Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1st Quarter Week 2 TOPIC - The Levels of Managers
1st Quarter Week 2 TOPIC - The Levels of Managers
Uploaded by
Romnick SarmientoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Solution Manual For Management 12th Edition by DaftDocument20 pagesSolution Manual For Management 12th Edition by DaftSaxon D Pinlac75% (4)
- Introduction To Management NotesDocument37 pagesIntroduction To Management NotesSaurabh Suman100% (2)
- Chapter 1 Management and OrganizationsDocument12 pagesChapter 1 Management and OrganizationsBo Zydarin100% (1)
- CH 1 Fundamentals of ManagementDocument8 pagesCH 1 Fundamentals of Managementpichhibabu100% (1)
- PM Review For FinalDocument11 pagesPM Review For FinalMai AnhNo ratings yet
- #1-Foundation of Management and OrganizationDocument26 pages#1-Foundation of Management and OrganizationJoanna Garcia100% (1)
- Assignment On Management Process and Organization BehaviorDocument48 pagesAssignment On Management Process and Organization Behaviordiplococcous72% (18)
- Assignment Individual - AsdDocument3 pagesAssignment Individual - AsdFrancisLigadu67% (3)
- Quarter 1 Week 2 - Organization and ManagementDocument11 pagesQuarter 1 Week 2 - Organization and ManagementRomnick MagdaraogNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Week 1 An Overview of Management and Org.Document10 pages1st Quarter Week 1 An Overview of Management and Org.Romnick SarmientoNo ratings yet
- ABM - 11 - 12 - Organization and Management - q3 - CLAS2 - FUNCTIONS ROLES AND SKILLS OF A MANAGER - v1 1 JOSEPH AURELLODocument23 pagesABM - 11 - 12 - Organization and Management - q3 - CLAS2 - FUNCTIONS ROLES AND SKILLS OF A MANAGER - v1 1 JOSEPH AURELLOZyrichNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 Y2013Document9 pagesTutorial 1 Y2013Zaha AzmanNo ratings yet
- WEEK-2-Organization and ManagementDocument13 pagesWEEK-2-Organization and ManagementSashiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2. Management and ManagerDocument4 pagesLesson 2. Management and ManagerNHASSER PASANDALANNo ratings yet
- Organization and Management Week 2Document8 pagesOrganization and Management Week 2kattNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Managment: BookDocument33 pagesIntroduction To Managment: Bookrizqikiki64No ratings yet
- Managerial Principles and Techniques: Online Based AssignmentDocument10 pagesManagerial Principles and Techniques: Online Based AssignmentEdmond Dantès100% (1)
- Seminarski Rad: Fakultet Za Pravo, Bezbednost I Menadžment ,,konstantin Veliki" BeogradDocument14 pagesSeminarski Rad: Fakultet Za Pravo, Bezbednost I Menadžment ,,konstantin Veliki" BeogradPavle PopovicNo ratings yet
- My Report For LeadershipDocument23 pagesMy Report For LeadershipNewgleer WengNo ratings yet
- At The End of This Chapter, The Students Are Expected To:: G.Rafol2020/Management 1a/page 1 of 10Document10 pagesAt The End of This Chapter, The Students Are Expected To:: G.Rafol2020/Management 1a/page 1 of 10Jessabel Rosas BersabaNo ratings yet
- Sas#3 Bam191Document7 pagesSas#3 Bam191Khel SedaNo ratings yet
- O&m PPT Module 2 2022 2023Document22 pagesO&m PPT Module 2 2022 2023Jaslor LavinaNo ratings yet
- Oam q1 Module2 Week2Document6 pagesOam q1 Module2 Week2Michael angelo MaroNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Midterm Exam - ReviewDocument6 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Midterm Exam - ReviewKimmy BeckNo ratings yet
- Managerial Roles OAMDocument4 pagesManagerial Roles OAMGaniu TayoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document16 pagesChapter 1Chickay GalosNo ratings yet
- Management Chap 1a-BDocument6 pagesManagement Chap 1a-BThư LuyệnNo ratings yet
- Organization and Management Module 2: Quarter 1 - Week 2Document15 pagesOrganization and Management Module 2: Quarter 1 - Week 2juvelyn luegoNo ratings yet
- Module1Document102 pagesModule1Jahnavi VurityNo ratings yet
- CH 01 GEDocument13 pagesCH 01 GEShariful ShishirNo ratings yet
- Managerial Skills ReportDocument35 pagesManagerial Skills ReportRohit Soni100% (1)
- Roles of ManagerDocument7 pagesRoles of ManagerShubham KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Roles and Skills of ManagersDocument9 pagesRoles and Skills of Managersarjun SinghNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Org & ManagementDocument4 pagesWeek 2 Org & ManagementVia Terrado CañedaNo ratings yet
- Organization and Management M2Document16 pagesOrganization and Management M2Lyka Niña Pason0% (1)
- True or False: Chapter 1: Managers and You in The Workplace-Management HistoryDocument3 pagesTrue or False: Chapter 1: Managers and You in The Workplace-Management HistoryShaarif Rajput100% (1)
