Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2122 Level M Biology IGCSE Top Questions
2122 Level M Biology IGCSE Top Questions
Uploaded by
-Bleh- WalkerCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Herpetology: Fourth EditionDocument723 pagesHerpetology: Fourth Editionnataliab.vieiraNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Holes Human Anatomy and Physiology 13th Edition by ShierDocument30 pagesTest Bank For Holes Human Anatomy and Physiology 13th Edition by ShierMarta Tronaas100% (36)
- Topic 1 MC 1Document68 pagesTopic 1 MC 1senpaiNo ratings yet
- Gut Health Guidebook 9 22Document313 pagesGut Health Guidebook 9 2219760227100% (3)
- Hewer's Textbook of Histology for Medical StudentsFrom EverandHewer's Textbook of Histology for Medical StudentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- BIOLOGY MODEL PAPER 9thDocument3 pagesBIOLOGY MODEL PAPER 9thHasnain Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Student's Copy Chapter3 BioDocument10 pagesStudent's Copy Chapter3 BioSaidatul Atyah Mohd ApendaiNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology 2017 2018 Sample Paper 4 PDFDocument9 pages11 Biology 2017 2018 Sample Paper 4 PDFRubhan kumarNo ratings yet
- Musingu High School Biology Topical Quick Revision Questions Topic 1: Introduction To BiologyDocument12 pagesMusingu High School Biology Topical Quick Revision Questions Topic 1: Introduction To BiologySheikhNo ratings yet
- (VCE Biology) 2017 YVG Unit 1 Exam v2Document10 pages(VCE Biology) 2017 YVG Unit 1 Exam v2Justine LyNo ratings yet
- G9 Absorption of FoodDocument4 pagesG9 Absorption of FoodkenzaNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document15 pagesCH 3Choi MingNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 Sem 1 p2 2016 JWPNDocument15 pagesBiology Form 4 Sem 1 p2 2016 JWPNMiz KarstzNo ratings yet
- Lucknow Public School Sample Paper-Ii Biology Class - XiDocument3 pagesLucknow Public School Sample Paper-Ii Biology Class - XiNishant singhNo ratings yet
- Biology Scheme Pertgh Penggal 2Document9 pagesBiology Scheme Pertgh Penggal 2Athirah Maestro100% (1)
- Kertas 1 SPM (Percubaan) 1-10Document76 pagesKertas 1 SPM (Percubaan) 1-10Hazizi HanapiNo ratings yet
- B 10 Ctsta 307Document6 pagesB 10 Ctsta 307Andhi SoesiloNo ratings yet
- Cds 2000101797439 Q 5 WMCCDocument15 pagesCds 2000101797439 Q 5 WMCCRISHI KUMARNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Life ProcessesDocument4 pagesWorksheet - Life ProcessesPadma pulivarthiNo ratings yet
- 2324 Level M (Gr11 UAE - GULF) Biology Course QuestionsDocument59 pages2324 Level M (Gr11 UAE - GULF) Biology Course QuestionsVan halenNo ratings yet
- Year 10 BiologyDocument15 pagesYear 10 BiologylkipsangNo ratings yet
- Bio Assignment 3 CompleteDocument8 pagesBio Assignment 3 Completeabby meadNo ratings yet
- Holes Human Anatomy and Physiology 15th Edition Shier Test BankDocument30 pagesHoles Human Anatomy and Physiology 15th Edition Shier Test BankKatherineBowenfojib100% (16)
- General InstructionsDocument5 pagesGeneral InstructionsMehak ShireenNo ratings yet
- Biology-Assignment 1Document2 pagesBiology-Assignment 1chethan reddyNo ratings yet
- Bio sp3Document9 pagesBio sp3imrupnarayanNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Holes Human Anatomy Physiology 15th by ShierDocument30 pagesTest Bank For Holes Human Anatomy Physiology 15th by ShierEthel Carver100% (35)
- Biology WorksheetDocument4 pagesBiology WorksheetAmmar RizwanNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Sample Paper Set 4Document3 pagesCBSE Class 11 Biology Sample Paper Set 4Unique InstituteNo ratings yet
- Biology Model Question Grade 12 Set 2Document2 pagesBiology Model Question Grade 12 Set 2Faris ShamimNo ratings yet
- 2324 Level L (Gr10 UAE - GULF) Biology Course QuestionsDocument75 pages2324 Level L (Gr10 UAE - GULF) Biology Course QuestionsVan halenNo ratings yet
- 2017 11 Sample Paper Biology 01 QPDocument2 pages2017 11 Sample Paper Biology 01 QPAlokNo ratings yet
- Class X Science BiologyDocument4 pagesClass X Science Biologydilipbanchhor8No ratings yet
- Biology 1Document4 pagesBiology 1Sam ManochaNo ratings yet
- CBSE SAMPLE PAPER - 01 (Solved) Class-XI Biology (Theory) Time: 3 Hrs MM: 70 General InstructionsDocument14 pagesCBSE SAMPLE PAPER - 01 (Solved) Class-XI Biology (Theory) Time: 3 Hrs MM: 70 General InstructionsMantri GNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper - Term - Ii: Session 2021-22 SET-1Document5 pagesSample Question Paper - Term - Ii: Session 2021-22 SET-1Yash BhagatNo ratings yet
- Regents Cell Membrane and DiffusionDocument5 pagesRegents Cell Membrane and Diffusionapi-303120399No ratings yet
- HY XI Bio QP Nov 2022Document6 pagesHY XI Bio QP Nov 2022Biswajit BeheraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 The Cellular Level of OrganizationDocument17 pagesChapter 3 The Cellular Level of Organizationjmjbioman100% (1)
- BIOLOGYDocument4 pagesBIOLOGYyogeshkumar090409No ratings yet
- General InstructionsDocument4 pagesGeneral InstructionsMehak ShireenNo ratings yet
- Modul SC Chapter 2 - f1Document14 pagesModul SC Chapter 2 - f1Raja InaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Movement Across The Plasma Membrane: Intervention-Biology Chapter 3 (Answer)Document4 pagesChapter 3: Movement Across The Plasma Membrane: Intervention-Biology Chapter 3 (Answer)Anonymous 6qork2No ratings yet
- Biochemistry & Cytology 1Document48 pagesBiochemistry & Cytology 1yumyum9No ratings yet
- First Pu Model Paper PDFDocument5 pagesFirst Pu Model Paper PDFMujeeb KhanNo ratings yet
- Bio SPM Intervensi m1Document10 pagesBio SPM Intervensi m1teahockNo ratings yet
- 4PxufKfnZtlpp6L9PIdV 2Document12 pages4PxufKfnZtlpp6L9PIdV 2GokulNo ratings yet
- Revision Worksheet-1Document2 pagesRevision Worksheet-1Abdul Muhi BakshiNo ratings yet
- Fcat Practice Booklet 8th GradeDocument130 pagesFcat Practice Booklet 8th Gradeapi-94846453100% (1)
- Biology Cells Practice TestDocument6 pagesBiology Cells Practice TestcamNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 Biology 1996 Paper 2+ansDocument19 pagesPaper 2 Biology 1996 Paper 2+ansapi-3812894100% (1)
- Biology Assignment SB015 Session 20232024 - StudentsDocument7 pagesBiology Assignment SB015 Session 20232024 - StudentsMuhd AzreenNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Science: Learning Area: Living Things and Their Environment Quarter: Fourth QuarterDocument4 pagesGrade 8 Science: Learning Area: Living Things and Their Environment Quarter: Fourth QuarterLexter CarmenNo ratings yet
- SamplePaper01 Class11 Biology QuestionsDocument10 pagesSamplePaper01 Class11 Biology QuestionsvnaynewadNo ratings yet
- 10 Bio - Worksheet 2022-23Document5 pages10 Bio - Worksheet 2022-23skyskyNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 TestDocument11 pagesTopic 1 Testrania samirNo ratings yet
- Bio Reviewer Q1Document8 pagesBio Reviewer Q1BruhNo ratings yet
- Biology Made FamiliarDocument71 pagesBiology Made Familiarwaiswakeneth4No ratings yet
- IB QBANK 6.1 - p1-p2Document35 pagesIB QBANK 6.1 - p1-p2Naz Gümüşlüoğlu100% (1)
- 9th Papers New PattrenDocument122 pages9th Papers New PattrenGul ZahraNo ratings yet
