Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 viewsQ3 - WEEK 2 - LAS-3-Mechanism-of-change-in-populations
Q3 - WEEK 2 - LAS-3-Mechanism-of-change-in-populations
Uploaded by
Anjhiene CambaThe document provides information on the different mechanisms that produce changes in populations: artificial selection, natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and recombination. It defines each mechanism and provides an example of how it causes changes in a population. The mechanisms discussed are artificial selection, natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and recombination.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Darwin FactsDocument3 pagesDarwin Factsapi-334125776No ratings yet
- 03 Modern Photoelectric Effect LabDocument3 pages03 Modern Photoelectric Effect LabMeagan TamplinNo ratings yet
- Q3 WEEK 3 LAS-1-Reproductive IsolationDocument1 pageQ3 WEEK 3 LAS-1-Reproductive IsolationAnjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Science, Technology, and SocietyDocument27 pagesScience, Technology, and SocietyAnjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Astm D 1142Document12 pagesAstm D 1142Erick Jhonhatan Limon100% (1)
- Understanding Natural SelectionDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Natural SelectionKaira JogNo ratings yet
- Mod 6 Evolution and ClassificationDocument7 pagesMod 6 Evolution and ClassificationrasingtanyaroseNo ratings yet
- NP - General Biology 2 11 & 12 - Q3 - W2 CDocument6 pagesNP - General Biology 2 11 & 12 - Q3 - W2 CIrrah Sheene De VegaNo ratings yet
- Bio Week 1 NotesDocument11 pagesBio Week 1 NotesIan SibalNo ratings yet
- Genetic Variability by Design: Chris AshcraftDocument54 pagesGenetic Variability by Design: Chris Ashcraftgabi_xyzNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science - Q2 - Week 4Document25 pagesEarth and Life Science - Q2 - Week 4Nikko SaiNo ratings yet
- GB2 - Q3 - Week 2bDocument8 pagesGB2 - Q3 - Week 2bMark Kevin G. SantosNo ratings yet
- 13 bt503Document2 pages13 bt503bc200204761 AMBREEN ASHRAFNo ratings yet
- AAP 2209 Notes 2018-1Document47 pagesAAP 2209 Notes 2018-1Kevin KahingaNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Science Fact SheetsDocument4 pages3rd Quarter Science Fact Sheetsdnlaligan8No ratings yet
- Heredity and Evolution NotesDocument5 pagesHeredity and Evolution NotesCapt Pradeep kumarNo ratings yet
- Transgenic Animals: (From CCAC Resource Supplement, Spring/Summer 1997. Used With Permission of CCAC)Document5 pagesTransgenic Animals: (From CCAC Resource Supplement, Spring/Summer 1997. Used With Permission of CCAC)nitralekhaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-Change Over Time: Lesson 3: Artificial SelectionDocument3 pagesUnit 1-Change Over Time: Lesson 3: Artificial SelectionGnaWYrreJNo ratings yet
- Week 9 10 Patterns of Descent With ModificationDocument13 pagesWeek 9 10 Patterns of Descent With ModificationKiel Tj Evangelista100% (1)
- The Process in Genetic Engineering (Crops)Document11 pagesThe Process in Genetic Engineering (Crops)Inio JarhylNo ratings yet
- EvolutionDocument42 pagesEvolutionEvangelene Esquillo SanaNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering: Title CardDocument10 pagesGenetic Engineering: Title CardJonathan YambaoNo ratings yet
- 1-Evolution Fundamentals Herbers EncyclopediaAnimalBeh2010Document9 pages1-Evolution Fundamentals Herbers EncyclopediaAnimalBeh2010Uriel RodríguezNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 9 - HeredityDocument11 pagesSCIENCE 9 - Heredityemanuel.ferrer.sbeNo ratings yet
- Yearly Revision ScienceDocument6 pagesYearly Revision SciencePeroNo ratings yet
- Biology Project TRANSGENIC ANIMALS Class 12Document19 pagesBiology Project TRANSGENIC ANIMALS Class 12Shaik FaisalNo ratings yet
- Chaprter 5 Environmental ScienceDocument6 pagesChaprter 5 Environmental Sciencejeboy DaquizNo ratings yet
- Bio q3 Week 1 and 2Document2 pagesBio q3 Week 1 and 2Vanessa Joy TombocNo ratings yet
- Ch. 23 Lecture Outline PDFDocument15 pagesCh. 23 Lecture Outline PDFCSERM UNASNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of EvolutionDocument7 pagesMechanisms of EvolutionHarry Jhonley LabisteNo ratings yet
- Module 6 8 Gen. Bio. 2 EvolutionDocument24 pagesModule 6 8 Gen. Bio. 2 EvolutionNoriel Anne EsternonNo ratings yet
- Recombination ReviewDocument12 pagesRecombination ReviewAravindan Muthu100% (1)
- General Biology ReviewerDocument15 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerArabelle VilanNo ratings yet
