Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Atomic Mass SCS (Semeon)
Atomic Mass SCS (Semeon)
Uploaded by
Junje Semeon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageThe document discusses atomic mass and how it is determined by the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom. Atomic mass is expressed in atomic mass units, which is relative to the mass of one carbon-12 atom. Isotopes of an element have the same number of protons and electrons but different numbers of neutrons, giving them different atomic masses. The average weight of isotopes in the environment is the relative atomic mass, which is standardized by IUPAC and represents most of Earth's crust. Average atomic mass takes into account the natural abundance of isotopes in a sample.
Original Description:
reviewer grade 12
Original Title
atomic mass SCS (semeon)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses atomic mass and how it is determined by the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom. Atomic mass is expressed in atomic mass units, which is relative to the mass of one carbon-12 atom. Isotopes of an element have the same number of protons and electrons but different numbers of neutrons, giving them different atomic masses. The average weight of isotopes in the environment is the relative atomic mass, which is standardized by IUPAC and represents most of Earth's crust. Average atomic mass takes into account the natural abundance of isotopes in a sample.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageAtomic Mass SCS (Semeon)
Atomic Mass SCS (Semeon)
Uploaded by
Junje SemeonThe document discusses atomic mass and how it is determined by the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom. Atomic mass is expressed in atomic mass units, which is relative to the mass of one carbon-12 atom. Isotopes of an element have the same number of protons and electrons but different numbers of neutrons, giving them different atomic masses. The average weight of isotopes in the environment is the relative atomic mass, which is standardized by IUPAC and represents most of Earth's crust. Average atomic mass takes into account the natural abundance of isotopes in a sample.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
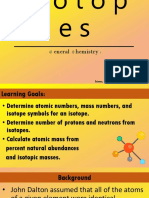
Atomic Mass
STUDY CHEAT SHEET BY JUNJE KHARYLLE A. SEMEON
∞ The number of electrons, protons, and
neutrons determines the mass of an
atom.
∞ It is possible to determine the mass of
one atom relative to another
experimentally.
∞ Atomic mass is the mass of the atom
expressed in atomic mass units (amu).
∞ One atomic mass unit is referred to as a
mass exactly equal to one-twelfth the
mass of one carbon-12 atom.
∞ Isotopes are atoms that have the same
number of protons and electrons but with
a different number of neutrons.
∞ This means isotopes also has a different
atomic mass.
∞ The average weight of all isotopes in a
normal environment is called the relative
atomic mass.
∞ The International Union of Pure and
Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) publishes
suggested values, which are updated
every year.
∞ The relative atomic mass is a
standardized number and is assumed to
be true for most of the planet Earth's
crust.
∞ When the natural percentage abundance
is considered in calculating the weight of
the naturally occurring isotopes of an
element, it is called an average atomic
mass.
∞ Average atomic mass differs depending
on the chemical sample.
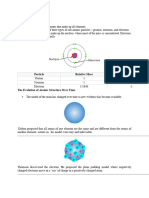
AVERAGE ATOMIC MASS
The general formula for the average atomic mass
is given below:
For example, carbon has two naturally
occurring isotopes, carbon-12 and carbon-13.
Their average atomic mass can be calculated
as follows:
You might also like
- Edexcel Chemistry AS NotesDocument101 pagesEdexcel Chemistry AS NotesMary Mannu100% (8)
- CHM1 11 - 12 Q1 0601 PF FDDocument35 pagesCHM1 11 - 12 Q1 0601 PF FDFrenche fate Marquez LoraNo ratings yet
- Atomic Mass: Wiki Loves Monuments: Photograph A Monument, Help Wikipedia and Win!Document13 pagesAtomic Mass: Wiki Loves Monuments: Photograph A Monument, Help Wikipedia and Win!Jennie KimNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument13 pagesChemMj CaraanNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Atomic Mass Atomic Number and Isotopes PDFDocument23 pages1.3 Atomic Mass Atomic Number and Isotopes PDFMARVIN DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Science Notes - 2024-05-08T125417.607Document2 pagesScience Notes - 2024-05-08T125417.607ASHNo ratings yet
- NucleiDocument17 pagesNucleiliebertj221No ratings yet
- Atoms, Isotopes, Ions, and Molecules: Key PointsDocument28 pagesAtoms, Isotopes, Ions, and Molecules: Key PointsCandyAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Discovery of NeutronsDocument12 pagesDiscovery of NeutronsEmnet SolomonNo ratings yet
- Chem ModuleDocument20 pagesChem Modulekeeno manzanoNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of AtomsDocument3 pagesFundamentals of AtomsMj CaraanNo ratings yet
- L2-Atoms and Atomic StructureDocument49 pagesL2-Atoms and Atomic Structurekoladejoy49No ratings yet
- Atomic Mass: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument15 pagesAtomic Mass: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchJennie KimNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theory: A Modern Model of The AtomDocument8 pagesAtomic Theory: A Modern Model of The AtomSophia MartinezNo ratings yet
- Textbook Medical Chemistry Revised Version 2020Document303 pagesTextbook Medical Chemistry Revised Version 2020deepdas1309No ratings yet