- Management Summary Chapter 01Document13 pagesManagement Summary Chapter 01ZainabNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ManagementDocument2 pagesIntroduction To ManagementJc JacksonNo ratings yet
- Maribeth Bautista Business ManagementDocument10 pagesMaribeth Bautista Business ManagementMa Ri BethNo ratings yet
- Management NotesDocument26 pagesManagement Notesydab gamesNo ratings yet
- Om 11 Module 2Document15 pagesOm 11 Module 2Aldrin Sarge TayagNo ratings yet
- MGT AssignmentDocument14 pagesMGT AssignmentigifariziNo ratings yet
- Robbins Mgmt11 Chapter 01Document13 pagesRobbins Mgmt11 Chapter 01Adil Hussain AdilNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Organization and OrganizationDocument52 pagesWeek 2 Organization and OrganizationFrancis Little AdventuresNo ratings yet
- It 32 Unit 2Document47 pagesIt 32 Unit 2shinhari332No ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Chapter 3 - ManagementDocument6 pagesUnit 2 - Chapter 3 - ManagementBlanny MacgawNo ratings yet
- Who Is A Manager?: Role of ManagersDocument64 pagesWho Is A Manager?: Role of ManagersMansiNo ratings yet
- Final Assignment of MPOBDocument47 pagesFinal Assignment of MPOBRahul GuptaNo ratings yet
- Bme 1 (Aubrey Desamito)Document6 pagesBme 1 (Aubrey Desamito)Mia Rose BuenoNo ratings yet
- Module 2-Organization and ManagementDocument6 pagesModule 2-Organization and ManagementnicNo ratings yet
- Managers Are Made or BornDocument27 pagesManagers Are Made or BornMihir Panchal100% (1)
- OM PPT Manager's Job Functions Roles and SkillsDocument17 pagesOM PPT Manager's Job Functions Roles and SkillsRosette UngabNo ratings yet
- Changing Nature of Managerial WorkDocument10 pagesChanging Nature of Managerial WorkakramNo ratings yet
- Basic ManagementDocument72 pagesBasic ManagementpaqsoriNo ratings yet
- Abm 211 Chapter 1 Module 1 Intro To Organization and MGTDocument18 pagesAbm 211 Chapter 1 Module 1 Intro To Organization and MGTnullas jesanNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Levels of Management and Management by ObjectivesDocument8 pages3.1 Levels of Management and Management by ObjectivesOre PerezNo ratings yet
- Organization and Management 1 Quarter Lesson 2: Nature and Concepts of Management (Continuation of Lesson 1)Document3 pagesOrganization and Management 1 Quarter Lesson 2: Nature and Concepts of Management (Continuation of Lesson 1)Sayno, Samantha Jade C.No ratings yet
- A Pragmatic Introduction to Middle Manager Fundamentals: Part 2 - Managing at a DistanceFrom EverandA Pragmatic Introduction to Middle Manager Fundamentals: Part 2 - Managing at a DistanceNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Guide to Successful Lean Transformation: Top Reasons Why Companies Fail to Achieve and Sustain Excellence through Lean ImprovementFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide to Successful Lean Transformation: Top Reasons Why Companies Fail to Achieve and Sustain Excellence through Lean ImprovementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Leading from Within: Unlocking the Power of Self-Leadership in the 21st Century OrganizationFrom EverandLeading from Within: Unlocking the Power of Self-Leadership in the 21st Century OrganizationNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Week 9 Forms of Business OwnershipDocument8 pages2nd Quarter Week 9 Forms of Business OwnershipRomnick SarmientoNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Week 7 and 8 Ethics and Social ResponsibilitiesDocument11 pages1st Quarter Week 7 and 8 Ethics and Social ResponsibilitiesRomnick SarmientoNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Week 5 and 6 Evolution of Management TheoriesDocument17 pages1st Quarter Week 5 and 6 Evolution of Management TheoriesRomnick SarmientoNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Week 3 and 4business and Its EnvironmentDocument17 pages1st Quarter Week 3 and 4business and Its EnvironmentRomnick SarmientoNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Week 1 An Overview of Management and Org.Document10 pages1st Quarter Week 1 An Overview of Management and Org.Romnick SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Bus - Ethics - q3 - Mod5 - Impact of Belief System - FinalDocument24 pagesBus - Ethics - q3 - Mod5 - Impact of Belief System - FinalRomnick Sarmiento100% (1)
- 1st Quarter Exam EntrepDocument3 pages1st Quarter Exam EntrepRomnick SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Bus - Ethics - q3 - Mod7 - Ways To Improve Business Practices Guided by The Philosophies, Belief System or Filipino Values - FinalDocument17 pagesBus - Ethics - q3 - Mod7 - Ways To Improve Business Practices Guided by The Philosophies, Belief System or Filipino Values - FinalRomnick SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Bus - Ethics - q3 - Mod6 - Filipino Value System and Their Influence in Business Practices - FinalDocument19 pagesBus - Ethics - q3 - Mod6 - Filipino Value System and Their Influence in Business Practices - FinalRomnick SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Essential Work Skills PPT 897Document31 pagesEssential Work Skills PPT 897aarti21No ratings yet