- Physics IGCSE Formula SheetDocument5 pagesPhysics IGCSE Formula Sheet-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- Should Animals Be Kept in ZoosDocument3 pagesShould Animals Be Kept in Zoos-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- MCQ Organic Chem Qs IGCSEDocument26 pagesMCQ Organic Chem Qs IGCSE-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- Balanced Arg LayoutDocument1 pageBalanced Arg Layout-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- (ML392-U) Geometry End of Year PracticeDocument55 pages(ML392-U) Geometry End of Year Practice-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Periodic wk11 - 221106 - 133505-1 - 221106 - 192711Document39 pagesChemistry Periodic wk11 - 221106 - 133505-1 - 221106 - 192711-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- The Devil's CoasterDocument1 pageThe Devil's Coaster-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- 2021 Level LS Physics Basic Questions Chap 1-5 (BTG)Document65 pages2021 Level LS Physics Basic Questions Chap 1-5 (BTG)-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- 2223 Level M Physics - Outer SpaceDocument178 pages2223 Level M Physics - Outer Space-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- 2021 Level L Biology Practical Based QuestionsDocument61 pages2021 Level L Biology Practical Based Questions-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- 2021 Level M SAT Grammar Tips T3 W7Document7 pages2021 Level M SAT Grammar Tips T3 W7-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- SAT Math Practice QuestionsDocument37 pagesSAT Math Practice Questions-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- Math Wk3 Quiz SolvedDocument26 pagesMath Wk3 Quiz Solved-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- Math Ams Wk8Document25 pagesMath Ams Wk8-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- Maths PDF WK 11Document8 pagesMaths PDF WK 11-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- 2021 Level L Biology Periodic 2-Revision Sheets T1 Wk10Document34 pages2021 Level L Biology Periodic 2-Revision Sheets T1 Wk10-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- Physics Quiz T2W2Document20 pagesPhysics Quiz T2W2-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- Math Wk3 Quiz SolvedDocument26 pagesMath Wk3 Quiz Solved-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- 0610 - s17 - QP - 42 AnsweredDocument20 pages0610 - s17 - QP - 42 Answered-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- BASIC BIOLOGY NOTES Sem 1 Part 1Document4 pagesBASIC BIOLOGY NOTES Sem 1 Part 1Polee SheaNo ratings yet
- Summary Book Abnormal Psychology Barlow Durand PDFDocument58 pagesSummary Book Abnormal Psychology Barlow Durand PDFLee DonghyuckNo ratings yet
- 4 Tutorial Biocatalysis 2021 - SkemaDocument4 pages4 Tutorial Biocatalysis 2021 - SkemaM Syarifuddin Mohd AminNo ratings yet
- Revision SB025 Set 1 AnswerDocument12 pagesRevision SB025 Set 1 Answerewine0529No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failuretinayko100% (1)
- Inflammatory Cytokine Response in Patients With Septic Shock Secondary To Generalized PeritonitisDocument9 pagesInflammatory Cytokine Response in Patients With Septic Shock Secondary To Generalized PeritonitisFerdian PriantoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology 1st Semester BSN Practice Mcqs With Key YT Insta Medico SlidesDocument11 pagesAnatomy and Physiology 1st Semester BSN Practice Mcqs With Key YT Insta Medico SlidesNaveed KhanNo ratings yet
- BCH 208 Course OutileDocument3 pagesBCH 208 Course OutileClinton DebrahNo ratings yet
- Cephalometric Evaluation of The Airway Dimensions in Subjects With Different Growth PatternsDocument6 pagesCephalometric Evaluation of The Airway Dimensions in Subjects With Different Growth PatternsJuán A. Nina LeonNo ratings yet
- 04 Lecture AnimationDocument66 pages04 Lecture AnimationJoshua VidalNo ratings yet
- Excretion by Rakshita SinghDocument37 pagesExcretion by Rakshita SinghPurplet 7No ratings yet
- MORAES-SILVA Et Al 2017Document20 pagesMORAES-SILVA Et Al 2017Luiza MartinsNo ratings yet
- CatSper Calcium Channels: 20 Years OnDocument16 pagesCatSper Calcium Channels: 20 Years OnBiblioteca Campus JuriquillaNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Plant Treasures of IndiaDocument150 pagesMedicinal Plant Treasures of Indiaahmad.electrocontrolNo ratings yet
- Drugs Toxicity 8Document24 pagesDrugs Toxicity 8اسامه عمر عثمانNo ratings yet
- Summative Assessment TaskDocument11 pagesSummative Assessment Taskapi-296545639No ratings yet
- Selective Androgen Receptor ModulatorsDocument7 pagesSelective Androgen Receptor ModulatorsRafael HelenoNo ratings yet
- Tinnitus Abordaje 2019Document17 pagesTinnitus Abordaje 2019Sara MartinezNo ratings yet
- 01 10Document10 pages01 10KcaBbe JavierNo ratings yet
- UNIT PLAN PIPRAMS 4th Year Bsc. NursingDocument9 pagesUNIT PLAN PIPRAMS 4th Year Bsc. NursingSuman Pandey100% (1)
- Figure 1 Human Nervous System Source:courses - Lumenlearning.c Om/microbiology/chapter/anato My-Of-The-Nervous-SystemDocument14 pagesFigure 1 Human Nervous System Source:courses - Lumenlearning.c Om/microbiology/chapter/anato My-Of-The-Nervous-SystemShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Body Asymmetries: Incidence, Etiology and Clinical ImplicationsDocument35 pagesBody Asymmetries: Incidence, Etiology and Clinical Implicationsok okNo ratings yet
- Unique Features of Plant DevelopmentDocument27 pagesUnique Features of Plant Developmentfatema100% (1)
- Immunology of Dental Caries and Caries Vaccine - Part IDocument6 pagesImmunology of Dental Caries and Caries Vaccine - Part IanviNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure (Compatibility Mode)Document40 pagesCell Structure (Compatibility Mode)Strive ShashaNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Module 2Document14 pagesGeriatric Module 2Cherry Joyce BascoNo ratings yet
- A Review On Response of Rice (Oryza Sativa L.) Under Salinity Stress in Terms of Its Growth, Development, Characteristics, and Biochemical LevelDocument6 pagesA Review On Response of Rice (Oryza Sativa L.) Under Salinity Stress in Terms of Its Growth, Development, Characteristics, and Biochemical LevelIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Module - Wk5&6 - The Biological Foundation of BehaviorDocument11 pagesModule - Wk5&6 - The Biological Foundation of Behavioraudree d. aldayNo ratings yet
2122 Level M Biology IGCSE Top Questions
2122 Level M Biology IGCSE Top Questions
Uploaded by
-Bleh- WalkerOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2122 Level M Biology IGCSE Top Questions
2122 Level M Biology IGCSE Top Questions
Uploaded by
-Bleh- WalkerCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology IGCSE Top Questions
1. Topic: Characteristics and classification of living organisms
Question description: Identify organisms using a dichotomous key.
Book Location: Biology Level L – Part 2 – Chapters 10
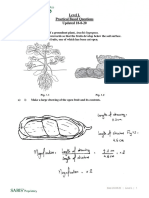
A scientist is studying different organisms found in a number of marine habitats. She made drawings
of several types of fish that were encountered in these areas. The following illustrations represent the
types of fish she encountered.
a. Use the partial dichotomous key provided below to identify each type of fish represented in the
figure.
