Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 6 Logarithmic and Exponential Functions
Chapter 6 Logarithmic and Exponential Functions
Uploaded by
HoaXOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 6 Logarithmic and Exponential Functions
Chapter 6 Logarithmic and Exponential Functions
Uploaded by
HoaXCopyright:
Available Formats
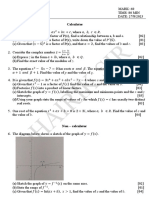
Chapter (6) Logarithmic and Exponential functions
0606/12/F/M/19
1. It is given that 𝑙𝑜𝑔4 𝑥 = 𝑝. Giving your answer in its simplest form, find, in terms of p,
a. 𝑙𝑜𝑔4 (16𝑥)
[2]
7
𝑥
b. 𝑙𝑜𝑔4 ( 256 )
[2]
Using your answers to parts (i) and (ii),
7
𝑥
c. solve 𝑙𝑜𝑔4 (16𝑥) − 𝑙𝑜𝑔4 ( 256 ) = 5, giving your answer correct to 2 decimal
places.
[3]
The Maths society
0606/12/F/M/19
𝑥
2. The function p is defined by 𝑝(𝑥) = 3𝑒 + 2 for all real 𝑥.
a. State the range of p.
[1]
−1
b. On the axes below, sketch and label the graphs of 𝑦 = 𝑝(𝑥) and 𝑦 = 𝑝 (𝑥).
State the coordinates of any points of intersection with the coordinate axes.
[3]
−1
c. Hence explain why the equation 𝑝 (𝑥) = 𝑝(𝑥) has no solutions.
[1]
The Maths Society
0606/11/M/J/19
3. (a) Solve 𝑙𝑜𝑔3𝑥 + 𝑙𝑜𝑔9𝑥 = 12.
[3]
2 1
(b) Solve 𝑙𝑜𝑔4(3𝑦 − 10) = 2𝑙𝑜𝑔4(𝑦 − 1) + 2
.
[5]
The Maths Society
𝑥
4. It is given that 𝑓(𝑥) = 5𝑒 − 1 for 𝑥 ϵ ℝ
a. Write down the range of f.
[1]
−1
b. Find 𝑓 and state its domain.
[3]
0606/13/M/J/19
3𝑥
5. 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑒 for 𝑥 ϵ ℝ
2
𝑔(𝑥) = 2𝑥 + 1 for 𝑥 ≥ 0
a. Write down the range of g.
[1]
−1
b. Show that 𝑓 𝑔( 62) = 𝑙𝑛 5.
[3]
The Maths Society
0606/22/M/J/19
2
6. Solve 𝑙𝑔(𝑥 − 3) = 0.
[2]
0606/11/O/N/19
2𝑥
7. 𝑓(𝑥) = 3𝑒 + 1 for 𝑥 ϵ ℝ
𝑔(𝑥) = 𝑥 + 1 for 𝑥 ϵ ℝ
(a) Write down the range of f and of g.
[2]
2
(b) Evaluate 𝑓𝑔 (0).
[2]
−1
(c) On the axes below, sketch and label the graphs of 𝑦 = 𝑓(𝑥) and 𝑦 = 𝑓 (𝑥). State the
coordinates of any points of intersection with the coordinate axes.
[3]
The Maths Society
0606/12/O/N/19
8. Solve 𝑙𝑜𝑔7𝑥 + 2𝑙𝑜𝑔𝑥7 = 3.
[4]
0606/13/O/N/19
9. (a) Given that 𝑙𝑜𝑔𝑎 𝑥 = 𝑝 and 𝑙𝑜𝑔𝑎 𝑦 = 𝑞, find in terms of 𝑝 and 𝑞.
2
(i) 𝑙𝑜𝑔𝑎 𝑎𝑥𝑦
[2]
3
𝑥
(ii) 𝑙𝑜𝑔𝑎 ( 𝑎𝑦 )
[2]
(iii) 𝑙𝑜𝑔𝑎 𝑥 + 𝑙𝑜𝑔𝑦𝑎.