- 6 Pursuit of KnowledgeDocument15 pages6 Pursuit of KnowledgeLee SuarezNo ratings yet
- Bateman M7e PPT Ch01 AccessibleDocument31 pagesBateman M7e PPT Ch01 AccessibleAisya GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Management 12 Edition by Daft - Chapter 1 Review QuestionsDocument34 pagesManagement 12 Edition by Daft - Chapter 1 Review QuestionsMỹ HuyềnNo ratings yet
- Soft Skills Are Abilities That Are Not Directly Related To A Specific Career, But ComplementDocument4 pagesSoft Skills Are Abilities That Are Not Directly Related To A Specific Career, But ComplementOscar ADSNo ratings yet
- The Complete Guide For New ManagersDocument28 pagesThe Complete Guide For New ManagersDahab Masr- YouTube100% (2)
- 1.0 - Communication Skills As Career FiltersDocument21 pages1.0 - Communication Skills As Career FiltersDaniella Marie AbrogarNo ratings yet
- CV - Elena-Denisa DimaDocument3 pagesCV - Elena-Denisa DimaDenisa DimaNo ratings yet
- Managerial SkillsDocument3 pagesManagerial Skillseshu100% (1)
- Case Shaping Future Business Leaders 9 June 2016Document7 pagesCase Shaping Future Business Leaders 9 June 2016Alka AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Effective Communication & Interpersonal SkillsDocument4 pagesEffective Communication & Interpersonal SkillsRavin DoraisamyNo ratings yet
- Principles of Management: Fundamentals of Management (9 Edition) by Stephen P. Robbins, David A. Decenzo and Mary CoulterDocument41 pagesPrinciples of Management: Fundamentals of Management (9 Edition) by Stephen P. Robbins, David A. Decenzo and Mary Coulterranim m7mdNo ratings yet
- Innovative Management For Turbulent TimesDocument16 pagesInnovative Management For Turbulent TimesDinnisa TiaraNo ratings yet
- Interpersonal SkillsDocument3 pagesInterpersonal SkillsKartikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Nature and Concept of ManagementDocument10 pagesChapter 1 Nature and Concept of ManagementMa Blesilda Michaela SarbuesNo ratings yet
- Admin ProcedureDocument24 pagesAdmin ProcedureZera Jean TinoyNo ratings yet
- Concept of Leadership and ManagementDocument13 pagesConcept of Leadership and ManagementPia Amistoso100% (1)
- TP 036-3-2015 Motor Vehicle Inspection 27 36Document10 pagesTP 036-3-2015 Motor Vehicle Inspection 27 36syafik tumiranNo ratings yet
- SOFT Skill Training and Its Impact On ProductivityDocument36 pagesSOFT Skill Training and Its Impact On ProductivityUpskillistNo ratings yet
- Terms of References For 5 Specialist Consultants Under World Bank ProjectDocument20 pagesTerms of References For 5 Specialist Consultants Under World Bank ProjectVetri VendanNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Supervisory Management 10th Edition Donald C Mosley Don C Mosley JR Paul H PietriDocument25 pagesTest Bank For Supervisory Management 10th Edition Donald C Mosley Don C Mosley JR Paul H PietriAnissa Trowery100% (33)
- Paint Chemist - Job Post - VacancyMail JobsDocument2 pagesPaint Chemist - Job Post - VacancyMail JobsKudzai MazangoNo ratings yet
- Home EconomicsDocument45 pagesHome EconomicsKenneth SantosNo ratings yet
- The Role of Libraries in Higher EducationDocument4 pagesThe Role of Libraries in Higher EducationHnin PwintNo ratings yet
- Ejemplo de Curriculum VitaeDocument8 pagesEjemplo de Curriculum VitaeJuriNo ratings yet
- REVISE CommunicationSkillsOfAccountancyBusinessAndManagementStudents BernardoE BernardoR DonggonV MangogtongA SigbaJDocument34 pagesREVISE CommunicationSkillsOfAccountancyBusinessAndManagementStudents BernardoE BernardoR DonggonV MangogtongA SigbaJbernardoellyjaneNo ratings yet
- Transferable Skills - 10 Skills That Work Across IndustriesDocument5 pagesTransferable Skills - 10 Skills That Work Across IndustriesjosieliraychanNo ratings yet
- Course Information: Universiti Teknologi MaraDocument8 pagesCourse Information: Universiti Teknologi MaraDR ADILAH OTHMANNo ratings yet
- ASM 2 525 (Full)Document14 pagesASM 2 525 (Full)Pham Nguyen Anh (FGW HCM)No ratings yet
1st Quarter Week 2 TOPIC - The Levels of Managers
1st Quarter Week 2 TOPIC - The Levels of Managers
Uploaded by
Romnick SarmientoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1st Quarter Week 2 TOPIC - The Levels of Managers
1st Quarter Week 2 TOPIC - The Levels of Managers
Uploaded by
Romnick SarmientoCopyright:
Available Formats
3rd Floor Ever Gotesco Building Commonwealth Ave.
