Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electromagnetic Effects
Electromagnetic Effects
Uploaded by
Tran Phuong LinhOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electromagnetic Effects
Electromagnetic Effects
Uploaded by
Tran Phuong LinhCopyright:
Available Formats
4B ELECTROMAGNETIC EFFECTS
Supplement
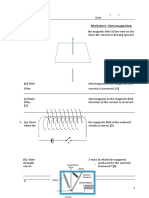
9 A bar magnet is moved in and out of a coil that is connected to a sensitive centre-zero meter,
as shown.
sensitive
centre-zero coil
meter
bar magnet
The meter needle swings to the left when the magnet is moving towards the coil. State how the
needle behaves when the bar magnet:
a is at rest inside the coil ..................................................................................................
b is moving back out of the coil ..........................................................................................
c moves more quickly towards the coil .................................................................................
d is at rest and the coil is moved away from the magnet. ........................................................
10 A straight wire is moved upwards through a horizontal magnetic field. Mark on the diagram the
direction in which current will flow in the wire if it is connected to a complete circuit.
wire
N
11 A bar magnet is moved towards a coil of wire connected to a meter, as shown.
72 Photocopying prohibited Cambridge IGCSE TM Physics Workbook Third Edition
4B Electromagnetic effects
An e.m.f. is induced in the coil and current flows in the circuit making the coil act like a magnet.
State the polarity of the end of the coil nearest the magnet when the N pole of the magnet:
a approaches the coil ..............................................................................
b is pulled back from the coil ...................................................................
c is at rest and the coil is moved towards the magnet. ..............................
12 Electricity transmission lines deliver 80 kW of power to the consumer at a voltage of 400 000 V.
The resistance of the transmission lines is 15 Ω.
a Calculate the current in the transmission lines. Show your working.
current = ..............................
b Calculate the rate of loss of energy from the transmission lines. Show your working.
rate of energy loss = ..............................
13 The pattern of magnetic field lines in and around a solenoid is shown below.
solenoid field line
A B
current direction
a A solenoid, like a bar magnet, has a N and a S pole.
i Is position A or B nearest to the S pole of the solenoid? ..............................
ii Explain how the polarity of the solenoid could be reversed. ....................................
iii In which direction would the N pole of a plotting compass point if placed at A?
...................................................................
Cambridge IGCSE TM Physics Workbook Third Edition Photocopying prohibited 73
4B ELECTROMAGNETIC EFFECTS
b State where the magnetic field is:
i strong .....................................................................................................................
ii weak. ......................................................................................................................
14 The current in the primary coil of a step-down transformer is 0.15 A. The input to the primary coil
is 240 V and the output from the secondary coil is 12 V.
Calculate and show your working for the current that can be drawn from the secondary coil if the
transformer is:
a 100% efficient in transferring power
secondary coil current = ..............................
b 90% efficient in transferring power.
secondary coil current = ..............................
15 A high-speed electron beam enters a region of uniform electric field, produced by a p.d. applied
to two parallel metal plates, as shown.
+
electrons
In which direction are the electrons deflected? ..............................
74 Photocopying prohibited Cambridge IGCSE TM Physics Workbook Third Edition
4B Electromagnetic effects
16 A high-speed electron beam enters a region of uniform magnetic field, as shown.
+ + + + + +
+ + + + + +
+ + + + + +
magnetic field
electrons
acting into page + + + + + +
+ + + + + +
+ + + + + +
In which direction are the electrons deflected? ..............................
Exam-style questions
Core
1 The diagram below represents a relay when it is switched off.
insulator springy metal
X
pivot
Q
iron armature
S
coil soft iron core
a Explain what will cause the relay to switch on. .......................................................................
........................................................................................................................................... [1]
b Explain why there is a soft iron core in the relay. ....................................................................
.......................................................................................................................................... [2]
c State what happens at X when the relay is switched on. ..........................................................
.......................................................................................................................................... [2]
d Give a reason for using a relay. ...............................................................................................
