Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kcse 2005 Biology Questions
Kcse 2005 Biology Questions
Uploaded by
Urex ZOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Kcse 2005 Biology Questions
Kcse 2005 Biology Questions
Uploaded by
Urex ZCopyright:
Available Formats
om
.c
rs
pe
BIOLOGY 231/1 K.C.S.E 2005
pa
QUESTIONS
st
pa
SECTION A (20 MARKS)
se
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided.
kc
ee
1. Apart from hearing, state another function of the human ear. (1mk)
fr
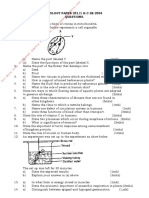
2 The diagram below represents a cell.
w.
ww
t
si
vi
rs
pe
pa
st
pa
SE
KC
ee
(a) Name the parts labeled X and Y (2mk)
Fr
X ……………………………………..
re
Mo
Y ……………………………………..
(b) Suggest why the structures labelled X would be more on one side
r
Fo
than the other. (1mks)
3. What is the role of the vascular bundles in plant nutrition? (3mks)
4. What is meant by
a) Organic evolution (1mks)
b) Continental drift? (1mks)
5. To which class does an animal with two body parts and four
Pairs of legs belong? (1mk)
6. Name the substance which accumulates in muscles when respiration
occurs with insufficient oxygen. (1mks)
7. State the importance of osmosis in plants. (3mks)
8. Name three factors in seeds that cause dormancy. (3mks)
9. Why would carboxyhaemoglobin lead to death? (2mks)
10. Name the organism that causes amoebic dysentery. (1mks)
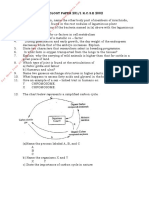
a) Name the process through which energy from the sun is
incorporated into the food web. (1mk)
b) State the mode of feeding of the birds in the food web (1mk)
c) Name two ecosystems in which the organisms in the food web live
(1mk)
d) From the information in the food web, construct a food chain
with the large bird as a quarternary consumer. (1mk)
e) What would happen to the organisms in the food web if bird N
migrated? (3mks)
f) Not all the energy from one trophic level is available to the
next level. Explain (3mks)
g) (i) Two organisms which play a role in the ecosystems are not
included in the food web. Name them. (2mks)
(ii) State the role played by the organisms named in g(i) above.
(1mk)
SECTION B (40 MARKS)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided.
11. The diagram below represents a part of the rib cage.
om
.c
rs
pe
pa
st
pa
se
kc
ee
fr
w.
ww
t
si
vi
a) Name the parts labeled W, Y and Z. (3mks)
rs
W ……………………………………………………
pe
pa
Y …………………………………………………….
st
Z ……………………………………………………..
pa
b) How does the part labeled Z facilitates breathing in? (3mks)
SE
12. In a garden with plants of same species, 705 plants had red flowers
KC
while 224 had white flowers.
ee
a) Work out the ratio of red to white flowered plants (1mk)
Fr
b) (i) Using letter R to represent the dominant gene, work out
re
Mo
a cross between F1 offspring and a white flowered plant.(4mks)
(ii) What is the genotypic ratio from the cross in b(i) above?(1mk)
r
Fo
c) What is meant by the term allele? (1mk)
13. The diagram below shows a section through the mammalian skin.
a) Name the parts labeled E, F and G. (3mks)
E …………………………………………
F …………………………………………
G …………………………………………
b) State two functions in each case of substance secreted by
the structures labeled.
(i) H ………………………………… (2mks)
(ii) I …………………………………. (2mks)
14. A set up that was used to investigate certain process in plants is
shown in the diagram below.
om
.c
rs
pe
pa
st
pa
se
kc
ee
fr
w.
ww
t
si
vi
a) What process was being investigated? (1mk)
rs
b) (i) State two precautions that should be taken when setting
pe
pa
up the experiment. (2mks)
st
(ii) Give a reason for each precaution stated in b(i) above.(2mks)
pa
c) State three environmental factors that influence the process
SE
Under investigation. (3mks)
KC
15. a) What is meant by the terms
ee
(i) Epigymous flower (1mk)
Fr
(ii) Staminate flower? (1mk)
re
Mo
b) How are the male parts of wild pollinated flowers adapted
to their function? (4mks)
r
Fo
16. a) Name two organisms that cause food spoilage (2mks)
b) Name two modern methods of food preservation and for each
state the biologic principle behind it. (4mks)
om
.c
rs
pe
SECTION C (40 MARKS)
pa
Answer question 17 (compulsory) and either question 18 or 19 in the spaces
st
pa
provided after question 19.