, Cor Batasan,
Quezon City, 1126 Metro Manila /
Tel. No. (028) 2533859
MODULE
Organization and Management
Grade 11
1st Quarter - Week Two
The Levels of Managers
Name: ______________________________________________ Date: ____________
Grade & Section: _____________________________________ Score: ___________
I. SUBJECT CONTENT:
The Levels of Managers
II. OBJECTIVES:
At the end of this lesson. The students are expected to:
1. Compare the types of managers
2. Examine the levels of managers in the organization;
3. Examine the skills required in managing;
III. REFERENCE/S
Book: Business Organization and Management
Publisher: (Roberto G. Medina Rex Book Store)
IV. PRE - TEST
Part 1.True or False: Write T if the statement is correct and F if is not.
__________ 1. Line managers are directly concerned with accomplishing the goals of the
organization.
__________ 2. A person with good human skills will have the feelings of others.
__________ 3. Administrators are managers working in government or non-profit organizations.
__________ 4. These are the roles the manager’s plays when he interacts with others like
figurehead.
Organization and Management 1
__________ 5. A very important aspect of the manager’s job is to receive and communicate
information what we called the interpersonal roles.
Part 2. Instruction: Select the answer from the choices given. Write the letter of your choice in
the blank provided for:
________1. What is a major function of management that deals with deciding in what to do in
advance?
a. planning b. organizing c. staffing d. directing
________2. What involves bringing together physical, financial & human resources to achieve
the goals and objective of the firm?
a. Planning b. organizing c. staffing d. directing
________3. What management function involves measuring the organization’s performance
against standards set by the industry or by the organization?
a. planning b. organizing c. staffing d. controlling.
________4. What function of management inspires people to a common goal?
a. planning b. organizing c. staffing d. directing
________5. What involves the provision of qualified personnel for the organization, through
reliable hiring practices, training and development etc.?
a. planning b. organizing c. staffing d. directing
________6. Who said that there are 10 managerial roles which fall into 3 categories of
interpersonal, informational and decisional roles?
a. Drucker b. Mintzberg c. Follet d. Taylor
________7. What is the role of a manager when he acts as the main contact to the rest of the
business community and the world?
a. figurehead b. leader c. liaison d. monitor
________8. What is the role of a manager when he directs and leads the entire organization to
pursue the goals of the organization?
a. figurehead b. leader c. liaison d. monitor
________9. What is the role of the manager when he performs ceremonial duties as head of
the organization like cutting the ceremonial ribbon for business opening, greeting VIPs who visit,
giving speech in the celebrations?
Organization and Management 2
a. figurehead b. leader c. liaison d. monitor ________
10. What is the manager’s role when he makes important announcements of plans, directions,
new policies of the organization?
a. figurehead b. leader c. liaison d. disseminator
________11. What is the role of the manager when he settles disputes to protect the integrity
of the organization?
a. entrepreneur b. spokesman c. disturbance handler d. monitor
________12. What role is played by the manager when he scans the business environment for
opportunities to take advantage of?
a. entrepreneur b. disturbance handler c. resource allocator d. negotiator
________13. The successful performance of a manager will depend on his competence and
skill. What skill is needed to be able to strategize and think ahead into the future?
a. technical skills b. human skills c. conceptual skills d. negotiation skill.
________14. What skill needs to be developed by the manager to be able to understand how
the different departments as well as their systems and processes work in the organization?
a. technical skill b. human skill c. conceptual skill d. negotiation skill.
________15. What managerial skill needs to be developed to be able to successfully make
positive people interaction?
a. technical skill b. human skill c. conceptual skill d. negotiation skill.
Organization and Management 3
3rd Floor Ever Gotesco Building Commonwealth Ave., Cor Batasan,
Quezon City, 1126 Metro Manila /
Tel. No. (028) 2533859
MODULE
Organization and Management
Grade 11
1st Quarter - Week Two
The Levels of Managers
Name: ______________________________________________ Date: ____________
Grade & Section: _____________________________________ Score: ___________
V. LESSON PROPER:
The organization and management’s success depends on how managers
perform their functions and roles. The term ‘manager’ is widely used term in the business
world. Manager is a person who has responsibility for the activities of other people in the
organization. Hence, firm’s president is called manager, a commander of a troop of managers.
Despite of company’s high end machineries, huge capital, strong brand, committed
employees, and loyal customers, still the success relies most on how managers effectively
and efficiently perform their functions, roles and equipped with managerial skills.
VI. A. MOTIVATION
List down the family members and identify each role. Explain their duties and responsibilities.
