Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1ST SEM - October 3-6, 2022
1ST SEM - October 3-6, 2022
Uploaded by
jenny obianoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1ST SEM - October 3-6, 2022
1ST SEM - October 3-6, 2022
Uploaded by
jenny obianoCopyright:
Available Formats
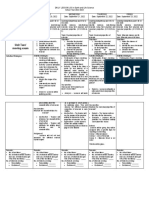
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL School: San Guillermo National High School Grade Level: Grade- 12 HE/ICT/ABM/IA/HUMSS - 3
DAILY LESSON LOG DRRR Instructor: JENNY A. OBIANO Learning Area: PHYSICAL SCIENCE
Inclusive Teaching Dates: October 3 - 6, 2022 Quarter: 1st. SEM. :1st Quarter: WEEK #
3-Oct 4-Oct 5-Oct 6-Oct
I. OBJECTIVES: To be able to develop critical thinking and life skills among learners in disaster readiness and basic disaster risk reduction.
The learner demonstrates understanding of: how the uses of different materials are related to their properties and
A. Content Standards:
structures. 2. the relationship between the function and structure of biological macromolecules.
B. Performance Standard:
_
(LC # 6): explain how the uses of the
(LC # 3): determine if a molecule is polar or (LC # 4): describe the general types (LC # 5): explain the effect of following materials depend on their
C. Learning Competencies: non polar given its structure; and relate the intermolecular forces on the properties
polarity of a molecule to its properties.
of intermolecular forces of substances
properties:
a. medical implants,
* CODE: S11/12PS-IIIc-15-16 S11/12PS-IIIc-d-17 S11/12PS-IIIc-18 S11/12PS-IIIc-d-19
How the properties of How the properties of How the properties of How the properties of
II. CONTENT matter relate to their
chemical structure
matter relate to their
chemical structure
matter relate to their
chemical structure
matter relate to their
chemical structure
III. LEARNING
RESOURCES
Instructional Materials: Laptop and speaker, Manila paper, Permanent Marker ( Red, Blue & Green) DLP \ LCD projector, Printed Materials, Scotch Tape,
1. References Learner's Guide: K-12 SHS Curriculum Guide for PHYSICAL SCIENCE
2. Textbook : PHYSICAL SCIENCE TEXTBOOK Manual for Senior High School 2008
3. Textbook Pages pages 91-94 pages 95-97 pages 99-101 pages 101-103
. Online References: https://www.physscieweb.net/files/26081_kp1concepphysicalscience1.pdf http://www.wikipedia.physicalscienceancientphilosophers.pdf
. Youtube Videos: https://www.youtube.com/user/physicalScie YOUTUBE LINK: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OBZitH8VFEc
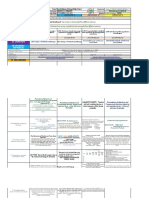
IV. PROCEDURES
Presentation of objectives and terms Presentation of objectives and terms
Communicate learning objectives and important term. Communicate learning objectives and important term.
A. Reviewing previous lesson Introduce the learning objectives below using any of the Introduce the learning objectives below using any of the
RECAP: Teacher will call a student to give a SALIENT POINTS! Teacher will call a student to
or presenting the new lesson suggested protocols (Verbatim, Own suggested protocols (Verbatim, Own Words, Read- short summary of the lesson yesterday. give a short summary of the lesson yesterday.
Words, Read-aloud): aloud): ICE BREAKER ACTIVITY!
The teacher will state the importance of the general
Presentation of objectives and terms. types intermolecular forces. Introduce the list of Presentation of objectives and terms.
TIME TO PONDER: State the importance of the
B. Establishing a purpose for Communicate learning objectives and important term. important terms that learners will encounter: Communicate learning objectives and important
intermolecular forces in human life. Cite examples for
the lesson: Establish the significance of a. Intermolecular forces . Adhesion term.
this.
the subject matter. b. Intramolecular forces Cohesion Introduce the learning objectives.
c. Ion-ion interaction l. Concave meniscus
The teacher will state the importance of the general
Presentation of objectives and terms. types intermolecular forces. Introduce the list of Presentation of objectives and terms.