Step 1
- Fish has a long and skinny shape…... go to step 2
- Fish has a short and fleshy shape…... go to step 3
Step 2
- Fish has pointed spines on top of its body…... Atlantic sturgeon (Acipenser oxyrinchus)
- Fish has fused fins running along its body…... European eel (Anguilla anguilla)
Step 3
- Fish has a v-shaped tail …... go to step 4
- Fish has a blunt tail …... go to step 5
Step 4
- Fish has one fin on top of its body with front edge much longer than back edge …... Quillback
(Carpiodes cyprinus)
- Fish has two fins on top of its body …... Atlantic horse mackerel (Trachurus trachurus)
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 1
Step 5
- Fish has spots on its body…... European flounder (Platichthys flesus)
- Fish lacks spots but has three alternating vertical white stripes on its body…...Saddleback clownfish
(Amphiprion polymnus)
b. Fish have a vertebral column and are commonly referred to as vertebrates.
i. To which phylum do fish belong?
ii. What are two general characteristics of fish?
c. In the dichotomous key, the scientific name of each fish is written in parentheses next to its common
name.
i. Which system is used by scientists to name organisms?
ii. What do each of the first term and second term of the scientific name refer to?
2. Topic: Gas Exchange in humans
Question description: Describe the inhalation process in humans.
Book Location: Biology Level M – Part 1 – Chapter 3
The diagram below shows the position of the diaphragm and ribs during inhalation and exhalation.
a. Indicate which figure illustrates exhalation.
b. Explain how movements of the diaphragm and ribs cause air to leave the lungs during exhalation.
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 2
c. The breathing rate of an athlete was measured while using an exercise machine at different work rates
and the results are summarized in the table below.
i. How does the breathing rate change with the variation in the work rate?
ii. Explain why the change in breathing rate is advantageous to the athlete in this case.
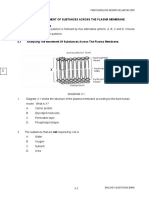
3. Topic: Organisation of the organism/Movement in and out of cells/Transport in animals
Question description: Describe passive transport in red blood cells.
Book Location: Biology Level M – Part 1– Chapter 4
Human red blood cells (RBCs) of normal size and shape were placed into three identical test tubes.
The contents of each tube are listed in the table below.
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 3
a. Knowing that the percentage of salt in human blood is about 9 g/L or 0.9 percent, complete the given
table.
b. Explain why doctors do not give pure water intravenously (through an IV bag) to patients who have
lost a large amount of blood.
c. Suggest the type of fluid replacement that would be given to patients who have lost blood. Explain
your answer.
4. Topic: Organisation of the organism/ Movement in and out of cells
Question description: Describe osmosis in a plant cell.
Book Location: Biology Level L – Part 1 – Chapter 4
Strips of epidermal cells taken from a plant were placed in three different sucrose solutions and were
left for 30 minutes. Then, the cells were observed under a light microscope and the observations are
recorded in the table below.
a. Describe the appearance of the plant cells in each solution.
b. What process is responsible for the changes observed in the cells’ appearance?
c. What characteristic of the plant cell membrane allows this process to occur?
d. What can you say about solution B that explains the appearance of the cells in this solution?
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 4
5. Topic: Organisation of the organism/Movement in and out of cells/Transport in plants
Question description: Describe the movement of water in plant cells.
Book Location: Biology Level L – Part 1 – Chapter 4
Strips of epidermal cells were taken from a plant and placed for 30 minutes in three different salt
solutions as shown in the table below.
a. The diagram below illustrates a plant cell after being placed in solution 1.
i. Identify A, B, and C.
ii. Describe the changes observed in the plant cell when placed in solution 1.
b. What process is responsible for the changes observed in the cells’ appearance?
c. What characteristic of the plant cell membrane allows this process to occur?
d. Could the plant cell illustrated in part (a) return to its normal shape? Explain your answer.
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 5
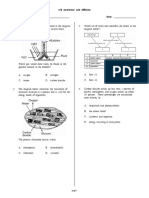
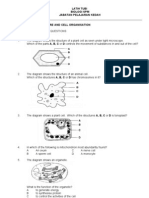
6. Topic: Human nutrition
Question description: Describe the role of villi in the small intestine.
Book Location: Biology Level M – Part 1 – Chapter 2
The figure below illustrates a section through a part of the small intestine in humans. Digestion and
absorption of nutrients occurs continuously as food is pushed along the small intestine.
a. Describe the process by which food is moved along the small intestine.
b. State three ways in which the small intestine is adapted for the absorption of digested food.
c. The figure below shows a magnification of the cells on top of structure B. Each cell has numerous
small projections on their surfaces.
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 6
i. What are these small projections called?
ii. What is the main function of these projections?
7. Topic: Human nutrition
Question description: Describe the effects of cholera infection in the small intestine.
Book Location: Biology Level M – Part 1 – Chapters 5
Cholera is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Vibrio cholerae. The cholera bacteria infect
the lumen of the small intestine and produce a toxin (i.e., a poisonous substance), as seen in the figure
below.
a. What is the effect of the cholera toxin on intestinal cells?
b. What are two symptoms of cholera infection?
c. What is the standard treatment of cholera infection?
d. Suggest one possible method to prevent the transmission of cholera bacterium.
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 7
8. Topic: Enzymes/Human nutrition
Question description: Describe the role of enzymes in chemical digestion.
Book Location: Biology Level L – Part 1 – Chapter 3
The diagram below illustrates an enzyme-catalyzed reaction.
a. State the names of structures A, B, C, and D.
b. Explain why the model of enzyme activity shown in this figure is known as the 'lock-and-key' model.
c. Some enzymes are produced by specific cells and released into the alimentary canal to aid in the
chemical digestion of consumed food. Explain why enzymes are important for the reactions occurring
during chemical digestion.
d. Use the 'lock-and-key' model to explain how the enzyme sucrase catalyzes the breakdown of sucrose
into fructose and glucose in the human body.
9. Topic: Human nutrition
Question description: Describe mechanical and chemical digestion in the alimentary canal.
Book Location: Biology Level M – Part 1 – Chapter 2
Digestion converts nutrients in ingested food into forms that can be absorbed by the body through
various mechanical and chemical processes.
a. Compare mechanical digestion and chemical digestion.
b. Complete the table below using an (X) to identify where different processes of the digestive system
take place.
c. Explain, using an example, how chemical digestion is carried out in one of the locations listed in the
above table.
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 8
10. Topic: Human nutrition
Question description: Describe the role of teeth in digestion.
Book Location: Biology Level M – Part 1 – Chapter 2
The drawing below shows a vertical section through a human tooth.
a. Name the structures labelled A, B, C, D, and E.
b. What is one function of structure D?
c. Tooth decay is caused when bacteria reach structure B. Explain how bacteria can reach this structure.
11. Topic: Plant nutrition
Question description: Describe the rate of photosynthesis under different conditions.
Book Location: Biology Level L – Part 1 – Chapter 6
The graph below shows changes in the relative rate of photosynthesis of two plants under different
temperatures.
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 9
a. Describe the changes in the rate of photosynthesis of each plant.
b. Give two reasons to explain the effect of the change in temperature on the rate of photosynthesis in
both plants.
c. Temperature is a limiting factor in A at temperature 35C. Explain this statement.
d. With reference to the given graph, suggest which curve corresponds to each of the following crops:
i. Sugar cane, which grows in warm climates
ii. Wheat, which grows in cool climates
12. Topic: Plant nutrition
Question description: Identify the effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis.
Book Location: Biology Level L – Part 1 – Chapter 6
A student set up the apparatus below to investigate the effect of light intensity on the rate of
photosynthesis in pondweed. The student placed the lamp at different distances from the pondweed
and counted the number of bubbles of gas released from the pondweed in 1 minute for each distance.
