Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 viewsAbdominal Trauma
Abdominal Trauma
Uploaded by
Yalc LapidThis document outlines abdominal trauma, including a definition, assessment, diagnostics, and complications. Abdominal trauma results from blunt force such as from a baseball bat or tight seatbelt. Assessment looks for signs of internal bleeding like decreasing blood pressure or increasing pallor. Diagnostics include abdominal X-rays, FAST scan, and pelvic X-rays. Complications include splenic or liver rupture. Splenic rupture is the most common organ injury and often caused by seatbelts or bicycle handlebars.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Common Cases in Vascular SurgeryDocument72 pagesCommon Cases in Vascular Surgerynohazz100% (2)
- 03 Abdominal TraumaDocument1 page03 Abdominal Traumabunso padillaNo ratings yet
- Management of Abdominal Trauma: By: Chong Lih YinDocument71 pagesManagement of Abdominal Trauma: By: Chong Lih YinRakaNo ratings yet
- Obscure Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Chylous AscitesDocument2 pagesObscure Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Chylous AscitesMintdonNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment: AbdomenDocument18 pagesHealth Assessment: AbdomenBatiao Camille ClaireNo ratings yet
- Sic ReportingDocument6 pagesSic ReportingCHRISTINE JOY. MOLINANo ratings yet
- Clinical Radiology For Surgical Conditions of The AbdomenDocument8 pagesClinical Radiology For Surgical Conditions of The AbdomenPreeti Joan Buxani100% (1)
- Surgery Cases: CASE 1: Blunt Abdominal TraumaDocument3 pagesSurgery Cases: CASE 1: Blunt Abdominal TraumaGio Tamaño BalisiNo ratings yet
- ERIA Abdominal Compartment Syndrome - Antonius PudjiadiDocument13 pagesERIA Abdominal Compartment Syndrome - Antonius PudjiadiDennyNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Wall and HerniasDocument17 pagesAbdominal Wall and HerniasananNo ratings yet
- Harpieee Positioning-Clients PDFDocument1 pageHarpieee Positioning-Clients PDFVijungcoNo ratings yet
- Positioning Clients Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument1 pagePositioning Clients Cheat Sheet: by ViaARISA VIJUNGCONo ratings yet
- Harpieee Positioning ClientsDocument1 pageHarpieee Positioning ClientsEdgardo Tolentino Jr.No ratings yet
- Abdominal Assessment HA LectureDocument44 pagesAbdominal Assessment HA LectureKatrina BeltranNo ratings yet
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument13 pagesEctopic PregnancyJonielyn LagunaNo ratings yet
- Abdominal AssessmentDocument7 pagesAbdominal AssessmentGlen Dale100% (1)
- Perdarahan Saluran Cerna Bagian BawahDocument33 pagesPerdarahan Saluran Cerna Bagian BawahGiyani LiberthiNo ratings yet
- NRG 401 PrefinalDocument48 pagesNRG 401 PrefinalIlyka Fe PañaNo ratings yet
- Medical TerminologiesDocument4 pagesMedical TerminologiesHNo ratings yet
- Toprank Review Pediatric Nursing NotesDocument12 pagesToprank Review Pediatric Nursing NotesCose online shopNo ratings yet
- Mrcem C AtlsDocument4 pagesMrcem C AtlsMohammad Irfan khanNo ratings yet
- .Right Side-Lying With Pillow Under Puncture SiteDocument14 pages.Right Side-Lying With Pillow Under Puncture SiteJay AbasoloNo ratings yet
- Digestive System PART 2Document31 pagesDigestive System PART 2Erika BecerrelNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario 1 1. Immediate ManagementDocument5 pagesCase Scenario 1 1. Immediate ManagementArtika MalaNo ratings yet
- Haemorrage During Late PregnencyDocument38 pagesHaemorrage During Late PregnencysuthaNo ratings yet
