Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kcse 2003 Biology Questions
Kcse 2003 Biology Questions
Uploaded by
Urex ZOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Kcse 2003 Biology Questions
Kcse 2003 Biology Questions
Uploaded by
Urex ZCopyright:
Available Formats
om
.c
rs
pe
BIOLOGY PAPER 231/1 K.C.S.E 2003
pa
st
pa
SECTION A (20 MARKS)
se
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided.
kc
ee
fr
1. A process that occurs in plants is represented by the equation below.
w.
C6H12O6 2C2H5OH + 2CO2 + Energy
ww
(Glucose) (Ethanol) (Carbon dioxide)
t
si
a) Name the process.
vi
b) State the economic importance of the process named in (a) above
rs
2. Name the phylum whose members possess notochord
pe
pa
3. How do the male gamete nuclei reach the ovule after pollen grains land
st
on the stigma?
pa
4. a) Name the bacteria found in root nodules of leguminous plants.
SE
b) What is the role of the bacteria named in (a) above?
KC
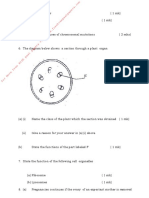
5. A bone obtained from a mammal is represented by the diagram below.
ee
Fr
re
Mo
a) Name the bone.
r
Fo
b) Which bones articulate with the bone shown in the diagram at the
notch?
6. Distinguish between analogous and homologous structures.
Analogous structures –
Homologous structures –
7. The diagram below represents regions of a root tip.
a) Name the tow regions above X in ascending order
b) State the function of the part labeled X
8. State a function of the large intestine in humans
9. Name the:
a) Material that strengthens xylem tissue.
b) Tissue that is removed when the bark of a dicotyledonous plant is
ringed.
10. How are leaves of submerged adapted plants for photosynthesis?
11. Name the causative agent of typhoid.
SECTION B (40 MARKS)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided.
12. a) What is meant by the term sex – linkage?
b) Name two sex – linked traits in humans.
c) In Drosophila Melanogaster, the inheritance of eye colour is sex –
linked. The gene of red eye is dominant. A cross was made between a
om
.c
rs
pe
homozygous red – eyed female and a white – eyed male. Work out the
pa
st
phenotypic ration of F1 generation. (Use R to represent the gene for red
pa
eyes).
se
13. The diagram below shows gaseous exchange in tissues.
kc
ee
fr
w.
ww
t
si
vi
rs
pe
pa
st
a)
Name the gas that diffuses:
pa
i)
To the body cells
SE
ii)
From the body cells
KC
b)
Which compound dissociates to release the gas named in (a) (i) above?
ee
c)
i) what is tissue fluid?
Fr
ii) What is the importance of tissue fluid?
re
Mo
d) Name the blood vessel with the highest concentration of:
i) Glucose
r
Fo
ii) Carbon dioxide
14. a) Explain how marine fish regulate their osmotic pressure.
b) Explain the role of antidiuretic hormone when there is excess water in
the human body.
15. A response exhibited by a certain plant tendril is illustrated below.
a) i) Name the type of response
ii) Explain how the response named in (a)(i) above occurs
b) What is the importance of tactic responses to microscopic plants?
c) State four applications of plant hormones in agriculture.
16. a) What is meant by:
i) Autecology
ii) Synecology?
b) The number and distribution of stomata on three different
leaves are shown in the table below:
Leaf Number of stomata
Upper Lower
epidermis epidermis
A 300
om
.c
rs
pe
B 150
pa
st
C 02
pa
se
Suggest the possible habitat of the plants from which the leaves were
kc
ee
obtained
fr
Leaf Habitat
w.
ww
A
B
t
C si
vi
(c) State the modifications found in the stomata of leaf C.
rs
pe
pa
SECTION C (40 marks)
st
Answer question 17 (compulsory) in the spaces provided and either
pa
question 18 or 19 in the spaces provided after question 19.
SE
17. Some students used a model to demonstrate the effect of sweating on human
KC
body temperature. Two boiling tubes A and B were filled with hot water. The
ee
temperature of water in the tubes was taken at the start of the experiment
Fr
and then at 5 minutes interval. The surface of tube A was continuously wiped
re
Mo
with a piece of cotton wool soaked in methylated spirit. The results obtained
r
are shown in the table below.
