Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Z-TRACK-METHOD Checklist
Z-TRACK-METHOD Checklist
Uploaded by
Daniela Villanueva Rosal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
47 views5 pagesThe document provides instructions for administering magnesium sulfate and parenteral iron injections using the Z-track method, which creates a zigzag path through tissues to prevent medication from tracking back up the needle tract. It describes each step of preparing the injection site, inserting the needle at a 90 degree angle, aspirating to check for blood vessels, injecting the medication, and sealing the injection site. The rationale for each step aims to safely and properly administer the injections while reducing patient discomfort.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides instructions for administering magnesium sulfate and parenteral iron injections using the Z-track method, which creates a zigzag path through tissues to prevent medication from tracking back up the needle tract. It describes each step of preparing the injection site, inserting the needle at a 90 degree angle, aspirating to check for blood vessels, injecting the medication, and sealing the injection site. The rationale for each step aims to safely and properly administer the injections while reducing patient discomfort.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
47 views5 pagesZ-TRACK-METHOD Checklist
Z-TRACK-METHOD Checklist
Uploaded by
Daniela Villanueva RosalThe document provides instructions for administering magnesium sulfate and parenteral iron injections using the Z-track method, which creates a zigzag path through tissues to prevent medication from tracking back up the needle tract. It describes each step of preparing the injection site, inserting the needle at a 90 degree angle, aspirating to check for blood vessels, injecting the medication, and sealing the injection site. The rationale for each step aims to safely and properly administer the injections while reducing patient discomfort.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 5
Republic of the Philippines
Laguna State Polytechnic University
Province of Laguna
College of Nursing and Allied Health
Name: __________________________________________ Date: ______________________________
Year & Section: _______________________________ Score: _____________________________
Z-TRACK METHOD: INJECTING MAGNESIUM SULFATE AND PARENTERAL IRON
Steps Rationale Performed Mastered Comments
1. Wash hands Reduces Yes No
thoroughly before transmission of
preparing infection.
medication. Prepare Hospitals must
medication for adopt
administration as medication
ordered. Observe administration
the 5 R's: right policy and
drug/medicine, procedure for
right dose, right timing of
time, right route of medication
administration, and administration
right patient. that considers
nature of
prescribed
medication,
specific clinical
application, and
patient needs
(DHHS, 2011;
ISMP, 2011)
2. Draw medication
into the syringe
using an aspirating
needle. Remove
needle.
3. Apply a new needle
to the syringe. The
injection needle
should be
appropriate for the
size of the woman:
gauge 19 to 23, 1to
1.5 in. On the
average, the large,
edematous,
preeclamptic
woman uses a gauge
21 needle that is 1.5
inches long.
4. Draw up to 0.2 to 0.3
mL of air to create an
air lock that
prevents tracking
medication into the
subcutaneous tissue
that favors its escape
onto the surface,
causing tissue
irritation (in the
case of magnesium
sulfate) and
tattooing of the skin
(in the case of iron).
5. Bring medication to
the bedside.
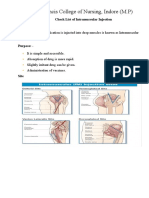
6. Provide essential Injection into
explanations, select correct
an intramuscular anatomical site
site, preferably the prevents injury
gluteal muscles to nerves, bone,
(dorsal gluteal or and blood
ventrogluteal). vessels
7. Prepare the site Mechanical
with an antiseptic action of swab
swab. removes
secretions
containing
microorganisms
8. Pull the skin and
subcutaneous
tissues 1 to 1.5
inches laterally.
9. Using the non- Z-track creates
dominant hand, hold zigzag path
the skin taut; then, through tissues
with the dominant that seals
hand, inject the needle track to
needle at a 90- avoid tracking
degree angle deep medication. A
into muscle tissue. quick dartlike
injection
reduces
discomfort. Use
Z-track for all
IM injections
(Hopkins and
Arias, 2013;
Nicoll and
Hesby, 2002;
Ogston-Tuck,
2014b).