The results are recorded in the table below.
a. What is the role of the thermometer placed in the water beaker?
b. What is the gas being released in the bubbles?
c. The student concluded that the rate of photosynthesis was inversely proportional to the distance of the
lamp from the plant.
i. Do the obtained results confirm this hypothesis or not?
ii. Explain your answer.
d. Explain how the number of bubbles would change if the pondweed was placed in complete darkness.
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 10
13. Topic: Transport in animals
Question description: Describe different components of the circulatory system.
Book Location: Biology Level M - Part 1 – Chapter 4
The figure below illustrates a cross section of an artery in the human body.
a. What are two structural features of an artery?
b. What is the main role of arteries in the human body?
c. The below figure illustrates a cross section of a vein.
i. By referring to the figure, what is one structural feature that distinguishes a vein from an artery?
ii. Explain the purpose of the feature you identified in the previous part.
d. Both arteries and veins transport blood within the human body. Compare the direction of blood flow
between the two types of blood vessels.
e. A third type of blood vessels is also present in the human body. Identify this blood vessel and
compare two of its characteristics to those of the arteries and veins.
14. Topic: Transport in animals/ Inheritance
Question description: Describe the process of blood clotting.
Book Location: Biology Level M – Chapter 4
The table below shows the composition of blood samples taken from three different individuals.
a. The three samples were taken from men at the same age. Explain why this would make the
comparison more effective.
b. Identify the main function of each of the RBCs and WBCs.
c. Which person is least likely able to fight an infection by a virus? Explain your answer.
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 11
d. Platelets are involved in the process of blood clotting illustrated in the figure below.
i. Describe briefly the stages involved in the process of blood clotting.
ii. People at risk of heart disease are sometimes advised to take aspirin which reduces the clotting
of blood. Which of the three individuals is most likely to be taking this drug? Explain your
answer.
15. Topic: Transport in plants
Question description: Describe the process of transpiration in plants.
Book Location: Biology Level L – Chapter 8
The main pulling force that draws water from the soil and through the plant is produced by a process
called transpiration which mostly takes place in the leaves. The figure below illustrates a section
through a leaf.
a. Label parts A to D.
b. Describe how structure B is specialized to perform its role of transporting water to the leaves.
c. Use the diagram to explain how water is lost from leaves during transpiration.
d. The rate of transpiration in a plant changes under different circumstances. Identify one environmental
condition that affects the rate of transpiration and describe its effects.
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 12
16. Topic: Plant nutrition/Transport in plants
Question description: Describe the different internal components of a leaf.
Book Location: Biology Level L – Chapter 8
Leaves may appear to be thin; however, they are made up of several layers of cells organized into
different tissues. The diagram below illustrates a section of a leaf.
a. Identify labels A to F.
b. Explain how cells in the tissue labelled B are adapted to photosynthesis.
c. Leaves contain many air spaces between their cells in region C. What is the purpose of these air
spaces?
d. During the day, gas X is released to the environment while gas Y is taken into the leaves.
i. Identify gases X and Y.
ii. By which process do these gases move into and out of the leaves?
iii. An important process that commonly occurs in green plants involves both of these gases. What
is this process and what is the role of each gas in it?
17. Topic: Gas exchange in humans
Question description: Describe gas exchange in humans.
Book Location: Biology Level M – Chapter 3
The figure below illustrates an alveolus and a blood capillary in the human body.
The alveoli are the site of exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the lungs.
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 13
a. Identify the process by which gases move from the air spaces in the alveoli in the lungs into the blood
and vice versa.
b. State whether the relative concentration of carbon dioxide is “high” or “low” at positions 1, 2, and 3
seen above.
c. List three features of alveoli that facilitate gas exchange.
d. The alveoli of a long-term smoker are less elastic than a non-smoker and their walls also suffer from
breakage. Explain how each of these differences would affect the functioning of a smoker’s lungs.
18. Topic: Respiration
Question description: Describe physiological changes that occur to the body during exercise.
Book Location: Biology Level M – Chapter 3
An athlete’s heart rate and breathing rate were measured at different work rates.
a. Which process supplies the athlete’s body with energy?
b. Describe the changes observed in the heart rate and breathing rate of the athlete.
c. Explain two advantages of these changes to the body during exercise.
d. The breathing rate and the amount of oxygen used were still high after exercise, even though the
athlete sat down to rest. Why were they still high?
19. Topic: Excretion in humans
Question description: Describe the role of kidneys in excretion.
Book Location: Biology Level M – Part 1 – Chapter 6
The excretory system in humans includes the kidneys, the ureters, the urinary bladder, and the
urethra, which form the urinary system, in addition to other organs, such as the skin, the lungs, and
the large intestine.
a. What is excretion?
b. Identify the roles of the skin and the lungs in excretion.
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 14
c. The figure below illustrates a section of a kidney.
Identify the structures labelled A to C.
d. Give one function of each of structures D, E, and F.
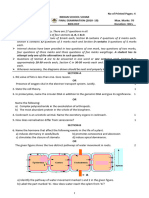
20. Topic: Excretion in humans
Question description: Describe the process of urine formation in the kidney.
Book Location: Biology Level M – Chapter 6
Urea and other excretory products accumulate in the blood of patients suffering from kidney failure.
Therefore, they must be admitted every few days into the hospital for dialysis treatment.
a. With reference to the figure above, explain the principle of dialysis as used in kidney machines.
b. How does the composition of the dialysis fluid compare to that of the patient’s blood in terms of urea,
water, and salts?
c. What would happen if the glucose concentration used in the dialysis fluid is lower than that in the
patient’s blood?
d. Transplanted kidneys are more efficient than dialysis but there are some issues regarding the
transplantation procedure. Give one concern of kidney transplants and explain how it may occur.
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 15
21. Topic: Diseases and immunity
Question description: Describe different types of medicinal drugs.
Book Location: Biology Level M – Chapter 9
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infects white blood cells. HIV infected individuals may be
treated with a variety of drugs.
a. Define the term drug.
b. Explain why antibiotics cannot be used to treat HIV.
c. Suggest the type of drugs that can be used to treat HIV.
d. Explain two reasons why patients need to follow the recommendations of their medical doctor and the
instructions of the medical prescription when taking medicinal drugs.
22. Topic: Drugs
Question description: Describe some harmful effects of using drugs for nonmedical purposes.
Book Location: Biology Level M – Chapter 9
Even though the misuse of many types of drugs is dangerous, some people are tempted to take drugs,
such as heroin, recreationally for nonmedical purposes. The table below shows the number of heroin
drug users who were diagnosed as HIV positive between 2002 to 2006 in countries of the European
region according to the World Health Organization.
a. Explain how people who take heroin are likely to become infected with HIV.
b. Describe the changes in the number of heroin drug users diagnosed as HIV positive between 2002 and
2006.
c. Suggest one explanation for the changes observed.
d. List two effects of heroin use on the body.
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 16
23. Topic: Coordination and response
Question description: Describe reflexes.
Book Location: Biology Level M – Chapter 7
The nervous system coordinates the responses of humans to changes in their environments. The chart
below shows the arrangement of the two major parts of the nervous system in the body.
a. Identify the missing parts (A, B, C) in the chart.
b. Distinguish between stimuli, receptors, and effectors.
c. Some responses of the human body are voluntary actions while others involuntary actions. The
flowchart below shows the general steps of how a reflex, an almost instantaneous involuntary
response, takes place in humans.
Stimulus receptor sensory neuron interneuron motor neuron effector response
i. Distinguish between a voluntary and an involuntary action.
ii. Identify the pathway of the reflex action that occurs in response to shining a bright light into the
eye.
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 17
24. Topic: Coordination and response
Question description: Describe the inheritance of color-blindness.
Book Location: Biology Level M – Chapter 11
The pedigree below shows the inheritance of color-blindness among members of the same family.
Colorblindness is characterized by the inability to perceive certain wavelengths of light.