Family Members Role Duties and Responsibilities
Organization and Management 4
B. DISCUSSION:
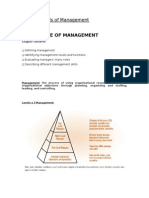
Managers function according to the levels they are in. In a small organization, there
would normally be just a single manager who is expected to perform all the managerial
roles and tasks. In the transition from a small to a large organization, there may be two
levels of managers who divided among themselves the managerial roles and tasks.
There are times when the size of the organization justifies setting up three levels of
managers: The Top management. The middle management and the lower
management. The figure below shows the levels at the various stages of organizational
growth.
Levels of Managers (by size of Organization)
Single Top Top
Manager Manager Manager
Frontline Middle
Employees Manager Manager
Frontline
Employees
Manager
Employees
Organization and Management 5
Top managers are responsible for the overall performance of the organization. They
formulate strategies, provide leadership, evaluate and shape the method of organizing and
control the direction of the organization in the effort to accomplish goals. Top managers usually
hold titles such as chief executive officer, president, chairman or senior vice president.
Middle managers direct the activities of other managers and sometimes also those of
operating employees. They work with top managers and coordinate with peers to develop and
implement action plans to accomplish organizational objectives. Examples of middle managers
are the dean of the business school in a university, the plant manager in the manufacturing
concern and branch manager of a trading firm.
Lower level managers are responsible for leading employees in the day to day tasks,
which contribute to the organization’s goals. Of the various levels of managers, they are the
ones in direct contract with the employees. Because of this, they are also referred to as “first
line” or “front line” managers. Apart from performing the other managerial functions of planning,
directing and organizing their tasks include correcting errors or solving problems directly related
to the production to the production of goods and services.
Types of Managers
Managers may be different from one another in terms of the work they do. They may be
briefly described as follows.
1. Line managers are directly concerned with accomplishing the goals of the organization. The
decisions they make with regards to operations are expected to be final and must be
implemented. For example, the university president, the dean, and the department heads all
have line responsibilities.
2. Staff managers are in charge of units that provide support line units. In doing their work, they
use special expertise to advise the line workers. The director of personnel and controller are
examples of staff managers.
3. Administrators are managers working in government or non-profit organizations. Examples
include school administrators, provincial administrators and hospital administrators.
Management Skills
The effective and efficient performance of management functions such as planning.
Organizing, leading, and controlling are possible only if the manager is well equipped with the
necessary management skills. Such requirements may be briefly described as follows.
1. Technical skills refers to the abilities to use special proficiencies or expertise in performing
specific tasks. They refer to the use of tools, techniques and specialized knowledge.
Organization and Management 6
2. Human skills refers to the abilities to work well in cooperation with other persons; whether
they are subordinates, peers or superiors. A person with good human skills will have the
feelings of others.
The Required Management Skills at Different Levels of Management
The application of various management skills from level to level in the management
hierarchy. As shown in Figure 2, first line manager need less conceptual skills in the
performance of his work and more human and technical skills. Compared to the first line
managers, middle need more conceptual skills, the same degree of human skills as that of first
line managers, but less on technical skills. The biggest concern of top management is on
conceptual skills; the same degree of human skills as these of first line and middle managers
and with the list concern about technical skills.
Figure 2
Management skills needed at different levels of Management
First line Managers Middle Managers Top Managers
Conceptual Conceptual Conceptual
Human
Human
Human
Technical
Technical Technical
Some of the human skills necessary for managers are effective oral and written
communications, creating positive attitude toward others and in the work setting, developing
cooperation among group members and motivating subordinates.
3. Conceptual skills refers to the ability of the managers to see the organizations as a whole and
to solve problems in ways that benefit the total system. Especially the manager who possess
Organization and Management 7
these skills is expected to analyse and solve complex problems. Thus the manager with good
conceptual skills will have the mental capacity to perform the following:
1. identify problems and opportunities
2. gather and interpret relevant information
3. execute problem solving decision that serve the organization’s purpose.
Managerial Roles
The manager is expected to lead his unit or department in achieving its objectives. As
such, he is bound to interact with people and deal with process. In the attempt to produce
results the manager assumes roles as varied as the following.
1. Interpersonal Roles. These are the roles the manager’s plays when he interacts with others.
The specific roles under this category are:
a. Figurehead
b. Leader
c. Liaison
2. Informational Roles. A very important aspect of the manager’s job is to receive and
communicate information. Such a roles are vital to his decision making task. One receiving and
sharing information the manager assumes these specific roles. These are briefly described as
follows.
a. Monitor
b. Disseminator
c. Spokesperson
3. Decisional Roles. The major part of the manager’s job is to make decision. As such, he must
use the information he processes to make decision that solve problems. As decision maker, the
manager assumes the following roles.
a. Entrepreneur
b. Disturbance
c. Resource Allocator
Organization and Management 8
C. ACTIVITIES
Part 1: Directions/Instructions: Plot the levels of management on the pyramid.
Part 2: Based on the pictures given below, answer this question, ‘What do managers do?
Write your answer on the blanks.