- Artical 1Document6 pagesArtical 1Srinjoy AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Are We There Yet? Tracking The Development of New Model SystemsDocument8 pagesAre We There Yet? Tracking The Development of New Model SystemsmioclaenusNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Module 4 Week 4Document4 pagesGen Bio Module 4 Week 4LouisseNo ratings yet
- GenBio2 Q3 M4 6 Learner PDFDocument48 pagesGenBio2 Q3 M4 6 Learner PDFFlores Carl JosephNo ratings yet
- Scientific ThoughtDocument4 pagesScientific ThoughtEPR PRNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity 11Document22 pagesBiodiversity 11Ma Naida EndrinalNo ratings yet
- A Third Way: More Articles On EvolutionDocument5 pagesA Third Way: More Articles On EvolutionjlventiganNo ratings yet
- Principles of Genetics and Animal BreedingDocument18 pagesPrinciples of Genetics and Animal BreedingJoshua BadongNo ratings yet
- What Is The Future of Animal BiotechnologyDocument9 pagesWhat Is The Future of Animal BiotechnologyIbnan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Essay 34Document2 pagesEssay 34api-213708874No ratings yet
- Genes and Their Role in Animal Productivity: Introduction To Animal ScienceDocument28 pagesGenes and Their Role in Animal Productivity: Introduction To Animal Sciencedreih MadrigNo ratings yet
- Forum/Open Discussion: - Lesson 1: Genetics, Evolution and Origin of Biodiversity ObjectivesDocument13 pagesForum/Open Discussion: - Lesson 1: Genetics, Evolution and Origin of Biodiversity ObjectivesArianne PoleaNo ratings yet
- The Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection Was First Formulated in Charles DarwinDocument5 pagesThe Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection Was First Formulated in Charles Darwinabeeraafzal45No ratings yet
- General Biology 2 Q3-M1 GeneticsDocument25 pagesGeneral Biology 2 Q3-M1 GeneticsAdrian DisuNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity 1: Natural Selection: Basic ConceptsDocument2 pagesBiodiversity 1: Natural Selection: Basic ConceptsMaya MerchantNo ratings yet
- Evolution of MechanismsDocument15 pagesEvolution of MechanismsJesmin ShumiNo ratings yet
- Princ of BiotechnologyDocument16 pagesPrinc of BiotechnologyBayu KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 2 Topic 4Document12 pagesBiology Unit 2 Topic 4Fahad MohammedNo ratings yet
- Dna Recombinant Technology BiotechnologyDocument172 pagesDna Recombinant Technology BiotechnologytasniyanNo ratings yet
- 2.8 ClassificationDocument8 pages2.8 Classificationebeth2987No ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument92 pagesGenetic EngineeringaurelylanieNo ratings yet
- Gene TherapyDocument58 pagesGene Therapynancy vargese100% (1)
- Module 28 - EditedDocument11 pagesModule 28 - Editedrichard reyesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Micro EvolutionDocument47 pagesLecture 6 - Micro EvolutionirosalejosNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 - GeneticsDocument3 pagesLESSON 3 - GeneticsRichelle MasingNo ratings yet
- Descent With ModificationDocument3 pagesDescent With ModificationJaymark HisonaNo ratings yet
- Evolution: - Evolution Means Change Over Time Changes in Species Over Long Periods of TimeDocument29 pagesEvolution: - Evolution Means Change Over Time Changes in Species Over Long Periods of TimeMalik FhaimNo ratings yet
- Las 5 Bio2 PDFDocument13 pagesLas 5 Bio2 PDFPeanut BlobNo ratings yet
- 2 EvolutionDocument7 pages2 EvolutionJamie Rose FontanillaNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering PTDocument16 pagesGenetic Engineering PTNicole Mae SumaltaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio1 Module 10Document20 pagesGen Bio1 Module 10Anjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- General Biology I M7Document19 pagesGeneral Biology I M7Anjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio1 Module 9Document23 pagesGen Bio1 Module 9Anjhiene Camba100% (2)
