Professional Documents
Culture Documents
04-Data Types
04-Data Types
Uploaded by
Devotional Songs0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views10 pagesThis document discusses different data types in C programming. It describes basic data types like integer, character, floating point, and double floating point. It also discusses derived data types like pointers, functions, and arrays. User-defined types like struct, union, and typedef are also mentioned. The document then provides details on the size and range of each data type for Turbo C and gcc compilers. It highlights some points to remember regarding data types and qualifiers. Finally, it elaborates on integer, floating point, double precision, and character data types.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses different data types in C programming. It describes basic data types like integer, character, floating point, and double floating point. It also discusses derived data types like pointers, functions, and arrays. User-defined types like struct, union, and typedef are also mentioned. The document then provides details on the size and range of each data type for Turbo C and gcc compilers. It highlights some points to remember regarding data types and qualifiers. Finally, it elaborates on integer, floating point, double precision, and character data types.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views10 pages04-Data Types
04-Data Types
Uploaded by
Devotional SongsThis document discusses different data types in C programming. It describes basic data types like integer, character, floating point, and double floating point. It also discusses derived data types like pointers, functions, and arrays. User-defined types like struct, union, and typedef are also mentioned. The document then provides details on the size and range of each data type for Turbo C and gcc compilers. It highlights some points to remember regarding data types and qualifiers. Finally, it elaborates on integer, floating point, double precision, and character data types.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 10
Programming Logic
Data Types
B.Bhuvaneswaran, AP (SG) / CSE
9791519152
bhuvaneswaran@rajalakshmi.edu.in
Data Types
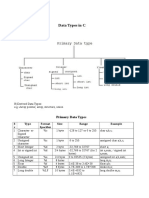
Basic (or primary or fundamental) data types:
• Integer (int)
• Character (char)
• Floating point (float) and
• Double floating point (double).
Derived data types: Derived data types are pointers, functions and
arrays.
User-defined types: struct, union and typedef are user-defined
data types.
void data type
Data Types Rajalakshmi Engineering College 2
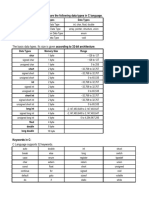
Size & Range of Data Types (Turbo C)
Type Length Range
unsigned char 8 bits 0 to 255
char (or) signed char 8 bits -128 to 127
unsigned int 16 bits 0 to 65,535
short (or) short int (or) signed short int 16 bits -32,768 to 32,767
int (or) signed int 16 bits -32,768 to 32,767
unsigned long (or) unsigned long int 32 bits 0 to 4,294,967,295
long (or) long int (or) signed long int 32 bits -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647
3.4 *(10**-38) to 3.4 * (10**+38)
float 32 bits
3.4E-38 to 3.4E+38
1.7 * (10**-308) to 1.7 * (10**+308)
double 64 bits
1.7E-308 to 1.7E+308
3.4 * (10**-4932) to 1.1 * (10**+4932)
long double 80 bits
3.4E-4932 to 1.1E+4932
Data Types Rajalakshmi Engineering College 3
Size & Range of Data Types (gcc)
Type Length Range
unsigned char 8 bits 0 to 255
char (or) signed char 8 bits -128 to 127
unsigned int 32 bits 0 to 4,294,967,295
short (or) short int (or) signed short int 16 bits -32,768 to 32,767
int (or) signed int 32 bits -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647
unsigned long (or) unsigned long int 32 bits 0 to 4,294,967,295
long (or) long int (or) signed long int 32 bits -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647
3.4 *(10**-38) to 3.4 * (10**+38)
float 32 bits
3.4E-38 to 3.4E+38
1.7 * (10**-308) to 1.7 * (10**+308)
double 64 bits
1.7E-308 to 1.7E+308
3.36210 * (10**-4932) to 1.18973 * (10**+4932)
long double 96 bits
3.36210E-4932 to 1.18973E+4932
Data Types Rajalakshmi Engineering College 4
Points to Remember
When an adjective (qualifier) short, long or unsigned is used with
a basic data type specifier, C compilers treat the data type as int.
If we want to declare a character variable as unsigned, then we
must do so using both the terms unsigned char.
Data Types Rajalakshmi Engineering College 5
Integer Data Type
Integers are whole numbers with a range supported by a
particular machine.
They have no fractional parts.
Integers are represented in C by int data type. An identifier
declared as int becomes an integer variable and can hold integer
values only.