se
kc
ee
17. After an ecological study of feeding relationships students
fr
Constructed the food web below.
w.
ww
t
si
vi
rs
pe
pa
st
pa
SE
KC
ee
Fr
re
Mo
a) i)State three human activities that would affect
r
Fo
the ecosystems. (3mks)
ii) Explain how the activities stated in h(i) above would
affect the ecosystems. (3mks)
18. Describe how gaseous exchange takes place in terrestrial
Plants. (20mks)
19. How is the human eye adapted to its function? (20mks)
om
.c
rs
pe
MARKING SCHEME BIOLOGY PAPER 2 (PRACTICAL)
pa
KCSE 2005
st
pa
se
Each candidate will require the following
kc
ee
A shoot of maize plant with some leaves labeled specimen X
fr
A leafy shoot of Bidens pilosa labeled specimen Y
w.
Iodine solution
ww
Benedict’s solution
t
si
Means of heating / water bath vi
Means of cutting / scalpel
rs
6 test tubes
pe
pa
Test tube rack
st
Test tube holder
pa
Water in 50ml beaker
SE
Dropper
KC
Means of labeling
ee
Pestle and mortar
Fr
A hand lens
re
Mo
Dissecting needle / pins
A leafy twig of hibiscus plant with regular flowers labelled specimen S1
r
Fo
A leafy twig of bougainvillea with some mature flowers labeled specimen S2
An onion bulb with growing roots and growing aerial leaves labelled specimen p.
A shoot of tradescantia with flowers labeled specimen Q
Note: onion bulbs can be made to develop roots and leaves by planting
them in saw dust / sand.
Fleshly picked growing onions with roots intact can be used.
1.
Specimen Steps followed Identity
S1 1a,2a,3b,4b,6b Malvaceae
S2 1a,2a,3b,4a,5b,8a Nyactaginaceae
Q 1a,2b, Commelinaceae
X 1a,2a,3a Graminae
Y 1b, Asteraceae
b) i) S1 - Dicotyledonous
Q- Monocotyledonae
ii) S1 – Floral parts in threes (3, s0 multiples of 3/6 stamens / 6 anthers
/3 petals.
c) -Presence of large brightly coloured bracts / petals / perianth, to attract
insects.
(Reject it is brightly coluored )
-Anthers and stigma enclosed in a tube, to be reached by insects
- Scented to attract insects.
om
.c
rs
pe
d)
pa
st
pa
se
kc
ee
fr
w.
ww
t
si
vi
rs
pe
pa
st
D1 – Continuous outline
pa
- No shading
SE
D2 – Proportionality and accuracy
KC
- Long stigma (feathering) stigma thinner than stigma and ovary
ee
- Oblong ovary
Fr
Magnification = Length of drawing / image (units)
re
Mo
Length of actual specimen (units)
= x (2-10)
r
Fo
* No units = Ref. answer
Wrong computation = Ref. answer
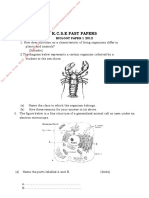
2. (a) T1 – Molar tooth
Reasons
i) Presence of cusps / ridges
ii) Presence of three roots
T2 - Incisors
Reasons
i) Chisel shaped / wide (sharp) edge / wedge shaped
Ref. one root
b) Cusps /ridges any upper white part
Crown – Black part below cusps
Neck - Boundary between white and black parts
Root – white lower part divided into 3
Enamel – All over the part seen
Dentine – Upper part below the cusps
c) J – vegetation, grass, shrubs, herbs, plants / leaves
Ref. vegetative , pasture, greens, grass eaters, herbivore, herbivorous but
mark reason.