- General Biology I M6Document19 pagesGeneral Biology I M6Anjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- General Biology I M4Document24 pagesGeneral Biology I M4Anjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Q3 - WEEK 7 - LAS-3-Dichotomous Keys For IdentificationDocument1 pageQ3 - WEEK 7 - LAS-3-Dichotomous Keys For IdentificationAnjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio1 - Module 13Document19 pagesGen Bio1 - Module 13Anjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Q3 - WEEK 3 - LAS-3-Timeline of Evolution ThoughtDocument1 pageQ3 - WEEK 3 - LAS-3-Timeline of Evolution ThoughtAnjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Q3 - WEEK 3 - LAS-2-SpeciationDocument1 pageQ3 - WEEK 3 - LAS-2-SpeciationAnjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Q3 - WEEK 7 - LAS-1-The Linnean System of ClassificationDocument1 pageQ3 - WEEK 7 - LAS-1-The Linnean System of ClassificationAnjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Q3 - WEEK 8 - LAS-3-Cladogram-Infer Evolutionary RelatednessDocument1 pageQ3 - WEEK 8 - LAS-3-Cladogram-Infer Evolutionary RelatednessAnjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Profession Module 1Document15 pagesTeaching Profession Module 1Anjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Q3 - WEEK 8 - LAS-2-Cladistics-Shared Derived CharacterDocument2 pagesQ3 - WEEK 8 - LAS-2-Cladistics-Shared Derived CharacterAnjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Q3 - WEEK 5 - LAS-3-Infering Relationships From Evidences of Evolution-FossilsDocument2 pagesQ3 - WEEK 5 - LAS-3-Infering Relationships From Evidences of Evolution-FossilsAnjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Letter of Application GPC 1111111Document4 pagesLetter of Application GPC 1111111Anjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Q3 - WEEK 7 - LAS-2-Classification of Organism Using Hierarchal SystemDocument2 pagesQ3 - WEEK 7 - LAS-2-Classification of Organism Using Hierarchal SystemAnjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Q3 - WEEK 6 - LAS-1-Multiple Lines of EvidenceDocument2 pagesQ3 - WEEK 6 - LAS-1-Multiple Lines of EvidenceAnjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 First QuarterDocument10 pagesGeneral Biology 1 First QuarterAnjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Quiz 3Document3 pagesGen Bio Quiz 3Anjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Student Learning Ii: Beed Module 2Document7 pagesAssessment of Student Learning Ii: Beed Module 2Anjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Student Learning Ii: Beed Module 2Document8 pagesAssessment of Student Learning Ii: Beed Module 2Anjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Social Dimensions Module 1Document14 pagesSocial Dimensions Module 1Anjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Arts in The Elemntary Module 1Document31 pagesTeaching Arts in The Elemntary Module 1Anjhiene Camba100% (1)
- PDF Module 2Document8 pagesPDF Module 2Anjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Physical Science: Schools Division of Alaminos CityDocument27 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Physical Science: Schools Division of Alaminos CityAnjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Complete Test Series ScheduleDocument12 pagesComplete Test Series ScheduleLively LipunNo ratings yet
- 269 Simulation and Performance Analysis of Solar Pv-Wind Hybrid Energy System Using Matlab SimulinkDocument6 pages269 Simulation and Performance Analysis of Solar Pv-Wind Hybrid Energy System Using Matlab SimulinkNikhil sharma100% (1)
- Factors Affecting The Ecological Conditions of Surkhandarya Region (Biotic, Abiotic, Anthropogin, Temperature, Water)Document5 pagesFactors Affecting The Ecological Conditions of Surkhandarya Region (Biotic, Abiotic, Anthropogin, Temperature, Water)Central Asian StudiesNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science IV FinalDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science IV FinalROCHELLE MATIRANo ratings yet
- General Education PRC 16-30Document105 pagesGeneral Education PRC 16-30Idyls SorongonNo ratings yet
- Module 5 6 EcosystemDocument3 pagesModule 5 6 Ecosystemaatorrico5967qcNo ratings yet
- Flood (Report Text)Document2 pagesFlood (Report Text)Abimanyu Ajipangestu0% (2)
- This Is Limited & Free Trial. You Must Pay For Full Access.: Your School'S Name & Logo Can Be Here!!!Document2 pagesThis Is Limited & Free Trial. You Must Pay For Full Access.: Your School'S Name & Logo Can Be Here!!!Shabbir HussainNo ratings yet
- Heat of Phase ChangeDocument15 pagesHeat of Phase ChangeLyza JavierNo ratings yet
- Depositional EnvironmentsDocument38 pagesDepositional EnvironmentsMohammad Iqbal Mahamad Amir67% (3)
- 8 The Power of WindDocument7 pages8 The Power of WindAnonymous HyOfbJ6No ratings yet
- Diagenesis of Clastic Sedimentary RocksDocument4 pagesDiagenesis of Clastic Sedimentary RocksElysha HenryNo ratings yet