VI. ASSIGNMENT
Answer the following questions. Explain your answer.
1. How do managers contribute to the achievement of organizational goals?
2. “As a student and aspiring young professional, how will you carry out your roles, functions
and skills in your family and school?
Organization and Management 9
Organization and Management 10
You might also like
- Solution Manual For Management 12th Edition by DaftDocument20 pagesSolution Manual For Management 12th Edition by DaftSaxon D Pinlac75% (4)
- Introduction To Management NotesDocument37 pagesIntroduction To Management NotesSaurabh Suman100% (2)
- Chapter 1 Management and OrganizationsDocument12 pagesChapter 1 Management and OrganizationsBo Zydarin100% (1)
- CH 1 Fundamentals of ManagementDocument8 pagesCH 1 Fundamentals of Managementpichhibabu100% (1)
- PM Review For FinalDocument11 pagesPM Review For FinalMai AnhNo ratings yet
- #1-Foundation of Management and OrganizationDocument26 pages#1-Foundation of Management and OrganizationJoanna Garcia100% (1)
- Assignment On Management Process and Organization BehaviorDocument48 pagesAssignment On Management Process and Organization Behaviordiplococcous72% (18)
- Assignment Individual - AsdDocument3 pagesAssignment Individual - AsdFrancisLigadu67% (3)
- Quarter 1 Week 2 - Organization and ManagementDocument11 pagesQuarter 1 Week 2 - Organization and ManagementRomnick MagdaraogNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Week 1 An Overview of Management and Org.Document10 pages1st Quarter Week 1 An Overview of Management and Org.Romnick SarmientoNo ratings yet
- ABM - 11 - 12 - Organization and Management - q3 - CLAS2 - FUNCTIONS ROLES AND SKILLS OF A MANAGER - v1 1 JOSEPH AURELLODocument23 pagesABM - 11 - 12 - Organization and Management - q3 - CLAS2 - FUNCTIONS ROLES AND SKILLS OF A MANAGER - v1 1 JOSEPH AURELLOZyrichNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 Y2013Document9 pagesTutorial 1 Y2013Zaha AzmanNo ratings yet
- WEEK-2-Organization and ManagementDocument13 pagesWEEK-2-Organization and ManagementSashiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2. Management and ManagerDocument4 pagesLesson 2. Management and ManagerNHASSER PASANDALANNo ratings yet
- Organization and Management Week 2Document8 pagesOrganization and Management Week 2kattNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Managment: BookDocument33 pagesIntroduction To Managment: Bookrizqikiki64No ratings yet
- Managerial Principles and Techniques: Online Based AssignmentDocument10 pagesManagerial Principles and Techniques: Online Based AssignmentEdmond Dantès100% (1)
- Seminarski Rad: Fakultet Za Pravo, Bezbednost I Menadžment ,,konstantin Veliki" BeogradDocument14 pagesSeminarski Rad: Fakultet Za Pravo, Bezbednost I Menadžment ,,konstantin Veliki" BeogradPavle PopovicNo ratings yet
- My Report For LeadershipDocument23 pagesMy Report For LeadershipNewgleer WengNo ratings yet
- At The End of This Chapter, The Students Are Expected To:: G.Rafol2020/Management 1a/page 1 of 10Document10 pagesAt The End of This Chapter, The Students Are Expected To:: G.Rafol2020/Management 1a/page 1 of 10Jessabel Rosas BersabaNo ratings yet
- Sas#3 Bam191Document7 pagesSas#3 Bam191Khel SedaNo ratings yet
- O&m PPT Module 2 2022 2023Document22 pagesO&m PPT Module 2 2022 2023Jaslor LavinaNo ratings yet
- Oam q1 Module2 Week2Document6 pagesOam q1 Module2 Week2Michael angelo MaroNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Midterm Exam - ReviewDocument6 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Midterm Exam - ReviewKimmy BeckNo ratings yet
- Managerial Roles OAMDocument4 pagesManagerial Roles OAMGaniu TayoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document16 pagesChapter 1Chickay GalosNo ratings yet
- Management Chap 1a-BDocument6 pagesManagement Chap 1a-BThư LuyệnNo ratings yet
- Organization and Management Module 2: Quarter 1 - Week 2Document15 pagesOrganization and Management Module 2: Quarter 1 - Week 2juvelyn luegoNo ratings yet
- Module1Document102 pagesModule1Jahnavi VurityNo ratings yet
- CH 01 GEDocument13 pagesCH 01 GEShariful ShishirNo ratings yet
- Managerial Skills ReportDocument35 pagesManagerial Skills ReportRohit Soni100% (1)
- Roles of ManagerDocument7 pagesRoles of ManagerShubham KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Roles and Skills of ManagersDocument9 pagesRoles and Skills of Managersarjun SinghNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Org & ManagementDocument4 pagesWeek 2 Org & ManagementVia Terrado CañedaNo ratings yet
- Organization and Management M2Document16 pagesOrganization and Management M2Lyka Niña Pason0% (1)