10. Aspirate on syringe Aspiration of
to make sure the blood into
needle is not in a syringe
blood vessel. indicates
possible
placement into
a vein.
Aspiration of
blood into
syringe
indicates
intravenous
(IV) placement
of needle. Slow
injection rate
reduces pain
and tissue
trauma and
reduces chance
of leakage of
medication
back through
needle track
(Hockenberry
and Wilson,
2015; Nicoll and
Hesby, 2002).
The CDC (2015)
11. Inject the
medication if no
blood return is
noted. Remove the
needle and locate
another site if blood
return is noted,
which means that a
blood vessel is hit.
Use a fresh syringe
and needle for re-
injection.
12. Withdraw the Allows time for
needle, then medication to
release the skin absorb into
immediately to muscle before
leave a zigzag path removing
that seals the syringe. Dry
medication within gauze
the muscle tissue. minimizes
discomfort
associated with
alcohol on non-
intact skin
13. Do not massage the
injection site and
have no tight
clothing over it to
prevent escaping of
the medication
from the
muscle
tissue. Just apply
pressure for a few
minutes.
14. For parenteral iron This is because
preparation, use two parenteral iron
needles, one for the tattoos the skin.
aspiration of the
drug from the vial
and other one for
injection.
You might also like
- Administering An IntradermalDocument7 pagesAdministering An IntradermalCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- Checklist of IM InjectionDocument5 pagesChecklist of IM InjectionSharon LawrenceNo ratings yet
- IntramuscularDocument4 pagesIntramusculargaatgaatNo ratings yet
- Administering Intradermal InjectionDocument2 pagesAdministering Intradermal InjectionMoiraMaeBeridoBalite100% (1)
- Ultrasound and clinically guided Injection techniques on the musculoskeletal systemFrom EverandUltrasound and clinically guided Injection techniques on the musculoskeletal systemNo ratings yet
- NEW Component TaskDocument54 pagesNEW Component TaskSamuel Crewz100% (7)
- Administering Intramuscular InjectionDocument7 pagesAdministering Intramuscular Injectionthanuja mathew100% (1)
- Administering IntradermalDocument28 pagesAdministering IntradermalSaul Remus Q. DasmariñasNo ratings yet
- Practice Teaching Demonstration: Intramuscular InjectionDocument13 pagesPractice Teaching Demonstration: Intramuscular InjectionMegha lakra100% (1)
- Assess Patient Data Such As Vital Signs, Laboratory Values, and Allergies Before Preparing and Administering Medications by InjectionDocument12 pagesAssess Patient Data Such As Vital Signs, Laboratory Values, and Allergies Before Preparing and Administering Medications by InjectionLRBNo ratings yet
- Intramuscular InjectionDocument15 pagesIntramuscular InjectionApin Pokhrel100% (1)
- INJECTION (Yoga Prilza)Document16 pagesINJECTION (Yoga Prilza)Yoga PrilzaNo ratings yet
- Administering Z-Track Intramuscular InjectionDocument5 pagesAdministering Z-Track Intramuscular InjectionRina Abigail Belleza AguedanNo ratings yet
- Administering An Intramuscular InjectionDocument3 pagesAdministering An Intramuscular Injectionapi-26570979100% (4)
- Final Pediatrics Procedure FileDocument78 pagesFinal Pediatrics Procedure FileJils SureshNo ratings yet
- Jose Rizal Memorial State University: College of Nursing and Allied Health SciencesDocument5 pagesJose Rizal Memorial State University: College of Nursing and Allied Health SciencesJustine CagatanNo ratings yet