.......................................................................................................................................... [2]
[Total: 7]
Cambridge IGCSE TM Physics Workbook Third Edition Photocopying prohibited 75
4B ELECTROMAGNETIC EFFECTS
2 An electromagnet, P, is used to lift some scrap iron. The table shows the maximum load that
can be lifted when there are different currents in the electromagnet.
Current/A 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5
Load/N 20 40 60 80 100
a Sketch a load–current graph with current along the x-axis and load along the y-axis. [4]
b Describe the shape of your graph. .............................. [1]
c Determine the current needed to lift a load of 30 N. .............................. [1]
d State the maximum load that could be lifted by a current of 1.25 A. .............................. [1]
e A second electromagnet, Q, has the same design as electromagnet P but has twice the
number of turns on the coil. State the advantages that electromagnet Q would have over
electromagnet P.
........................................................................................................................................... [1]
.................................................................................................................................................
[Total: 8]
76 Photocopying prohibited Cambridge IGCSE TM Physics Workbook Third Edition
4B Electromagnetic effects
Supplement
3 The diagram below shows a simple generator.
coil rotation
N S
slip rings
(rotate
with coil)
brushes (fixed)
a Explain the function of the slip rings.
........................................................................................................................................... [1]
b Sketch the voltage output of the generator against time for one revolution of the coil.
[3]
c State the position of the coil when the induced voltage is a maximum.
........................................................................................................................................... [1]
d State the type of current there would be in a circuit connected to the brushes.
........................................................................................................................................... [1]
[Total: 6]
4 In a d.c. electric motor, a current-carrying coil attached to a split-ring commutator is mounted
between the poles of a magnet. The coil experiences a turning effect.
coil
N S
brush brush
(fixed) (fixed)
split-ring
commutator
(rotates with coil)
Cambridge IGCSE TM Physics Workbook Third Edition Photocopying prohibited 77
4B ELECTROMAGNETIC EFFECTS
a State the result of the turning effect on the coil.
........................................................................................................................................... [1]
b State how the size of the turning effect on the coil can be increased.
.................................................................................................................................................
.......................................................................................................................................... [3]
c Describe the effect on the coil of increasing the turning effect.
........................................................................................................................................... [1]
d Explain the function of the split-ring commutator.
.................................................................................................................................................
.......................................................................................................................................... [2]
[Total: 7]
5 When 250 V a.c. is applied to the primary coil of a step-up transformer, the output from the
secondary coil is 1000 V. The current in the primary coil is 0.8 A and there are 100 turns on the
primary coil.
a Calculate the number of turns on the secondary coil.
number of turns on secondary coil = .............................. [3]
b Calculate the power input to the transformer.
power input = .............................. [2]
c Calculate the current in the secondary coil if no energy were lost in the transformer.
current in secondary coil = .............................. [3]
d Explain the effect the resistance of the coil windings has on the efficiency of a transformer.
