Professional Documents
Culture Documents
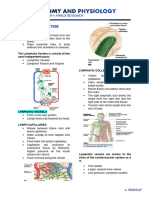
Lymphatic System
Lymphatic System
Uploaded by
Chelsie NicoleOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lymphatic System
Lymphatic System
Uploaded by
Chelsie NicoleCopyright:
Available Formats
• Thoracic duct:
- Rest of body empties from lymphatic
vessels
- Empties into left subclavian vein
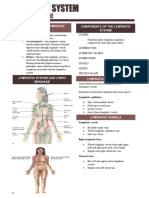
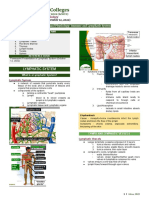
FUNCTIONS LYMPHATIC ORGANS
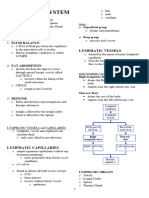
• Fluid balance • Tonsils:
• Fat absorption - palatine tonsils on each side of oral
• Defense cavity
COMPONENTS: - pharyngeal tonsils near internal
opening of nasal cavity (adenoid)
• Lymph: fluid that enters lymphatic - lingual tonsils posterior surface of
capillaries composed of water and some tongue
solutes - form a protective ring of lymphatic
• Lymphocytes tissue around nasal and oral cavities
• Lymphatic vessels • Lymph nodes:
• Lymph nodes - Can vary in size
• Tonsils - Filters any invading microorganisms
• Spleen - Armpit, joint, neck
• Thymus gland - Lymph passes through the lymph nodes
before entering the blood
- Moves through in immune system is
LYMPHATIC CAPILLARIES AND BLOOD VESSELS activated
- Detect foreign substances
• Carries fluid in one direction from tissues to
• Spleen
circulatory system
- Located in abdomen
• fluid moves from blood capillaries into
- Filters blood
tissue spaces
- Detect and respond to foreign
• Lymphatic capillaries: substances
- Tiny, closed-ended vessels - Destroy old red blood cells
- Fluid moves easily into - Blood reservoir
- In most tissues - White pulp: lymphatic tissue
- Join to form lymphatic vessels surrounding arteries
• Lymphatic vessels - Red pulp: contains macrophages and
- Resemble small veins res blood cells that connect to veins
- Where lymphatic capillaries join • Thymus gland
- One-way valves - Bilobed gland
• Right lymphatic duct: - Located in mediastinum behind the
- Where lymphatic vessels from right sternum
upper limb and right head, neck, chest - Stops growing at age 1 and decreases in
empty size at age 60
- Empties into right subclavian vein - Responsible for producing matures
lymphocytes
strategy: chemotaxis,
phagocytosis)
IMMUNITY
o Macrophages:
• Ability to resist damage from foreign ➢ Monocytes
substances like parasites, bacteria, cancer ➢ Killing strategy: Leave
• Type of immunity blood and enter tissues
- Innate (Nonspecific) ➢ Can ingest more than
- Adaptive (Specific) neutrophils
➢ Protect lymph in lymph
nodes and blood in
INNATE IMMUNITY spleen and liver
o Basophils:
• Present at birth ➢ Leave blood and enter
• First defense against pathogen infected tissues
• Accomplished by physical barriers, chemical ➢ made in red bone
mediators, cells, inflammatory response marrow
• Physical Barriers ➢ can release histamine
- First line of defense o Mast cells:
- Skin and mucous membranes to act ➢ Made in red bone
barriers marrow
- Tears, saliva, urine wash away ➢ Fond in skin, lungs, GI,
pathogens urogenital tract
• Chemical Mediators ➢ Can release leukotrienes
- Chemicals that can kill microbes and o Eosinophils:
prevent their entry into cells ➢ Produced in red bone
- Lysozyme: found in tears and saliva to marrow
kill bacteria ➢ Release chemicals to
- Mucous membrane: prevent entry of reduce inflammation
microbe o Natural killer cells:
- Histamine: promote inflammation by ➢ Type of lymphocyte
causing vasodilation ➢ Produce in bone marrow
- Interferons: proteins that protect ➢ Recognize classes of cells
against viral infections by stimulating such as tumor cells or
surrounding cells to produce antiviral virus infected cells
proteins ➢ Release chemical to lysis
• Cells cells
- White blood cells: produce in red
marrow and lymphatic tissue that fight
foreign substances INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE
- Phagocytic cells: ingest and destroy
foreign substances like macrophages • Involves chemical and cells due to injury