[1]
The Maths Society
𝑥 𝑥 1+2𝑥
(b) Using the substitution 𝑚 = 3 , or otherwise, solve 3 − 3 +4=0
[3]
The Maths Society
You might also like
- The Star and Criss Supervision: Proactive and Reactive Practices of A Supervisor Instructional LeadershipDocument31 pagesThe Star and Criss Supervision: Proactive and Reactive Practices of A Supervisor Instructional LeadershipEvangeline LapitanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document79 pagesChapter 4Clarizza0% (1)
- Chapter 1 Function Ws 3 (2019)Document5 pagesChapter 1 Function Ws 3 (2019)hninNo ratings yet
- Queen'S College CAPE 1.1 TEST 2018-2019Document2 pagesQueen'S College CAPE 1.1 TEST 2018-2019SweeticlebbgNo ratings yet
- 2023 Pure Maths p2 (Final Revision)Document8 pages2023 Pure Maths p2 (Final Revision)Lawrence Trust MunyatiNo ratings yet
- Share Online Revision: Pure Mathematics 6042/1Document8 pagesShare Online Revision: Pure Mathematics 6042/1Tafadzwa MachongweNo ratings yet
- AA Summative Test FNNDocument13 pagesAA Summative Test FNNDaniel TululaNo ratings yet
- Ut 27 8 2023Document2 pagesUt 27 8 2023Dynamite X23No ratings yet
- Math Xi Set A First Term 2080 FinalDocument4 pagesMath Xi Set A First Term 2080 Finalrajshgupta01No ratings yet
- Wa0008Document4 pagesWa0008nkafor7No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 To 5 TestDocument7 pagesChapter 1 To 5 TestHoaXNo ratings yet
- Pure Mathematic Revision Worksheet Month 3Document2 pagesPure Mathematic Revision Worksheet Month 3Le Jeu LifeNo ratings yet
- Pure Mathematics Revision Worksheet Month 7Document3 pagesPure Mathematics Revision Worksheet Month 7Le Jeu LifeNo ratings yet
- 2023 l6 Test 1 Pure Maths MR ShareDocument1 page2023 l6 Test 1 Pure Maths MR ShareAsher MahasoNo ratings yet
- Sub Math Seminar QuestionsDocument6 pagesSub Math Seminar QuestionsMukasa NajibNo ratings yet
- SMK Sam Tet Mathematics T s2 2021 QDocument2 pagesSMK Sam Tet Mathematics T s2 2021 QZurainiNo ratings yet
- Sba 2012 (Unit2 Test 1) PDFDocument2 pagesSba 2012 (Unit2 Test 1) PDFkkkkllllNo ratings yet
- Sba 2012 (Unit1 Test 1) PDFDocument2 pagesSba 2012 (Unit1 Test 1) PDFkkkkllllNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 QuizDocument6 pagesChapter 18 QuizBruce ZhouNo ratings yet
- P2 MEGA REVISION For JAN 21 Candidates PDFDocument3 pagesP2 MEGA REVISION For JAN 21 Candidates PDFblob bleepNo ratings yet
- Preview Unit 2 Test 1 2016Document2 pagesPreview Unit 2 Test 1 2016Eq BrownNo ratings yet
- Pure Mathematics Preview Unit 2 - Test 1Document2 pagesPure Mathematics Preview Unit 2 - Test 1kkkkllllNo ratings yet
- Sba 2017 Unit 2 Test 1 With SolutionsDocument5 pagesSba 2017 Unit 2 Test 1 With SolutionskkkkllllNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Practice Assignment-26Feb2024Document7 pagesFinal Exam Practice Assignment-26Feb2024Arvind KumarNo ratings yet
- Queen'S College CAPE 1.1 TEST 2016-2017Document2 pagesQueen'S College CAPE 1.1 TEST 2016-2017SweeticlebbgNo ratings yet
- Cape Unit 2 2019 Paper 2 SolutionsDocument20 pagesCape Unit 2 2019 Paper 2 SolutionsalexNo ratings yet
- Cape Unit 2 2019 Paper 2 SolutionsDocument20 pagesCape Unit 2 2019 Paper 2 SolutionsalexNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Test 2Document2 pagesGrade 10 Test 2Mateu ChanganoNo ratings yet
- Trials Examination 2021mathematics Paper 1Document20 pagesTrials Examination 2021mathematics Paper 1Wessel PretoriusNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xi Maths QB Remesh 2. Relations and FunctionsDocument9 pagesHsslive Xi Maths QB Remesh 2. Relations and FunctionsINDRAJITH H B 1S1ANo ratings yet
- HC Sba 2020 Unit 2 Test 1Document2 pagesHC Sba 2020 Unit 2 Test 1kkkkllllNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Seminar Questions Scheduled On 30th September 2023Document24 pagesMathematics Seminar Questions Scheduled On 30th September 2023Obembi Da terribleNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - DifferentiationDocument20 pagesWorksheet - Differentiationmohammedhider71No ratings yet