- True or False: Chapter 1: Managers and You in The Workplace-Management HistoryDocument3 pagesTrue or False: Chapter 1: Managers and You in The Workplace-Management HistoryShaarif Rajput100% (1)
- Management Summary Chapter 01Document13 pagesManagement Summary Chapter 01ZainabNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ManagementDocument2 pagesIntroduction To ManagementJc JacksonNo ratings yet
- Maribeth Bautista Business ManagementDocument10 pagesMaribeth Bautista Business ManagementMa Ri BethNo ratings yet
- Management NotesDocument26 pagesManagement Notesydab gamesNo ratings yet
- Om 11 Module 2Document15 pagesOm 11 Module 2Aldrin Sarge TayagNo ratings yet
- MGT AssignmentDocument14 pagesMGT AssignmentigifariziNo ratings yet
- Robbins Mgmt11 Chapter 01Document13 pagesRobbins Mgmt11 Chapter 01Adil Hussain AdilNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Organization and OrganizationDocument52 pagesWeek 2 Organization and OrganizationFrancis Little AdventuresNo ratings yet
- It 32 Unit 2Document47 pagesIt 32 Unit 2shinhari332No ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Chapter 3 - ManagementDocument6 pagesUnit 2 - Chapter 3 - ManagementBlanny MacgawNo ratings yet
- Who Is A Manager?: Role of ManagersDocument64 pagesWho Is A Manager?: Role of ManagersMansiNo ratings yet
- Final Assignment of MPOBDocument47 pagesFinal Assignment of MPOBRahul GuptaNo ratings yet
- Bme 1 (Aubrey Desamito)Document6 pagesBme 1 (Aubrey Desamito)Mia Rose BuenoNo ratings yet
- Module 2-Organization and ManagementDocument6 pagesModule 2-Organization and ManagementnicNo ratings yet
- Managers Are Made or BornDocument27 pagesManagers Are Made or BornMihir Panchal100% (1)
- OM PPT Manager's Job Functions Roles and SkillsDocument17 pagesOM PPT Manager's Job Functions Roles and SkillsRosette UngabNo ratings yet
- Changing Nature of Managerial WorkDocument10 pagesChanging Nature of Managerial WorkakramNo ratings yet
- Basic ManagementDocument72 pagesBasic ManagementpaqsoriNo ratings yet
- Abm 211 Chapter 1 Module 1 Intro To Organization and MGTDocument18 pagesAbm 211 Chapter 1 Module 1 Intro To Organization and MGTnullas jesanNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Levels of Management and Management by ObjectivesDocument8 pages3.1 Levels of Management and Management by ObjectivesOre PerezNo ratings yet
- Organization and Management 1 Quarter Lesson 2: Nature and Concepts of Management (Continuation of Lesson 1)Document3 pagesOrganization and Management 1 Quarter Lesson 2: Nature and Concepts of Management (Continuation of Lesson 1)Sayno, Samantha Jade C.No ratings yet
- A Pragmatic Introduction to Middle Manager Fundamentals: Part 2 - Managing at a DistanceFrom EverandA Pragmatic Introduction to Middle Manager Fundamentals: Part 2 - Managing at a DistanceNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Guide to Successful Lean Transformation: Top Reasons Why Companies Fail to Achieve and Sustain Excellence through Lean ImprovementFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide to Successful Lean Transformation: Top Reasons Why Companies Fail to Achieve and Sustain Excellence through Lean ImprovementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Leading from Within: Unlocking the Power of Self-Leadership in the 21st Century OrganizationFrom EverandLeading from Within: Unlocking the Power of Self-Leadership in the 21st Century OrganizationNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Week 9 Forms of Business OwnershipDocument8 pages2nd Quarter Week 9 Forms of Business OwnershipRomnick SarmientoNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Week 7 and 8 Ethics and Social ResponsibilitiesDocument11 pages1st Quarter Week 7 and 8 Ethics and Social ResponsibilitiesRomnick SarmientoNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Week 5 and 6 Evolution of Management TheoriesDocument17 pages1st Quarter Week 5 and 6 Evolution of Management TheoriesRomnick SarmientoNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Week 3 and 4business and Its EnvironmentDocument17 pages1st Quarter Week 3 and 4business and Its EnvironmentRomnick SarmientoNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Week 1 An Overview of Management and Org.Document10 pages1st Quarter Week 1 An Overview of Management and Org.Romnick SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Bus - Ethics - q3 - Mod5 - Impact of Belief System - FinalDocument24 pagesBus - Ethics - q3 - Mod5 - Impact of Belief System - FinalRomnick Sarmiento100% (1)
