Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gambar 8.13
Gambar 8.13
Uploaded by
topan hidayatOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gambar 8.13
Gambar 8.13
Uploaded by
topan hidayatCopyright:
Available Formats
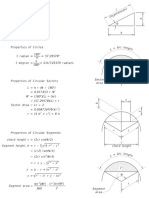
Section 8.
4 Application of K to Design and Analysis 351
M P/2
a h a h
t
P
t
(a) (b) b Ph
b M= 2
P/2
6
K = FS g πa
5 6M
Sg =
b2 t
4
F 3
(a)
2
(b) h/b = 2
0
0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
α = a/b
Values for small a/b and limits for 10% accuracy:
√
(a, b) K = 1.12Sg πa (a/b ≤ 0.4)
Expressions for any α = a/b:
% π α &4
! 0.923 + 0.199 1 − sin
2 πα 2
(a) F = tan π α (large h/b)
πα 2 cos
2
(b) F is within 3% of (a) for h/b = 4, and within 6% for h/b = 2, at any a/b:
* +
1.99 − α (1 − α) 2.15 − 3.93α + 2.7α 2
F= √ (h/b = 2)
π (1 + 2α) (1 − α)3/2
Figure 8.13 Stress intensity factors for two cases of bending. Geometries, curves, and
equations labeled (a) all correspond to the same case, and similarly for (b). Case (b) with
h/b = 2 is the ASTM standard bend specimen. (Equations from [Tada 85] p. 2.14, and
[ASTM 97] Std. E399.)
You might also like
- Bruce Mau PolimiDocument59 pagesBruce Mau PolimiDouglas PastoriNo ratings yet
- Gambar 8.12Document1 pageGambar 8.12topan hidayatNo ratings yet
- (2015 12 8) 高等結構學第二次期中考 PDFDocument2 pages(2015 12 8) 高等結構學第二次期中考 PDF侯柏毅No ratings yet
- Solution To 2017-1 Problem 4 With Division by ZeroDocument4 pagesSolution To 2017-1 Problem 4 With Division by ZeroEudes CunhaNo ratings yet
- sin (θ) = a ÷ c cos (θ) = b ÷ c tan (θ) = a ÷ b θ: c po en us e)Document1 pagesin (θ) = a ÷ c cos (θ) = b ÷ c tan (θ) = a ÷ b θ: c po en us e)NikuRikuNo ratings yet
- Ps4sols Euf22Document15 pagesPs4sols Euf22Ammar QasimNo ratings yet
- Monopitch RoofDocument5 pagesMonopitch RoofKhalid CaliNo ratings yet
- Maxima&Minima-Solution JEE @GB SirDocument28 pagesMaxima&Minima-Solution JEE @GB SirAkash KhannaNo ratings yet
- Econ 11 Midterm 1 Review Question: Dr. Petre December 7, 2017Document3 pagesEcon 11 Midterm 1 Review Question: Dr. Petre December 7, 2017mkinnetxNo ratings yet
- Some Bounds For The Complete Elliptic Integrals of The First and Second KindsDocument13 pagesSome Bounds For The Complete Elliptic Integrals of The First and Second Kindsahmet çolakNo ratings yet
- CC Assignment2 PDFDocument6 pagesCC Assignment2 PDFrimsha4chNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument7 pagesPDFرضا حسنNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument7 pagesPDFرضا حسنNo ratings yet
- EM319 Review Spring 2008: T. Determine The Force Induced in Each Rod byDocument10 pagesEM319 Review Spring 2008: T. Determine The Force Induced in Each Rod byTyler MabryNo ratings yet
- Y (A A) P: N N+K I IDocument15 pagesY (A A) P: N N+K I INgọc ToảnNo ratings yet
- Y (A A) P: N N+K I IDocument15 pagesY (A A) P: N N+K I INgọc ToảnNo ratings yet
- Dis09 Sol PDFDocument4 pagesDis09 Sol PDFpoopyNo ratings yet
- ACESORIADocument2 pagesACESORIAjv680802No ratings yet
- Sb3 Hw10 KeyDocument12 pagesSb3 Hw10 KeyOlivia ChoiNo ratings yet
- Cantr RetainingDocument46 pagesCantr RetainingDINESHNo ratings yet
- FoundationDocument2 pagesFoundationAndrés GranadosNo ratings yet
- Tuto 7 533Document1 pageTuto 7 5332023606862No ratings yet
- AdvMath (Unit 3)Document17 pagesAdvMath (Unit 3)Eleonor Mhey CaridoNo ratings yet
- MIT8 044S13 pss11 PDFDocument10 pagesMIT8 044S13 pss11 PDF*83*22*No ratings yet
- Trig NoteDocument5 pagesTrig NoteSubin ParkNo ratings yet
- Practice Test - 7, Atomic Structure and Gaseous StateDocument12 pagesPractice Test - 7, Atomic Structure and Gaseous StateBadNik 007No ratings yet
- Thick Pressure Vessels - Engineering LibraryDocument5 pagesThick Pressure Vessels - Engineering LibraryAvishay TufikianNo ratings yet
- sm5 139Document1 pagesm5 139Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 SolutionsDocument6 pagesChapter 9 Solutionsapandiani95.apNo ratings yet