- Gastro HistoryDocument4 pagesGastro HistoryAsma SikanderNo ratings yet
- General Surgery: (Acute Abdomen)Document1 pageGeneral Surgery: (Acute Abdomen)MattNo ratings yet
- 1 - Abdomen 1Document23 pages1 - Abdomen 1noushad aminNo ratings yet
- Abdominal TraumaDocument16 pagesAbdominal Traumachehak.kumar2000No ratings yet
- CT InfographicDocument1 pageCT Infographiclailatul husnaNo ratings yet
- Captopril Is An ACE Inhibitor and Works by Relaxing Blood Vessels So That Blood Can Flow More EasilyDocument4 pagesCaptopril Is An ACE Inhibitor and Works by Relaxing Blood Vessels So That Blood Can Flow More EasilyKsksksksNo ratings yet
- Table 13-1 Rapid Triage and Transport GuidelinesDocument2 pagesTable 13-1 Rapid Triage and Transport GuidelinesMarios GhobrialNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Trauma: (Emergency Department Approaches & Management)Document82 pagesAbdominal Trauma: (Emergency Department Approaches & Management)edward iskandarNo ratings yet
- Poster Alarmer HaemostasisDocument8 pagesPoster Alarmer HaemostasisJeremi FerdianNo ratings yet
- Quiz BukasDocument3 pagesQuiz BukasDYRAH GRACE COPAUSNo ratings yet
- Trauma Tumpul Abdomen - Dr. Monica, SP.BDocument54 pagesTrauma Tumpul Abdomen - Dr. Monica, SP.Brizky sitanayaNo ratings yet
- S T A R T: Imple Riage ND Apid ReatmentDocument17 pagesS T A R T: Imple Riage ND Apid ReatmentNavine NavNo ratings yet
- DIALYSIS Brochure - RAMOSDocument2 pagesDIALYSIS Brochure - RAMOSJan Clarisse RamosNo ratings yet
- GI OutlineDocument11 pagesGI OutlineLiz TollefsonNo ratings yet
- POSTPARTAL HEMORRAGE Editable NotesDocument4 pagesPOSTPARTAL HEMORRAGE Editable NotesJkimNo ratings yet
- ABC AbdomenDocument57 pagesABC AbdomenSyahmi KhalidNo ratings yet
- ACUTE PANCREATITISDocument19 pagesACUTE PANCREATITISMaaz MansoorNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Examination IBDDocument6 pagesCardiovascular Examination IBDTRINIDAD, ALYANNA V.No ratings yet
- #4 - NCM 109 - TransesDocument22 pages#4 - NCM 109 - TransesJaimie BanaagNo ratings yet
- Bambang Sugeng Bag Bedah FK-UnissulaDocument27 pagesBambang Sugeng Bag Bedah FK-UnissulaRahmat SyahiliNo ratings yet
- BAIRANIAH GOGO - NGT Learning TaskDocument5 pagesBAIRANIAH GOGO - NGT Learning TaskDm KeeNo ratings yet
- Placental Abnormalities Normal Placenta: © Mary Andrea G. Agorilla, Ust-Con 2021 - 1Document3 pagesPlacental Abnormalities Normal Placenta: © Mary Andrea G. Agorilla, Ust-Con 2021 - 1Mary AgorillaNo ratings yet
- The SpleenDocument7 pagesThe Spleeneiuj497No ratings yet
- History Taking For CholelithiasisDocument6 pagesHistory Taking For CholelithiasisToria053100% (1)
- CORNELL NOTE Physical and Developmental Disorders in NewbornDocument4 pagesCORNELL NOTE Physical and Developmental Disorders in NewbornMargareth DandanNo ratings yet
- Colon, Rectum & AnusDocument6 pagesColon, Rectum & AnusLeikkaNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document5 pagesWeek 2Maica LectanaNo ratings yet
- Spine & Extremities / Abdomen / Neurologic Exam: PalpationDocument8 pagesSpine & Extremities / Abdomen / Neurologic Exam: PalpationBrent DizonNo ratings yet
- 10.disorders of LaborDocument8 pages10.disorders of LaborWoo Rin ParkNo ratings yet
- Abruptio Placentae: (Accidental Hemorrhage, Premature Separation of Placenta)Document25 pagesAbruptio Placentae: (Accidental Hemorrhage, Premature Separation of Placenta)Akashdeep singhNo ratings yet
- SURGERY Lecture 5 - Abdominal Wall, Omentum, Mesentery, Retroperitoneum (Dr. Wenceslao)Document13 pagesSURGERY Lecture 5 - Abdominal Wall, Omentum, Mesentery, Retroperitoneum (Dr. Wenceslao)Medisina101No ratings yet
