wave Optics PDFDocument22 pagesChapter 10 Wave Optics PDFMohitha Reddy CNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Science Reviwer 2nd QuarterDocument8 pagesGrade 10 Science Reviwer 2nd Quartercharlize roque100% (1)
- BUMHS MDCAT Past PapersDocument26 pagesBUMHS MDCAT Past Papersfirasahmed171No ratings yet
- Kinematics, Decays and Reactions: Particle and Nuclear PhysicsDocument42 pagesKinematics, Decays and Reactions: Particle and Nuclear Physicsaleacunia87No ratings yet
CH 07
CH 07
Uploaded by
Mohammed Abdul Majid0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views4 pagesThis document contains multiple physics problems and their solutions. It addresses topics like work, energy, springs, vectors, relativity, and more. The problems involve calculating things like the work done by forces, kinetic energies of objects, speeds and distances traveled, spring constants, and more. The solutions provide quantitative answers to the calculation questions posed in each problem.
Original Description:
Original Title
ch07
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains multiple physics problems and their solutions. It addresses topics like work, energy, springs, vectors, relativity, and more. The problems involve calculating things like the work done by forces, kinetic energies of objects, speeds and distances traveled, spring constants, and more. The solutions provide quantitative answers to the calculation questions posed in each problem.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views4 pagesCH 07
CH 07
Uploaded by
Mohammed Abdul MajidThis document contains multiple physics problems and their solutions. It addresses topics like work, energy, springs, vectors, relativity, and more. The problems involve calculating things like the work done by forces, kinetic energies of objects, speeds and distances traveled, spring constants, and more. The solutions provide quantitative answers to the calculation questions posed in each problem.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
1, 2, 3 = straightforward, intermediate, second spring (acting with the first)
challenging increases the force so that additional
compression occurs, as shown in the graph.
1. A tugboat exerts a constant force of If the car is brought to rest 50.0 cm after
5 000 N on a ship moving at constant speed first contacting the two-spring system, find
through a harbor. How much work does the car’s initial speed.
the tugboat do on the ship in a distance of
3.00 km?
Answer: 15.0 MJ
4. A sledge loaded with bricks has a
total mass of 18.0 kg and is pulled at
constant speed by a rope. The rope is
inclined at 20.0° above the horizontal, and
the sledge moves a distance of 20.0 m on a
horizontal surface. The coefficient of kinetic
friction between the sledge and the surface
is 0.500. (a) What is the tension of the rope?
(b) How much work is done on the sledge
by the rope? (c) What is the energy lost due
to friction?
Answer: (a) 79.4 N; (b) 1.49 kJ; (c) –1.49 kJ
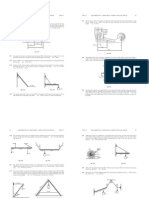
Figure P7.21
9. Vector A extends from the origin to a
Answer: 0.299 m/s
point having polar coordinates (7, 70°), and
vector B extends from the origin to a point
24. If it takes work W to stretch a
having polar coordinates (4, 130°). Find A ·
Hooke’s-law spring a distance d from its
B.
unstressed length, determine the extra work
required to stretch it an additional distance
Answer: 14.0
d.
21. A 6 000-kg freight car rolls along
Answer: 3W
rails with negligible friction. The car is
brought to rest by a combination of two
30. A mechanic pushes a 2 500-kg car,
coiled springs, as illustrated in Figure P7.21.
moving it from rest and making it
Both springs obey Hooke’s law with k1 =
accelerate from rest to a speed v. He does
1 600 N/m and k2 = 3 400 N/m. After the first
5 000 J of work in the process. During this
spring compresses a distance of 30.0 cm, the
time, the car moves 25.0 m. If friction 44. If a certain horse can maintain 1.00
between the car and the road is negligible, hp of output for 2.00 h, how many 70.0-kg
(a) what is the final speed v of the car? (b) bundles of shingles can the horse hoist
What constant horizontal force did he exert (using some pulley arrangement) to the
on the car? roof of a house 8.00 m tall, assuming 70.0%
efficiency?