- BIO120 Test 2 FlashcardsDocument21 pagesBIO120 Test 2 FlashcardsBon AppleteaNo ratings yet
- Final Green MarketingDocument22 pagesFinal Green MarketingHarish KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Activation EnergyDocument3 pagesEnzymes Activation EnergyDanielle WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- DRRR Module 1Document8 pagesDRRR Module 1Marie LivennaNo ratings yet
- 01-02 APM30 Product DescriptionDocument14 pages01-02 APM30 Product DescriptionMahdiNo ratings yet
- CIVE1129 Course Guide Part BDocument3 pagesCIVE1129 Course Guide Part BMike ChanNo ratings yet
- Mountain Waves-1Document18 pagesMountain Waves-1FixNo ratings yet
- Making Decisions With InsulationDocument12 pagesMaking Decisions With InsulationAbdallah MansourNo ratings yet
- BTD Question Bank (18ME33)Document5 pagesBTD Question Bank (18ME33)RaviparasheraNo ratings yet
- Foam Lok 2000 4g Cut Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesFoam Lok 2000 4g Cut Sheet PDFCam VistainNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1: First Quarter-Module 9: Gas LawsDocument24 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: First Quarter-Module 9: Gas LawsElysha Mae RamirezNo ratings yet
- Lec 6 Entropy and The Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocument77 pagesLec 6 Entropy and The Second Law of ThermodynamicsACCOUNT ONENo ratings yet
- Soils Written .....Document39 pagesSoils Written .....JessieJameEOculamNo ratings yet
- PETRONAS HSE KPI Definition and Reporting Guideline R0 Final Draft 121120Document61 pagesPETRONAS HSE KPI Definition and Reporting Guideline R0 Final Draft 121120almamunmolla96No ratings yet
- Stage 8 Sci T1 Activties FinDocument7 pagesStage 8 Sci T1 Activties FinRoxanneNo ratings yet
- CH1 Designing For Hope - Why Do We NeedDocument16 pagesCH1 Designing For Hope - Why Do We NeedVictor kakaNo ratings yet
Q3 - WEEK 2 - LAS-3-Mechanism-of-change-in-populations
Q3 - WEEK 2 - LAS-3-Mechanism-of-change-in-populations
Uploaded by
Anjhiene Camba0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views2 pagesThe document provides information on the different mechanisms that produce changes in populations: artificial selection, natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and recombination. It defines each mechanism and provides an example of how it causes changes in a population. The mechanisms discussed are artificial selection, natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and recombination.
Original Description:
Original Title
Q3_WEEK 2_LAS-3-Mechanism-of-change-in-populations
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides information on the different mechanisms that produce changes in populations: artificial selection, natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and recombination. It defines each mechanism and provides an example of how it causes changes in a population. The mechanisms discussed are artificial selection, natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and recombination.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views2 pagesQ3 - WEEK 2 - LAS-3-Mechanism-of-change-in-populations
Q3 - WEEK 2 - LAS-3-Mechanism-of-change-in-populations
Uploaded by
Anjhiene CambaThe document provides information on the different mechanisms that produce changes in populations: artificial selection, natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and recombination. It defines each mechanism and provides an example of how it causes changes in a population. The mechanisms discussed are artificial selection, natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and recombination.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Name: ____________________________ Grade & Section: 12 Score: ____________
School: ___________________________ Teacher: ______________________Subject: Gen. Bio 2
LAS Writers: Milanie M. Pauya
Evaluators: Emma T. Surita and Michael Dave M. Nalagon, Christine Joy G. Sua, Murdy F. Bautista
and Retchie Joy B. Pisana
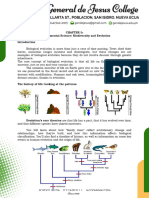
Lesson Topic: Mechanism of Change in Populations Quarter 3, Week 2, LAS 6
Learning Targets: Discuss the mechanism ( Artificial Selection, Natural Selection, Genetic Drift,
Gene Flow, Mutation and recombination that produces changes in populations.
Reference(s): Rea, Maria Angelica D., Dagamac, Nikki Heherson A. General Biology 2. First Edition, Rex
Book Store. 2017. Page 141 -146.