- ANEURSYMDocument24 pagesANEURSYMMYLENE GRACE ELARCOSANo ratings yet
- 189 Gotera, Chloe Lynn Activity 2 Day 2 Sigmoid VolvulusDocument6 pages189 Gotera, Chloe Lynn Activity 2 Day 2 Sigmoid VolvulusChloe GoteraNo ratings yet
- Blood TransfusionDocument4 pagesBlood TransfusionYalc LapidNo ratings yet
- Animal BiteDocument1 pageAnimal BiteYalc LapidNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDocument9 pagesPregnancy Induced HypertensionYalc LapidNo ratings yet
- Catheterization HANDOUTSDocument9 pagesCatheterization HANDOUTSYalc LapidNo ratings yet
- Enema - HANDOUTSDocument4 pagesEnema - HANDOUTSYalc LapidNo ratings yet
- Code of Ethics For PharmacistsDocument6 pagesCode of Ethics For PharmacistsYalc LapidNo ratings yet
- Psychopharmacology ReviewerDocument13 pagesPsychopharmacology ReviewerYalc LapidNo ratings yet
- 2NE1Document3 pages2NE1Yalc LapidNo ratings yet
- Kapampangan MassDocument31 pagesKapampangan MassYalc Lapid100% (1)
- Muscle Disease: Neurology Rotation Lecture SeriesDocument10 pagesMuscle Disease: Neurology Rotation Lecture SeriesYalc LapidNo ratings yet
- National Artists of The PhilippinesDocument43 pagesNational Artists of The PhilippinesYalc Lapid67% (6)
- Sports Medicine & Recreational Management BrochureDocument2 pagesSports Medicine & Recreational Management Brochurebulldogs2013No ratings yet
- NTCC Daily Log SheetDocument27 pagesNTCC Daily Log SheetMuskan SukhejaNo ratings yet
- Case Study AchalasiaDocument26 pagesCase Study AchalasiaZoe Anna50% (2)
- Advanced Resuscitation of The Newborn Infant Algorithm 2021Document1 pageAdvanced Resuscitation of The Newborn Infant Algorithm 2021Silviu MorteanuNo ratings yet
- JawetzDocument3 pagesJawetzAvissa Fadlika DausawatiNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Bag Physics J PhilipDocument44 pagesReservoir Bag Physics J PhilipJashim JumliNo ratings yet
- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome From Vagus Nerve InfectionDocument10 pagesChronic Fatigue Syndrome From Vagus Nerve InfectionLevente BalázsNo ratings yet
- UWorld Medicine - Paeds - Surgery (COMPLETE)Document226 pagesUWorld Medicine - Paeds - Surgery (COMPLETE)abdulmoiz92100% (1)
- On Catatonia Seizures and BradycardiaDocument1 pageOn Catatonia Seizures and BradycardiaFlorin TudoseNo ratings yet
- Headache Clinic CRFDocument12 pagesHeadache Clinic CRFNasirNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes ImbalanceDocument49 pagesFluid and Electrolytes ImbalanceMohamed Na3eemNo ratings yet
- Dementia and Alzheimers Topic ReportingDocument9 pagesDementia and Alzheimers Topic ReportingROGEN KATE AZARCONNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Summary Abnormal Psychology An Integrative ApproachDocument12 pagesChapter 12 Summary Abnormal Psychology An Integrative ApproachDjane VillarinNo ratings yet
- Forceps Delivery: Potential Benefits and A Call For Continued TrainingDocument2 pagesForceps Delivery: Potential Benefits and A Call For Continued TrainingTyron ChuaNo ratings yet
- Ayurveda Consultation SydneyDocument5 pagesAyurveda Consultation SydneyAnand Singh ContentNo ratings yet
- FAVA2023 Leaflets PDFDocument4 pagesFAVA2023 Leaflets PDFDrh Aang HasanudinNo ratings yet
- 97893990619016Document14 pages97893990619016Khawla BahryNo ratings yet
- Diabetes in Palliative Care CompletedDocument4 pagesDiabetes in Palliative Care Completedaya PermatasariNo ratings yet
- ReferensiDocument126 pagesReferensiFatchul ChoiriNo ratings yet