Answer: (a) 2.00 m/s; (b) 200 N
Answer: 685 bundles
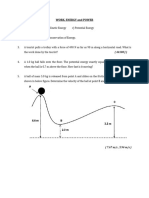
36. A block of mass 12.0 kg slides from
rest down a frictionless 35.0° incline and is 45. A certain automobile engine delivers
stopped by a strong spring with k = 3.0 × 104 2.24 × 104 W (30.0 hp) to its wheels when
N/m. The block slides 3.00 m from the point moving at a constant speed of 27.0 m/s (≈ 60
of release to the point where it comes to rest mi/h). What is the resistive force acting on
against the spring. When the block comes to the automobile at that speed?
rest, how far has the spring been
compressed? Answer: 830 N
Answer: 0.116 m 51. When an air conditioner is added to
the car described in Problem 50, the
39. A bullet with a mass of 5.00 g and a additional output power required to
speed of 600 m/s penetrates a tree to a operate the air conditioner is 1.54 kW. If the
depth of 4.00 cm. (a) Use work and energy fuel economy of the car is 6.40 km/L
considerations to find the average frictional without the air conditioner, what is it when
force that stops the bullet. (b) Assuming the air conditioner is operating?
that the frictional force is constant,
determine how much time elapsed between Answer: 5.90 km/L
the moment the bullet entered the tree and
the moment it stopped. 52. An electron moves with a speed of
0.995c. (a) What is its kinetic energy? (b) If
Answer: (a) 2.25 × 104 N; (b) 1.33 × 10–4 s you use the classical expression to calculate
its kinetic energy, what percentage error
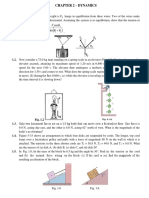
40. An Atwood’s machine (see Fig. 5.15) results?
supports masses of 0.200 kg and 0.300 kg.
The masses are held at rest beside each Answer: (a) 7.38 × 10–13 J; (b) 94.5%
other and then released. Neglecting friction,
what is the speed of each mass the instant it 53. A proton in a high-energy
has moved 0.400 m? accelerator moves with a speed of c/2.
Using the work–kinetic energy theorem,
Answer: 1.25 m/s
find the work required to increase its speed the rail. When subject to a steady
to (a) 0.750c and (b) 0.995c. acceleration of 0.800g, the mass is to assume
a location 0.500 cm away from its
Answer: (a) 5.37 × 10–11 J; (b) 1.33 × 10–9 J equilibrium position. Find the stiffness
constant required for the spring.
54. Find the kinetic energy of a 78.0-kg
spacecraft launched out of the Solar System Answer: 7.37 N/m
with a speed of 106 km/s using (a) the
classical equation K = ½ mv2 and (b) the 64. A cyclist and her bicycle have a
relativistic equation. combined mass of 75.0 kg. She coasts down
a road inclined at 2.00° with the horizontal
Answer: (a) 4.38 × 1011 J; (b) 4.38 × 1011 J at 4.00 m/s and down a road inclined at
4.00° at 8.00 m/s. She then holds on to a
57. A particle of mass m moves with a moving vehicle and coasts on a level road.
constant acceleration a. If the initial position What power must the vehicle expend to
vector and velocity of the particle are ri and maintain her speed at 3.00 m/s? Assume
vi, respectively, use energy arguments to that the force of air resistance is
show that its speed vf at any time satisfies proportional to her speed and that other
the equation frictional forces remain constant. (Warning:
You must not attempt this dangerous
vf 2 = vi2 + 2a · (rf – ri) maneuver.)
where rf is the position vector of the particle Answer: 57.7 W
at that same time.