Data Types Rajalakshmi Engineering College 6
Floating Point Data Type
Floating point (or real) numbers are stored in 32 bits (on all 16 bit
and 32 bit machines) with 6 digits of precision.
A number having fractional part is a called floating point number.
For example, the number 12 is an integer, but 12.0 is a floating
point number.
Floating point numbers can also be written in exponent form.
An identifier declared as float data type becomes a floating point
variable and can hold floating point numbers only.
Data Types Rajalakshmi Engineering College 7
Double Precision Data Type
When the accuracy provided by a float number is not sufficient,
the type double can be used to define the number.
A double data type number uses 64 bits giving a precision of 14
digits.
These are known as double precision numbers.
To extend the precision further, use long double.
Data Types Rajalakshmi Engineering College 8
Character Data Type
A single character can be defined as a character (char) type data.
An identifier declared as char data type becomes a character
variable.
Characters are usually stored in 1 byte (8 bits) of internal storage.
The qualifiers signed or unsigned may be explicitly applied to char.
A signed char is same as ordinary char and has range from -128 to
127, whereas unsigned char has a range from 0 to 255.
Data Types Rajalakshmi Engineering College 9
Thank You
You might also like
- Itm 207 ExamDocument20 pagesItm 207 ExamKai BowenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 09 Embedded Firmware Design and DevelopmentDocument63 pagesChapter 09 Embedded Firmware Design and DevelopmentAbhishek73% (15)
- CBLM-Computer ProgrammingDocument90 pagesCBLM-Computer ProgrammingJERIKO PELIMIANO100% (1)
- Data Types in CDocument3 pagesData Types in Cayan shaikhNo ratings yet
- C Data Types and Sizes: No Data Type Full Form Range of ValuesDocument2 pagesC Data Types and Sizes: No Data Type Full Form Range of ValuesNanda KumarNo ratings yet
- CS3353 Unit1Document43 pagesCS3353 Unit1Padmapriya ThianuNo ratings yet
- Data Types in C Language: Int Float Char VoidDocument3 pagesData Types in C Language: Int Float Char VoidThe Indian MenNo ratings yet
- Data TypeDocument6 pagesData TypeAquibul Rehman NadafNo ratings yet
- Introduction To C ProgrammingDocument13 pagesIntroduction To C ProgrammingLokesh KhedekarNo ratings yet
- Sizes and Ranges of Basic Data Types in C For A 16 Bit ComputerDocument1 pageSizes and Ranges of Basic Data Types in C For A 16 Bit ComputerPriyanka DobhalNo ratings yet
- Data PDFDocument8 pagesData PDFAhmed MatarNo ratings yet
- C Sharp (C#) Online Training: By: Ajeet KumarDocument21 pagesC Sharp (C#) Online Training: By: Ajeet KumarKumar KashyapNo ratings yet
- C Notes - Module1Document35 pagesC Notes - Module1Manish GuptaNo ratings yet
- Variable, Expressions, Statements and OperatorsDocument28 pagesVariable, Expressions, Statements and OperatorsShahid NiaziNo ratings yet
- Variable, Expressions, Statements and Operators: By: Daniel T. Ursulum, Jr. CSU - SM Graduate School (MIT)Document29 pagesVariable, Expressions, Statements and Operators: By: Daniel T. Ursulum, Jr. CSU - SM Graduate School (MIT)blaze moniqueNo ratings yet
- 7-23 Fundamentals of CDocument25 pages7-23 Fundamentals of CSachin DhayatadakNo ratings yet
- Bule Hora UniversityDocument11 pagesBule Hora Universitynagaasaamulataa32No ratings yet
- Input and Output of C++Document40 pagesInput and Output of C++Priyanka khedkarNo ratings yet
- COSC226 Module3Document74 pagesCOSC226 Module3Fadare AkindimejiNo ratings yet
- Data TypesDocument5 pagesData TypesAli HamzaNo ratings yet
- BSC C++ Unit IDocument31 pagesBSC C++ Unit Ikudikala kalabharathiNo ratings yet
- GKS - Data Type in CDocument5 pagesGKS - Data Type in CAryan DasNo ratings yet
- Example Types of VariableDocument4 pagesExample Types of VariableCherry Ann Labandero SayloonNo ratings yet