Reasons
-Presence of diastema
- Absence of teeth (incisors and canines) at the front part of the upper jaw
-Presence of horny pad
-Presence of( premolars)cusps(for grinding vegetation)
K- Flesh/meat
Rej; carnivores/carnivorous, flesh eater but mark reason
Reasons
om
.c
rs
pe
Presence of (pronounced) long curved sharp pointed canines for gripping /
pa
st
tearing, holding/grasping prey
pa
Ref; large
se
-Presence of carnassial teeth, for cutting and crushing bone
kc
ee
fr
w.
ww
t
si
vi
rs
pe
pa
st
pa
Inset – last on both sided
SE
Photo – 2nd to the inside
KC
ee
e) J – 2 (10/3Co/1pm3/3m 3/3 ) = 32
Fr
K – 2 (13/3C1/1pm4/4m 2/3 ) =42
re
Mo
*teeth types must be identified using letters
Rej; If missing
r
Fo
*Demacating lines must be present
f) J
g) Refer to diagram area below main white part.
3. P(onion bulb with leaves and roots)
a) i) Inner succulent/ juicy /flesh while outer is dry
- Inner is thicker while outer is thin / membranous / scally
NB: Comparison must be seen otherwise deny a marks
ii) Inner swollen with food for storage and outer for protection against
dessication /mechanical injury / excessive loss of water/
microorganisms / invasion by fungi.
Rej: Storage of water alone, & prevent water loss.
om
.c
rs
pe
5.
pa
st
Extract Procedure Observations Conclusion
pa
Roots Add iodine No colour Starch absent
se
changed colour of
kc
ee
iodine Brown
fr
yellow retained /
w.
ww
persist
Add benedicts Blue to green to Reducing
t
si
solution and orange/ brown sugars
vi
boil/ (acc. brick present/simple
rs
pe
heat/warm/place red,ref.red sugars.
pa
in a hot water
st
bath
pa
Bulbs Add iodine No colour change Starch absent
SE
colour of iodine
KC
Add benedict Green to yellow to Reducing
ee
Fr
solution and boil orange /brown sugars present
Aerial Add iodine No colour change Starch absent
re
Mo
leaves
r
Add benedicts Green to yellow to Reducing
Fo
solution and boil orange to brown sugars present
* Green end – conclusions must be traces of reducing sugars
* Wrong procedures, deny observation and conclusion marks
c) Roots
- Presence of reducing sugars translocated from the bulb/aerial
Leaves, for provision of energy/respiration for growth and
development/respiration for growth and development/metabolic
activities.
- Absence of starch because roots are not a storage organ.
ii) Bulb
- Presence of reducing sugars translocated from aerial leaves, for storage
to be stored.
- Absence of starch because fleshy leaves of the bulb do not
store starch (Stores Volatile oils)
Aerial leaves
- Presence of reducing sugars due to photosynthesis
- Absence of starch because the reducing sugars had not been
converted into starch.
You might also like
- Kcse 2023 Biology Replica ExamsDocument120 pagesKcse 2023 Biology Replica Examsmicah isaboke100% (3)
- Rationalization of Shape and Related Stress Distribution in Posterior Teeth: A Finite Element Study Using Nonlinear Contact AnalysisDocument9 pagesRationalization of Shape and Related Stress Distribution in Posterior Teeth: A Finite Element Study Using Nonlinear Contact AnalysisAnderson ChamblasNo ratings yet
- UACE BIO PAPER TWO SET 5 2023-JusanDocument3 pagesUACE BIO PAPER TWO SET 5 2023-JusanUG LATEST MUSIC100% (2)
- Dental DecksDocument4 pagesDental DecksSamer Malh100% (5)
- MCQDocument4 pagesMCQArif Azfar100% (3)
- Bevels in DentistryDocument52 pagesBevels in DentistryNaghman Zuberi75% (4)