- Pure Maths p1Document4 pagesPure Maths p1tapuwanashemuchinaNo ratings yet
- Pure Mathematics Revision Worksheet Month 5Document4 pagesPure Mathematics Revision Worksheet Month 5Le Jeu LifeNo ratings yet
- Cape Unit 2 2019 Paper 2 SolutionsDocument20 pagesCape Unit 2 2019 Paper 2 SolutionsTashane officialNo ratings yet
- P3 Revision Worksheet (AUGUST 20) : P3: Chapter 1 and 2 (Up To Inverse Function)Document2 pagesP3 Revision Worksheet (AUGUST 20) : P3: Chapter 1 and 2 (Up To Inverse Function)Bibi Marium SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Sample Test 1-1 For Calculus 1Document2 pagesSample Test 1-1 For Calculus 1Teodora MihaiNo ratings yet
- Jan 2015 Paper 2Document16 pagesJan 2015 Paper 2RashedaNo ratings yet
- Sec 2 Mock Exam WA2 2024Document7 pagesSec 2 Mock Exam WA2 2024ednovatuitionNo ratings yet
- Pure Mathematics Preview Unit 2 - Test 1 1 Hour 20 MinutesDocument2 pagesPure Mathematics Preview Unit 2 - Test 1 1 Hour 20 MinuteskkkkllllNo ratings yet
- 2021 2 ActualDocument2 pages2021 2 ActualcatherineliewclNo ratings yet
- P3 May 21 Revision Worksheet CH, 1, 2, 3 & 6Document3 pagesP3 May 21 Revision Worksheet CH, 1, 2, 3 & 6Bibi Marium SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- 12 TH M Holiday ASS NEDocument5 pages12 TH M Holiday ASS NEgunapranes15No ratings yet
- Syjc Prelim Maths Comm 2022Document7 pagesSyjc Prelim Maths Comm 2022Kyna KothariNo ratings yet
- Math -Xi-Annual Exam 2081 New FormatDocument4 pagesMath -Xi-Annual Exam 2081 New FormatfghughjjguhvjiNo ratings yet
- SpecimenPaperCoreMaths - No CalculatorDocument4 pagesSpecimenPaperCoreMaths - No CalculatorBelay BeleteNo ratings yet
- Add MathsDocument2 pagesAdd MathsFelix KhawNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xi Maths QB 2. Relations and FunctionsDocument9 pagesHsslive Xi Maths QB 2. Relations and FunctionsheizzenclovNo ratings yet
- IGCSE - FPM - Chapter 1 - Graphs - Assignment 4Document1 pageIGCSE - FPM - Chapter 1 - Graphs - Assignment 4binuk wNo ratings yet
- SECTION A: Short Response: Question 1 (5 Marks)Document3 pagesSECTION A: Short Response: Question 1 (5 Marks)NOPEENo ratings yet
- O Level Additional Maths SpecimenDocument8 pagesO Level Additional Maths SpecimenGershom MahoriNo ratings yet
- AAHL-Algebra Practice PaperDocument6 pagesAAHL-Algebra Practice PaperAnkush ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Seminario CpuDocument2 pagesSeminario CpuNsqnombreponerNo ratings yet
- Sba 2016 Unit 2 Test 1Document7 pagesSba 2016 Unit 2 Test 1kkkkllllNo ratings yet
- 01 Complex Numbers IDocument4 pages01 Complex Numbers IJesse JNo ratings yet
- A212 MidTermDocument10 pagesA212 MidTermMuhammad Ashraf Hafis Bin KamarudinNo ratings yet
- AlgebraDocument1 pageAlgebrasanjidasabia.1412No ratings yet
- Additional MathematicsDocument22 pagesAdditional MathematicsEnzo LeeNo ratings yet
- Trockers Online Revision: Final Revision 2020 Session 3 HoursDocument4 pagesTrockers Online Revision: Final Revision 2020 Session 3 HoursIsheanesu Collins MashipeNo ratings yet
- 20-21 MYE S3E Math QP FBPDocument14 pages20-21 MYE S3E Math QP FBPHC GamerNo ratings yet
- 4ES1 01 Que 20210429Document28 pages4ES1 01 Que 20210429HoaXNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/21Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/21HoaXNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/22Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/22HoaXNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/41Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/41HoaXNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 To 5 TestDocument7 pagesChapter 1 To 5 TestHoaXNo ratings yet