Mechanisms of Change in Population
Artificial Selection is the intentional breeding of plants or animals. It means the same thing as Selective
breeding and an ancient method of genetic engineering. Selective breeding domesticated animals, such as
dogs, pigeons or cattle.
Example: Chicken that produce large egg
Natural Selection is the process whereby organisms better adapted to their environment tend to survive
and produce more offspring. The theory of this action was first fully expounded by Charles Darwin and it is now
believed to be the main process that brings about evolution
Example: Wing-color changes in peppered moth.
Genetic drift is the change in the frequency of an existing gene variant in a population due to random
sampling of organisms. The allele in the offspring are a sample of those in the parent and chance has a role in
determining whether a given individual survives and reproduce
Example: A population of rabbit can have brown fur and white fur with brown the dominant allele.
Mutation is a change in DNA sequence result from DNA copying mistakes made during cell division,
exposure to chemicals called mutagens or infection by viruses.
Example: Sickle Cell anemia, caused by single point mutation in the beta hemoglobin gene.
Gene Flow is the movement of genes from one population to another population. Some events that lead
to gene flow may be in pollen or spores being disperse by air in a new location, animals hibernating and
transferring to a new locale due to changes in temperatures, or humans moving to new cities or countries.
Example: A bee carrying pollen from one flower population to another.
Recombination is the process by which pieces of DNA are broken and recombined to produce new
combination of alleles. This recombination process creates genetic diversity at the level of genes that reflect
differences in the DNA sequence of different organisms.
Example: The system of integration of some bacteriophage, such as L, into a bacterial
chromosomes and the rearrangement of immunoglobulin genes in vertebrates animals.
Activity:
Identify the correct terms that fit in the given sentences. Write your answer on the space provided.
Mutations Radiation Genetic Drift
Population Charles Darwin Recombination
Natural selection Mutagens Viruses
Gene Flow Artificial Selection DNA
1. A result of migrating individual that breed in a new location is described as ___________.
2. The alteration of DNA sequence during cell Division.___________
3. Organisms are better adapted to their environment and tend to survived and produce
more offspring.___________
4. An intentional breeding of plants or animals. ____________
5. DNA is broken and recombined to produce new combination of alleles._______________
6. The number of individual living in a particular area. _______________
7. Molecules that contain genetic code of organisms. __________________
8. English Naturalist credited for the theory of evolution. _______________
9. An Agent, such as radiations or chemical substances, which causes genetic mutations. __________
10. A submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of the organisms.______
You might also like
- Darwin FactsDocument3 pagesDarwin Factsapi-334125776No ratings yet
- 03 Modern Photoelectric Effect LabDocument3 pages03 Modern Photoelectric Effect LabMeagan TamplinNo ratings yet
- Q3 WEEK 3 LAS-1-Reproductive IsolationDocument1 pageQ3 WEEK 3 LAS-1-Reproductive IsolationAnjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Science, Technology, and SocietyDocument27 pagesScience, Technology, and SocietyAnjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Astm D 1142Document12 pagesAstm D 1142Erick Jhonhatan Limon100% (1)
- Understanding Natural SelectionDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Natural SelectionKaira JogNo ratings yet
- Mod 6 Evolution and ClassificationDocument7 pagesMod 6 Evolution and ClassificationrasingtanyaroseNo ratings yet
- NP - General Biology 2 11 & 12 - Q3 - W2 CDocument6 pagesNP - General Biology 2 11 & 12 - Q3 - W2 CIrrah Sheene De VegaNo ratings yet
- Bio Week 1 NotesDocument11 pagesBio Week 1 NotesIan SibalNo ratings yet
- Genetic Variability by Design: Chris AshcraftDocument54 pagesGenetic Variability by Design: Chris Ashcraftgabi_xyzNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science - Q2 - Week 4Document25 pagesEarth and Life Science - Q2 - Week 4Nikko SaiNo ratings yet