- Administering Intramuscular Injection: Name & Sec. InstructorDocument2 pagesAdministering Intramuscular Injection: Name & Sec. InstructorDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- 16 Administering Intradermal InjectionsDocument3 pages16 Administering Intradermal InjectionsMarky RoqueNo ratings yet
- Administering A Subcutaneous InjectionDocument3 pagesAdministering A Subcutaneous Injectionapi-26570979100% (5)
- Safe Giving Meds SCDocument13 pagesSafe Giving Meds SCRuffy AbdulazisNo ratings yet
- Safe Giving Meds Intradermal SCDocument13 pagesSafe Giving Meds Intradermal SCRuffy AbdulazisNo ratings yet
- Intramuscular Injection (IM) InjectionDocument17 pagesIntramuscular Injection (IM) InjectionArunesh 456100% (1)
- Administering Intramuscular and Subcutaneous Injections CANVASDocument54 pagesAdministering Intramuscular and Subcutaneous Injections CANVASAinaB ManaloNo ratings yet
- Funda Lab Sas26 Antonette CawalingDocument3 pagesFunda Lab Sas26 Antonette CawalingAntonette CawalingNo ratings yet
- Education Sub Cutaneous Injection Lesson PlanDocument12 pagesEducation Sub Cutaneous Injection Lesson Planamrutha h s100% (1)
- Injection by Arnaldio Dan Intan JyyDocument14 pagesInjection by Arnaldio Dan Intan JyyIntan Juita IINo ratings yet
- Performance Checklist ID and IM MedicationsDocument7 pagesPerformance Checklist ID and IM MedicationsJ-eliNo ratings yet
- Adminstration of Intramusclar InjectionDocument3 pagesAdminstration of Intramusclar InjectionDenise CastroNo ratings yet
- Z-Track TechniqueDocument16 pagesZ-Track TechniqueclaireNo ratings yet
- Proper Injection TechniquesDocument5 pagesProper Injection TechniquesAnonymous 0qsVKO0cNNo ratings yet
- Parental Administration of DrugsDocument15 pagesParental Administration of DrugsShimo AldobbaghNo ratings yet
- Types Injection "Intramuscular (Im), Intradermal (Id), Subcutan (SC), and Intravenous (Iv) "Document5 pagesTypes Injection "Intramuscular (Im), Intradermal (Id), Subcutan (SC), and Intravenous (Iv) "Ani SuryaniNo ratings yet
- Preparing and Administering Subcutaneous Injection PurposeDocument11 pagesPreparing and Administering Subcutaneous Injection PurposeLRBNo ratings yet
- Injections ImDocument4 pagesInjections ImMariya DantisNo ratings yet
- IM Injuction: Definition of Intramuscular InjectionDocument8 pagesIM Injuction: Definition of Intramuscular InjectiondhanasundariNo ratings yet
- Administering Intramuscular Injection: Deltoid MuscleDocument2 pagesAdministering Intramuscular Injection: Deltoid MuscleGloredaine BelicarioNo ratings yet
- Op 02 PDFDocument13 pagesOp 02 PDFHujjjjNo ratings yet
- SRM I Year I Basic NursingDocument97 pagesSRM I Year I Basic Nursingmbok diyirNo ratings yet
- IV InjectionDocument10 pagesIV Injectionpreeti sharmaNo ratings yet
- 7-IM InjectionDocument19 pages7-IM InjectionarlixNo ratings yet
- IV Checklist 2014Document3 pagesIV Checklist 2014İrem YaşaNo ratings yet
- IM injection 2024Document27 pagesIM injection 2024Collective CompanyNo ratings yet
- IMI'sDocument6 pagesIMI'sanitha lakshminarayanaNo ratings yet
- 2 Intramuscular InjectionDocument5 pages2 Intramuscular InjectionKEANNA ZURRIAGANo ratings yet
- Administering IntradermalDocument4 pagesAdministering IntradermalNezukoNo ratings yet