- Medicine For Consumers 1St Edition Full ChapterDocument41 pagesMedicine For Consumers 1St Edition Full Chapteredward.weisner630100% (22)
- Madya Visha & MadatyayaDocument33 pagesMadya Visha & Madatyayaraghabendrasahu1998No ratings yet
- NCP 1 AND SOAPIE 1) Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument5 pagesNCP 1 AND SOAPIE 1) Ineffective Breathing PatternMicaela CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- 64315-Nursing CPD ApplicationDocument30 pages64315-Nursing CPD Applicationprc.zamboanga.regulationcpdNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Fast Tracks in The Emergency Department 1Document11 pagesRunning Head: Fast Tracks in The Emergency Department 1FikriNo ratings yet
- CLB 3-4 at The Walk-In Clinic (Complete Module)Document78 pagesCLB 3-4 at The Walk-In Clinic (Complete Module)Olga AmyNo ratings yet
- Law & Medicine Unit - 1Document4 pagesLaw & Medicine Unit - 1RosylaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid StormDocument33 pagesThyroid StormVaibhav Krishna50% (2)
- Daftar Pustaka 4Document5 pagesDaftar Pustaka 4Devinta Nurul ErlanggaNo ratings yet
- Q Fever-The Superstition of Avoiding The Word QuieDocument6 pagesQ Fever-The Superstition of Avoiding The Word QuiePhilippus Von HohenheimNo ratings yet
- Mds SyllabusDocument78 pagesMds SyllabusFrancis PrathyushaNo ratings yet
Abdominal Trauma
Abdominal Trauma
Uploaded by
Yalc Lapid0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageThis document outlines abdominal trauma, including a definition, assessment, diagnostics, and complications. Abdominal trauma results from blunt force such as from a baseball bat or tight seatbelt. Assessment looks for signs of internal bleeding like decreasing blood pressure or increasing pallor. Diagnostics include abdominal X-rays, FAST scan, and pelvic X-rays. Complications include splenic or liver rupture. Splenic rupture is the most common organ injury and often caused by seatbelts or bicycle handlebars.
Original Description:
NURSING NOTES
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines abdominal trauma, including a definition, assessment, diagnostics, and complications. Abdominal trauma results from blunt force such as from a baseball bat or tight seatbelt. Assessment looks for signs of internal bleeding like decreasing blood pressure or increasing pallor. Diagnostics include abdominal X-rays, FAST scan, and pelvic X-rays. Complications include splenic or liver rupture. Splenic rupture is the most common organ injury and often caused by seatbelts or bicycle handlebars.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageAbdominal Trauma
Abdominal Trauma
Uploaded by
Yalc LapidThis document outlines abdominal trauma, including a definition, assessment, diagnostics, and complications. Abdominal trauma results from blunt force such as from a baseball bat or tight seatbelt. Assessment looks for signs of internal bleeding like decreasing blood pressure or increasing pallor. Diagnostics include abdominal X-rays, FAST scan, and pelvic X-rays. Complications include splenic or liver rupture. Splenic rupture is the most common organ injury and often caused by seatbelts or bicycle handlebars.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
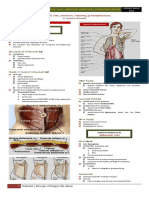
ABDOMINAL They may hold their left shoulder elevated, so that
the diaphragm is raised on the left side, to keep this
from happening
TRAUMA Child notices radiated left shoulder pain while lying
in a supine position (Kehr’s sign)
Course Outline
Note: Broken rib over the spleen suggesting the extent of the
Definition trauma.