- Data Types in CDocument6 pagesData Types in CBharath B.v.pNo ratings yet
- Unit1 Data TypesDocument2 pagesUnit1 Data TypesSelvaNo ratings yet
- Integer Types: S.N - Types & DescriptionDocument5 pagesInteger Types: S.N - Types & DescriptionComputer FacultyNo ratings yet
- Basic Data TypesDocument3 pagesBasic Data TypesSnigdha DasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Programming 1Document43 pagesIntroduction To Programming 1nandu111103No ratings yet
- Basic Data Types and Sizes:: OperatorsDocument21 pagesBasic Data Types and Sizes:: OperatorsRaavi Vamsi SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Lectuskje - Constant and DataDocument28 pagesLectuskje - Constant and Datagye soNo ratings yet
- SQL Part1Document15 pagesSQL Part1mohan satyaraoNo ratings yet
- C Programming LanguageDocument191 pagesC Programming LanguageKarthikeyan KNo ratings yet
- Dodatak Za Vežbu 1Document3 pagesDodatak Za Vežbu 1Marko DabovicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document14 pagesChapter 3asnakechwube28No ratings yet
- VariablesDocument7 pagesVariablesrussellrada135No ratings yet
- C Programming Session 3 Ip Op Var Data OperatorDocument13 pagesC Programming Session 3 Ip Op Var Data OperatorKiran KardileNo ratings yet
- C++ Data TypesDocument8 pagesC++ Data TypesQuratulain NaqviNo ratings yet
- Data Types in C LanguageDocument4 pagesData Types in C Languagefaraz8385No ratings yet
- Basic Derived User Defined: Data TypesDocument7 pagesBasic Derived User Defined: Data TypesmuthumaninNo ratings yet
- What Are Keywords? o Reserved Words - Examples of KeywordDocument5 pagesWhat Are Keywords? o Reserved Words - Examples of KeywordHannanNo ratings yet
- CDocument86 pagesCgashuNo ratings yet
- Data Types in C LanguageDocument1 pageData Types in C LanguageHtun Minn OoNo ratings yet
- Data Type Summary (Visual Basic)Document2 pagesData Type Summary (Visual Basic)SupolNo ratings yet
- R. C. Patel Polytechnic, Shirpur: First Year Diploma in Computer EngineeringDocument51 pagesR. C. Patel Polytechnic, Shirpur: First Year Diploma in Computer EngineeringTech R&BNo ratings yet
- Mme 238Document129 pagesMme 238api-3701823No ratings yet
- DT, Variable, OpratorsDocument6 pagesDT, Variable, Opratorsdinzd135No ratings yet
- SQL - Data TypesDocument4 pagesSQL - Data TypesMarlon MagtibayNo ratings yet
- VBA Data Type SummaryDocument2 pagesVBA Data Type SummaryJorge Hernan Aguado QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Lecture Handout 4Document9 pagesLecture Handout 4Kirubai DNo ratings yet
- Datatype in C:: Type Storage Size Value RangeDocument2 pagesDatatype in C:: Type Storage Size Value RangeHarsh TripathiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Variables and Constants: StructureDocument10 pagesUnit 3 Variables and Constants: Structurert1220011No ratings yet
- Object Oriented Programming PDFDocument5 pagesObject Oriented Programming PDFArivu AnandNo ratings yet
- Data Types PDFDocument2 pagesData Types PDFGajanan BuchalwarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 ProgrammingDocument19 pagesLesson 3 ProgrammingMarvin LopecilloNo ratings yet
- 1 - Variables, Data Types and OperatorsDocument18 pages1 - Variables, Data Types and Operatorsshared tecNo ratings yet
- Data Types - GeeksforGeeksDocument8 pagesData Types - GeeksforGeeksIndian ComplaintNo ratings yet
- Visual Basic Data TypesDocument3 pagesVisual Basic Data Typesbertho usyorNo ratings yet
- Data Types: Range of Different Data Types in Following Languages: 1) C++Document4 pagesData Types: Range of Different Data Types in Following Languages: 1) C++Sandhya YadavNo ratings yet
- Database Systems COMP-213: By: Shahid M HmoodDocument46 pagesDatabase Systems COMP-213: By: Shahid M HmoodTranceNo ratings yet
- SQL Server Data TypesDocument7 pagesSQL Server Data TypesabcNo ratings yet
- C++ Data Types PDFDocument4 pagesC++ Data Types PDFsiddharthNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 ComDocument25 pagesUnit-2 Comfaiza ansariNo ratings yet