- CS AssignmentDocument11 pagesCS AssignmentHoaXNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE (9-1) : MATHEMATICS 0980/32Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE (9-1) : MATHEMATICS 0980/32HoaXNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument16 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationHoaXNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE (9-1) : English As A Second Language 0993/22Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE (9-1) : English As A Second Language 0993/22HoaXNo ratings yet
- Alkenes QPDocument13 pagesAlkenes QPHoaXNo ratings yet
- Alkenes 1 QPDocument7 pagesAlkenes 1 QPHoaXNo ratings yet
- Changing Landscape of Recruitment IndustryDocument5 pagesChanging Landscape of Recruitment IndustryNupur SinghNo ratings yet
- Me 04-601Document15 pagesMe 04-601Vishnu DasNo ratings yet
- Cicol NT Slurry: Constructive SolutionsDocument3 pagesCicol NT Slurry: Constructive SolutionstalatzahoorNo ratings yet
- Catalog 2010 - 2011 Optical Warning SystemsDocument56 pagesCatalog 2010 - 2011 Optical Warning SystemsSamir FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Neyhns: Eticket ItineraryDocument3 pagesNeyhns: Eticket Itineraryadi saputraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Skills To Put On ResumeDocument6 pagesNursing Skills To Put On Resumeaflkubfrv100% (1)
- ABB Control TP180DA DatasheetDocument3 pagesABB Control TP180DA Datasheetntdien923100% (1)
- Syllabus: Cambridge Igcse First Language EnglishDocument52 pagesSyllabus: Cambridge Igcse First Language EnglishNdache PermataNo ratings yet
- AC Traction ManualDocument162 pagesAC Traction ManualBiju MenonNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Dh321Document20 pagesDatasheet Dh32193082No ratings yet
- W Hoov TM001 E1 PDFDocument48 pagesW Hoov TM001 E1 PDFDrewNo ratings yet
- Janelle Resume Updated 100614Document3 pagesJanelle Resume Updated 100614api-266674096No ratings yet
- Acupressure Animal SheltersDocument1 pageAcupressure Animal SheltersIoana SavaNo ratings yet
- Maths Coursework Mark SchemeDocument4 pagesMaths Coursework Mark Schemef5d7ejd0100% (2)
- Final Fortran Questions 1Document5 pagesFinal Fortran Questions 1Serdar BilgeNo ratings yet
- THE LAW PERTAINING TO PRIVATE PERSONAL & COMML RELATIONS - AdDU Bar NotesDocument54 pagesTHE LAW PERTAINING TO PRIVATE PERSONAL & COMML RELATIONS - AdDU Bar NotesDevilleres Eliza DenNo ratings yet
- Analyzing The Value of Vehicle Maintenance Activities: Selin Dönmez Mahasin ZemmouriDocument71 pagesAnalyzing The Value of Vehicle Maintenance Activities: Selin Dönmez Mahasin ZemmouriAgnys Gomes - DR UNITECNo ratings yet
- Example 3 Relating Downhole Rate With The Rate at Standard ConditionsDocument8 pagesExample 3 Relating Downhole Rate With The Rate at Standard ConditionsMaisam AbbasNo ratings yet
- Roll No. 31 - SportsDocument8 pagesRoll No. 31 - SportsAdnan NawabNo ratings yet
- FCG - List of Top 100 Stockholders Q1 (Common Shares) Ending 31 March 2024Document5 pagesFCG - List of Top 100 Stockholders Q1 (Common Shares) Ending 31 March 2024Amino BenitoNo ratings yet
- Treasure Trove Workbook Answers Daffodils: Passage-1Document4 pagesTreasure Trove Workbook Answers Daffodils: Passage-1Rohan CharlesNo ratings yet
- 7th Mathematics 1,2,3Document3 pages7th Mathematics 1,2,3Khamalesh C.ANo ratings yet
- PreliminariesDocument11 pagesPreliminariesGhabbFloresPalNo ratings yet
- Analisis de Pesticidas Usandom FragmentacionDocument159 pagesAnalisis de Pesticidas Usandom FragmentacionroxanaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 PtgsDocument46 pagesLesson 4 Ptgsnami chanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computational Finance and Financial EconometricsDocument54 pagesIntroduction To Computational Finance and Financial EconometricsMR 2No ratings yet
- Investment Analysis and Portfolio Management: Lecture Presentation SoftwareDocument43 pagesInvestment Analysis and Portfolio Management: Lecture Presentation SoftwareNoman KhalidNo ratings yet
- GSK 218M CNC System Connection and PLC ManualDocument192 pagesGSK 218M CNC System Connection and PLC ManualsunhuynhNo ratings yet