Assessment
Diagnostics Diagnostics
Complications of Abdominal Trauma
- Splenic Rupture □ IV pyelogram
- Live Rupture □ MRI
□ FAST
□ CBC
DEFINITION □ Blood typing
It is a result from object striking the abdomen, such as Management
baseball bat or a seatbelt drawn tight in a motor vehicle
Admission
crash.
IVF
“E” explore laparotomy
ASSESSMENT Antibiotics
Assess vital signs frequently until stable
Hypotension (less than 80mmHg systolic LIVER RUPTURE
pressure in an older child; less than 60mmHg in
an infant) usually suggests hemorrhage, which - More prone to rupture in children rather than adults
may be hidden abdominal bleeding - Because it is not completely not shattered by the rib
May have increasing pallor cage.
May have rapid respirations
Assessment
If internal bleeding is present, blood pressure
will show little improvement when IV fluid is Severe abdominal pain that is most marked on
administered. inspiration, when the diaphragm descends and
Nasogastric Tube (NGT) is passed and stomach touches the liver
contents are aspirated to be checked visually Symptoms of blood loss: tachycardia, hypotension,
for blood and to test for occult blood anxiety and pallor
Low intermittent suction was done to if Hematocrit is low or falling
presence of blood is established.
Foley Catheter (IFC) is also inserted to evaluate urine Note:
for blood and urine output
Evidence of blood in the urine or decreased - Communication between an artery and the bile duct occurs
output may indicate accompanying kidney or at the time of trauma. (symptoms are not immediate)
bladder trauma.
- Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding such as hematemesis or
melena, may occur in a few days
DIAGNOSTICS
- May have colicky upper abdominal pain that is relieved by
□ Abdominal X-Ray
emesis
□ FAST
□ Pelvic X-Ray - Liver arteriogram are necessary to reveal the extent of the
problem
Note:
After either liver or spleen surgery, children need careful
- Air under the diaphragm on the radiograph suggest gastric observation for return of bowel function, assessment for the
or intestinal rupture with escape of air from these organs into possibility that peritonitis may develop, and careful
the peritoneal cavity reintroduction of oral nutrition.
- Free fluid in the abdomen, shown on the radiograph when
the child is turned on the side; suggest leakage of bowel fluid
or splenic rupture and pooling of blood.
COMPLICATIONS OF ABDOMINAL TRAUMA
SPLENIC RUPTURE
- Most frequently injured organ, because it is usually
palpable under the lower left ribs
- Frequently injured by inappropriately applied seat
belts and by handlebar injuries in bicycle accidents
Assessment
Have tenderness in the left upper quadrant,
especially on deep inspiration, when the diaphragm
moves down and touches the spleen
@NurseMD_
You might also like
- Common Cases in Vascular SurgeryDocument72 pagesCommon Cases in Vascular Surgerynohazz100% (2)
- 03 Abdominal TraumaDocument1 page03 Abdominal Traumabunso padillaNo ratings yet
- Management of Abdominal Trauma: By: Chong Lih YinDocument71 pagesManagement of Abdominal Trauma: By: Chong Lih YinRakaNo ratings yet
- Obscure Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Chylous AscitesDocument2 pagesObscure Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Chylous AscitesMintdonNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment: AbdomenDocument18 pagesHealth Assessment: AbdomenBatiao Camille ClaireNo ratings yet
- Sic ReportingDocument6 pagesSic ReportingCHRISTINE JOY. MOLINANo ratings yet