73. A horizontal string is attached to a
Answer: vi2 + 2a ∙ (r – ri) = vf2 0.250-kg mass lying on a rough, horizontal
table. The string passes over a light,
61. When a certain spring is stretched frictionless pulley, and a 0.400-kg mass is
beyond its proportional limit, the restoring then attached to its free end. The coefficient
force satisfies the equation F = –kx + βx3. If k of sliding friction between the 0.250-kg
= 10.0 N/m and β = 100 N/m3, calculate the mass and the table is 0.200. Using the work–
work done by this force when the spring is kinetic energy theorem, determine (a) the
stretched 0.100 m. speed of the masses after each has moved
20.0 m from rest and (b) the mass that must
Answer: –4.75 × 10–2 J be added to the 0.250-kg mass so that, given
an initial velocity, the masses continue to
62. In a control system, an accelerometer move at a constant speed. (c) What mass
consists of a 4.70-g mass sliding on a low- must be removed from the 0.400-kg mass so
friction horizontal rail. A low-mass spring that the same outcome as in part (b) is
attaches the mass to a flange at one end of achieved?
Answer: (a) 14.5 m/s; (b) 1.75 kg; (c) 0.350
kg
You might also like
- Thesis of Sieve Machine 2010Document36 pagesThesis of Sieve Machine 2010nigus gereziher50% (2)
- Examples MomentumDocument9 pagesExamples Momentumettypasewang0% (1)
- Pisiks 71 Prob SetsDocument8 pagesPisiks 71 Prob SetsAndroNo ratings yet
- 004 Problem Sheet 4 - Energy Methods For Particles DEN5108 PS4-2Document4 pages004 Problem Sheet 4 - Energy Methods For Particles DEN5108 PS4-2JoséRobertoNo ratings yet
- P6 TonetDocument12 pagesP6 TonetAlyssa Fermin0% (1)
- PhyDocument56 pagesPhyJohn Ray CuevasNo ratings yet
- Physics I ProblemsDocument1 pagePhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNo ratings yet
- 8 CE199L-1 Physics2Document3 pages8 CE199L-1 Physics2IwaNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Physics Problem SetDocument3 pagesPhysics Problem SetLilian GauiranNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document4 pagesTutorial 5Cheryl LowNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Force and MotionDocument4 pagesChapter 3 - Force and MotionJerico LlovidoNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1 FinalsDocument2 pagesProblem Set 1 FinalsJaysel PamittanNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document4 pagesCH 10Mohammed Abdul MajidNo ratings yet
- CH 05Document6 pagesCH 05Mohammed Abdul MajidNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM - SOLVING - Friction and 2nd Law UstDocument34 pagesPROBLEM - SOLVING - Friction and 2nd Law UstMarj Ladica MangaNo ratings yet
- Extra Problem Phys 1 CH 3Document2 pagesExtra Problem Phys 1 CH 3Tú NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Extra Problem Phys 1 CH 3Document2 pagesExtra Problem Phys 1 CH 3Quỳnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Grav and Energy Practice AP: Multiple ChoiceDocument11 pagesGrav and Energy Practice AP: Multiple ChoiceJohnNo ratings yet
- Extra Problem Phys 1 CH 3Document2 pagesExtra Problem Phys 1 CH 311Sinh1-16-Nguyễn Phúc QuangNo ratings yet
- Extra Problem Phys 1 CH 3Document2 pagesExtra Problem Phys 1 CH 3Thu HòaNo ratings yet
- Standard of Excellence Work Energy ProblemsDocument2 pagesStandard of Excellence Work Energy ProblemsNamhey MaanNo ratings yet
- PHYS1020 Practice Test 2 SolutionsDocument10 pagesPHYS1020 Practice Test 2 SolutionsAaisha SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Examples 2 MeasurementDocument43 pagesExamples 2 Measurementmoon starNo ratings yet