and neutrophils • Signaled by presence of foreign substances
o Neutrophils: first to respond to • Stimulates release of chemical mediators
infect but die quickly (killing
ADAPTIVE IIMMUNITY - Move to lymphatic tissue
after mature
• Defense that involves specific recognition to
- Lead to production of
a specific antigen
antibodies
• Acquired after birth
- War strategy: recognize
• Reacts when innate defenses don’t work enemy (B cell receptor)
• Slower than innate immunity - Detect invaders and will act
• Has memory according to its weaknesses
• Uses lymphocytes (B and T cells) o T-cells
• 2 types: - involved in cell mediated
- Antibody mediated immunity primarily and
- Cell mediated antibody mediated immunity
- Mature in thymus gland
TERMS RELATED TODAPTIVE IMMUNITY - Move to lymphatic tissue
after mature
• Antigen: substance that stimulates immune - 4 Types:
response (Ex. bacteria, virus, pollen, food, ➢ ????
rugs, etc)
• Self-antigen: molecule produced by persons
body that stimulates immune system ANTIGEN RECOGNITION
response • Lymphocytes have antigen receptors on
• Antibody: proteins the body produces in their surface
response to specific antigen • Called B-cell receptors on B cells and T-cell
receptors on T cells
ORIGIN AND DEVELOPMENT OF LYMPHOCYTES • Each receptor only binds with a specific
antigen
• Stem cells: • When antigen receptors combine with
- Red bone marrow antigen the lymphocyte is activated and
- Give rise to all blood cells adaptive immunity begins
- Give rise to some pre-T cells and pre-B • Major histocompatibility complex
cells molecule (MHC):
- contain binding sites for antigens
- Specific for certain antigens
LYMPHOCYTES - Hold and present a processed antigen
• Type of white blood cell on the surface of the cell membrane
• Involved in adaptive immunity - Bind to antigen receptor on B or T cells
and stimulate response
• Develop from stem cells
• Cytokinesis:
• Differentiate into specific lymphocytes such
- proteins secreted by a cell that regulates
as B or T cells
neighboring cells (Ex. Interleukin 1 released
o B cells
by macrophages stimulates helper T cells)
- involved in antibody
mediated immunity
- Mature in red bone marrow
LYMPHOCYTE PROLIFERATION EFFECTS OF ANTIBODIES
1. After antigen is processed and present to • Inactivate antigen
helper T cells, helper T cell produces • Bind antigens together
interleukin-2 and interleukin-2 receptors • Active complement cascades
2. Interleukin-2 binds to receptors and • Initiate release of inflammatory chemicals
stimulates more helper T cells production • Facilitate phagocytosis
3. Helper T cells are needed to produce B cells
4. B cells produce antibodies
ANTIBODY PRODUCTION
ANTIBODY- MEDIATED Primary Response
• Effective against antigen in body fluids • 1st exposure of B cell antigen
(blood and lymph) • B cell undergoes division and forms plasma
• Effective against bacteria, virus, toxins cell and memory cells
• Uses B cells to produce antigens • Plasma cells:
• Structure: - Produce antibodies
- Letter Y shape - 3-14 days to by effective against antigen
- Variable region: - Person develops disease symptoms
o V of Y Secondary Response
o Bind to epitopes of antigen using
antigen-binding site (site on • Memory cells:
antibody where antigen binds) - Occurs when immune system is exposed
- Constant region: to antigen that has been seen before
o Stem of Y - B memory cells quickly divided to form
o Each class of immunoglobulin plasma cells which produce antibodies
has same structure - Produces new memory cells
• Valence: number of antigen-binding sites
on antibody
• 5 immunoglobins used to destroy antigens: CELL- MEDIATED IMMUNITY
IgG, IgM, IgA, IgE, IgD • Effective against antigens in cells and
tissues
• Effective against bacteria, viruses, fungi,
and protozoa,
• Uses different types of T cells
TYPES OF T-CELLS
• Helper T cells (𝑻𝑯 )
- Produces new memory cells
- Activate macrophages
- Help form B cells
- Promote production of Tc