Fo
Time (minutes) Temperature 0C in tubes
A B
0 80 80
5 54 67
10 40 59
15 29 52
20 21 47
25 18 46
a) On the same axes, plot graphs of temperature of water in the tubes
against time.
b) At what rate was the water – cooling in tube A?
c) Why was tube B included in the set up?
d) Account for the rate of cooling in tube A.
e) State two processes of heat loss in tube b.
f) What would be the expected results if tube A was insulated?
g) What would the insulation be comparable to in:
i) Bird
ii) Mammals?
h) Name the structures in the human body that detect:
i) External temperature changes
ii) Internal temperature changes
18. Describe the functions of the various parts of the human eye.
19. Describe how fruits and seeds are suited to their modes of dispersal.
om
.c
rs
pe
BIOLOGY PAPER 232/2 K.C.S.E 2003
pa
PRACTICAL MARKING SCHEME
st
pa
1. You are provided with specimens labelled C, D and a solution labelled L
se
(a) (i) State the habitat of specimen C
kc
ee
a. Aquatic/ water
fr
w.
(ii) Name the trophic level occupied by specimen C.
ww
Producer/ first trophic level
t
si
vi
(iii) Give a reason for your answer in (a) (ii) above
rs
It has chlorophyll for photosynthesis
pe
pa
st
(b) (i) Place 5cm3 of solution L into a 100ml beaker. Using a straw, blow
pa
gently into the solution.
SE
Colour changes to yellow / greenish yellow/orange
KC
(ii) Give a reason for the observation in (b) (i) above.
ee
Carbon dioxide in exhaled air / exhaled an contains carbon
Fr
dioxide or carbon dioxide /carbon dioxide in air;
re
Mo
(c) Place 5cm3 of a solution L into 100ml beaker. Put the forceps, submerge
specimen C into one of the 100ml beaker. Put the two beakers in the dark.
r
Fo
Leave the set up for at least one hour and observe.
(i) Record your observation.
Solution in the beaker with spirogyra turns yellow; while the other
remained blue or solution in the beaker containing specimen
C/spogyra turns yellow / green / greenish yellow;
(ii) Explain the observation in (c)(i) above.
Spirogyra respires, in the dark producing carbon dioxide; which
changes the colour of solution to yellow while the solution in other
beaker served as a control;
(d) Examine specimen D using a hand lens.
Giving a reason, state the division to which the specimen belongs.
Division: Micophyta / mycophyta;
Reason: Non – green / has hyphae / has no chlophyll.
(e) What role is played by specimen D in an ecosystem?
Decomposer / causes decay of dead organic matter;
(f) Draw and label specimen D.
Sporangium
om
.c
rs
pe
pa
st
pa
se
kc
ee
fr
w.
ww
t
si
vi
rs
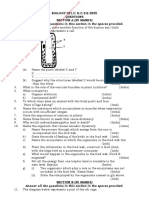
2. You are provided with a specimen labeled E, 0.01% DCPIP and 0.1
pe
pa
Ascorbic acid. Examine specimen E.
st
a) (i) What part of the plant is specimen E.
pa
Fruit
SE
(ii) Give a reason fro your answer in (a)(i) above.
KC
b) Cut a transverse section through specimen E.
ee
(i) Draw and label one of the cut surfaces.
Fr
re
Mo
r
Fo
State the magnification of your drawing?
Mag: range between X ½ to x 3(must be x not x)
(ii) State the type off placentation of specimen E.
Axial / Axile (accept axile for axial.)
c) Name the agent of dispersal of specimen E.
Animal; accept man alone as an agent.
d) State how specimen C is adapted to its mode of dispersal.
Seeds have hard / slimmy seed coats / with mucus which
prevent indigestion.
Scented to attract animal / dispersal animal;
Succulent to attract / so that it is edible /can be eaten;
e) i) To 1cm3 of DCPIP in a test tube, add 0.1% solution of ascorbic cid
drop by drop until the colour of DCPIP disappears. Shake the test tube
after addition of each drop. Record the number of droplets used.
2 drops; drops from 1 to 4 drops.
Squeeze out the juice from specimen E into a beaker. Filter and
discard the residue.
om
.c
rs
pe
ii) To another 1cm3 of DCPIP in a test tube add the juice from
pa
st
specimen E drop by drop. Shake the test tube after addition of
pa
each
se
drop until the colour of DCPIP disappears. Record the number
kc
ee
of drops used?
fr
iii) From the results obtained in (e) (i) above, calculate the
w.
percentage of ascorbic acid in the juice obtained from specimen
ww
E.
t
si
Show your working
vi
2/8x0.1;025%
rs
Calculation done only if the drops are within the stated rang
pe
pa
above.
st
iv) State two factors that would influence the accuracy of the results.
pa
Size of dropper / size of the drops.