- Clinical Radiology For Surgical Conditions of The AbdomenDocument8 pagesClinical Radiology For Surgical Conditions of The AbdomenPreeti Joan Buxani100% (1)
- Surgery Cases: CASE 1: Blunt Abdominal TraumaDocument3 pagesSurgery Cases: CASE 1: Blunt Abdominal TraumaGio Tamaño BalisiNo ratings yet
- ERIA Abdominal Compartment Syndrome - Antonius PudjiadiDocument13 pagesERIA Abdominal Compartment Syndrome - Antonius PudjiadiDennyNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Wall and HerniasDocument17 pagesAbdominal Wall and HerniasananNo ratings yet
- Harpieee Positioning-Clients PDFDocument1 pageHarpieee Positioning-Clients PDFVijungcoNo ratings yet
- Positioning Clients Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument1 pagePositioning Clients Cheat Sheet: by ViaARISA VIJUNGCONo ratings yet
- Harpieee Positioning ClientsDocument1 pageHarpieee Positioning ClientsEdgardo Tolentino Jr.No ratings yet
- Abdominal Assessment HA LectureDocument44 pagesAbdominal Assessment HA LectureKatrina BeltranNo ratings yet
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument13 pagesEctopic PregnancyJonielyn LagunaNo ratings yet
- Abdominal AssessmentDocument7 pagesAbdominal AssessmentGlen Dale100% (1)
- Perdarahan Saluran Cerna Bagian BawahDocument33 pagesPerdarahan Saluran Cerna Bagian BawahGiyani LiberthiNo ratings yet
- NRG 401 PrefinalDocument48 pagesNRG 401 PrefinalIlyka Fe PañaNo ratings yet
- Medical TerminologiesDocument4 pagesMedical TerminologiesHNo ratings yet
- Toprank Review Pediatric Nursing NotesDocument12 pagesToprank Review Pediatric Nursing NotesCose online shopNo ratings yet
- Mrcem C AtlsDocument4 pagesMrcem C AtlsMohammad Irfan khanNo ratings yet
- .Right Side-Lying With Pillow Under Puncture SiteDocument14 pages.Right Side-Lying With Pillow Under Puncture SiteJay AbasoloNo ratings yet
- Digestive System PART 2Document31 pagesDigestive System PART 2Erika BecerrelNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario 1 1. Immediate ManagementDocument5 pagesCase Scenario 1 1. Immediate ManagementArtika MalaNo ratings yet
- Haemorrage During Late PregnencyDocument38 pagesHaemorrage During Late PregnencysuthaNo ratings yet
- Gastro HistoryDocument4 pagesGastro HistoryAsma SikanderNo ratings yet
- General Surgery: (Acute Abdomen)Document1 pageGeneral Surgery: (Acute Abdomen)MattNo ratings yet
- 1 - Abdomen 1Document23 pages1 - Abdomen 1noushad aminNo ratings yet
- Abdominal TraumaDocument16 pagesAbdominal Traumachehak.kumar2000No ratings yet
- CT InfographicDocument1 pageCT Infographiclailatul husnaNo ratings yet
- Captopril Is An ACE Inhibitor and Works by Relaxing Blood Vessels So That Blood Can Flow More EasilyDocument4 pagesCaptopril Is An ACE Inhibitor and Works by Relaxing Blood Vessels So That Blood Can Flow More EasilyKsksksksNo ratings yet
- Table 13-1 Rapid Triage and Transport GuidelinesDocument2 pagesTable 13-1 Rapid Triage and Transport GuidelinesMarios GhobrialNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Trauma: (Emergency Department Approaches & Management)Document82 pagesAbdominal Trauma: (Emergency Department Approaches & Management)edward iskandarNo ratings yet
- Poster Alarmer HaemostasisDocument8 pagesPoster Alarmer HaemostasisJeremi FerdianNo ratings yet
- Quiz BukasDocument3 pagesQuiz BukasDYRAH GRACE COPAUSNo ratings yet
- Trauma Tumpul Abdomen - Dr. Monica, SP.BDocument54 pagesTrauma Tumpul Abdomen - Dr. Monica, SP.Brizky sitanayaNo ratings yet
- S T A R T: Imple Riage ND Apid ReatmentDocument17 pagesS T A R T: Imple Riage ND Apid ReatmentNavine NavNo ratings yet