........................................................................................................................................... [1]
[Total: 9]
78 Photocopying prohibited Cambridge IGCSE TM Physics Workbook Third Edition
You might also like
- Sell Ovens ManualDocument243 pagesSell Ovens Manuallakshmimurugesan100% (1)
- Waves WorksheetDocument2 pagesWaves WorksheetMarilyn LaquindanumNo ratings yet
- Checkpoint 11.1Document2 pagesCheckpoint 11.1Az MY100% (1)
- AQA Physics: 4 Waves Exam-Style QuestionsDocument8 pagesAQA Physics: 4 Waves Exam-Style QuestionsMoses AhmedNo ratings yet
- Light Prism Pandathe Test2 Question PaperDocument4 pagesLight Prism Pandathe Test2 Question Paperboltu100% (1)
- Lab Report PhysicsDocument8 pagesLab Report PhysicssuryanshranaNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Elements & Compounds 1 MS PDFDocument8 pagesAtoms, Elements & Compounds 1 MS PDFClinton ChikengezhaNo ratings yet
- Physics 15 - Thermal Properties and Temperature - 2Document59 pagesPhysics 15 - Thermal Properties and Temperature - 2Hakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- Static Electricity - Notes PDFDocument4 pagesStatic Electricity - Notes PDFsabastian johnsNo ratings yet
- WorkEnergy P2Document26 pagesWorkEnergy P2dhairya gandhi100% (1)
- Flemings Left RuleDocument5 pagesFlemings Left RuleZaina A LeeNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Current ExerciseDocument12 pagesMagnetic Effect of Current Exercisemaatla monkge100% (1)
- Cambridge O Level: Physics 5054/11Document16 pagesCambridge O Level: Physics 5054/11AdeenaNo ratings yet
- Pendulum ExpDocument4 pagesPendulum ExpRoyston EbenezerNo ratings yet
- Q1L7 ElectricityDocument61 pagesQ1L7 ElectricityCarmella Raguindin100% (2)
- Magnet 4 DocDocument4 pagesMagnet 4 DocMIS NURUL IMAN JakbarNo ratings yet
- Moment of Forces WorksheetDocument4 pagesMoment of Forces WorksheetjessicaNo ratings yet
- AQA A Level Applied Physics Chapter 2 ThermodynamicsDocument33 pagesAQA A Level Applied Physics Chapter 2 ThermodynamicsJ3TL1No ratings yet
- Chem Energetics TestDocument7 pagesChem Energetics TestJkaurbhsNo ratings yet
- 9702 Physics P2 QP Mock 2020 PDFDocument12 pages9702 Physics P2 QP Mock 2020 PDFTasneemNo ratings yet
- MCE IGCSE Physics TWB C03 - Full SolutionsDocument2 pagesMCE IGCSE Physics TWB C03 - Full SolutionsXIN ZHANGNo ratings yet
- 5054 s20 QP 11 PDFDocument16 pages5054 s20 QP 11 PDFJack KowmanNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Worksheet + MCQ Questions - 2Document26 pagesUnit 4 Worksheet + MCQ Questions - 2Hoor Nafa100% (1)
- Space Physics MCQDocument16 pagesSpace Physics MCQaliyameen2006No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/22Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/22jad obaidNo ratings yet
- Phase Difference (Final)Document7 pagesPhase Difference (Final)Muhammad ShahzebNo ratings yet
- Resultant Forces - Practice QsDocument9 pagesResultant Forces - Practice Qsphydotsi50% (2)
- Theory Workbook (TE) Chapter 2Document24 pagesTheory Workbook (TE) Chapter 2scribduser0811972No ratings yet
- Usman Public School System: Pressure WorksheetDocument2 pagesUsman Public School System: Pressure Worksheetmarium khanNo ratings yet
- Energy Stores and Transfers WorksheetDocument3 pagesEnergy Stores and Transfers WorksheetAndreas LambriasNo ratings yet
- IGCSE 2 Phy General Properties of WavesDocument102 pagesIGCSE 2 Phy General Properties of WavesKanwal KhanNo ratings yet
- Terminal VelocityDocument18 pagesTerminal VelocityZubairHassanNo ratings yet