• Cytotoxic T cells (Tc): precursor to Cytotoxic
T Lymphocytes (CCTL) = destroys antigen on
contact
• Regulatory T cells: turn off immune system
response when antigen is gone
TYPES OF ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY
Naturally Acquired Immunity
• Active:
- Natural exposure to antigens causes
production of antibodies
- Can be lifelong immunity
- Ex. Mononucleosis
• Passive:
- Transfer of antibodies from mother to
child
- Ex. Breast milk or placenta
Artificially Acquired Immunity
• Active:
- Injection of antigens using vaccines
which cause the production of
antibodies
- Vaccine or immunization: process off
introducing killed, live, or inactivated
pathogen
• Passive:
- Injection of antibodies from another
person or an animal
You might also like
- Lymphatic System and Immunity - Seeleys - NotesDocument9 pagesLymphatic System and Immunity - Seeleys - NotesLol lol100% (2)
- Lymphatic SystemDocument4 pagesLymphatic Systempriya garciaNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic and Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesLymphatic and Endocrine Systemshanelhello1No ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument4 pagesLymphatic SystemleixxaneNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System Transes 1Document8 pagesLymphatic System Transes 1Sophia Margarette CawalingNo ratings yet
- Chapt11 Lecture AnimDocument4 pagesChapt11 Lecture AnimIvanNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Transes 1stYear1stSemFinalsDocument48 pagesAnaphy Transes 1stYear1stSemFinalszyrenejoy.motita.mnlNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument8 pagesLymphatic SystemKate BambalanNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic SystemDocument9 pagesThe Lymphatic Systemmeichantoyuu10No ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Lymphatic System and Body Defenses ReviewerDocument5 pagesChapter 12 - Lymphatic System and Body Defenses Reviewerkoshiaiko21No ratings yet
- The Lymphatic SystemDocument4 pagesThe Lymphatic SysteminitaygracileshayneNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument8 pagesLymphatic SystemHannah Faye PacomaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 Lymphatic SystemDocument99 pagesCHAPTER 8 Lymphatic SystemAdlyn ShaheeraNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic Drainage of Head and Neck Region.: Presented by DR Fatema YusufDocument46 pagesLymphatic Drainage of Head and Neck Region.: Presented by DR Fatema YusufFatema86No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Cells and Organs IIDocument30 pagesLecture 3 - Cells and Organs IIAhmed Examination100% (1)
- Anaphy 11Document5 pagesAnaphy 11fio.maglaya13No ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument6 pagesLymphatic Systemshane.surigaoNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic System: Albert Grazia, M.S., N.D. (516) 486-8332 WWW - Naturedoc.infoDocument70 pagesThe Lymphatic System: Albert Grazia, M.S., N.D. (516) 486-8332 WWW - Naturedoc.infoRiaz RahmanNo ratings yet
- V. Anat 121 Lecture 21-23Document5 pagesV. Anat 121 Lecture 21-23mjdangca0111No ratings yet
- Lymphatic System FinalsDocument11 pagesLymphatic System FinalsMarietesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Physiology Lecture Endterm ReviewerDocument34 pagesAnatomy Physiology Lecture Endterm ReviewerKristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Human Body: Circulatory SystemDocument46 pagesHuman Body: Circulatory SystemAlvin U. DumdumaNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic and Immune SystemDocument5 pagesLymphatic and Immune SystemShiera Mae BernalesNo ratings yet
- Immunology NursingDocument9 pagesImmunology Nursingerbuenaventura3937valNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic-System SolidDocument23 pagesLymphatic-System Solidcontemporarysaad16No ratings yet