- DIALYSIS Brochure - RAMOSDocument2 pagesDIALYSIS Brochure - RAMOSJan Clarisse RamosNo ratings yet
- GI OutlineDocument11 pagesGI OutlineLiz TollefsonNo ratings yet
- POSTPARTAL HEMORRAGE Editable NotesDocument4 pagesPOSTPARTAL HEMORRAGE Editable NotesJkimNo ratings yet
- ABC AbdomenDocument57 pagesABC AbdomenSyahmi KhalidNo ratings yet
- ACUTE PANCREATITISDocument19 pagesACUTE PANCREATITISMaaz MansoorNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Examination IBDDocument6 pagesCardiovascular Examination IBDTRINIDAD, ALYANNA V.No ratings yet
- #4 - NCM 109 - TransesDocument22 pages#4 - NCM 109 - TransesJaimie BanaagNo ratings yet
- Bambang Sugeng Bag Bedah FK-UnissulaDocument27 pagesBambang Sugeng Bag Bedah FK-UnissulaRahmat SyahiliNo ratings yet
- BAIRANIAH GOGO - NGT Learning TaskDocument5 pagesBAIRANIAH GOGO - NGT Learning TaskDm KeeNo ratings yet
- Placental Abnormalities Normal Placenta: © Mary Andrea G. Agorilla, Ust-Con 2021 - 1Document3 pagesPlacental Abnormalities Normal Placenta: © Mary Andrea G. Agorilla, Ust-Con 2021 - 1Mary AgorillaNo ratings yet
- The SpleenDocument7 pagesThe Spleeneiuj497No ratings yet
- History Taking For CholelithiasisDocument6 pagesHistory Taking For CholelithiasisToria053100% (1)
- CORNELL NOTE Physical and Developmental Disorders in NewbornDocument4 pagesCORNELL NOTE Physical and Developmental Disorders in NewbornMargareth DandanNo ratings yet
- Colon, Rectum & AnusDocument6 pagesColon, Rectum & AnusLeikkaNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document5 pagesWeek 2Maica LectanaNo ratings yet
- Spine & Extremities / Abdomen / Neurologic Exam: PalpationDocument8 pagesSpine & Extremities / Abdomen / Neurologic Exam: PalpationBrent DizonNo ratings yet
- 10.disorders of LaborDocument8 pages10.disorders of LaborWoo Rin ParkNo ratings yet
- Abruptio Placentae: (Accidental Hemorrhage, Premature Separation of Placenta)Document25 pagesAbruptio Placentae: (Accidental Hemorrhage, Premature Separation of Placenta)Akashdeep singhNo ratings yet
- SURGERY Lecture 5 - Abdominal Wall, Omentum, Mesentery, Retroperitoneum (Dr. Wenceslao)Document13 pagesSURGERY Lecture 5 - Abdominal Wall, Omentum, Mesentery, Retroperitoneum (Dr. Wenceslao)Medisina101No ratings yet
- ANEURSYMDocument24 pagesANEURSYMMYLENE GRACE ELARCOSANo ratings yet
- 189 Gotera, Chloe Lynn Activity 2 Day 2 Sigmoid VolvulusDocument6 pages189 Gotera, Chloe Lynn Activity 2 Day 2 Sigmoid VolvulusChloe GoteraNo ratings yet
- Blood TransfusionDocument4 pagesBlood TransfusionYalc LapidNo ratings yet
- Animal BiteDocument1 pageAnimal BiteYalc LapidNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDocument9 pagesPregnancy Induced HypertensionYalc LapidNo ratings yet
- Catheterization HANDOUTSDocument9 pagesCatheterization HANDOUTSYalc LapidNo ratings yet
- Enema - HANDOUTSDocument4 pagesEnema - HANDOUTSYalc LapidNo ratings yet
- Code of Ethics For PharmacistsDocument6 pagesCode of Ethics For PharmacistsYalc LapidNo ratings yet
- Psychopharmacology ReviewerDocument13 pagesPsychopharmacology ReviewerYalc LapidNo ratings yet
- 2NE1Document3 pages2NE1Yalc LapidNo ratings yet
- Kapampangan MassDocument31 pagesKapampangan MassYalc Lapid100% (1)
- Muscle Disease: Neurology Rotation Lecture SeriesDocument10 pagesMuscle Disease: Neurology Rotation Lecture SeriesYalc LapidNo ratings yet
- National Artists of The PhilippinesDocument43 pagesNational Artists of The PhilippinesYalc Lapid67% (6)
- Sports Medicine & Recreational Management BrochureDocument2 pagesSports Medicine & Recreational Management Brochurebulldogs2013No ratings yet