- Kcse 2004 Biology QuestionsDocument7 pagesKcse 2004 Biology QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 2006 Biology QuestionsDocument8 pagesKcse 2006 Biology QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 2003 Biology QuestionsDocument6 pagesKcse 2003 Biology QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 1999 Biology QuestionsDocument7 pagesKcse 1999 Biology QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 1999 Biology p1Document3 pagesKcse 1999 Biology p1Urex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 2007 Biology QuestionsDocument11 pagesKcse 2007 Biology QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 2009 Biology QuestionsDocument18 pagesKcse 2009 Biology QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 2001 Biology QuestionsDocument7 pagesKcse 2001 Biology QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 1997 Biology p1Document5 pagesKcse 1997 Biology p1Urex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 1997 Biology QuestionsDocument10 pagesKcse 1997 Biology QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 1995 Biology p1Document4 pagesKcse 1995 Biology p1Urex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 1995 Biology QuestionsDocument10 pagesKcse 1995 Biology QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 2002 Biology QuestionsDocument6 pagesKcse 2002 Biology QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- Biology F2T1 2024 - QSDocument9 pagesBiology F2T1 2024 - QSL WNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 1 Term 1Document13 pagesBiology Form 1 Term 1mekatilili20No ratings yet
- Biology 2023 Mocks BookletDocument167 pagesBiology 2023 Mocks BookletMasega Daniel ManaliNo ratings yet
- Form 3 BioDocument4 pagesForm 3 BioBen ChelagatNo ratings yet
- Form Ii Biology End Term of Term IiDocument7 pagesForm Ii Biology End Term of Term IioyooNo ratings yet
- BIO-PP2-Teacher Co KeDocument8 pagesBIO-PP2-Teacher Co KeraymurigiNo ratings yet
- Biology Paper 1 001Document111 pagesBiology Paper 1 001Makembu Wa Mwangi0% (1)
- Kcse 2012 Biology QuestionsDocument13 pagesKcse 2012 Biology QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- Classification 1 and 2.Document4 pagesClassification 1 and 2.VernonNo ratings yet
- 2004 Biology Paper 1Document3 pages2004 Biology Paper 1wyclyfjonesNo ratings yet
- Kcse Biology TopicalsDocument272 pagesKcse Biology Topicalsalivistaharriet5No ratings yet
- 1995 Kcse Physics Papers - 2Document3 pages1995 Kcse Physics Papers - 2DappsNo ratings yet
- Panam Academy End of Term Iii July 2021 Module Beginner Morning Biology PaperDocument7 pagesPanam Academy End of Term Iii July 2021 Module Beginner Morning Biology PaperSamuel MainaNo ratings yet
- MB Biology MorningDocument7 pagesMB Biology MorningSamuel MainaNo ratings yet
- Panam Academy End of Term Iii July 2021 Module Beginner Morning Biology PaperDocument7 pagesPanam Academy End of Term Iii July 2021 Module Beginner Morning Biology PaperSamuel MainaNo ratings yet
- Biology Quizs FNLDocument92 pagesBiology Quizs FNLAbdul WasayNo ratings yet
- Termly Exams: F3 Biology Pp2Document37 pagesTermly Exams: F3 Biology Pp2celineandesoNo ratings yet
- Biology Form1 April Holiday Assignment, 2024-3Document19 pagesBiology Form1 April Holiday Assignment, 2024-3JANSHI CYBERNo ratings yet
- Set2 Bio MidTerm 1 2021 Teacher - Co .Ke F2 ExamDocument5 pagesSet2 Bio MidTerm 1 2021 Teacher - Co .Ke F2 ExamDenisNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 2 May 6th 12thDocument8 pagesBiology Form 2 May 6th 12thEliud BrianNo ratings yet
- 1996-2009 Bio KCSEDocument130 pages1996-2009 Bio KCSECecilia KhaombiNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Form 3 Holiday Assignment QuestionsDocument9 pagesBIOLOGY Form 3 Holiday Assignment QuestionsgurlavatarNo ratings yet
- Biology F1T3 QSDocument10 pagesBiology F1T3 QSalexNo ratings yet
- Gaseous Exchange QDocument4 pagesGaseous Exchange QDenisNo ratings yet
- BIO-PP1-Teacher Co KeDocument7 pagesBIO-PP1-Teacher Co KelyshantahlynahNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY-FORM-1 AbubaydaDocument8 pagesBIOLOGY-FORM-1 AbubaydaHaron HB WritersNo ratings yet
- Bio F1Document4 pagesBio F1milly khisaNo ratings yet
- Bio F2 QSDocument9 pagesBio F2 QSsolutiongrandtechNo ratings yet
- Assgt Biology-Form-1-End-Term-1-2020 PDFDocument8 pagesAssgt Biology-Form-1-End-Term-1-2020 PDFAnthonyNo ratings yet