SE
Period of storage of specimen E/extent/degree of ripening.
KC
Impurities.
ee
(f) (i) Suggest the expected results if the juice from specimen E
Fr
was boiled for 30 minutes, cooled and added drop by
re
Mo
drop to DCPIP solution.
(ii) Explain the expected results in (f) (i) above.
r
Fo
Boiling/heat destroys Ascorbic acid;
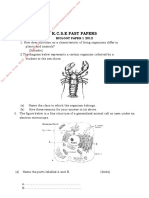
3. You are provided with a specimen labeled B.
a) i) Name the class to which the specimen belongs
ii) Give two reasons from your answer in (a)(i) above.
b) What term is used to describe the shape of the specimen?
c) Stroke the specimen from the :
i) Head to tail. Record your observation
ii) Tail towards the head. Record your observation
iii) What is the significance of your observation in c (i) and (ii)
above?
d) Measure in millimeters the length of the :
i) Specimen from the tip of the mouth to the tip of the tail.
Length_______________ cm.
ii) Tail from the anus to the tip of the tail’
length __________________ cm
iii) Using the measurements in (d) (i) and (ii) above, calculate
the tail power.
e) Name and draw the fins on the specimen that:
i) Enable the specimen to balance, brake and change direction.
ii) Prevent the fish from rolling and yawing.
You might also like
- Transpiration POGIL Answer KeyDocument8 pagesTranspiration POGIL Answer KeyJade Tapper50% (2)
- Combined Science NotesDocument61 pagesCombined Science NotesShawn ChimbwandaNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology January 2013 P1 SolutionsDocument11 pagesCSEC Biology January 2013 P1 Solutionsaliyah ramdeo100% (2)
- Cambodian Tree SpeciesDocument61 pagesCambodian Tree Speciesfredericodalmeida33% (3)
- Leaf ShapeDocument9 pagesLeaf ShapeMohan KumarNo ratings yet
- Kcse 2001 Biology QuestionsDocument7 pagesKcse 2001 Biology QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 2004 Biology QuestionsDocument7 pagesKcse 2004 Biology QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 2002 Biology QuestionsDocument6 pagesKcse 2002 Biology QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 2000 Biology QuestionsDocument8 pagesKcse 2000 Biology QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 1999 Biology QuestionsDocument7 pagesKcse 1999 Biology QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 2005 Biology QuestionsDocument8 pagesKcse 2005 Biology QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 1999 Biology p1Document3 pagesKcse 1999 Biology p1Urex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 1997 Biology QuestionsDocument10 pagesKcse 1997 Biology QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 1997 Biology p1Document5 pagesKcse 1997 Biology p1Urex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 1998 Biology QuestionsDocument8 pagesKcse 1998 Biology QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 1998 Biology p1Document4 pagesKcse 1998 Biology p1Urex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 2006 Biology QuestionsDocument8 pagesKcse 2006 Biology QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 2012 Biology QuestionsDocument13 pagesKcse 2012 Biology QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 2007 Biology QuestionsDocument11 pagesKcse 2007 Biology QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 1995 Biology p1Document4 pagesKcse 1995 Biology p1Urex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 1995 Biology QuestionsDocument10 pagesKcse 1995 Biology QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- G11 Biology Model Exam Qp-Jan - Set BDocument8 pagesG11 Biology Model Exam Qp-Jan - Set BPriyanshu BadhiaNo ratings yet
- Kcse 2009 Biology QuestionsDocument18 pagesKcse 2009 Biology QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- Science Sample Paper - 4Document13 pagesScience Sample Paper - 4ShwetaNo ratings yet
- Past Papers: CBGDocument5 pagesPast Papers: CBGMalavikaNNo ratings yet