Note that the shaded square and circle refer to an affected man and affected woman, respectively. The
half-shaded circle refers to a carrier woman.
a. What do the roman numbers on the left side of the pedigree indicate?
b. With reference to the pedigree shown above, identify the type of inheritance of color-blindness in
humans.
c. Explain why all the male offspring of parents 1 and 2 are not colorblind even though their father is.
d. Explain why all the females of parents 1 and 2 are carriers even though their mother is healthy.
e. Explain why only woman 19 in this pedigree is colorblind.
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 18
25. Topic: Coordination and response
Question description: Describe the pupil reflex action.
Book Location: Biology Level M – Chapter 7
The figure below illustrates a reflex action that involves the eye. Part A shows an eye in bright light
conditions, while part B shows an eye in dim light conditions.
a. Identify the stimulus to which the eye responds.
b. State the receptor cells that detect the stimulus.
c. Name the effector that responds to the stimulus.
d. What is the name of the nerve that transmits nerve impulses to the brain?
e. Describe how the nervous system coordinates the response in each case (A and B) shown in the
figure.
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 19
26. Topic: Coordination and response
Question description: Describe thermoregulation.
Book Location: Biology Level M – Chapter 8
One aspect of homeostasis in the human body is thermoregulation which is controlled by the
hypothalamus. The graph below shows the changes in the body temperature of a person over a certain
duration of time.
a. What is homeostasis?
b. What possibly caused the change observed from time 45 minutes till point X?
c. What possibly caused the change observed between points X and Y?
d. Give three
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 20
27. Topic: Drugs
Question description: Describe the misuse of drugs.
Book Location: Biology Level M – Chapter 9
The following graph shows the relative risk of having a fatal car accident as a function of blood alcohol
concentration.
a. The blood alcohol limit for a person driving a motor vehicle is 0.08 g/dL. If a person has a blood alcohol
concentration of 0.12 g/dL, how much would his alcohol limit be above the legal limit?
b. Give two reasons why it is dangerous to drive when having a blood alcohol concentration above the legal
limit.
c. Alcohol is cleared from the bloodstream by the action of the liver, at a rate of about 20 (mg/dL) per hour.
How many hours after drinking the alcohol by the person described in part (a) would that person be safe to
drive i.e. (have blood alcohol concentration below legal limit)?
28. Topic: Reproduction
Question description: Describe sexual reproduction in humans.
Book Location: Biology Level M – Chapter 12
The table below lists several functions of some structures of the female reproductive system.
a. Complete the table by identifying the structure that performs each function.
b. After implantation, the embryo (and later on the fetus) relies on its mother's diet to sustain its
nutritional needs for growth and development in the womb. Which organ allows the exchange of
material between maternal and embryonic blood in order to provide the embryo with nutrients and
other material necessary for its growth?
c. Which structure connects this organ to the embryo?
d. What are two other roles of the organ identified in part (b)?
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 21
29. Topic: Reproduction
Question description: Describe different types of pollination in plants.
Book Location: Biology Level L – Chapter 9
The figure below illustrates two types of pollination in flowering plants.
a. Name the type of pollination illustrated in each of case 1 and 2.
b. List one advantage and one disadvantage of pollination in case 2.
c. Identify the pollinating agent(s) that most likely aided in the process of pollination in case 1.
d. In some rare cases, the pollen grains fall on to the receptive stigmas due to gravity. In which case (1
or 2) shown in the figure, is this kind of pollination possible? Explain your answer.
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 22
30. Topic: Reproduction
Question description: Identify the role of the different flower parts.
Book Location: Biology Level L – Chapter 9
The diagram below illustrates a cross section of a flower belonging to a certain plant species. Bees
gather food material from these flowers and in doing so, they help in the reproductive process of this
plant species.
a. Label structures A, B, and C and state the function of each.
b. Identify the stage in the reproduction of the plants in which the bee is involved.
c. Explain how this process might take place between different flowers of the same plant species with
the help of the bees.
d. Explain why reproduction in flowers is considered to be sexual rather than asexual.
31. Topic: Reproduction
Question description: Describe the process of fertilization and identify methods of birth control.
Book Location: Biology Level M – Chapter 12
The figure below illustrates the stages of embryo development after the process of fertilization in the
human body.
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 23
a. List the stages of embryo development shown in the figure in the correct order.
b. The sperm and egg cells that combine during fertilization are called haploid, while the produced
fertilized egg cell is called diploid. Explain this statement.
c. Explain what determines if a fertilized egg develops into a female rather than a male.
d. Couples can control the number of children they want to have by using different methods of birth
control or contraception. These include natural, mechanical, chemical, and surgical methods.
Describe briefly two of these methods using an example.
32. Topic: Reproduction
Question description: Describe the human female gametes.
Book Location: Biology Level M – Chapter 12
The figure below illustrates different parts of the female human reproductive system.
a. Name the structures labelled A to E.
b. Identify the site where the processes of fertilization and implantation take place.
c. The figure below illustrates a female gamete cell.
i. Identify the site of production of the female gamete cells.
ii. The gamete cell is viewed at 100X magnification. Calculate the actual size of the cell.
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 24
33. Topic: Reproduction
Question description: Describe structures of the male reproductive system.
Book Location: Biology Level M – Chapter 12
The diagram below shows part of the human male reproductive system.
a. Name the parts labelled A to F.
b. Identify the part that produces the male gametes and name the process by which gamete cells are
produced in humans.
c. A gamete cell is called haploid. Explain this statement with referring to the chromosome content in
the gamete cells compared to body cells.
34. Topic: Inheritance
Question description: Describe the inheritance of a dominant condition using a pedigree.
Book Location: Biology Level M – Chapter 11
The pedigree below shows the inheritance of Huntington disease (a progressive brain disorder) in a
family.
a. Huntington’s disease is caused by an autosomal trait. Explain this statement.
b. There are no carriers for Huntington’s disease; an individual either has it or does not. Is the trait
coding for this disease dominant or recessive?
c. Identify the genotype of individuals 1, 2, 3, and 4 using appropriate symbols.
d. Couple 3 and 4 decided to have another child. What is the probability that the resulting child will
have Huntington disease? Explain your answer using a genetic diagram.
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 25
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 26
35. Topic: Inheritance
Question description: Describe the genome of muntjac deer.
Book Location: Biology Level M – Chapters 10
The diagram below illustrates the chromosomes found in a gamete cell of a mammal.
a. What are chromosomes?
b. Where are chromosomes usually located in an animal cell?
c. Indicate the number of chromosomes that would be present in a body cell of this animal. Explain your
answer.
d. Name the type of cell division by which the gamete cell was produced.
e. Explain the importance of this type of cell division for the production of gametes.
36. Topic: Inheritance
Question description: Describe incomplete dominance.
Book Location: Biology Level M – Chapter 11
A student wanted to investigate the inheritance of flower color in snapdragon plants. Snapdragon
flowers may have one of three colors: red, white, or pink. The students performed a cross between
two purebred plants, one with red flowers and the other with white flowers. The results are
summarized below.
a. Identify the inheritance pattern of flower color in snapdragon plants and explain how it occurs.
b. The student then crossed members of the first generation. Illustrate the cross showing the gametes of
the parents, the possible genotypes of the offspring, and the possible phenotypes of the offspring.
c. What do we call the offspring that resulted from the cross between the first generation plants?
d. What is the probability that an offspring with red flowers results from the cross described in part (b)?
e. What would the probability of having offspring with white flowers in a cross between a snapdragon
with pink flowers and another with red flowers be?
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 27
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 28
37. Topic: Variation and selection/Organisms and their environment
Question description: Distinguish between pyramids of numbers and pyramids of biomass.
Book Location: Biology Level L – Chapter 13
The table below lists the different animals feeding on an oak tree and some of the animals that feed on
them.
a. Draw the food web involving the animals described in the table.
b. Draw a pyramid of numbers for the animals described in the table indicating the number of trophic
levels and including the total number of organisms that would be present at each trophic level.
c. How would a pyramid of biomass differ from the pyramid of numbers in this case?