- GB2 - Q3 - Week 2bDocument8 pagesGB2 - Q3 - Week 2bMark Kevin G. SantosNo ratings yet
- 13 bt503Document2 pages13 bt503bc200204761 AMBREEN ASHRAFNo ratings yet
- AAP 2209 Notes 2018-1Document47 pagesAAP 2209 Notes 2018-1Kevin KahingaNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Science Fact SheetsDocument4 pages3rd Quarter Science Fact Sheetsdnlaligan8No ratings yet
- Heredity and Evolution NotesDocument5 pagesHeredity and Evolution NotesCapt Pradeep kumarNo ratings yet
- Transgenic Animals: (From CCAC Resource Supplement, Spring/Summer 1997. Used With Permission of CCAC)Document5 pagesTransgenic Animals: (From CCAC Resource Supplement, Spring/Summer 1997. Used With Permission of CCAC)nitralekhaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-Change Over Time: Lesson 3: Artificial SelectionDocument3 pagesUnit 1-Change Over Time: Lesson 3: Artificial SelectionGnaWYrreJNo ratings yet
- Week 9 10 Patterns of Descent With ModificationDocument13 pagesWeek 9 10 Patterns of Descent With ModificationKiel Tj Evangelista100% (1)
- The Process in Genetic Engineering (Crops)Document11 pagesThe Process in Genetic Engineering (Crops)Inio JarhylNo ratings yet
- EvolutionDocument42 pagesEvolutionEvangelene Esquillo SanaNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering: Title CardDocument10 pagesGenetic Engineering: Title CardJonathan YambaoNo ratings yet
- 1-Evolution Fundamentals Herbers EncyclopediaAnimalBeh2010Document9 pages1-Evolution Fundamentals Herbers EncyclopediaAnimalBeh2010Uriel RodríguezNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 9 - HeredityDocument11 pagesSCIENCE 9 - Heredityemanuel.ferrer.sbeNo ratings yet
- Yearly Revision ScienceDocument6 pagesYearly Revision SciencePeroNo ratings yet
- Biology Project TRANSGENIC ANIMALS Class 12Document19 pagesBiology Project TRANSGENIC ANIMALS Class 12Shaik FaisalNo ratings yet
- Chaprter 5 Environmental ScienceDocument6 pagesChaprter 5 Environmental Sciencejeboy DaquizNo ratings yet
- Bio q3 Week 1 and 2Document2 pagesBio q3 Week 1 and 2Vanessa Joy TombocNo ratings yet
- Ch. 23 Lecture Outline PDFDocument15 pagesCh. 23 Lecture Outline PDFCSERM UNASNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of EvolutionDocument7 pagesMechanisms of EvolutionHarry Jhonley LabisteNo ratings yet
- Module 6 8 Gen. Bio. 2 EvolutionDocument24 pagesModule 6 8 Gen. Bio. 2 EvolutionNoriel Anne EsternonNo ratings yet
- Recombination ReviewDocument12 pagesRecombination ReviewAravindan Muthu100% (1)
- General Biology ReviewerDocument15 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerArabelle VilanNo ratings yet
- Artical 1Document6 pagesArtical 1Srinjoy AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Are We There Yet? Tracking The Development of New Model SystemsDocument8 pagesAre We There Yet? Tracking The Development of New Model SystemsmioclaenusNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Module 4 Week 4Document4 pagesGen Bio Module 4 Week 4LouisseNo ratings yet
- GenBio2 Q3 M4 6 Learner PDFDocument48 pagesGenBio2 Q3 M4 6 Learner PDFFlores Carl JosephNo ratings yet
- Scientific ThoughtDocument4 pagesScientific ThoughtEPR PRNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity 11Document22 pagesBiodiversity 11Ma Naida EndrinalNo ratings yet
- A Third Way: More Articles On EvolutionDocument5 pagesA Third Way: More Articles On EvolutionjlventiganNo ratings yet
- Principles of Genetics and Animal BreedingDocument18 pagesPrinciples of Genetics and Animal BreedingJoshua BadongNo ratings yet
- What Is The Future of Animal BiotechnologyDocument9 pagesWhat Is The Future of Animal BiotechnologyIbnan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Essay 34Document2 pagesEssay 34api-213708874No ratings yet
- Genes and Their Role in Animal Productivity: Introduction To Animal ScienceDocument28 pagesGenes and Their Role in Animal Productivity: Introduction To Animal Sciencedreih MadrigNo ratings yet
- Forum/Open Discussion: - Lesson 1: Genetics, Evolution and Origin of Biodiversity ObjectivesDocument13 pagesForum/Open Discussion: - Lesson 1: Genetics, Evolution and Origin of Biodiversity ObjectivesArianne PoleaNo ratings yet
- The Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection Was First Formulated in Charles DarwinDocument5 pagesThe Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection Was First Formulated in Charles Darwinabeeraafzal45No ratings yet