- Work Energy Worksheet 1Document5 pagesWork Energy Worksheet 1TheOnesNo ratings yet
- HowDocument43 pagesHowAudrey Ruth V. SirunoNo ratings yet
- FHSC1014 Mechanics Tutorial 5Document3 pagesFHSC1014 Mechanics Tutorial 5许敬霖No ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet - 5Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet - 5chewe chewe100% (1)
- Rev2, ENGR 62, StanfordDocument40 pagesRev2, ENGR 62, StanfordsuudsfiinNo ratings yet
- CH 06Document3 pagesCH 06Mohammed Abdul MajidNo ratings yet
- Laboratory No. 2 F DynamicsDocument2 pagesLaboratory No. 2 F Dynamicsjutr ruyluNo ratings yet
- Problems On DynamicsDocument3 pagesProblems On DynamicsPablo AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Work, Energy and PowerDocument5 pagesTutorial Work, Energy and PowerAimeenul AzfarNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems 11 - Dynamics Part 2Document1 pagePractice Problems 11 - Dynamics Part 2Jayve BasconNo ratings yet
- Recitation CH 4 1 CompressDocument6 pagesRecitation CH 4 1 Compressallan zenarosaNo ratings yet
- Physics 11Document12 pagesPhysics 11Jane100% (1)
- Physics I ProblemsDocument1 pagePhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- 221HCh04 PDFDocument25 pages221HCh04 PDFisele1977No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - DynamicsDocument8 pagesChapter 2 - DynamicsTHIÊN LÊ TRẦN THUẬNNo ratings yet
- Extra Problem Phys 1 CH 2Document2 pagesExtra Problem Phys 1 CH 2Quỳnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- 2022 - Tutorial - 5 - Work - Energy - PowerDocument3 pages2022 - Tutorial - 5 - Work - Energy - PowerBEN CHILUFYANo ratings yet
- Quiz 2Document5 pagesQuiz 2Nurul AinNo ratings yet
- Practice Test2 ps150Document3 pagesPractice Test2 ps150Antoine S. NdiayeNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document2 pagesTutorial 2Clinton DebrahNo ratings yet
- Tut Test 4 MemoDocument8 pagesTut Test 4 MemoVogelNo ratings yet
- Physics - Textbook - Cambridge 6th Edition 2014.pdf - ExtractDocument2 pagesPhysics - Textbook - Cambridge 6th Edition 2014.pdf - ExtractTheodore KimNo ratings yet
- 1st Yr Hy 09Document4 pages1st Yr Hy 09Grezzju CauchiNo ratings yet
- Topic 7: Kinetics: Momentum: The Quantity of Motion Possessed by A Moving BodyDocument3 pagesTopic 7: Kinetics: Momentum: The Quantity of Motion Possessed by A Moving BodyTom ManNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-Dynamics-Kinematics-KineticsDocument36 pagesChapter 6-Dynamics-Kinematics-Kineticsعمر صرانNo ratings yet
- All AnswersDocument22 pagesAll AnswersNadiatul JannahNo ratings yet
- Work Energy Power 1Document4 pagesWork Energy Power 1Gaming baseNo ratings yet
- Unit-Two INSTRUCTION - Work Out The Following ProblemsDocument3 pagesUnit-Two INSTRUCTION - Work Out The Following ProblemsKhalid A.No ratings yet
- Unit-Two INSTRUCTION - Work Out The Following ProblemsDocument3 pagesUnit-Two INSTRUCTION - Work Out The Following ProblemsKhalid A.No ratings yet
- Tutorial Das14103 - Chapter 6Document4 pagesTutorial Das14103 - Chapter 6Najiha SufianNo ratings yet
- Assignment PHY12Document7 pagesAssignment PHY12Nadine FrisnediNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- CH 13Document4 pagesCH 13Mohammed Abdul MajidNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document4 pagesCH 10Mohammed Abdul MajidNo ratings yet
- CH 04Document3 pagesCH 04Mohammed Abdul MajidNo ratings yet