- Answers To End-Of-Chapter QuestionsDocument2 pagesAnswers To End-Of-Chapter Questionsjn hgvhvhnmNo ratings yet
- Magnetism NotesDocument13 pagesMagnetism Notesmaatla monkge100% (1)
- Electromagnetism WorksheetDocument3 pagesElectromagnetism WorksheetGuan Jie KhooNo ratings yet
- Igcse Physics P2 Worksheet 2019Document23 pagesIgcse Physics P2 Worksheet 2019ertugozNo ratings yet
- Light Practice QuestionsDocument3 pagesLight Practice QuestionsHem HemNo ratings yet
- Static Electricity Question PaperDocument4 pagesStatic Electricity Question Papertheja sudarshaniNo ratings yet
- Kirchoff's Laws Part 2Document13 pagesKirchoff's Laws Part 2alexobama100% (1)
- Quiz On Work, Energy, and PowerDocument2 pagesQuiz On Work, Energy, and PowerNathaniel DimaocorNo ratings yet
- Beaconhouse School System Southern Region Middle I, Gulshan Chapter Remedial Worksheet 4 Class VIIIDocument7 pagesBeaconhouse School System Southern Region Middle I, Gulshan Chapter Remedial Worksheet 4 Class VIIIMustufa KhalilNo ratings yet
- Wave PropertiesDocument2 pagesWave PropertiesAshok Kumar Dondati100% (1)
- A2 - Workbook 1 PDFDocument294 pagesA2 - Workbook 1 PDFHaadi NaqviNo ratings yet
- Magnetism ExerciseDocument9 pagesMagnetism Exerciseletangletty07No ratings yet
- Ib Magnetism - AllDocument14 pagesIb Magnetism - AllAarav VermaNo ratings yet
- Moments QuestionsDocument12 pagesMoments Questionsmuxadey100% (1)
- Worksheet (AS) PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet (AS) PDFMahad AsimNo ratings yet
- Electronic Control Questions FOR IGCSE PHYSICSDocument20 pagesElectronic Control Questions FOR IGCSE PHYSICSFahim Ahmed100% (1)
- 9 Worksheet 1: Intermediate LevelDocument3 pages9 Worksheet 1: Intermediate LeveltuvvacNo ratings yet
- Suvat Equation WorksheetDocument1 pageSuvat Equation WorksheetDelano PeteNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/22Document16 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/22NigelNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Bearings Higher IGCSE Questions 9 1 StandardDocument2 pagesTrigonometry Bearings Higher IGCSE Questions 9 1 StandardHaddonesKimberlyNo ratings yet
- Energy, Work and PowerDocument47 pagesEnergy, Work and PowerMaria BhaijiNo ratings yet
- Turning Effect of ForcesDocument19 pagesTurning Effect of ForcesFavaz TajwarNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 The Particulate Nature of Matter NotesDocument7 pagesTopic 1 The Particulate Nature of Matter Notessteve KingNo ratings yet
- Turning Effect of ForceDocument4 pagesTurning Effect of ForceIbrahim Khurram100% (1)
- Nebulae and Tectonic PlatesDocument4 pagesNebulae and Tectonic PlatesDeeva SethiNo ratings yet
- SPM Physics Form 5Document46 pagesSPM Physics Form 5Woody CysNo ratings yet
- Homework For Magnetic Effects ..Document72 pagesHomework For Magnetic Effects ..Kids World School SystemNo ratings yet
- 46.2-Electromagnetic EffectsDocument14 pages46.2-Electromagnetic Effectskatise1794No ratings yet
- Ans Elctromagnetic Spectrum Physics 1000+Document3 pagesAns Elctromagnetic Spectrum Physics 1000+Tran Phuong LinhNo ratings yet
- ForcesDocument5 pagesForcesTran Phuong LinhNo ratings yet
- Energy, Work & Power 04 QPDocument10 pagesEnergy, Work & Power 04 QPTran Phuong LinhNo ratings yet
- Capacitors 2Document4 pagesCapacitors 2Tran Phuong LinhNo ratings yet
- EM Iduction 2Document3 pagesEM Iduction 2Tran Phuong LinhNo ratings yet
- Electric Field and Culomb Law CBDocument8 pagesElectric Field and Culomb Law CBTran Phuong LinhNo ratings yet