- Lecture Lymphatic 2Document16 pagesLecture Lymphatic 2qNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System and ImmunityDocument5 pagesLymphatic System and ImmunityRheeanne AmilasanNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic Organs and TissuesDocument3 pagesLymphatic Organs and TissuesHan SoloNo ratings yet
- Sistem Limfatik Dan Imun: Siti Hamidatul Aliyah, S.PD, M.SC STIKES Harapan Ibu JambiDocument60 pagesSistem Limfatik Dan Imun: Siti Hamidatul Aliyah, S.PD, M.SC STIKES Harapan Ibu JambiPutriantiNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY LEC Lymphatic Sytem 1Document6 pagesANAPHY LEC Lymphatic Sytem 1christinemaeloslos10No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Handout # 14 Lympatic SystemDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Handout # 14 Lympatic SystemJounri Arsted Dimabuyu (Kaiz)No ratings yet
- Introduction To Immunology PDFDocument44 pagesIntroduction To Immunology PDFPATRICK SICHINSAMBWENo ratings yet
- Immune System and Lymphoid OrgansDocument15 pagesImmune System and Lymphoid Organscatalia fuaresNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Introduction To Lymphatic and Immune SystemDocument7 pagesLecture Notes Introduction To Lymphatic and Immune SystemKirstie Goc-ongNo ratings yet
- MIDTERMS - Immune and LymphaticDocument5 pagesMIDTERMS - Immune and LymphaticNicole AlinaNo ratings yet
- AP11-Lymphatic SystemDocument9 pagesAP11-Lymphatic SystemPay per PrintNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument11 pagesLymphatic SystemPlacido Edgar MagaNo ratings yet
- Hematologic DisorderDocument7 pagesHematologic Disordermawel100% (2)
- Gmae Lymph System 1aaa 1 1Document26 pagesGmae Lymph System 1aaa 1 1AIRA BIANCA B. MANALANGNo ratings yet
- Human Body: Circulatory SystemDocument46 pagesHuman Body: Circulatory SystemAndra HijratulNo ratings yet
- HistologyDocument31 pagesHistologyassihuda2No ratings yet
- (Transes) Human Histology - 13 Lymphoid SystemDocument17 pages(Transes) Human Histology - 13 Lymphoid SystemReina CastronuevoNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic and Immune SystemsDocument94 pagesLymphatic and Immune Systemsistep100% (1)
- Lymphatic SystemDocument70 pagesLymphatic SystemMarin Jr., Reynaldo J.No ratings yet
- Lympathic System TransesDocument9 pagesLympathic System TransesMonica SabarreNo ratings yet
- 9 Lymphatic SystemDocument64 pages9 Lymphatic SystemM TalhaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lymphatic SystemDocument7 pagesAnaphy Lymphatic Systemheyraheyra70No ratings yet
- HPP Lec Lymph & ImmuDocument5 pagesHPP Lec Lymph & Immucarlo baculiNo ratings yet
- Lymph Nodes of Head and NeckDocument33 pagesLymph Nodes of Head and NeckGautham Venkatramani100% (1)
- Lymphatic System TransesDocument6 pagesLymphatic System Transesadrielvamos28No ratings yet
- Lymphatic System: (Anatomical Approach)Document38 pagesLymphatic System: (Anatomical Approach)Rizki PerdanaNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument22 pagesLymphatic SystemdrynwhylNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System BAYLONDocument16 pagesLymphatic System BAYLONElijah Joaquin Payumo BaylonNo ratings yet
- 12 Lymphatic SystemDocument12 pages12 Lymphatic SystemPauline AñesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 Review QuestionsDocument6 pagesChapter 22 Review Questionsjoeyseo00No ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument22 pagesLymphatic SystemKim, Seyoung Cristine G.No ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument22 pagesLymphatic SystemArnab GuinNo ratings yet
- Self Test 2Document5 pagesSelf Test 2202310446No ratings yet
- Lymphatic System TransDocument17 pagesLymphatic System TransRheeanne AmilasanNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Blood Cells, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Blood Cells, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument5 pagesBloodChelsie NicoleNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Lab WinemakingDocument8 pagesOrganic Chemistry Lab WinemakingChelsie NicoleNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument8 pagesCardiovascular SystemChelsie NicoleNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesRespiratory SystemChelsie NicoleNo ratings yet