B. Establishing a purpose for Communicate learning objectives and important term. important terms that learners will encounter: Communicate learning objectives and important
the lesson: Establish the significance of a. Intermolecular forces . Adhesion term.
the subject matter. b. Intramolecular forces Cohesion Introduce the learning objectives.
c. Ion-ion interaction l. Concave meniscus
Bond Polarity RECALL: String Engineering
Review Grade 9 chemistry discussions on properties of Video clip: (Methanol and Water--Hydrogen Present a dilemma to learners of making a piece of string
C. Presenting examples/ elements found in the periodic table such asboiling points, bonding) Teacher will Baesa on gthe video A mind map also works as an alternative to a strong enough to lift a 3 kg weight. OnIn its current state,
instances of the new lesson: melting points, oxidation number, etc. Point out that one of the clip the teacher will explain the difference of table. the string can only lift a portion of the weight before it
properties found inthe periodic table is the electronegativity of breaks. The learners need to figure out how to make it
elements.
Inter and Intra Molecular Forces. stronger.
LECTURE: Electronegativity (EN), Introduce polar Recall Exercise:
covalent and non-polar covalent bonds. Have the learners
IN-DEAPTH ANALYSIS;
LECTURETTE: The teacher discuss the lesson: Types Use a “talking stick” to help the class LECTURETTE: Have the learners watch a short
familiarize themselves of Intermolecular Forces First establish the distinction remember the lesson. This is when a stick gets
D. Discussing new concepts with the periodic table. Let them find the between intramolecular forces and intermolecular forces passed around from one learner to the next. The one
video on Kevlar as an introduction.
practicing new skills : EN value of several elements. Have them
of attraction. who has a stick will recall a lesson point out loud The video can be found at
determine the most electronegative https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KFVP8A_G5VI
element and the least electronegative Gather observations from the video clip experiment. then pass the stick to any classmate who has to
recall another point. (last accessed March 27, 2016)
element. II. Molecular Geometry
Reinforcement:
Seatwork: Provide several examples and have the learners Facts on Johannes Diderik van der Waals. (the Vander
determine if the bond between elements are:
Waals Forces ) Introduce the four main types of
polar covalent or non-polar covalent. Reinforcement: Determine which topic the learners FLASH CARD- FAST TALK: Select students to
E. Developing Mastery intermolecular forces:
1. Ion-ion interaction remember most and least. Reinforce certain topics answer the Guide questions flashed on the screen.
(Leads to Formative Assessment) CH4 CF4 O2 H Br Vanden 2. Dipole-dipole interaction as needed. CONCEPT: All about types of intermolecular forces.
Bout. (2011). VSEPR Theory: Introduction. Retrieved from 3. Hydrogen bonding
https://www.youtube.com/ 4. Dispersion forces also known as London forces in honor of
watch?v=keHS-CASZfc
Fritz London
From the previous Polarity Experiment, Learners should be able to Reflective Analysis: using the OB-IN-AP model, call
From the given lecture, Flashed on the screen FACT
F. Finding practical application find the practical application of the concept to their day to day life.
SHEET. Comparison of INTRA and INTER Molecular
Give a short Quiz (10 items) to Evaluate student from each group to share his/her thoughts on how
of concepts and skills in daily living Mention that one of the most practical manifestations of polarity is
Bonding and its Sub-Types. their Learnings. to apply the concept of intermolecular forces in human
solubility and miscibility. industry.
From the previous discussion and the experiment,
Summarize the lesson with emphasis to the fact that molecules Recall the experiments and the following: (Perfect 7): In making generalization,encourage the
G. Making generalizations and (Perfect 7): In making generalization,encourage the
are polar or non-polar based on the type of covalent bond and intramolecular vs intermolecular forces learners to summarize what they have learned in seven learners to summarize what they have learned in seven
abstractions about the lesson its molecular geometry.
- Van der Waals forces words/ phrases relative to the concept. words/ phrases relative to the concept.