38. Topic: Characteristics and classification of living organisms/Variation and selection/Organisms and
their environment
Question description: Describe how organisms are adapted to their respective environments.
Book Location: Biology Level M – Chapter 11
Various adaptive features can be found among animal and plant species. For example, camels have
several adaptive features that make them more fit and allows them to survive in the harsh conditions
of deserts. Another example is the polar bear which is adapted to the arctic region.
a. What is an adaptive feature?
b. What does the fitness of an organism mean?
c. What are two features of camels that make them well adapted to their environment?
d. The polar bear is characterized by its thick white fur, small ears, sharp teeth, and large paws. Choose
two of these traits and explain how each helps the polar bear survive in its environment.
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 29
39. Topic: Variation and selection
Question description: Describe continuous variation in a population of plants.
Book Location: Biology Level M – Chapter 11
The below graph shows the variation in the stem length among the members of a population of plants.
a. What does variations in a population mean?
b. The graph shows a normal distribution. Explain this statement.
c. What type of phenotypic variation does this graph show? Explain your answer.
d. Variations in the stem length can be caused by mutations. Define mutations and explain how can they
give rise to variations in a population.
40. Topic: Characteristics and classification of living organisms /Variation and selection
Question description: Distinguish between natural selection and selective breeding.
Book Location: Biology Level M – Chapter 11
Humans have selectively bred plants and animals for thousands of years including dogs that possess
specific desirable traits which make them suited to jobs like herding sheep and aid in hunting.
a. List the general steps of the process of selective breeding.
b. Selective breeding is also called artificial selection and differs from natural selection that occurs
naturally and spontaneously in the environment without human intervention. How does natural
selection occur in a population?
c. Both natural and artificial selection can cause changes in the distribution of adaptive features in a
population over generations. However, dogs and other domesticated species are usually less fit than
their wild relatives. Explain this statement.
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 30
41. Topic: Organisms and their environment
Question description: Describe the flow of energy in a food chain.
Book Location: Biology Level L – Chapter 13
The below diagram illustrates the flow of energy along a food chain in a grassland ecosystem.
a. Only 10% of the energy trapped by the plant from the sun is passed to the deer. State two processes
that the plant uses the remaining energy for.
b. Calculate how much energy reaches the deer and how much energy reaches the lion.
c. Identify process X and give one probable reason why it is higher in lions than in deer.
d. Identify the number of trophic levels in the given food chain and explain why food chains rarely
consist of more than 5 levels.
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 31
42. Topic: Organisms and their environment
Question description: Describe predator-prey relationship in an ecosystem.
Book Location: Biology Level L – Chapter 13
The below graph illustrates the changes in the number of individuals in a population of rabbits and a
population of foxes found in a forest ecosystem during a specific period of time.
a. In which year did the rabbit population reach its maximum size? Suggest two reasons for this increase
in population size.
b. The increase in the rabbit population causes an increase in the fox population. Indicate if this
statement is correct or wrong using specific examples from the provided graph.
c. Identify the relationship between the populations of rabbits and foxes. Explain your answer.
d. If the foxes experience widespread disease which causes high levels of death in the fox population,
how would this change affect the rabbit population in this ecosystem?
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 32
43. Topic: Organisms and their environment
Question description: Describe the cycling of nitrogen in an ecosystem.
Book Location: Biology Level L – Chapter 13
The diagram below represents part of the nitrogen cycle in an ecosystem.
a. Gaseous nitrogen is abundant in the atmosphere. However, living things cannot make use of nitrogen
in its gaseous form. In order for nitrogen to become accessible to living things, nitrogen fixation must
take place. This can be done by nitrogen-fixing bacteria and other methods. Give a brief description
of two ways other than bacteria that nitrogen can be fixated.
b. Why is nitrogen important to plants and animals?
c. Several other stages of the nitrogen cycle involve the action of bacteria. Two of these processes are
labelled X and Y in the diagram. Identify these processes.
d. Which group of bacteria convert ammonia into nitrates in the nitrogen cycle?
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 33
44. Topic: Organisms and their environment/Human influences on ecosystems
Question description: Describe the water cycle.
Book Location: Biology Level L – Chapter 13
The diagram below illustrates some stages of the water cycle.
a. Identify the processes labelled A to F on the figure.
b. Describe the roles of plants and animals in the water cycle.
c. Water bodies such as lakes are often naturally enriched by nutrients that move from mountain slopes
and hills into the water bodies. By which process does this happen?
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 34
45. Topic: Human influences on ecosystems
Question description: Describe the impact of plastic use on the environment.
Book Location: Biology Level L – Chapter 14
The production of plastics is an important source of non-biodegradable solid waste. These plastic
materials are considered a great threat for human, plant, and animal health. Different sources of
microplastics in aquatic ecosystems and the methods by which they are taken up by marine organisms
are listed below.
a. Define non-biodegradable waste.
b. The microplastics cause decreased photosynthesis in microalgae. Identify the effects of this on other
organisms in the aquatic ecosystem.
c. Predict two possible effects of the direct ingestion of microplastics on aquatic animals.
d. State one method that can be used to decrease the amount of microplastics that reach aquatic
ecosystems.
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 35
46. Topic: Human influences on ecosystems
Question description: Describe eutrophication.
Book Location: Biology Level L – Chapter 14
Excessive mineral enrichment of bodies of water (e.g., rivers, lakes, and oceans) due to runoff from
the land causes eutrophication. It can be of a natural origin (natural eutrophication) but is often
dramatically increased by human activities. The sources of the most common nutrients causing
eutrophication (nitrogen and phosphorus) were studied in a lake and the results are listed in the tabled
below.
a. Rural runoff mostly contains waste from farmlands. Explain why the highest contribution of nitrogen
and phosphorus minerals is from rural runoff.
b. Describe briefly the major steps of the process of eutrophication.
c. Identify two ways to decrease the harmful effects of eutrophication.
47. Topic: Biotechnology and genetic engineering
Question description: Describe the use of bacteria in genetic engineering.
Book Location: Biology Level M – Chapter 11
Human insulin can now be made using bacteria that have been genetically engineered while in the
past, it used to be collected from animal tissues.
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 36
a. Define genetic engineering.
b. State the advantage of using bacteria to produce insulin rather than collecting it from animal tissues.
c. Identify the structures labelled A to D on the figure.
d. What is one other product that can be produced using genetically-modified bacteria?
48. Topic: Biotechnology and genetic engineering
Question description: Describe the production of penicillin in fermenters.
Book Location: Biology Level L – Chapter 11
Penicillin is one of the earliest discovered and most widely used antibiotic agents. It is still used today
to treat a wide range of infections. Nowadays, pharmaceutical industries prepare penicillin by
growing the fungus Penicillium in special containers (fermenters) under optimal conditions for the
fungus to grow and reproduce.
a. State the purpose of the cooling water around the fermenter.
b. Why acids or bases are added to the fermenter?
c. Suggest three factors that must be kept constant to obtain the fastest growth of the fungus.
d. Explain why antibiotics, such as penicillin, affect bacteria but not viruses.
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 37
49. Topic: Biotechnology and genetic engineering
Question description: Describe the role of alcoholic fermentation in the process of bread making.
Book Location: Biology Level L – Chapter 5
A specific type of anaerobic respiration that is carried out by some microorganisms is commercially
used in the baking industries. The basic requirements of making bread using these microorganisms
are summarized below.
a. Identify the microorganism used in the process of bread making.
b. Name the type of anaerobic respiration used in bread making.
c. Identify gas X that is produced as a result of this process.
d. The graph below illustrates the changes in the rate of reaction of the microorganism used in break
making with respect to temperature.
i. Describe how the rate of reaction changes with temperature.
ii.
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 38
50. Topic: Biotechnology and genetic engineering
Question description: Describe the uses of genetically-engineered bacteria.
Book Location: Biology Level M – Chapter 11
A group of proteins called tissue plasminogen activators (TPAs) that are involved in the breakdown
of blood clots have been recently successfully manufactured using genetic engineering techniques.