- Electric Field and Culomb LawDocument13 pagesElectric Field and Culomb LawTran Phuong LinhNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion 2Document12 pagesCircular Motion 2Tran Phuong LinhNo ratings yet
- Light RevisionDocument5 pagesLight RevisionTran Phuong LinhNo ratings yet
- Magnetically Coupled CircuitDocument38 pagesMagnetically Coupled CircuitAlfred MoresNo ratings yet
- RCA 14M041 Service ManualDocument34 pagesRCA 14M041 Service ManualferdialvascribdNo ratings yet
- PF 520 530 FS C2026MFP C2126MFP PL UkDocument8 pagesPF 520 530 FS C2026MFP C2126MFP PL Ukradutranzy1No ratings yet
- EC8761-Advanced Communication Lab ManualDocument116 pagesEC8761-Advanced Communication Lab ManualparantnNo ratings yet
- Final Year Project ReportDocument32 pagesFinal Year Project ReportRahul PatilNo ratings yet
- Fire Shield ManualDocument68 pagesFire Shield ManualMike SaundersNo ratings yet
- MECH 1100 Quiz 4 Practice PDFDocument12 pagesMECH 1100 Quiz 4 Practice PDFKloyd EurolfanNo ratings yet
- TR 670408Document34 pagesTR 670408gerenciaNo ratings yet
- Fler Umc NetworkDocument18 pagesFler Umc Networkmonter10No ratings yet
- 7035te Manual de InstalacionDocument10 pages7035te Manual de InstalacionJose Antonio Acosta OrtizNo ratings yet
- Infineon Designing Li ION Battery Chargers Article Whitepaper v01 00 enDocument4 pagesInfineon Designing Li ION Battery Chargers Article Whitepaper v01 00 enfegyo123No ratings yet
- H4092-4 Bow Thruster StarterDocument38 pagesH4092-4 Bow Thruster StarteradinaNo ratings yet
- Introducing Unisab II Version 2.05.1 and 2.05.2Document4 pagesIntroducing Unisab II Version 2.05.1 and 2.05.2Mahmoud Mohamed100% (1)
- Protection Coordination Analysis Under A Real-Time Architecture For Industrial Distribution Systems Based On The STD IEEE 242-2001Document8 pagesProtection Coordination Analysis Under A Real-Time Architecture For Industrial Distribution Systems Based On The STD IEEE 242-2001Isai Gallardo VazquezNo ratings yet
- Manual Inversor-Vlt2800 PDFDocument165 pagesManual Inversor-Vlt2800 PDFLeandro de FigueiredoNo ratings yet
- High Bandwidth Memory Interface Design Based On Ddr3 Sdram and FpgaDocument2 pagesHigh Bandwidth Memory Interface Design Based On Ddr3 Sdram and FpgaKirubalani ANo ratings yet
- Sc20Mpc: Spinel 2MP Serial JPEG Color CameraDocument2 pagesSc20Mpc: Spinel 2MP Serial JPEG Color CameramhasansharifiNo ratings yet
- 520CSD01 DS enDocument5 pages520CSD01 DS enDJ ThangNo ratings yet
- Lec # 04 Substation Bus SchemesDocument12 pagesLec # 04 Substation Bus SchemesAwesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Determining The Initial States in Forward-Backward LteringDocument8 pagesDetermining The Initial States in Forward-Backward LteringgimmiNo ratings yet
- Valve and Actuator CatalogueDocument60 pagesValve and Actuator Catalogueashfaq-matte-79930% (1)
- Digiflex KMTDocument58 pagesDigiflex KMTsarafciger12350% (2)
- Wimax SeminarDocument32 pagesWimax SeminarPuspala Manojkumar100% (1)
- HG10LG050MDocument3 pagesHG10LG050MJohnielyn DeleonioNo ratings yet
- SM 25xx ETA2 DB ENGDocument24 pagesSM 25xx ETA2 DB ENGidris_pmNo ratings yet
- Sharp Photodevices Application CirquitsDocument7 pagesSharp Photodevices Application CirquitsbackvlackoNo ratings yet
- Driverless TrainDocument57 pagesDriverless TrainRoshan MNo ratings yet
- Modul Compact Vario Manual UKDocument48 pagesModul Compact Vario Manual UKEdgar Enrique Flores GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Audio Noise Reduction From Audio Signals and Speech Signals: Nishan Singh, Dr. Vijay LaxmiDocument5 pagesAudio Noise Reduction From Audio Signals and Speech Signals: Nishan Singh, Dr. Vijay LaxmiReshma JocyNo ratings yet