- ion-ion interaction
- dipole-dipole interaction
H. Evaluating Learning .>> The teacher evaluates the learner's ability and confidence to express their thoughts ( in making a sound conclusion \ abstraction ) from the Learning Activity Cell to the discussion \ presentation part.
J. Additional Activities for
V. REMARKS:
application or remediation
Everyone in the class participated well during the class discussions and group Activity ( LB Session) .
V. REFLECTION
A. No. of learners who earned 80% on the
formative assessment. Grade- 12 HE/ICT/ABM/IA/HUMSS - 3 Grade- 12 HE/ICT/ABM/IA/HUMSS - 3 Grade- 12 HE/ICT/ABM/IA/HUMSS - 3 Grade- 12 HE/ICT/ABM/IA/HUMSS - 3
B. No. of learners who require additional
activities for remediation Grade- 12 HE/ICT/ABM/IA/HUMSS - 3 Grade- 12 HE/ICT/ABM/IA/HUMSS - 3 Grade- 12 HE/ICT/ABM/IA/HUMSS - 3 Grade- 12 HE/ICT/ABM/IA/HUMSS - 3
B. No. of learners who require additional
activities for remediation Grade- 12 HE/ICT/ABM/IA/HUMSS - 3 Grade- 12 HE/ICT/ABM/IA/HUMSS - 3 Grade- 12 HE/ICT/ABM/IA/HUMSS - 3 Grade- 12 HE/ICT/ABM/IA/HUMSS - 3
C. Did the remedial lessons work?
No. of Learners who have caught up Grade- 12 HE/ICT/ABM/IA/HUMSS - 3 Grade- 12 HE/ICT/ABM/IA/HUMSS - 3 Grade- 12 HE/ICT/ABM/IA/HUMSS - 3 Grade- 12 HE/ICT/ABM/IA/HUMSS - 3
with the lesson
D.No. of Learners who continue to require
remediation. Grade- 12 HE/ICT/ABM/IA/HUMSS - 3 Grade- 12 HE/ICT/ABM/IA/HUMSS - 3 Grade- 12 HE/ICT/ABM/IA/HUMSS - 3 Grade- 12 HE/ICT/ABM/IA/HUMSS - 3
E. Which of my teaching strategies worked
well? Why did these work?
F. What difficulties did I encounter which my
principal or supervisor can help me solve? Students need an extra cooling fan for ventilation and to facilitate better learning environment.
G. What innovation localized materials
did I used/ discover which I wich to share with the
teachers?
Core Subject Description: Disaster Readiness & Risk reduction: This course focuses on the application of scientific knowledge and the solution of practical problems in a physical environment. It is designed to bridge the gap between theoretical science and
daily living.
Prepared by: Checked by:
JENNY A. OBIANO JENNELYN JABALLA EdD JOSEPHINE RAGUINI PhD.