- 1st Quarter Exam EntrepDocument3 pages1st Quarter Exam EntrepRomnick SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Bus - Ethics - q3 - Mod7 - Ways To Improve Business Practices Guided by The Philosophies, Belief System or Filipino Values - FinalDocument17 pagesBus - Ethics - q3 - Mod7 - Ways To Improve Business Practices Guided by The Philosophies, Belief System or Filipino Values - FinalRomnick SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Bus - Ethics - q3 - Mod6 - Filipino Value System and Their Influence in Business Practices - FinalDocument19 pagesBus - Ethics - q3 - Mod6 - Filipino Value System and Their Influence in Business Practices - FinalRomnick SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Essential Work Skills PPT 897Document31 pagesEssential Work Skills PPT 897aarti21No ratings yet
- 6 Pursuit of KnowledgeDocument15 pages6 Pursuit of KnowledgeLee SuarezNo ratings yet
- Bateman M7e PPT Ch01 AccessibleDocument31 pagesBateman M7e PPT Ch01 AccessibleAisya GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Management 12 Edition by Daft - Chapter 1 Review QuestionsDocument34 pagesManagement 12 Edition by Daft - Chapter 1 Review QuestionsMỹ HuyềnNo ratings yet
- Soft Skills Are Abilities That Are Not Directly Related To A Specific Career, But ComplementDocument4 pagesSoft Skills Are Abilities That Are Not Directly Related To A Specific Career, But ComplementOscar ADSNo ratings yet
- The Complete Guide For New ManagersDocument28 pagesThe Complete Guide For New ManagersDahab Masr- YouTube100% (2)
- 1.0 - Communication Skills As Career FiltersDocument21 pages1.0 - Communication Skills As Career FiltersDaniella Marie AbrogarNo ratings yet
- CV - Elena-Denisa DimaDocument3 pagesCV - Elena-Denisa DimaDenisa DimaNo ratings yet
- Managerial SkillsDocument3 pagesManagerial Skillseshu100% (1)
- Case Shaping Future Business Leaders 9 June 2016Document7 pagesCase Shaping Future Business Leaders 9 June 2016Alka AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Effective Communication & Interpersonal SkillsDocument4 pagesEffective Communication & Interpersonal SkillsRavin DoraisamyNo ratings yet
- Principles of Management: Fundamentals of Management (9 Edition) by Stephen P. Robbins, David A. Decenzo and Mary CoulterDocument41 pagesPrinciples of Management: Fundamentals of Management (9 Edition) by Stephen P. Robbins, David A. Decenzo and Mary Coulterranim m7mdNo ratings yet
- Innovative Management For Turbulent TimesDocument16 pagesInnovative Management For Turbulent TimesDinnisa TiaraNo ratings yet
- Interpersonal SkillsDocument3 pagesInterpersonal SkillsKartikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Nature and Concept of ManagementDocument10 pagesChapter 1 Nature and Concept of ManagementMa Blesilda Michaela SarbuesNo ratings yet
- Admin ProcedureDocument24 pagesAdmin ProcedureZera Jean TinoyNo ratings yet
- Concept of Leadership and ManagementDocument13 pagesConcept of Leadership and ManagementPia Amistoso100% (1)
- TP 036-3-2015 Motor Vehicle Inspection 27 36Document10 pagesTP 036-3-2015 Motor Vehicle Inspection 27 36syafik tumiranNo ratings yet
- SOFT Skill Training and Its Impact On ProductivityDocument36 pagesSOFT Skill Training and Its Impact On ProductivityUpskillistNo ratings yet
- Terms of References For 5 Specialist Consultants Under World Bank ProjectDocument20 pagesTerms of References For 5 Specialist Consultants Under World Bank ProjectVetri VendanNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Supervisory Management 10th Edition Donald C Mosley Don C Mosley JR Paul H PietriDocument25 pagesTest Bank For Supervisory Management 10th Edition Donald C Mosley Don C Mosley JR Paul H PietriAnissa Trowery100% (33)
- Paint Chemist - Job Post - VacancyMail JobsDocument2 pagesPaint Chemist - Job Post - VacancyMail JobsKudzai MazangoNo ratings yet
- Home EconomicsDocument45 pagesHome EconomicsKenneth SantosNo ratings yet
- The Role of Libraries in Higher EducationDocument4 pagesThe Role of Libraries in Higher EducationHnin PwintNo ratings yet
- Ejemplo de Curriculum VitaeDocument8 pagesEjemplo de Curriculum VitaeJuriNo ratings yet
- REVISE CommunicationSkillsOfAccountancyBusinessAndManagementStudents BernardoE BernardoR DonggonV MangogtongA SigbaJDocument34 pagesREVISE CommunicationSkillsOfAccountancyBusinessAndManagementStudents BernardoE BernardoR DonggonV MangogtongA SigbaJbernardoellyjaneNo ratings yet
- Transferable Skills - 10 Skills That Work Across IndustriesDocument5 pagesTransferable Skills - 10 Skills That Work Across IndustriesjosieliraychanNo ratings yet
- Course Information: Universiti Teknologi MaraDocument8 pagesCourse Information: Universiti Teknologi MaraDR ADILAH OTHMANNo ratings yet
- ASM 2 525 (Full)Document14 pagesASM 2 525 (Full)Pham Nguyen Anh (FGW HCM)No ratings yet