- Beige Scrapbook Project Presentation 20240502 134440 0000Document63 pagesBeige Scrapbook Project Presentation 20240502 134440 0000SarikaNo ratings yet
- 68w Chapter 05Document28 pages68w Chapter 05smith.kevin1420344No ratings yet
- Administering Subcutaneous InjectionDocument6 pagesAdministering Subcutaneous InjectionAnggrian Clara DewiNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris: Taking Vital Sign (Injection)Document7 pagesBahasa Inggris: Taking Vital Sign (Injection)iyal09No ratings yet
- Parenteral PDF Copy For StudentsDocument69 pagesParenteral PDF Copy For StudentsRegine Prongoso DagumanpanNo ratings yet
- InjectionDocument29 pagesInjectionIlham S. GaniNo ratings yet
- What Do You Say As You Are Giving A Shot?Document3 pagesWhat Do You Say As You Are Giving A Shot?Venska TrianaNo ratings yet
- Year I Basic NursingDocument99 pagesYear I Basic Nursingmbok diyirNo ratings yet
- Injection TechniquesDocument27 pagesInjection Techniquescharliesangelnav03No ratings yet
- Intra - Muscular Injection 2020Document13 pagesIntra - Muscular Injection 2020رافت العواضيNo ratings yet
- How To Do Injection CikaDocument2 pagesHow To Do Injection CikaLiza AryaniNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthetic TechniquesDocument81 pagesLocal Anesthetic TechniquesMohanad BraziNo ratings yet
- Nursing CS Intramuscular Medication Administration 02 1Document1 pageNursing CS Intramuscular Medication Administration 02 1solisetherealNo ratings yet
- PARENTERAL MEDICATION Manual and Checklist 1Document14 pagesPARENTERAL MEDICATION Manual and Checklist 1Hazel Shaine BaybayanNo ratings yet
- Administration of Intramuscular and Sub Cutaneous InjectionsDocument13 pagesAdministration of Intramuscular and Sub Cutaneous InjectionsSundeep SharmaNo ratings yet
- Caudal Epidural InjectionDocument6 pagesCaudal Epidural InjectionRS BaptisNo ratings yet
- Rosal, M.D - Concept Map MeningitisDocument1 pageRosal, M.D - Concept Map MeningitisDaniela Villanueva RosalNo ratings yet
- NCM 108 - CorrelationDocument2 pagesNCM 108 - CorrelationDaniela Villanueva RosalNo ratings yet
- Assessment FormDocument1 pageAssessment FormDaniela Villanueva RosalNo ratings yet
- NCP For Acute Pain, Drug RationalizationDocument6 pagesNCP For Acute Pain, Drug RationalizationDaniela Villanueva RosalNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 5-14-23Document5 pagesDrug Study 5-14-23Daniela Villanueva RosalNo ratings yet
- Rosal, M.D - Comic StripDocument1 pageRosal, M.D - Comic StripDaniela Villanueva RosalNo ratings yet
- Gec 105-PT1Document2 pagesGec 105-PT1Daniela Villanueva RosalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics ImportanceDocument3 pagesNursing Informatics ImportanceDaniela Villanueva RosalNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 - Reflective Analysis C30-33Document4 pagesNCM 107 - Reflective Analysis C30-33Daniela Villanueva RosalNo ratings yet
- Reflective Analysis On Fetal Kicks, Specimen Collection and Mid Stream Urine SampleDocument3 pagesReflective Analysis On Fetal Kicks, Specimen Collection and Mid Stream Urine SampleDaniela Villanueva RosalNo ratings yet
- Insights On Pregnancy and Weight Monitoring - A Feasibility Study of Weight Charts and Midwife SupportDocument3 pagesInsights On Pregnancy and Weight Monitoring - A Feasibility Study of Weight Charts and Midwife SupportDaniela Villanueva RosalNo ratings yet