- 10-Formatted Input FunctionsDocument18 pages10-Formatted Input FunctionsDevotional SongsNo ratings yet
- 09-Unformatted Output FunctionsDocument17 pages09-Unformatted Output FunctionsDevotional SongsNo ratings yet
- Dijkstra's AlgorithmDocument44 pagesDijkstra's AlgorithmDevotional SongsNo ratings yet
- 06 ExpressionsDocument13 pages06 ExpressionsDevotional SongsNo ratings yet
- Graph Introduction, TypesDocument25 pagesGraph Introduction, TypesDevotional SongsNo ratings yet
- Arducam Usb Camera C/C++ SDK: User GuideDocument12 pagesArducam Usb Camera C/C++ SDK: User GuideOz SusejNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Faculty: Nangarhar UniversityDocument32 pagesComputer Science Faculty: Nangarhar UniversityNasir khanNo ratings yet
- NIBSS QR Code Payment Integration Technical Specification - V1.699Document63 pagesNIBSS QR Code Payment Integration Technical Specification - V1.699Samuel EroweleNo ratings yet
- Atari ST Machine LanguageDocument290 pagesAtari ST Machine Languageremow100% (1)
- Sandeep Nagar Introduction To Python - For Scientists and Engineers PDFDocument141 pagesSandeep Nagar Introduction To Python - For Scientists and Engineers PDFThiagoCarvalhoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Introduction To Markup LanguagesDocument41 pagesUnit 1: Introduction To Markup Languagesasesino1No ratings yet
- Goldengate Internationalization Best Practices For V11.2.1: Oracle-To-OracleDocument14 pagesGoldengate Internationalization Best Practices For V11.2.1: Oracle-To-OracleTebs ANo ratings yet
- Basic Elements of C++Document49 pagesBasic Elements of C++Neil BasabeNo ratings yet
- Migrating From DB2 To PostgreSQL - What You Should Know - SeveralninesDocument13 pagesMigrating From DB2 To PostgreSQL - What You Should Know - Severalninesgeojava123No ratings yet
- CH12 COA10e UpdatedDocument36 pagesCH12 COA10e UpdatedMuhammad UmairNo ratings yet
- Learn C++ in A DAYDocument67 pagesLearn C++ in A DAYArcon Solite BarbanidaNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1 Information Representation: Unit 1: Theory FundamentalsDocument32 pages1.1.1 Information Representation: Unit 1: Theory FundamentalsRonald PorterNo ratings yet
- SQL DatatypeDocument7 pagesSQL Datatypetesting engNo ratings yet
- Starter Pack - ASAL Computer ScienceDocument99 pagesStarter Pack - ASAL Computer ScienceNicholas Jonathan100% (1)
- Lesson Plan - FOR DEMO (Variables and Data Types)Document4 pagesLesson Plan - FOR DEMO (Variables and Data Types)Joshua Almuete100% (1)
- File and StreamDocument41 pagesFile and StreamMichael NegashNo ratings yet
- XFS MIB Architecture and SNMP ExtentionsDocument55 pagesXFS MIB Architecture and SNMP ExtentionsChiheb Ben JemiaNo ratings yet
- Schneider - Ch04 - Inv To CS 8eDocument61 pagesSchneider - Ch04 - Inv To CS 8eTwinky CasidsidNo ratings yet
- Python Assignment-2 Solutions PDFDocument91 pagesPython Assignment-2 Solutions PDFRAMYA S HNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Notes & Review QuestionsDocument31 pagesModule 5 Notes & Review QuestionsAbhimanyu KudlaNo ratings yet
- ModbusDocument34 pagesModbusTecnicoItcaNo ratings yet
- Data - Structures Using C PDFDocument122 pagesData - Structures Using C PDFjegadeeswarNo ratings yet
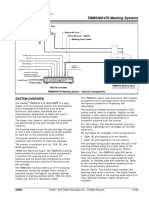
- TMM5400/470 Marking Systems: System OverviewDocument12 pagesTMM5400/470 Marking Systems: System OverviewJhon Parker DimitrinskyNo ratings yet
- Ict Chapter 2Document9 pagesIct Chapter 2Izwan Jamaluddin33% (3)
- CSC128 Topic 2Document27 pagesCSC128 Topic 2WHfamilyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01 Introduction To ProgrammingDocument41 pagesLecture 01 Introduction To ProgrammingRehan Nazam MinhasNo ratings yet
- Java Programming: - Syed Ashik Naina S MDocument16 pagesJava Programming: - Syed Ashik Naina S MSyed Yusuf AsfarNo ratings yet