- General Biology 2 Q3-M1 GeneticsDocument25 pagesGeneral Biology 2 Q3-M1 GeneticsAdrian DisuNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity 1: Natural Selection: Basic ConceptsDocument2 pagesBiodiversity 1: Natural Selection: Basic ConceptsMaya MerchantNo ratings yet
- Evolution of MechanismsDocument15 pagesEvolution of MechanismsJesmin ShumiNo ratings yet
- Princ of BiotechnologyDocument16 pagesPrinc of BiotechnologyBayu KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 2 Topic 4Document12 pagesBiology Unit 2 Topic 4Fahad MohammedNo ratings yet
- Dna Recombinant Technology BiotechnologyDocument172 pagesDna Recombinant Technology BiotechnologytasniyanNo ratings yet
- 2.8 ClassificationDocument8 pages2.8 Classificationebeth2987No ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument92 pagesGenetic EngineeringaurelylanieNo ratings yet
- Gene TherapyDocument58 pagesGene Therapynancy vargese100% (1)
- Module 28 - EditedDocument11 pagesModule 28 - Editedrichard reyesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Micro EvolutionDocument47 pagesLecture 6 - Micro EvolutionirosalejosNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 - GeneticsDocument3 pagesLESSON 3 - GeneticsRichelle MasingNo ratings yet
- Descent With ModificationDocument3 pagesDescent With ModificationJaymark HisonaNo ratings yet
- Evolution: - Evolution Means Change Over Time Changes in Species Over Long Periods of TimeDocument29 pagesEvolution: - Evolution Means Change Over Time Changes in Species Over Long Periods of TimeMalik FhaimNo ratings yet
- Las 5 Bio2 PDFDocument13 pagesLas 5 Bio2 PDFPeanut BlobNo ratings yet
- 2 EvolutionDocument7 pages2 EvolutionJamie Rose FontanillaNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering PTDocument16 pagesGenetic Engineering PTNicole Mae SumaltaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio1 Module 10Document20 pagesGen Bio1 Module 10Anjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- General Biology I M7Document19 pagesGeneral Biology I M7Anjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio1 Module 9Document23 pagesGen Bio1 Module 9Anjhiene Camba100% (2)
- General Biology I M6Document19 pagesGeneral Biology I M6Anjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- General Biology I M4Document24 pagesGeneral Biology I M4Anjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Q3 - WEEK 7 - LAS-3-Dichotomous Keys For IdentificationDocument1 pageQ3 - WEEK 7 - LAS-3-Dichotomous Keys For IdentificationAnjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio1 - Module 13Document19 pagesGen Bio1 - Module 13Anjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Q3 - WEEK 3 - LAS-3-Timeline of Evolution ThoughtDocument1 pageQ3 - WEEK 3 - LAS-3-Timeline of Evolution ThoughtAnjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Q3 - WEEK 3 - LAS-2-SpeciationDocument1 pageQ3 - WEEK 3 - LAS-2-SpeciationAnjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Q3 - WEEK 7 - LAS-1-The Linnean System of ClassificationDocument1 pageQ3 - WEEK 7 - LAS-1-The Linnean System of ClassificationAnjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Q3 - WEEK 8 - LAS-3-Cladogram-Infer Evolutionary RelatednessDocument1 pageQ3 - WEEK 8 - LAS-3-Cladogram-Infer Evolutionary RelatednessAnjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Profession Module 1Document15 pagesTeaching Profession Module 1Anjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Q3 - WEEK 8 - LAS-2-Cladistics-Shared Derived CharacterDocument2 pagesQ3 - WEEK 8 - LAS-2-Cladistics-Shared Derived CharacterAnjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Q3 - WEEK 5 - LAS-3-Infering Relationships From Evidences of Evolution-FossilsDocument2 pagesQ3 - WEEK 5 - LAS-3-Infering Relationships From Evidences of Evolution-FossilsAnjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Letter of Application GPC 1111111Document4 pagesLetter of Application GPC 1111111Anjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Q3 - WEEK 7 - LAS-2-Classification of Organism Using Hierarchal SystemDocument2 pagesQ3 - WEEK 7 - LAS-2-Classification of Organism Using Hierarchal SystemAnjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Q3 - WEEK 6 - LAS-1-Multiple Lines of EvidenceDocument2 pagesQ3 - WEEK 6 - LAS-1-Multiple Lines of EvidenceAnjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 First QuarterDocument10 pagesGeneral Biology 1 First QuarterAnjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Quiz 3Document3 pagesGen Bio Quiz 3Anjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Student Learning Ii: Beed Module 2Document7 pagesAssessment of Student Learning Ii: Beed Module 2Anjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Student Learning Ii: Beed Module 2Document8 pagesAssessment of Student Learning Ii: Beed Module 2Anjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Social Dimensions Module 1Document14 pagesSocial Dimensions Module 1Anjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Arts in The Elemntary Module 1Document31 pagesTeaching Arts in The Elemntary Module 1Anjhiene Camba100% (1)