- CH 06Document3 pagesCH 06Mohammed Abdul MajidNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document3 pagesCH 02Mohammed Abdul MajidNo ratings yet
- CH 05Document6 pagesCH 05Mohammed Abdul MajidNo ratings yet
- What Is The Meaning of The Wave Function?Document20 pagesWhat Is The Meaning of The Wave Function?nNo ratings yet
- Ch.4 Elastic Collisions in 1DDocument1 pageCh.4 Elastic Collisions in 1D17latifaNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 2 NotesDocument35 pagesPhysics Form 2 NotesLeon MzarabaniNo ratings yet
- Forces and Motion1Document29 pagesForces and Motion1DesNo ratings yet
- GRFP01 CRU Gr12 Ch01 ALLDocument20 pagesGRFP01 CRU Gr12 Ch01 ALLNyiNo ratings yet
- CHM02 - CO1 - LESSON2 - Intermolecular ForceDocument20 pagesCHM02 - CO1 - LESSON2 - Intermolecular ForceMeg IglianeNo ratings yet
- FE-based Multiscale Modelling of Soft Acoustic MetamaterialsDocument8 pagesFE-based Multiscale Modelling of Soft Acoustic MetamaterialsDonald ZekaNo ratings yet
- PMC Mock Test 1 by WisegotDocument17 pagesPMC Mock Test 1 by WisegotblahNo ratings yet
- Unit I-D - Defects in SolidsDocument16 pagesUnit I-D - Defects in Solidsjyoti kumariNo ratings yet
- Planck Units - WikipediaDocument24 pagesPlanck Units - WikipediaSrujan SubashNo ratings yet
- Pptu-5 Oscillation 1Document19 pagesPptu-5 Oscillation 1Abraham DamtewNo ratings yet
- Franco Ivaldi - Concept of Energy Seen in The Light of Resonance PhysicsDocument10 pagesFranco Ivaldi - Concept of Energy Seen in The Light of Resonance PhysicsJoel Gallardo ParamoNo ratings yet
- Graduation Project PV English VersionDocument56 pagesGraduation Project PV English VersionabidineNo ratings yet
- String Theory Research ContentDocument7 pagesString Theory Research ContentAround the WorldNo ratings yet
- Session 16 - Newton's LawsDocument35 pagesSession 16 - Newton's LawsClemence Marie FuentesNo ratings yet
- 16 - Clicker - Question SolutionsDocument9 pages16 - Clicker - Question SolutionsFati AzNo ratings yet
- Conducting MaterialsDocument9 pagesConducting MaterialsGauri Deshmukh KaranjgaokarNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Week 16Document6 pagesScience 10 - Week 16Mira VeranoNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure TheoryDocument36 pagesAtomic Structure TheoryDhritismita KalitaNo ratings yet
- Tugas TTT A - 1910953009 - Muhammad Fajar Ruhud ManurungDocument8 pagesTugas TTT A - 1910953009 - Muhammad Fajar Ruhud ManurungFajar AsheqafNo ratings yet
- Modern PhysicsDocument37 pagesModern Physicsgambo_dcNo ratings yet
- Algebra Assignment 7 TransformationDocument14 pagesAlgebra Assignment 7 TransformationĐỗ ĐạtNo ratings yet
- Physics DPP XDocument15 pagesPhysics DPP XAlok RanjanNo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual For Fluid Mechanics 5th PDFDocument20 pagesSolutions Manual For Fluid Mechanics 5th PDFchala nigussieNo ratings yet
- Recombination of Electrons in SemiconductorDocument6 pagesRecombination of Electrons in SemiconductorAnkit ThalorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Wave Optics PDFDocument22 pagesChapter 10 Wave Optics PDFMohitha Reddy CNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Science Reviwer 2nd QuarterDocument8 pagesGrade 10 Science Reviwer 2nd Quartercharlize roque100% (1)
- BUMHS MDCAT Past PapersDocument26 pagesBUMHS MDCAT Past Papersfirasahmed171No ratings yet
- Kinematics, Decays and Reactions: Particle and Nuclear PhysicsDocument42 pagesKinematics, Decays and Reactions: Particle and Nuclear Physicsaleacunia87No ratings yet