- NTCC Daily Log SheetDocument27 pagesNTCC Daily Log SheetMuskan SukhejaNo ratings yet
- Case Study AchalasiaDocument26 pagesCase Study AchalasiaZoe Anna50% (2)
- Advanced Resuscitation of The Newborn Infant Algorithm 2021Document1 pageAdvanced Resuscitation of The Newborn Infant Algorithm 2021Silviu MorteanuNo ratings yet
- JawetzDocument3 pagesJawetzAvissa Fadlika DausawatiNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Bag Physics J PhilipDocument44 pagesReservoir Bag Physics J PhilipJashim JumliNo ratings yet
- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome From Vagus Nerve InfectionDocument10 pagesChronic Fatigue Syndrome From Vagus Nerve InfectionLevente BalázsNo ratings yet
- UWorld Medicine - Paeds - Surgery (COMPLETE)Document226 pagesUWorld Medicine - Paeds - Surgery (COMPLETE)abdulmoiz92100% (1)
- On Catatonia Seizures and BradycardiaDocument1 pageOn Catatonia Seizures and BradycardiaFlorin TudoseNo ratings yet
- Headache Clinic CRFDocument12 pagesHeadache Clinic CRFNasirNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes ImbalanceDocument49 pagesFluid and Electrolytes ImbalanceMohamed Na3eemNo ratings yet
- Dementia and Alzheimers Topic ReportingDocument9 pagesDementia and Alzheimers Topic ReportingROGEN KATE AZARCONNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Summary Abnormal Psychology An Integrative ApproachDocument12 pagesChapter 12 Summary Abnormal Psychology An Integrative ApproachDjane VillarinNo ratings yet
- Forceps Delivery: Potential Benefits and A Call For Continued TrainingDocument2 pagesForceps Delivery: Potential Benefits and A Call For Continued TrainingTyron ChuaNo ratings yet
- Ayurveda Consultation SydneyDocument5 pagesAyurveda Consultation SydneyAnand Singh ContentNo ratings yet
- FAVA2023 Leaflets PDFDocument4 pagesFAVA2023 Leaflets PDFDrh Aang HasanudinNo ratings yet
- 97893990619016Document14 pages97893990619016Khawla BahryNo ratings yet
- Diabetes in Palliative Care CompletedDocument4 pagesDiabetes in Palliative Care Completedaya PermatasariNo ratings yet
- ReferensiDocument126 pagesReferensiFatchul ChoiriNo ratings yet
- Medicine For Consumers 1St Edition Full ChapterDocument41 pagesMedicine For Consumers 1St Edition Full Chapteredward.weisner630100% (22)
- Madya Visha & MadatyayaDocument33 pagesMadya Visha & Madatyayaraghabendrasahu1998No ratings yet
- NCP 1 AND SOAPIE 1) Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument5 pagesNCP 1 AND SOAPIE 1) Ineffective Breathing PatternMicaela CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- 64315-Nursing CPD ApplicationDocument30 pages64315-Nursing CPD Applicationprc.zamboanga.regulationcpdNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Fast Tracks in The Emergency Department 1Document11 pagesRunning Head: Fast Tracks in The Emergency Department 1FikriNo ratings yet
- CLB 3-4 at The Walk-In Clinic (Complete Module)Document78 pagesCLB 3-4 at The Walk-In Clinic (Complete Module)Olga AmyNo ratings yet
- Law & Medicine Unit - 1Document4 pagesLaw & Medicine Unit - 1RosylaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid StormDocument33 pagesThyroid StormVaibhav Krishna50% (2)
- Daftar Pustaka 4Document5 pagesDaftar Pustaka 4Devinta Nurul ErlanggaNo ratings yet
- Q Fever-The Superstition of Avoiding The Word QuieDocument6 pagesQ Fever-The Superstition of Avoiding The Word QuiePhilippus Von HohenheimNo ratings yet
- Mds SyllabusDocument78 pagesMds SyllabusFrancis PrathyushaNo ratings yet