- PDF Module 2Document8 pagesPDF Module 2Anjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Physical Science: Schools Division of Alaminos CityDocument27 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Physical Science: Schools Division of Alaminos CityAnjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Complete Test Series ScheduleDocument12 pagesComplete Test Series ScheduleLively LipunNo ratings yet
- 269 Simulation and Performance Analysis of Solar Pv-Wind Hybrid Energy System Using Matlab SimulinkDocument6 pages269 Simulation and Performance Analysis of Solar Pv-Wind Hybrid Energy System Using Matlab SimulinkNikhil sharma100% (1)
- Factors Affecting The Ecological Conditions of Surkhandarya Region (Biotic, Abiotic, Anthropogin, Temperature, Water)Document5 pagesFactors Affecting The Ecological Conditions of Surkhandarya Region (Biotic, Abiotic, Anthropogin, Temperature, Water)Central Asian StudiesNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science IV FinalDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science IV FinalROCHELLE MATIRANo ratings yet
- General Education PRC 16-30Document105 pagesGeneral Education PRC 16-30Idyls SorongonNo ratings yet
- Module 5 6 EcosystemDocument3 pagesModule 5 6 Ecosystemaatorrico5967qcNo ratings yet
- Flood (Report Text)Document2 pagesFlood (Report Text)Abimanyu Ajipangestu0% (2)
- This Is Limited & Free Trial. You Must Pay For Full Access.: Your School'S Name & Logo Can Be Here!!!Document2 pagesThis Is Limited & Free Trial. You Must Pay For Full Access.: Your School'S Name & Logo Can Be Here!!!Shabbir HussainNo ratings yet
- Heat of Phase ChangeDocument15 pagesHeat of Phase ChangeLyza JavierNo ratings yet
- Depositional EnvironmentsDocument38 pagesDepositional EnvironmentsMohammad Iqbal Mahamad Amir67% (3)
- 8 The Power of WindDocument7 pages8 The Power of WindAnonymous HyOfbJ6No ratings yet
- Diagenesis of Clastic Sedimentary RocksDocument4 pagesDiagenesis of Clastic Sedimentary RocksElysha HenryNo ratings yet
- BIO120 Test 2 FlashcardsDocument21 pagesBIO120 Test 2 FlashcardsBon AppleteaNo ratings yet
- Final Green MarketingDocument22 pagesFinal Green MarketingHarish KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Activation EnergyDocument3 pagesEnzymes Activation EnergyDanielle WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- DRRR Module 1Document8 pagesDRRR Module 1Marie LivennaNo ratings yet
- 01-02 APM30 Product DescriptionDocument14 pages01-02 APM30 Product DescriptionMahdiNo ratings yet
- CIVE1129 Course Guide Part BDocument3 pagesCIVE1129 Course Guide Part BMike ChanNo ratings yet
- Mountain Waves-1Document18 pagesMountain Waves-1FixNo ratings yet
- Making Decisions With InsulationDocument12 pagesMaking Decisions With InsulationAbdallah MansourNo ratings yet
- BTD Question Bank (18ME33)Document5 pagesBTD Question Bank (18ME33)RaviparasheraNo ratings yet
- Foam Lok 2000 4g Cut Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesFoam Lok 2000 4g Cut Sheet PDFCam VistainNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1: First Quarter-Module 9: Gas LawsDocument24 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: First Quarter-Module 9: Gas LawsElysha Mae RamirezNo ratings yet
- Lec 6 Entropy and The Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocument77 pagesLec 6 Entropy and The Second Law of ThermodynamicsACCOUNT ONENo ratings yet
- Soils Written .....Document39 pagesSoils Written .....JessieJameEOculamNo ratings yet
- PETRONAS HSE KPI Definition and Reporting Guideline R0 Final Draft 121120Document61 pagesPETRONAS HSE KPI Definition and Reporting Guideline R0 Final Draft 121120almamunmolla96No ratings yet
- Stage 8 Sci T1 Activties FinDocument7 pagesStage 8 Sci T1 Activties FinRoxanneNo ratings yet
- CH1 Designing For Hope - Why Do We NeedDocument16 pagesCH1 Designing For Hope - Why Do We NeedVictor kakaNo ratings yet