- (Spmsoalan) Skema Biologi K2 Terengganu 2014Document12 pages(Spmsoalan) Skema Biologi K2 Terengganu 2014zaihassniNo ratings yet
- Smart Test Series: 1-Circle The Correct Answer. (12x1 12)Document3 pagesSmart Test Series: 1-Circle The Correct Answer. (12x1 12)Dr. AyshaNo ratings yet
- Topical Test Chapter 5 Form 4Document5 pagesTopical Test Chapter 5 Form 4AMOS TING QI TAO MoeNo ratings yet
- 10 Holiday Homework ScienceDocument3 pages10 Holiday Homework ScienceDurgadas KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Science Class 10 Term 2 Sample Paper 2Document5 pagesScience Class 10 Term 2 Sample Paper 2Sangeeta SharmaNo ratings yet
- BSC Zoology M Sem 1 Paper 1.2 2014Document2 pagesBSC Zoology M Sem 1 Paper 1.2 2014Haasee Rahman SkNo ratings yet
- KS3 Biology Baseline TestDocument9 pagesKS3 Biology Baseline Testfadua barakatNo ratings yet
- CBCS - BSC - HONS - Sem-5 - ZOOLOGY - CC-12 - PRINCIPLE OF GENETICS-10480Document2 pagesCBCS - BSC - HONS - Sem-5 - ZOOLOGY - CC-12 - PRINCIPLE OF GENETICS-10480Sohan kunduNo ratings yet
- CSIR NET Life Sciences June 2011 Question Paper Key PDFDocument47 pagesCSIR NET Life Sciences June 2011 Question Paper Key PDFAmrita NepaliaNo ratings yet
- 1st PUC Biology Nov 2017Document2 pages1st PUC Biology Nov 2017Abhi50% (2)
- B.Sc. (H) Botany-2nd Semester-2018Document9 pagesB.Sc. (H) Botany-2nd Semester-2018Ashvani Maurya MauryaNo ratings yet
- 23 Xi Biology Annual QPDocument4 pages23 Xi Biology Annual QPbb681592No ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Eas 100 - Example Midterm QuestionsDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Eas 100 - Example Midterm QuestionsHarsh PatelNo ratings yet
- 11th Biology EM 2nd Revision Exam 2023 Original Question Paper Thenkasi District English Medium PDF DownloadDocument2 pages11th Biology EM 2nd Revision Exam 2023 Original Question Paper Thenkasi District English Medium PDF DownloadDhar DharNo ratings yet
- Biology 2023Document4 pagesBiology 2023chauhanadityarNo ratings yet
- Third Year Chemistry Test On The 18 September, 2013Document7 pagesThird Year Chemistry Test On The 18 September, 2013CHRISTOPHER NSENGIYUMVANo ratings yet
- SQ03/N5/01 Biology Section 1-Questions: National Quali Cations Specimen OnlyDocument48 pagesSQ03/N5/01 Biology Section 1-Questions: National Quali Cations Specimen OnlyDoraNo ratings yet
- GATE XL 2016 L Zoology Solved Question PaperDocument5 pagesGATE XL 2016 L Zoology Solved Question PaperRaj RastogiNo ratings yet
- Children'S Palace H. S. School: Class:-TH Subject: - BiologyDocument12 pagesChildren'S Palace H. S. School: Class:-TH Subject: - BiologyRavindra Kumar GondNo ratings yet
- Third Term Biology TestDocument9 pagesThird Term Biology TestTheogene NTEGEREJIMANANo ratings yet
- Ujian P3:2018 BioDocument11 pagesUjian P3:2018 BioThen MoliNo ratings yet
- XI Botany Chapterwise Prvs Questions Hsslive PDFDocument25 pagesXI Botany Chapterwise Prvs Questions Hsslive PDFJoshua VargheseNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Practice Problems, Chapters 1 - 4Document4 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Practice Problems, Chapters 1 - 4EduCartNo ratings yet
- B. Sc. (Hons) Botany 4th Semester-2022-MergedDocument44 pagesB. Sc. (Hons) Botany 4th Semester-2022-MergedAnsh KumarNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 17 Jun 2023Document16 pagesAdobe Scan 17 Jun 2023siddhi VaishnavNo ratings yet
- P5 Science SA2 2017 Raffles Exam PapersDocument41 pagesP5 Science SA2 2017 Raffles Exam Papersjanus.zhangNo ratings yet
- IB Biology: Topic 10 Genetics TestDocument8 pagesIB Biology: Topic 10 Genetics TestJune ChowNo ratings yet
- Kcse 1995 Biology p2Document6 pagesKcse 1995 Biology p2Urex ZNo ratings yet
- 2022 Eng IATDocument30 pages2022 Eng IATChandan kumar MohantaNo ratings yet
- Class Xi Biology Annual Exam 2017 18Document6 pagesClass Xi Biology Annual Exam 2017 18r7153676No ratings yet