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of PhysicsDocument5 pagesMassachusetts Institute of Technology Department of PhysicsNeha SinghNo ratings yet
- An Introductory Course of Modeling and Computation For Chemical EngineersDocument15 pagesAn Introductory Course of Modeling and Computation For Chemical EngineersMadhukar ScribdNo ratings yet
- Landslide Repair Design Based On 2018 IBC & AASHTO 17thDocument7 pagesLandslide Repair Design Based On 2018 IBC & AASHTO 17thChowdhury PriodeepNo ratings yet
- Gravity Wall CalculationDocument4 pagesGravity Wall CalculationBogie Prastowo Mahardhika100% (1)
- Approximate Analysis: PD P A A HDocument4 pagesApproximate Analysis: PD P A A HWalterNo ratings yet
- KAS303, MathsIII - PUE, SET1 (Final)Document2 pagesKAS303, MathsIII - PUE, SET1 (Final)vaibhavchaudhary701744No ratings yet
- MHT-CET - Mathematics - TP 10 HintsDocument7 pagesMHT-CET - Mathematics - TP 10 Hintsharsh.69691No ratings yet
- Coulson - Appendix A3Document8 pagesCoulson - Appendix A3Lusiana OliviaNo ratings yet
- Snchalbn HP: Ee Fad AP B 2alDocument4 pagesSnchalbn HP: Ee Fad AP B 2alraj patel A/86No ratings yet
- Chapman-Enskog EquationDocument7 pagesChapman-Enskog EquationScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Diseño Mecanico ShigleyDocument6 pagesEjercicios Diseño Mecanico ShigleyBrajack RhNo ratings yet
- Difusión MethodsDocument5 pagesDifusión MethodsKeily VilcarromeroNo ratings yet
- 03.1 Proračun Zid 1Document7 pages03.1 Proračun Zid 1Elmo TabakovićNo ratings yet
- Geometric Properties of A Parabolic Section, Dr. Victor M. Ponce and Jhonath W. Mejía G., 2021Document1 pageGeometric Properties of A Parabolic Section, Dr. Victor M. Ponce and Jhonath W. Mejía G., 2021Mmreza ShamaeiNo ratings yet
- 02.06 Isobaric Heating of Ethylene Using A High Precision Equation of StateDocument10 pages02.06 Isobaric Heating of Ethylene Using A High Precision Equation of StateMartin VenichNo ratings yet
- P Set 01Document2 pagesP Set 01tejpal38329No ratings yet
- PT1 GR12 Phy Ak 2023-24set1 1164Document4 pagesPT1 GR12 Phy Ak 2023-24set1 1164Aharnish ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11, Solution 44.: Choose X Positive Upward. Constant Acceleration ADocument2 pagesChapter 11, Solution 44.: Choose X Positive Upward. Constant Acceleration ALUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- CHPT 9 UzaysalDocument22 pagesCHPT 9 UzaysalNASREE HAYEESAMA-AENo ratings yet
- Load Chase Down On Beam (Ab) : GV, QV: Loads For Calculation of Shear GM, QM: Loads For Claculation of MomentDocument2 pagesLoad Chase Down On Beam (Ab) : GV, QV: Loads For Calculation of Shear GM, QM: Loads For Claculation of MomentSES DESIGNNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 12Document7 pagesPhysics Chapter 12Prashant SahNo ratings yet
- Ae2235 Exercises Lecture 1Document6 pagesAe2235 Exercises Lecture 1Sarieta SarrahNo ratings yet
- 811purl TOC TYSDocument18 pages811purl TOC TYSVivek RanjanNo ratings yet
- Problems 2dtransformationsDocument3 pagesProblems 2dtransformationsjiales225No ratings yet
- Sol 5Document6 pagesSol 5SaMi ALiNo ratings yet
- Formule AriiDocument3 pagesFormule AriiTea CupNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Failure Prediction For Static LoadingDocument29 pagesChapter 6: Failure Prediction For Static Loadinghasan abwiniNo ratings yet
- Process Modelling, Simulation and Control For Chemical Engineers. Solved Problems. Chapter 6: Time-Domain Dy-Namics: Part IDocument20 pagesProcess Modelling, Simulation and Control For Chemical Engineers. Solved Problems. Chapter 6: Time-Domain Dy-Namics: Part IJohnNo ratings yet
- 02.05 Density of Supercritical Ethylene Using A High Precision Equation of StateDocument9 pages02.05 Density of Supercritical Ethylene Using A High Precision Equation of StateMartin VenichNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Mathematics - StudentDocument3 pagesFundamentals of Mathematics - StudentRaushan KumarNo ratings yet