- Chemistry Note-1Document27 pagesChemistry Note-1mematugoldahmunu21No ratings yet
- 1C Atomic StructureDocument24 pages1C Atomic Structurejustme.azma.meNo ratings yet
- CHME2101: Chemistry For Engineers I: 1.1 Constitution of AtomsDocument16 pagesCHME2101: Chemistry For Engineers I: 1.1 Constitution of AtomsSangmo landryNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and The Periodic TableDocument6 pagesAtomic Structure and The Periodic TablecalimagandaNo ratings yet
- Mass Relationship in Chemical Reaction - Atomic MassDocument5 pagesMass Relationship in Chemical Reaction - Atomic MassLovely RamNo ratings yet
- Atomic NumberDocument4 pagesAtomic NumberYhantii Ferdinansyah SinagaNo ratings yet
- Atom Notes: Element-Pure Substance That Cannot Be Separated Into Simpler Substances byDocument3 pagesAtom Notes: Element-Pure Substance That Cannot Be Separated Into Simpler Substances bykarla callejaNo ratings yet
- Gen. Chem. PT Sitjar, Cyril P. Stem11 BDocument14 pagesGen. Chem. PT Sitjar, Cyril P. Stem11 BPerez CyrilNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument28 pagesAtomic StructureJohn Vince Ramos PapNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - ChemistryDocument9 pagesChapter 4 - ChemistryHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Atomic Mass - NCUKDocument27 pagesAtomic Structure and Atomic Mass - NCUKphonepyaehtut2006No ratings yet
- II. ATOMS, MOLECULES and IONSDocument18 pagesII. ATOMS, MOLECULES and IONSHania ABDULNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Isotopes NotesDocument5 pagesAtomic Structure and Isotopes Notesyanny280906No ratings yet
- Fundamental Particles of An AtomDocument5 pagesFundamental Particles of An AtomOmar QasimNo ratings yet
- The Atomic StructureDocument22 pagesThe Atomic StructureDeonLeo CuencaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: The Structure of The Atom Mass Spectrometry Electronic Structure Ionisation EnergiesDocument22 pagesAtomic Structure: The Structure of The Atom Mass Spectrometry Electronic Structure Ionisation EnergiesVijithaNo ratings yet
- Atomic MassDocument2 pagesAtomic MasscrazynupNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Atomic TheoryDocument17 pagesLecture 4 - Atomic TheoryEwartNo ratings yet
- Physical ScienceDocument27 pagesPhysical ScienceCarlos MasikaNo ratings yet
- Charge of Protons, Neutrons and ElectronsDocument6 pagesCharge of Protons, Neutrons and ElectronsjiwonahnNo ratings yet
- Isotopes and Atomic MassDocument8 pagesIsotopes and Atomic Massapi-182809945No ratings yet
- Additional MathematicsDocument6 pagesAdditional Mathematicslonydon23No ratings yet
- Chemistry Lecture PowerpointDocument39 pagesChemistry Lecture Powerpointapi-308666520No ratings yet
- AtomsDocument40 pagesAtomsJeNo ratings yet
- Lecture Pt. 4Document35 pagesLecture Pt. 4zy- SBGNo ratings yet
- Dalton's Atomic TheoryDocument19 pagesDalton's Atomic TheoryKatherine CampillosNo ratings yet
- Simple Model of An Atom: IsotopesDocument4 pagesSimple Model of An Atom: IsotopesLilaNo ratings yet
- A-Level Chemistry Atomic Structure NotesDocument22 pagesA-Level Chemistry Atomic Structure NotesAndreea Maria Pavel100% (1)
- G Eneral Chemistry 1: Science, Technology, Engineering and MathematicsDocument15 pagesG Eneral Chemistry 1: Science, Technology, Engineering and MathematicsGiveson TolentinoNo ratings yet
- MCQSDocument1 pageMCQSOsamaNo ratings yet
- CHAP4 AtomicStructureDocument34 pagesCHAP4 AtomicStructureJex AsupardoNo ratings yet
- KBAT Chemi CHAP 1Document15 pagesKBAT Chemi CHAP 1Chong HyenNo ratings yet
- Lesson-2_013153Document8 pagesLesson-2_013153natashalouisse103No ratings yet
- Notes 2 - Atoms and Atomic TheoryDocument6 pagesNotes 2 - Atoms and Atomic Theoryochiengjoseph122No ratings yet
- Elements and MoleculesDocument26 pagesElements and MoleculesTrevor NamalawaNo ratings yet
- Note For EJUDocument18 pagesNote For EJUmr.draungnaingwinNo ratings yet
- Chem Assignment 4Document7 pagesChem Assignment 4ttamNo ratings yet
- Chem 11 Unit 7 PPT 1 HebdenDocument27 pagesChem 11 Unit 7 PPT 1 HebdenMarina XuNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument9 pagesAtomic StructurehenryNo ratings yet
- Chem 1 Atomic Number Mass Number Periodic Table2Document15 pagesChem 1 Atomic Number Mass Number Periodic Table2Alexandria BaldedaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Atomic Structure The Structure of The Atom A) Protons, Neutrons and ElectronsDocument21 pagesChapter 1: Atomic Structure The Structure of The Atom A) Protons, Neutrons and ElectronsTeneshwaran Muniandy MunusamyNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Nuclear Medicine Volume I: Concepts of Nuclear Medicine, #1From EverandConcepts of Nuclear Medicine Volume I: Concepts of Nuclear Medicine, #1No ratings yet
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Your Journey To The Basics Of Quantum Realm Volume II: Your Journey to The Basics Of Quantum Realm, #2From EverandYour Journey To The Basics Of Quantum Realm Volume II: Your Journey to The Basics Of Quantum Realm, #2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- RationaleDocument1 pageRationaleJunje SemeonNo ratings yet
- Excretory System SCS (Semeon)Document6 pagesExcretory System SCS (Semeon)Junje SemeonNo ratings yet
- Human Cardiovascular System: Introduction ToDocument76 pagesHuman Cardiovascular System: Introduction ToJunje SemeonNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System SCS (Semeon)Document8 pagesCardiovascular System SCS (Semeon)Junje SemeonNo ratings yet