- S5 BIOLOGY TEST I TERM II 2024 and MARKING GUIDEDocument16 pagesS5 BIOLOGY TEST I TERM II 2024 and MARKING GUIDEmunyanezaolivier422No ratings yet
- Biology Form 1: Answer All The Questions in The Spaces ProvidedDocument7 pagesBiology Form 1: Answer All The Questions in The Spaces ProvidedoyooNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 1: Answer All The Questions in The Spaces ProvidedDocument7 pagesBiology Form 1: Answer All The Questions in The Spaces ProvidedOchieng WilberforceNo ratings yet
- UACE BIO PAPER TWO SET 4 2023-JusanDocument3 pagesUACE BIO PAPER TWO SET 4 2023-JusanCampbell OGENRWOTNo ratings yet
- Cs2-782021-Atika School-5172016 - Bioform4 Paper 1Document7 pagesCs2-782021-Atika School-5172016 - Bioform4 Paper 1bosirejanet526No ratings yet
- Form Two 2024 April Holiday AssignmentDocument15 pagesForm Two 2024 April Holiday Assignmentsam cyberNo ratings yet
- CBSE Sample Paper Class 9 Science Set 4Document7 pagesCBSE Sample Paper Class 9 Science Set 4Phani Raj100% (1)
- Cell PhysiologyDocument4 pagesCell PhysiologyVernon100% (1)
- Biology f2 2022 QsDocument8 pagesBiology f2 2022 QsMAGDALENE MWANGANGINo ratings yet
- Bio 22072021 012 pp1Document13 pagesBio 22072021 012 pp1MARK SIMIYUNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Plants and Animals.Document16 pagesNutrition in Plants and Animals.JohnNo ratings yet
- November Midterm 2021Document9 pagesNovember Midterm 2021PaulNo ratings yet
- Biology s3 Exams 2019Document3 pagesBiology s3 Exams 2019NSABIMANA JANVIERNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants QDocument8 pagesTransport in Plants QfranciskutkutNo ratings yet
- Kcse Chemistry QuestionsDocument227 pagesKcse Chemistry QuestionsTony MorerwaNo ratings yet
- KCSE 2006 Business Studies PAPER 1Document7 pagesKCSE 2006 Business Studies PAPER 1Urex ZNo ratings yet
- 1kcse Business Studies 565Document6 pages1kcse Business Studies 565Urex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 1996 Biology QuestionsDocument4 pagesKcse 1996 Biology QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- 2006 Business AnalysisDocument6 pages2006 Business AnalysisUrex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 1997 Biology p1Document5 pagesKcse 1997 Biology p1Urex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 2001 Biology QuestionsDocument7 pagesKcse 2001 Biology QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 2010 Business Studies p1Document5 pagesKcse 2010 Business Studies p1Urex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 2011 Business Studies p1Document9 pagesKcse 2011 Business Studies p1Urex ZNo ratings yet
- KCSE 2006 Business Studies PAPER 2Document3 pagesKCSE 2006 Business Studies PAPER 2Urex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 2012 Business Studies p2Document3 pagesKcse 2012 Business Studies p2Urex ZNo ratings yet
- KCSE 2007 Business Studies PAPER 2Document2 pagesKCSE 2007 Business Studies PAPER 2Urex ZNo ratings yet
- KCSE 2007 Business Studies PAPER 1Document8 pagesKCSE 2007 Business Studies PAPER 1Urex ZNo ratings yet
- KCSE 2009 Business Studies PAPER 2Document5 pagesKCSE 2009 Business Studies PAPER 2Urex ZNo ratings yet
- KCSE 2008 Agriculture P2Document5 pagesKCSE 2008 Agriculture P2Urex ZNo ratings yet
- 2008 Kcse Business AnswersDocument14 pages2008 Kcse Business AnswersUrex ZNo ratings yet
- KCSE 2010 Agriculture P1Document3 pagesKCSE 2010 Agriculture P1Urex ZNo ratings yet
- KCSE 2011 Agriculture P1Document11 pagesKCSE 2011 Agriculture P1Urex ZNo ratings yet
- June 2021 Examiner ReportDocument18 pagesJune 2021 Examiner ReportUrex ZNo ratings yet
- 2009 Business Analysis of QuestionsDocument5 pages2009 Business Analysis of QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 2012 Business Studies p1Document3 pagesKcse 2012 Business Studies p1Urex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse Business PPR 2565 2Document2 pagesKcse Business PPR 2565 2Urex ZNo ratings yet