- Classifying Spaces for Surgery and Corbordism of Manifolds. (AM-92), Volume 92From EverandClassifying Spaces for Surgery and Corbordism of Manifolds. (AM-92), Volume 92No ratings yet
- Sheet-Piles Design Using Free-Earth Support MethodDocument7 pagesSheet-Piles Design Using Free-Earth Support MethodJulien MhannaNo ratings yet
- Longitudinal Vibration BarsDocument83 pagesLongitudinal Vibration BarsGerson Cordoba Barco75% (4)
- AssignQuiz2 141.417 23TP11Document9 pagesAssignQuiz2 141.417 23TP11Alex WhittakerNo ratings yet
- ExamTimeTableReportSubjectWise HTMDocument110 pagesExamTimeTableReportSubjectWise HTMpratyay gangulyNo ratings yet
- Continuous Flight Auger (Cfa) Piles: Design GuidanceDocument10 pagesContinuous Flight Auger (Cfa) Piles: Design GuidanceGrzegorz WilkNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0141029622015401 MainDocument13 pages1 s2.0 S0141029622015401 Mainhamza shadowNo ratings yet
- Physics Grade 11 1st Work SheetDocument8 pagesPhysics Grade 11 1st Work SheetMikas TesfuNo ratings yet
- CH 03Document10 pagesCH 03Qassem MohaidatNo ratings yet
- Quality ReviewDocument6 pagesQuality ReviewShashi Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Gary Backhaus - Georg Simmel As An Eidetic SocialDocument13 pagesGary Backhaus - Georg Simmel As An Eidetic SocialJESUS MARMANILLO PEREIRANo ratings yet
- How To Use A Digital TalismanDocument13 pagesHow To Use A Digital TalismanMadeleiGOOGYX100% (1)
- 21 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (A2) : E E E EDocument3 pages21 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (A2) : E E E EvinuyeNo ratings yet
- Course Outline ENGR 311 - 2023Document2 pagesCourse Outline ENGR 311 - 2023neilsani2002No ratings yet
- PGL-Lesson 94-97Document17 pagesPGL-Lesson 94-97Jomabelle UbaldoNo ratings yet
- VCE Specialist Mathematics Curriculum and Khan Academy LinksDocument2 pagesVCE Specialist Mathematics Curriculum and Khan Academy LinksValerie GanNo ratings yet
- Applied Mathematics-I (MATH114) : Lecture1: Introduction and Basic of MatricesDocument15 pagesApplied Mathematics-I (MATH114) : Lecture1: Introduction and Basic of MatricesAkanksha ThakurNo ratings yet
- 04 PSD Fire Sim LN4Document17 pages04 PSD Fire Sim LN4Ahmad mkNo ratings yet
- b1p1c1 FunctionlimitcontinuityDocument46 pagesb1p1c1 FunctionlimitcontinuityGodsent SongNo ratings yet
- GS Ques Set 13 by DR Vipan GoyalDocument7 pagesGS Ques Set 13 by DR Vipan GoyalJames Joy PNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 2 Velocity and Acceleration: 1.0. Objectives 1.1. 1.2. 2.0. Learning Outcomes 2.1. 3.0. 3.1Document2 pagesExperiment No. 2 Velocity and Acceleration: 1.0. Objectives 1.1. 1.2. 2.0. Learning Outcomes 2.1. 3.0. 3.1mil salinasNo ratings yet
- RMS Inlet Pressure Calculation TheoryDocument22 pagesRMS Inlet Pressure Calculation TheoryRajesh SarkarNo ratings yet
- Load Cell Burster Series 8416Document2 pagesLoad Cell Burster Series 8416ALEJANDRO IPATZINo ratings yet
- Calculating Uncertainty Using Digital Multimeter Ratio Measurement TechniquesDocument8 pagesCalculating Uncertainty Using Digital Multimeter Ratio Measurement TechniquesGordinhorsNo ratings yet
- Diagnostics 11 00161 v2Document14 pagesDiagnostics 11 00161 v2sara.dj.7cuNo ratings yet
- Science6 Co3Document7 pagesScience6 Co3LOIDA OJASCASTRONo ratings yet
- EE102 ManualDocument20 pagesEE102 ManualPiyush ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Yarn Experiment No 1Document3 pagesYarn Experiment No 1কষ্টের ফেরিওয়ালাNo ratings yet
- ProblemsDocument34 pagesProblemsAkshay KaushikNo ratings yet
- A Robust Autonomous Following Method For Mobile Robots in Dynamic EnvironmentsDocument15 pagesA Robust Autonomous Following Method For Mobile Robots in Dynamic Environmentsabinaya_359109181No ratings yet