- The Molecular Genetics of Head Development in Drosophila Melanogaster PDFDocument16 pagesThe Molecular Genetics of Head Development in Drosophila Melanogaster PDFJomaira MedinaNo ratings yet
- SET-A Worksheet-1 General Science (086) Term - II: Marking SchemeDocument12 pagesSET-A Worksheet-1 General Science (086) Term - II: Marking SchemeSnehasish MohantyNo ratings yet
- B.Sc. Degree Examination - 2012: Total No. of Pages: 2Document2 pagesB.Sc. Degree Examination - 2012: Total No. of Pages: 2Malaya Kumar BhoiNo ratings yet
- A Level Practicals Meetlearn-1Document173 pagesA Level Practicals Meetlearn-1Augustine CHII NgekNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper - Biology - XiDocument5 pagesSample Paper - Biology - Xishrutinbrc2007No ratings yet
- Higher Secondary I Year Biology Model Question Paper Bio-BotanyDocument5 pagesHigher Secondary I Year Biology Model Question Paper Bio-Botanysen education senthil kumaranNo ratings yet
- Topical Guidebook For GCE O Level Biology 3 Part 2From EverandTopical Guidebook For GCE O Level Biology 3 Part 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Biochemistry of Development: International Series of Monographs on Pure and Applied BiologyFrom EverandThe Biochemistry of Development: International Series of Monographs on Pure and Applied BiologyNo ratings yet
- Kcse 2001 Biology QuestionsDocument7 pagesKcse 2001 Biology QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 1997 Biology p1Document5 pagesKcse 1997 Biology p1Urex ZNo ratings yet
- 1kcse Business Studies 565Document6 pages1kcse Business Studies 565Urex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 1996 Biology QuestionsDocument4 pagesKcse 1996 Biology QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 2012 Business Studies p2Document3 pagesKcse 2012 Business Studies p2Urex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 2011 Business Studies p1Document9 pagesKcse 2011 Business Studies p1Urex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 2010 Business Studies p1Document5 pagesKcse 2010 Business Studies p1Urex ZNo ratings yet
- KCSE 2007 Business Studies PAPER 2Document2 pagesKCSE 2007 Business Studies PAPER 2Urex ZNo ratings yet
- KCSE 2006 Business Studies PAPER 1Document7 pagesKCSE 2006 Business Studies PAPER 1Urex ZNo ratings yet
- KCSE 2007 Business Studies PAPER 1Document8 pagesKCSE 2007 Business Studies PAPER 1Urex ZNo ratings yet
- 2008 Kcse Business AnswersDocument14 pages2008 Kcse Business AnswersUrex ZNo ratings yet
- KCSE 2006 Business Studies PAPER 2Document3 pagesKCSE 2006 Business Studies PAPER 2Urex ZNo ratings yet
- 2006 Business AnalysisDocument6 pages2006 Business AnalysisUrex ZNo ratings yet
- KCSE 2009 Business Studies PAPER 2Document5 pagesKCSE 2009 Business Studies PAPER 2Urex ZNo ratings yet
- 2007 Business Qar KitDocument23 pages2007 Business Qar KitUrex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 2012 Business Studies p1Document3 pagesKcse 2012 Business Studies p1Urex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse Business PPR 2565 2Document2 pagesKcse Business PPR 2565 2Urex ZNo ratings yet
- K2cse Business Studies Papers QuestionsDocument91 pagesK2cse Business Studies Papers QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- 2009 Business Analysis of QuestionsDocument5 pages2009 Business Analysis of QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 2010 Business Studies p2Document3 pagesKcse 2010 Business Studies p2Urex ZNo ratings yet
- June 2021 Examiner ReportDocument18 pagesJune 2021 Examiner ReportUrex ZNo ratings yet
- KCSE 2008 Agriculture P2Document5 pagesKCSE 2008 Agriculture P2Urex ZNo ratings yet
- KCSE 2010 Agriculture P1Document3 pagesKCSE 2010 Agriculture P1Urex ZNo ratings yet
- 24kcse Business Studies PPR 1 565Document6 pages24kcse Business Studies PPR 1 565Urex ZNo ratings yet
- KCSE 2009 Agriculture P1Document7 pagesKCSE 2009 Agriculture P1Urex ZNo ratings yet
- KCSE 2010 Agriculture P2Document5 pagesKCSE 2010 Agriculture P2Urex ZNo ratings yet