Phys. Scie TEACHER SHS_ Coordinator School Principal
You might also like
- Thermodynamics 1Document84 pagesThermodynamics 1Nick Decillo90% (145)
- Balancing Activity - SkittlesDocument10 pagesBalancing Activity - SkittlesRhyz Mareschal DongonNo ratings yet
- 7 CH 3 Sec 2 Physical and Chemical Changes UploadDocument25 pages7 CH 3 Sec 2 Physical and Chemical Changes Uploadapi-294483847No ratings yet
- Molecular GeometryDocument1 pageMolecular Geometrybooty holeNo ratings yet
- 1st Sem - September 19 - 22, 2022 (HE - ICT)Document3 pages1st Sem - September 19 - 22, 2022 (HE - ICT)jenny obianoNo ratings yet
- 1st Sem - October 10 - 13, 2022Document3 pages1st Sem - October 10 - 13, 2022jenny obianoNo ratings yet
- DLL PHY-SCI (Aug Week1)Document7 pagesDLL PHY-SCI (Aug Week1)Jesse GabrielNo ratings yet
- DRRR ReportDocument23 pagesDRRR ReportDaniella MangahasNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives: To Conserve and Protect The Soil?Document2 pagesI. Objectives: To Conserve and Protect The Soil?allanrnmanalotoNo ratings yet
- Tos SHS - Physical ScienceDocument5 pagesTos SHS - Physical ScienceJojimar JulianNo ratings yet
- MTS Trace The PatternDocument1 pageMTS Trace The PatternPetar PanNo ratings yet
- Physical Science 1st Quater ExamDocument3 pagesPhysical Science 1st Quater ExamRenier Dela Vega FloresNo ratings yet
- Core - Earth and Life Science Learning GuideDocument3 pagesCore - Earth and Life Science Learning GuideJerico Karlos Logarta CortesNo ratings yet
- PhysicalScience Week4 2Document4 pagesPhysicalScience Week4 2MICHAEL ANGELO MAYORDONo ratings yet
- Crutch Walking Up DownDocument1 pageCrutch Walking Up DownMhel MGNo ratings yet
- ES DLP 6-28-2017 Continental DriftDocument1 pageES DLP 6-28-2017 Continental DriftCharline A. RadislaoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Guide in Earth and Life Science I. ObjectivesDocument3 pagesLesson Guide in Earth and Life Science I. ObjectivesallanrnmanalotoNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Week 3 Day 1Document2 pagesPhysical Science Week 3 Day 1daniel loberizNo ratings yet
- DLL PHY SCI Week 11Document5 pagesDLL PHY SCI Week 11kent100% (2)
- The Concept of Life Based On Emerging Pieces of EvidenceDocument41 pagesThe Concept of Life Based On Emerging Pieces of EvidenceJerah Mae MacajelosNo ratings yet
- q2 w3 Perpetuation of LifeDocument8 pagesq2 w3 Perpetuation of LifeMeryll Jade PonceNo ratings yet
- DLL Aug 26-30, 19 EslDocument4 pagesDLL Aug 26-30, 19 EslCristina MaquintoNo ratings yet
- Biological MacromoleculesDocument39 pagesBiological Macromoleculesapi-337296800No ratings yet
- DAILY LESSON LOG in Earth and Life ScienceDocument2 pagesDAILY LESSON LOG in Earth and Life SciencejessaNo ratings yet
- DLL Bio LatestDocument4 pagesDLL Bio LatestGlenda AstodilloNo ratings yet
- Midterm ExamDocument3 pagesMidterm Exambernadeth barajasNo ratings yet
- ExamDocument2 pagesExamLyn SyNo ratings yet
- PHYSICAL SCIENCE MODULE 15-EditedDocument24 pagesPHYSICAL SCIENCE MODULE 15-EditedLove Joy JumawanNo ratings yet
- 8 - MODULE 3 - Molecular Polarity Rev 2022Document20 pages8 - MODULE 3 - Molecular Polarity Rev 2022ROGELIO RIVERA100% (1)
- CatalystDocument26 pagesCatalystrebeccaNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson LOG: School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time QuarterDocument4 pagesDaily Lesson LOG: School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time QuarterArlynn Arcaño IslaNo ratings yet
- Handout No. 10 in Physical Science: MelcDocument11 pagesHandout No. 10 in Physical Science: MelcDulce J. LuatonNo ratings yet