- Post Lab AnswersDocument1 pagePost Lab AnswersChelsie NicoleNo ratings yet
- Group ExperimentDocument9 pagesGroup ExperimentChelsie NicoleNo ratings yet
- MITOSISDocument28 pagesMITOSIShariz mikhaelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - NeoplasiaDocument23 pagesChapter 7 - NeoplasiaAgnieszka WisniewskaNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Genetics 2nd Edition Brooker Solutions ManualDocument14 pagesConcepts of Genetics 2nd Edition Brooker Solutions ManualgeoffreyjimenezxtyfnzwrkcNo ratings yet
- Ecology Introduction - Print - QuizizzDocument4 pagesEcology Introduction - Print - QuizizzandieNo ratings yet
- Antigens - Definition, Properties, Types & Antigen RecognitionDocument11 pagesAntigens - Definition, Properties, Types & Antigen RecognitionАнна КатраженкоNo ratings yet
- Ecology Practice OSSDDocument3 pagesEcology Practice OSSDoc0% (1)
- Chapter 13. Meiosis and Sexual Life CyclesDocument3 pagesChapter 13. Meiosis and Sexual Life CyclesYukyung ShinNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Embryology Lab Exercise 2Document4 pagesVeterinary Embryology Lab Exercise 2john benedickNo ratings yet
- Reproduction AND Development: (In Plants and Animals)Document29 pagesReproduction AND Development: (In Plants and Animals)Samarra LouisseNo ratings yet
- Disease Lesson 1 & 2Document39 pagesDisease Lesson 1 & 2Harsimrat Kaur KohliNo ratings yet
- Biology The Dynamic Science 3rd Edition Russell Test Bank DownloadDocument21 pagesBiology The Dynamic Science 3rd Edition Russell Test Bank DownloadJamie Hayes100% (21)
- Cell DifferentiationDocument7 pagesCell DifferentiationRahul MishraNo ratings yet
- Biology Cycle 3 Section 9.2 Mitosis and CytokinesisDocument18 pagesBiology Cycle 3 Section 9.2 Mitosis and CytokinesisSuhaib BayadoNo ratings yet
- Final Demo DLP Abenio MaristellaDocument15 pagesFinal Demo DLP Abenio Maristellaapi-668289592No ratings yet
- Technological University of The Philippines: ManilaDocument7 pagesTechnological University of The Philippines: ManilapauliNo ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument11 pagesEcosystemSunil 2doNo ratings yet
- Pathways of Evolution and Are Based On Parsimony or Likelihood Methods. TheDocument1 pagePathways of Evolution and Are Based On Parsimony or Likelihood Methods. TheecogandhiNo ratings yet
- The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle and CancerDocument3 pagesThe Eukaryotic Cell Cycle and CancerKaren SinorNo ratings yet
- History LawsDocument3 pagesHistory Lawsreygie cardenoNo ratings yet
- 08 Colin-UK Modificado B Cell DevelopmentDocument43 pages08 Colin-UK Modificado B Cell DevelopmentNayeli MendozaNo ratings yet
- OlarteDocument1 pageOlarteKim QuinitNo ratings yet
- 7.07mitosis QuizDocument1 page7.07mitosis QuizYay SandovalNo ratings yet
- Immune System Review QuestionsDocument2 pagesImmune System Review Questionsapi-524061079No ratings yet
- Mitosis PowerpointDocument55 pagesMitosis PowerpointAbegail CahatianNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Word SearchDocument1 pageMitosis Word SearchArshe OmaguingNo ratings yet
- Control Mechanisms WorksheetDocument2 pagesControl Mechanisms WorksheetTamsyn GreenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 NRODocument27 pagesLecture 10 NROAnindita MishiNo ratings yet
- DARPA 2009 Budget Includes 'Silent Talk' Mind Reading Project, Remote EEG (Electroencephalography) / MEG (Magnetoencephalography)Document471 pagesDARPA 2009 Budget Includes 'Silent Talk' Mind Reading Project, Remote EEG (Electroencephalography) / MEG (Magnetoencephalography)IdeaTrack0% (1)
- Cleavage: Types and PatternsDocument15 pagesCleavage: Types and PatternstrivikramraoNo ratings yet
- 143 SG 9Document43 pages143 SG 9cake girlsNo ratings yet