- KCSE 2011 Agriculture P1Document11 pagesKCSE 2011 Agriculture P1Urex ZNo ratings yet
- KCSE 2011 Agriculture P2Document9 pagesKCSE 2011 Agriculture P2Urex ZNo ratings yet
- KCSE 2012 Agriculture P 1 2Document11 pagesKCSE 2012 Agriculture P 1 2Urex ZNo ratings yet
- KCSE 2012 Agriculture P2Document6 pagesKCSE 2012 Agriculture P2Urex ZNo ratings yet
- Scince Notes Part II Edited 21 OctDocument11 pagesScince Notes Part II Edited 21 OctSANJAY GANGANNo ratings yet
- Definition of Plant TissueDocument3 pagesDefinition of Plant TissueCrash Zerocool67% (3)
- Eschweilera CaudiculataDocument3 pagesEschweilera CaudiculataKlaus PieslingerNo ratings yet
- Macmillan Science Level 3 Pupil S Book Topic 1 PP 8 11Document4 pagesMacmillan Science Level 3 Pupil S Book Topic 1 PP 8 11reema2050reemaNo ratings yet
- Takhtajan's SystemDocument5 pagesTakhtajan's SystemAlecioNo ratings yet
- © Ncert Not To Be Republished: Nutrition in PlantsDocument10 pages© Ncert Not To Be Republished: Nutrition in PlantsbalajiNo ratings yet
- Exploration of Yeast and Bacteria As Antagonist Agent Candidate of Citrus Foot Rot Disease (Botryodplodia Theobromae (Pat.) )Document37 pagesExploration of Yeast and Bacteria As Antagonist Agent Candidate of Citrus Foot Rot Disease (Botryodplodia Theobromae (Pat.) )Nur Annisa ShalehahNo ratings yet
- 10th Biology PracticalDocument4 pages10th Biology Practicaldivyanshyadav2019No ratings yet
- Brown Leaf AbstractDocument5 pagesBrown Leaf AbstractAditi DeodharNo ratings yet
- 5 Nutrition Petiole AnalysisDocument5 pages5 Nutrition Petiole AnalysisD. Deepak BornareNo ratings yet
- IB Style Test - Topic 9: Plant Biology: Includes New Elements of The 2016 GuideDocument9 pagesIB Style Test - Topic 9: Plant Biology: Includes New Elements of The 2016 GuideUkjun JungNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Soil PH On The Stomatal Density of Tradescantia SpathaceaDocument13 pagesThe Effect of Soil PH On The Stomatal Density of Tradescantia SpathaceaAnnelyn Ruth SucayanNo ratings yet
- Cross Sections of Leaf Stem and RootDocument15 pagesCross Sections of Leaf Stem and Rootlwandlemkhonza96No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants Full Chapter NotesDocument69 pagesAnatomy of Flowering Plants Full Chapter NotesmonikaNo ratings yet
- Second Periodical Test in Science Vi Table of Specification Objectives No. of Days Taught Percent No. of Items Item PlacementDocument14 pagesSecond Periodical Test in Science Vi Table of Specification Objectives No. of Days Taught Percent No. of Items Item PlacementNida Espinas FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Chapter Xii - Diseases and Pests of Date PalmDocument46 pagesChapter Xii - Diseases and Pests of Date PalmSaadia YaghiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy BioHackDocument16 pagesAnatomy BioHackMohammed HamedNo ratings yet
- IJIVP Vol 7 Iss 4 Paper 7 1515 1524 PDFDocument10 pagesIJIVP Vol 7 Iss 4 Paper 7 1515 1524 PDFSri kantaNo ratings yet
- ReadingDocument3 pagesReadinglara cherissaNo ratings yet
- Tax Morfo Ast Cardueae Susanna2019Document11 pagesTax Morfo Ast Cardueae Susanna2019J CamiloNo ratings yet
- 1BI0 2H June19 QP-GCSE-Edexcel-Biology-2Document28 pages1BI0 2H June19 QP-GCSE-Edexcel-Biology-2Aimee GraceNo ratings yet
- The Effectiveness of Aloe Vera Extract As An Antibacterial SoapDocument19 pagesThe Effectiveness of Aloe Vera Extract As An Antibacterial SoapHoney ForfiedaNo ratings yet
- SL C1.3 Photosynthesis QPDocument10 pagesSL C1.3 Photosynthesis QPteddyenNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level Biology Paper 1 Multiple Choice May/June 2004 1 HourDocument20 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level Biology Paper 1 Multiple Choice May/June 2004 1 HourImanNo ratings yet
- Exploring Science SB6Document193 pagesExploring Science SB6Subashini ChryshanthusNo ratings yet
- 5th Class ScienceDocument6 pages5th Class ScienceM Saadat SaeediNo ratings yet