- Week-2-Q1-Gen Chem-Sep-4-8-DllDocument15 pagesWeek-2-Q1-Gen Chem-Sep-4-8-DllJennette BelliotNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Region X Division of Lanao Del Norte Diego H. Patigayon National High School Mukas, Kolambugan, Lanao Del NorteDocument91 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Region X Division of Lanao Del Norte Diego H. Patigayon National High School Mukas, Kolambugan, Lanao Del NorteChristine De San JoseNo ratings yet
- DLL 4Document2 pagesDLL 4Rizalyn Tatotz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Rate of Chemical ReactionDocument22 pagesRate of Chemical Reactionkatrina freoNo ratings yet
- Physical Science DLP Q2W2Document7 pagesPhysical Science DLP Q2W2junar asentistaNo ratings yet
- Shs Daily Lesson in Earth ScienceDocument53 pagesShs Daily Lesson in Earth ScienceCherry Mae100% (1)
- Teacher Grade Level 11 Learning Area Unit 2 How The Properties of MatterDocument5 pagesTeacher Grade Level 11 Learning Area Unit 2 How The Properties of MatterHelen Grace Llemos CabalagNo ratings yet
- Physical Science DLL (Week7)Document6 pagesPhysical Science DLL (Week7)jessiry lascanoNo ratings yet
- Hydrometeorological HazardsDocument115 pagesHydrometeorological HazardsKim DiazNo ratings yet
- MacromoleculesDocument16 pagesMacromoleculesLou MenesesNo ratings yet
- New DLL SHS - Earth & Life Science July 8-12, 2019-2020Document2 pagesNew DLL SHS - Earth & Life Science July 8-12, 2019-2020BeeWinNo ratings yet
- Precautionaryandsafetymeasuresfor Hydrometeorological HazardsDocument35 pagesPrecautionaryandsafetymeasuresfor Hydrometeorological HazardsNikki CrystelNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Rock Behaviors Under StressDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Rock Behaviors Under StressHomer NasolNo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Plan in Physical ScienceDocument1 pageWeekly Home Learning Plan in Physical ScienceLea Mae MimayNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson LOG: School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time QuarterDocument5 pagesDaily Lesson LOG: School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time QuarterArlynn Arcaño IslaNo ratings yet
- Budget of Lesson Earth and Life ScienceDocument7 pagesBudget of Lesson Earth and Life Sciencejeseca cincoNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document7 pagesWeek 2CHRISTIANNE LYN JANE ALIGANGANo ratings yet
- Reviewer PSDocument7 pagesReviewer PSJeegj Ecco MedinaNo ratings yet
- Personality Development Weeks 1-2 ModuleDocument13 pagesPersonality Development Weeks 1-2 ModuleCzarina Ciara AndresNo ratings yet
- DLP For SHS 7 E's Physical ScienceDocument9 pagesDLP For SHS 7 E's Physical ScienceJoseph GutierrezNo ratings yet
- DLL PHY-SCI (Aug Week2)Document5 pagesDLL PHY-SCI (Aug Week2)Jesse GabrielNo ratings yet
- PhysicalScience Week5 1Document3 pagesPhysicalScience Week5 1MICHAEL ANGELO MAYORDONo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces Lesson PlanDocument34 pagesIntermolecular Forces Lesson Planapi-442754652No ratings yet
- Physical Science Grade 11 - St. Lorenzo Module 2 - : Saint Louis School of Pacdal, IncDocument10 pagesPhysical Science Grade 11 - St. Lorenzo Module 2 - : Saint Louis School of Pacdal, IncNo nameNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan Fire HazardsDocument5 pagesDaily Lesson Plan Fire HazardsMA. HAZEL TEOLOGONo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP)Document2 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP)Catherine VillaruzNo ratings yet
- TQ - Q2 - Earth and Life ScienceDocument7 pagesTQ - Q2 - Earth and Life SciencePrudevenoNo ratings yet
- DLL-EARTHSCI-SHEILA-MAE w3-4Document3 pagesDLL-EARTHSCI-SHEILA-MAE w3-4Sheila EllesoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Polar and Nonpolar Molecules Jones 2014Document2 pagesWorksheet - Polar and Nonpolar Molecules Jones 2014Gideon CavidaNo ratings yet
- M2 Polarity of MoleculesDocument77 pagesM2 Polarity of MoleculesEvangeline AgtarapNo ratings yet