- Kcse 2010 Business Studies p2Document3 pagesKcse 2010 Business Studies p2Urex ZNo ratings yet
- K2cse Business Studies Papers QuestionsDocument91 pagesK2cse Business Studies Papers QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- 2007 Business Qar KitDocument23 pages2007 Business Qar KitUrex ZNo ratings yet
- 24kcse Business Studies PPR 1 565Document6 pages24kcse Business Studies PPR 1 565Urex ZNo ratings yet
- KCSE 2009 Agriculture P1Document7 pagesKCSE 2009 Agriculture P1Urex ZNo ratings yet
- KCSE 2011 Agriculture P2Document9 pagesKCSE 2011 Agriculture P2Urex ZNo ratings yet
- KCSE 2010 Agriculture P2Document5 pagesKCSE 2010 Agriculture P2Urex ZNo ratings yet
- KCSE 2012 Agriculture P2Document6 pagesKCSE 2012 Agriculture P2Urex ZNo ratings yet
- KCSE 2012 Agriculture P 1 2Document11 pagesKCSE 2012 Agriculture P 1 2Urex ZNo ratings yet
- Occlusion 7Document10 pagesOcclusion 7krondanNo ratings yet
- Class I Compound CavityDocument79 pagesClass I Compound CavityShahid HameedNo ratings yet
- Lab Steps - Dies, Wax PatternsDocument86 pagesLab Steps - Dies, Wax PatternsSonila Joseph75% (4)
- Class 2Document5 pagesClass 2SadanandaHotaNo ratings yet
- Teeth SelectionDocument77 pagesTeeth SelectionAnurag AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Okeson Chapter 3 Alignment and Occlusion of The DentitionDocument22 pagesOkeson Chapter 3 Alignment and Occlusion of The DentitionMaryam AbdulqadirNo ratings yet
- Complete Denture Complaints IIDocument65 pagesComplete Denture Complaints IIbkprosthoNo ratings yet
- Guide For Setting Denture Teeth On F-FDocument0 pagesGuide For Setting Denture Teeth On F-FPrince AhmedNo ratings yet
- Logitudinal Tooth Fractures Findings and Diagnosis3Document30 pagesLogitudinal Tooth Fractures Findings and Diagnosis3JuanTabarésNo ratings yet
- Balanced OcclusionDocument9 pagesBalanced OcclusionDrShweta Saini100% (1)
- Posterior Teeth ArrangementDocument1 pagePosterior Teeth ArrangementVy HuynhNo ratings yet
- StabilityDocument21 pagesStabilityDrYashvi ShahNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Outcomes of Hybrid and Conventional Hyrax Expanders Par Daniela Garib Angle Ortho 2021Document9 pagesOrthopedic Outcomes of Hybrid and Conventional Hyrax Expanders Par Daniela Garib Angle Ortho 2021NANA NANA Arnel redonNo ratings yet
- Age by Dental DataDocument40 pagesAge by Dental DataAnanda KumarNo ratings yet
- Comparision Between First and Second PremolarDocument25 pagesComparision Between First and Second Premolarparee1No ratings yet
- Anatomical Landmarks of The CrownDocument3 pagesAnatomical Landmarks of The CrownHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Single Complete Denture FinalDocument15 pagesSingle Complete Denture FinalVikas Aggarwal100% (1)
- Concept of Normal OcclusionDocument39 pagesConcept of Normal OcclusionAlok Avinash100% (1)
- Morphological Differences Between The First and Second Permanent Upper MolarsDocument6 pagesMorphological Differences Between The First and Second Permanent Upper MolarsShinta AlfianiNo ratings yet
- Mandibular 2nd MolarDocument8 pagesMandibular 2nd Molarcelestina dawn peterNo ratings yet
- Mandibular First PremolarDocument5 pagesMandibular First PremolarHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Remounting Dan SGDocument32 pagesRemounting Dan SGanon_817492527No ratings yet
- 1 March 2009 Dental Anatomy TestDocument15 pages1 March 2009 Dental Anatomy TestManish AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Teeth Selection and ArrangementDocument118 pagesTeeth Selection and Arrangementaakankshakanwar100% (2)
- Dental MorfologiDocument43 pagesDental MorfologiAvirna IdayantiNo ratings yet
- Evolution Occlusion and Occlusal Instruments: AcademicsDocument11 pagesEvolution Occlusion and Occlusal Instruments: AcademicsMelissa Perez GuerreroNo ratings yet