The major steps involved in this process are illustrated below.
a. Identify the structures labelled A and B.
b. Name the enzymes used in both steps 1 and 2 of this process.
c. Specify the enzymes used in step 3 of this process.
d. Explain what happens after step 4.
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 39
51. Topic: Respiration
Question description: Describe the effect of exercise on the rate of respiration in the human body.
Book Location: Biology Level M – Chapter 4
The table below shows several changes that occur in the body of a professional athlete and in that of a
beginner athlete while performing the same physical exercise.
a. Explain why the heart rate and blood pressure increase in both athletes during exercise.
b. During strenuous exercise, muscle cells make ATP using the anaerobic pathway, in which lactic is
produced.
i. Name the process by which muscles make ATP anaerobically.
ii. Identify the reactants and the products of this process.
c. The lactic acid that accumulates in the muscles is later broken down in the liver in the presence of
oxygen. Based on the information in the table, indicate which athlete will be able to break down lactic
acid faster after exercise. Explain your answer.
Date 25-08-21 | Level M | 40
You might also like
- Herpetology: Fourth EditionDocument723 pagesHerpetology: Fourth Editionnataliab.vieiraNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Holes Human Anatomy and Physiology 13th Edition by ShierDocument30 pagesTest Bank For Holes Human Anatomy and Physiology 13th Edition by ShierMarta Tronaas100% (36)
- Topic 1 MC 1Document68 pagesTopic 1 MC 1senpaiNo ratings yet
- Gut Health Guidebook 9 22Document313 pagesGut Health Guidebook 9 2219760227100% (3)
- Hewer's Textbook of Histology for Medical StudentsFrom EverandHewer's Textbook of Histology for Medical StudentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- BIOLOGY MODEL PAPER 9thDocument3 pagesBIOLOGY MODEL PAPER 9thHasnain Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Student's Copy Chapter3 BioDocument10 pagesStudent's Copy Chapter3 BioSaidatul Atyah Mohd ApendaiNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology 2017 2018 Sample Paper 4 PDFDocument9 pages11 Biology 2017 2018 Sample Paper 4 PDFRubhan kumarNo ratings yet
- Musingu High School Biology Topical Quick Revision Questions Topic 1: Introduction To BiologyDocument12 pagesMusingu High School Biology Topical Quick Revision Questions Topic 1: Introduction To BiologySheikhNo ratings yet
- (VCE Biology) 2017 YVG Unit 1 Exam v2Document10 pages(VCE Biology) 2017 YVG Unit 1 Exam v2Justine LyNo ratings yet
- G9 Absorption of FoodDocument4 pagesG9 Absorption of FoodkenzaNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document15 pagesCH 3Choi MingNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 Sem 1 p2 2016 JWPNDocument15 pagesBiology Form 4 Sem 1 p2 2016 JWPNMiz KarstzNo ratings yet
- Lucknow Public School Sample Paper-Ii Biology Class - XiDocument3 pagesLucknow Public School Sample Paper-Ii Biology Class - XiNishant singhNo ratings yet
- Biology Scheme Pertgh Penggal 2Document9 pagesBiology Scheme Pertgh Penggal 2Athirah Maestro100% (1)
- Kertas 1 SPM (Percubaan) 1-10Document76 pagesKertas 1 SPM (Percubaan) 1-10Hazizi HanapiNo ratings yet
- B 10 Ctsta 307Document6 pagesB 10 Ctsta 307Andhi SoesiloNo ratings yet
- Cds 2000101797439 Q 5 WMCCDocument15 pagesCds 2000101797439 Q 5 WMCCRISHI KUMARNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Life ProcessesDocument4 pagesWorksheet - Life ProcessesPadma pulivarthiNo ratings yet
- 2324 Level M (Gr11 UAE - GULF) Biology Course QuestionsDocument59 pages2324 Level M (Gr11 UAE - GULF) Biology Course QuestionsVan halenNo ratings yet
- Year 10 BiologyDocument15 pagesYear 10 BiologylkipsangNo ratings yet
- Bio Assignment 3 CompleteDocument8 pagesBio Assignment 3 Completeabby meadNo ratings yet
- Holes Human Anatomy and Physiology 15th Edition Shier Test BankDocument30 pagesHoles Human Anatomy and Physiology 15th Edition Shier Test BankKatherineBowenfojib100% (16)
- General InstructionsDocument5 pagesGeneral InstructionsMehak ShireenNo ratings yet
- Biology-Assignment 1Document2 pagesBiology-Assignment 1chethan reddyNo ratings yet
- Bio sp3Document9 pagesBio sp3imrupnarayanNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Holes Human Anatomy Physiology 15th by ShierDocument30 pagesTest Bank For Holes Human Anatomy Physiology 15th by ShierEthel Carver100% (35)
- Biology WorksheetDocument4 pagesBiology WorksheetAmmar RizwanNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Sample Paper Set 4Document3 pagesCBSE Class 11 Biology Sample Paper Set 4Unique InstituteNo ratings yet
- Biology Model Question Grade 12 Set 2Document2 pagesBiology Model Question Grade 12 Set 2Faris ShamimNo ratings yet
- 2324 Level L (Gr10 UAE - GULF) Biology Course QuestionsDocument75 pages2324 Level L (Gr10 UAE - GULF) Biology Course QuestionsVan halenNo ratings yet
- 2017 11 Sample Paper Biology 01 QPDocument2 pages2017 11 Sample Paper Biology 01 QPAlokNo ratings yet
- Class X Science BiologyDocument4 pagesClass X Science Biologydilipbanchhor8No ratings yet
- Biology 1Document4 pagesBiology 1Sam ManochaNo ratings yet
- CBSE SAMPLE PAPER - 01 (Solved) Class-XI Biology (Theory) Time: 3 Hrs MM: 70 General InstructionsDocument14 pagesCBSE SAMPLE PAPER - 01 (Solved) Class-XI Biology (Theory) Time: 3 Hrs MM: 70 General InstructionsMantri GNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper - Term - Ii: Session 2021-22 SET-1Document5 pagesSample Question Paper - Term - Ii: Session 2021-22 SET-1Yash BhagatNo ratings yet
- Regents Cell Membrane and DiffusionDocument5 pagesRegents Cell Membrane and Diffusionapi-303120399No ratings yet
- HY XI Bio QP Nov 2022Document6 pagesHY XI Bio QP Nov 2022Biswajit BeheraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 The Cellular Level of OrganizationDocument17 pagesChapter 3 The Cellular Level of Organizationjmjbioman100% (1)
- BIOLOGYDocument4 pagesBIOLOGYyogeshkumar090409No ratings yet
- General InstructionsDocument4 pagesGeneral InstructionsMehak ShireenNo ratings yet
- Modul SC Chapter 2 - f1Document14 pagesModul SC Chapter 2 - f1Raja InaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Movement Across The Plasma Membrane: Intervention-Biology Chapter 3 (Answer)Document4 pagesChapter 3: Movement Across The Plasma Membrane: Intervention-Biology Chapter 3 (Answer)Anonymous 6qork2No ratings yet
- Biochemistry & Cytology 1Document48 pagesBiochemistry & Cytology 1yumyum9No ratings yet
- First Pu Model Paper PDFDocument5 pagesFirst Pu Model Paper PDFMujeeb KhanNo ratings yet
- Bio SPM Intervensi m1Document10 pagesBio SPM Intervensi m1teahockNo ratings yet
- 4PxufKfnZtlpp6L9PIdV 2Document12 pages4PxufKfnZtlpp6L9PIdV 2GokulNo ratings yet
- Revision Worksheet-1Document2 pagesRevision Worksheet-1Abdul Muhi BakshiNo ratings yet
- Fcat Practice Booklet 8th GradeDocument130 pagesFcat Practice Booklet 8th Gradeapi-94846453100% (1)
- Biology Cells Practice TestDocument6 pagesBiology Cells Practice TestcamNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 Biology 1996 Paper 2+ansDocument19 pagesPaper 2 Biology 1996 Paper 2+ansapi-3812894100% (1)