- Reflective Analysis 2 - EBPDocument2 pagesReflective Analysis 2 - EBPDaniela Villanueva RosalNo ratings yet
- USP 1 Packaging Determination of Volume of InjectionDocument1 pageUSP 1 Packaging Determination of Volume of InjectiongamesrcoolNo ratings yet
- IVTDocument11 pagesIVTNoorwashilaNo ratings yet
- General Therapy by RyodorakuDocument8 pagesGeneral Therapy by Ryodorakumarcopcvieira100% (1)
- Important ISO Standards For Medical DevicesDocument8 pagesImportant ISO Standards For Medical DevicesBhargav krishnaNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Drug AdministrationDocument33 pagesIntravenous Drug Administrationleiann_jessicaNo ratings yet
- Haneke-2006-Journal of Cosmetic DermatologyDocument11 pagesHaneke-2006-Journal of Cosmetic DermatologyGuillermo RomeroNo ratings yet
- Locater UpdateDocument46 pagesLocater UpdatenovaaputryNo ratings yet
- Prep and Admin SummaryDocument3 pagesPrep and Admin SummaryAna ChicasNo ratings yet
- SIA GuidelinesDocument18 pagesSIA Guidelinestamtam06100% (1)
- Funda PharmaDocument9 pagesFunda PharmaShiangNo ratings yet
- Ketamine Hydrochloride Bayer Price Comparison: UsDocument18 pagesKetamine Hydrochloride Bayer Price Comparison: UslacoindesaNo ratings yet
- Training On Pfizer Vaccine ManagementDocument132 pagesTraining On Pfizer Vaccine ManagementClaudia YuniarNo ratings yet
- Medical Emergencies in The Dental Practice Poster: Revised and UpdatedDocument8 pagesMedical Emergencies in The Dental Practice Poster: Revised and UpdatedMelissa Gabriela Sánchez SaucedoNo ratings yet
- AD Iver Nion AD Iver NionDocument14 pagesAD Iver Nion AD Iver NionMad River UnionNo ratings yet
- Giving Safe Injections: A Guide For Nurses and Others Who Give InjectionsDocument43 pagesGiving Safe Injections: A Guide For Nurses and Others Who Give Injectionsanon_21114707No ratings yet
- Is 10258 2002Document30 pagesIs 10258 2002animeluisNo ratings yet
- The Future Doctors Academy Orthopedic CourseDocument77 pagesThe Future Doctors Academy Orthopedic CourseAnton ScheepersNo ratings yet
- Injections - IdDocument3 pagesInjections - IdMariya DantisNo ratings yet
- NCM103 SL - MedsDocument200 pagesNCM103 SL - MedsZen Gesner Kenneth G. EganaNo ratings yet
- HCP 210 Reading 10Document17 pagesHCP 210 Reading 10papillon1211No ratings yet
- Checklist On Intramuscular InjectionDocument2 pagesChecklist On Intramuscular InjectionClarice Jamille RazonNo ratings yet
- Assisting-in-Lumbar-Puncture Procedure GuideDocument6 pagesAssisting-in-Lumbar-Puncture Procedure GuideLeigh Chanelle OngNo ratings yet
- Administering Medication Through Intradermal InjectionDocument3 pagesAdministering Medication Through Intradermal InjectionHarvey T. Dato-onNo ratings yet
- The Magic Mushrooms Growers GuideDocument50 pagesThe Magic Mushrooms Growers Guidemoorebetter100% (4)
- Radiometer - Blood Gas Analyzer - Abl80 Flex Operator Manual-3 (287-344)Document58 pagesRadiometer - Blood Gas Analyzer - Abl80 Flex Operator Manual-3 (287-344)Miguel FigueroaNo ratings yet
- NP1Document14 pagesNP1rexinne noahNo ratings yet
- Needle Prick Injury & PreventionDocument17 pagesNeedle Prick Injury & Preventioniman zainuddinNo ratings yet
- Venipuncture 1Document57 pagesVenipuncture 1Pearce Gabrielle PinlacNo ratings yet
- FT Jeringa para Gases en SangreDocument2 pagesFT Jeringa para Gases en SangreALMACEN INSULABNo ratings yet