- Biology Assignment SB015 Session 20232024 - StudentsDocument7 pagesBiology Assignment SB015 Session 20232024 - StudentsMuhd AzreenNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Science: Learning Area: Living Things and Their Environment Quarter: Fourth QuarterDocument4 pagesGrade 8 Science: Learning Area: Living Things and Their Environment Quarter: Fourth QuarterLexter CarmenNo ratings yet
- SamplePaper01 Class11 Biology QuestionsDocument10 pagesSamplePaper01 Class11 Biology QuestionsvnaynewadNo ratings yet
- 10 Bio - Worksheet 2022-23Document5 pages10 Bio - Worksheet 2022-23skyskyNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 TestDocument11 pagesTopic 1 Testrania samirNo ratings yet
- Bio Reviewer Q1Document8 pagesBio Reviewer Q1BruhNo ratings yet
- Biology Made FamiliarDocument71 pagesBiology Made Familiarwaiswakeneth4No ratings yet
- IB QBANK 6.1 - p1-p2Document35 pagesIB QBANK 6.1 - p1-p2Naz Gümüşlüoğlu100% (1)
- 9th Papers New PattrenDocument122 pages9th Papers New PattrenGul ZahraNo ratings yet
- Physics IGCSE Formula SheetDocument5 pagesPhysics IGCSE Formula Sheet-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- Should Animals Be Kept in ZoosDocument3 pagesShould Animals Be Kept in Zoos-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- MCQ Organic Chem Qs IGCSEDocument26 pagesMCQ Organic Chem Qs IGCSE-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- Balanced Arg LayoutDocument1 pageBalanced Arg Layout-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- (ML392-U) Geometry End of Year PracticeDocument55 pages(ML392-U) Geometry End of Year Practice-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Periodic wk11 - 221106 - 133505-1 - 221106 - 192711Document39 pagesChemistry Periodic wk11 - 221106 - 133505-1 - 221106 - 192711-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- The Devil's CoasterDocument1 pageThe Devil's Coaster-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- 2021 Level LS Physics Basic Questions Chap 1-5 (BTG)Document65 pages2021 Level LS Physics Basic Questions Chap 1-5 (BTG)-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- 2223 Level M Physics - Outer SpaceDocument178 pages2223 Level M Physics - Outer Space-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- 2021 Level L Biology Practical Based QuestionsDocument61 pages2021 Level L Biology Practical Based Questions-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- 2021 Level M SAT Grammar Tips T3 W7Document7 pages2021 Level M SAT Grammar Tips T3 W7-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- SAT Math Practice QuestionsDocument37 pagesSAT Math Practice Questions-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- Math Wk3 Quiz SolvedDocument26 pagesMath Wk3 Quiz Solved-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- Math Ams Wk8Document25 pagesMath Ams Wk8-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- Maths PDF WK 11Document8 pagesMaths PDF WK 11-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- 2021 Level L Biology Periodic 2-Revision Sheets T1 Wk10Document34 pages2021 Level L Biology Periodic 2-Revision Sheets T1 Wk10-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- Physics Quiz T2W2Document20 pagesPhysics Quiz T2W2-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- Math Wk3 Quiz SolvedDocument26 pagesMath Wk3 Quiz Solved-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- 0610 - s17 - QP - 42 AnsweredDocument20 pages0610 - s17 - QP - 42 Answered-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- BASIC BIOLOGY NOTES Sem 1 Part 1Document4 pagesBASIC BIOLOGY NOTES Sem 1 Part 1Polee SheaNo ratings yet
- Summary Book Abnormal Psychology Barlow Durand PDFDocument58 pagesSummary Book Abnormal Psychology Barlow Durand PDFLee DonghyuckNo ratings yet
- 4 Tutorial Biocatalysis 2021 - SkemaDocument4 pages4 Tutorial Biocatalysis 2021 - SkemaM Syarifuddin Mohd AminNo ratings yet
- Revision SB025 Set 1 AnswerDocument12 pagesRevision SB025 Set 1 Answerewine0529No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failuretinayko100% (1)
- Inflammatory Cytokine Response in Patients With Septic Shock Secondary To Generalized PeritonitisDocument9 pagesInflammatory Cytokine Response in Patients With Septic Shock Secondary To Generalized PeritonitisFerdian PriantoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology 1st Semester BSN Practice Mcqs With Key YT Insta Medico SlidesDocument11 pagesAnatomy and Physiology 1st Semester BSN Practice Mcqs With Key YT Insta Medico SlidesNaveed KhanNo ratings yet
- BCH 208 Course OutileDocument3 pagesBCH 208 Course OutileClinton DebrahNo ratings yet
- Cephalometric Evaluation of The Airway Dimensions in Subjects With Different Growth PatternsDocument6 pagesCephalometric Evaluation of The Airway Dimensions in Subjects With Different Growth PatternsJuán A. Nina LeonNo ratings yet
- 04 Lecture AnimationDocument66 pages04 Lecture AnimationJoshua VidalNo ratings yet
- Excretion by Rakshita SinghDocument37 pagesExcretion by Rakshita SinghPurplet 7No ratings yet
- MORAES-SILVA Et Al 2017Document20 pagesMORAES-SILVA Et Al 2017Luiza MartinsNo ratings yet
- CatSper Calcium Channels: 20 Years OnDocument16 pagesCatSper Calcium Channels: 20 Years OnBiblioteca Campus JuriquillaNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Plant Treasures of IndiaDocument150 pagesMedicinal Plant Treasures of Indiaahmad.electrocontrolNo ratings yet
- Drugs Toxicity 8Document24 pagesDrugs Toxicity 8اسامه عمر عثمانNo ratings yet
- Summative Assessment TaskDocument11 pagesSummative Assessment Taskapi-296545639No ratings yet
- Selective Androgen Receptor ModulatorsDocument7 pagesSelective Androgen Receptor ModulatorsRafael HelenoNo ratings yet
- Tinnitus Abordaje 2019Document17 pagesTinnitus Abordaje 2019Sara MartinezNo ratings yet
- 01 10Document10 pages01 10KcaBbe JavierNo ratings yet
- UNIT PLAN PIPRAMS 4th Year Bsc. NursingDocument9 pagesUNIT PLAN PIPRAMS 4th Year Bsc. NursingSuman Pandey100% (1)
- Figure 1 Human Nervous System Source:courses - Lumenlearning.c Om/microbiology/chapter/anato My-Of-The-Nervous-SystemDocument14 pagesFigure 1 Human Nervous System Source:courses - Lumenlearning.c Om/microbiology/chapter/anato My-Of-The-Nervous-SystemShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Body Asymmetries: Incidence, Etiology and Clinical ImplicationsDocument35 pagesBody Asymmetries: Incidence, Etiology and Clinical Implicationsok okNo ratings yet
- Unique Features of Plant DevelopmentDocument27 pagesUnique Features of Plant Developmentfatema100% (1)
- Immunology of Dental Caries and Caries Vaccine - Part IDocument6 pagesImmunology of Dental Caries and Caries Vaccine - Part IanviNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure (Compatibility Mode)Document40 pagesCell Structure (Compatibility Mode)Strive ShashaNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Module 2Document14 pagesGeriatric Module 2Cherry Joyce BascoNo ratings yet
- A Review On Response of Rice (Oryza Sativa L.) Under Salinity Stress in Terms of Its Growth, Development, Characteristics, and Biochemical LevelDocument6 pagesA Review On Response of Rice (Oryza Sativa L.) Under Salinity Stress in Terms of Its Growth, Development, Characteristics, and Biochemical LevelIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Module - Wk5&6 - The Biological Foundation of BehaviorDocument11 pagesModule - Wk5&6 - The Biological Foundation of Behavioraudree d. aldayNo ratings yet