- 1st SEm - September 26 - 29, 2022 (ABM - IA)Document3 pages1st SEm - September 26 - 29, 2022 (ABM - IA)jenny obianoNo ratings yet
- 1st SEm - September 26 - 29, 2022 (ABM - IA)Document3 pages1st SEm - September 26 - 29, 2022 (ABM - IA)jenny obianoNo ratings yet
- 1st Sem - September 19 - 22, 2022 (HE - ICT)Document3 pages1st Sem - September 19 - 22, 2022 (HE - ICT)jenny obianoNo ratings yet
- 1st Sem - October 10 - 13, 2022Document3 pages1st Sem - October 10 - 13, 2022jenny obianoNo ratings yet
- 1st Sem - October 17 - 20, 2022Document4 pages1st Sem - October 17 - 20, 2022jenny obianoNo ratings yet
- Quality & Composition of Cement Clinker - INFINITY FOR CEMENT EQUIPMENT PDFDocument74 pagesQuality & Composition of Cement Clinker - INFINITY FOR CEMENT EQUIPMENT PDFSiddharth Singh100% (1)
- Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy, Atomic Emission Spectroscopy, and Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass SpectrometryDocument22 pagesAtomic Absorption Spectroscopy, Atomic Emission Spectroscopy, and Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass SpectrometryBryandSigalesNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of ElementsDocument27 pagesDual Nature of ElementsTarnate Tacay100% (1)
- Fizkem Seminar ExDocument22 pagesFizkem Seminar ExZsolt Dürvanger100% (1)
- Carbon-13 NMR: Mr. Faheem Shaikh. (M.Pharm 1 SEM.)Document18 pagesCarbon-13 NMR: Mr. Faheem Shaikh. (M.Pharm 1 SEM.)Niraj GuptaNo ratings yet
- Reg. No.: Name:: Q.No. Sub. Sec. Question Description MarksDocument2 pagesReg. No.: Name:: Q.No. Sub. Sec. Question Description MarksLaxmitej ManchikantiNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower-ExcelDocument14 pagesCooling Tower-ExcelpartoNo ratings yet
- 1012 - Turbine Lubricating OilDocument9 pages1012 - Turbine Lubricating OilAnonymous ieWpd823LgNo ratings yet
- Lithium Recovery From Artificial Brine Using Energyefficient Membrane Distillation and Nanofiltration2020Journal of Membrane ScienceDocument7 pagesLithium Recovery From Artificial Brine Using Energyefficient Membrane Distillation and Nanofiltration2020Journal of Membrane ScienceYesid Tapiero MartínezNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) Butadiene: Product IdentificationDocument4 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) Butadiene: Product IdentificationRia AprianiNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument6 pagesLab ReportElise LeongNo ratings yet
- Potassium Chloride: Alkali Metals Production (Li, Na, K)Document15 pagesPotassium Chloride: Alkali Metals Production (Li, Na, K)Nurul RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Chapter 4Document37 pagesChemical Reaction Chapter 4Portia A. EgkenNo ratings yet
- Dpps ElectroDocument14 pagesDpps ElectroVanshika MiglaniNo ratings yet
- 156Document12 pages156Jorge Armando Carlos SixtoNo ratings yet
- An Introduction GPC - AgilentDocument32 pagesAn Introduction GPC - AgilentelenitabastosNo ratings yet
- Kinetics - Edexcel A Level ChemistryDocument4 pagesKinetics - Edexcel A Level ChemistryMaddie BaughNo ratings yet
- Biophotonics Concepts To Applications, 2nd - 9811934819 - CompressedDocument409 pagesBiophotonics Concepts To Applications, 2nd - 9811934819 - CompressedManci PeterNo ratings yet
- AbsorptionDocument54 pagesAbsorptionBebo El MasryNo ratings yet
- Heat Exercise 16 AugDocument4 pagesHeat Exercise 16 AugAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Lec 4B - Enviro Chem Anal2 - ModDocument14 pagesLec 4B - Enviro Chem Anal2 - ModBuTter ScoTch100% (1)
- GTFC QueDocument13 pagesGTFC QueAjal Shajahan100% (1)
- PreosDocument15 pagesPreosRitesh Dev MaityNo ratings yet
- 1463486214physical ChemistryDocument4 pages1463486214physical ChemistryShilp ShahNo ratings yet
- Exercise Grade 7Document3 pagesExercise Grade 7dekagielNo ratings yet
- Psychrometry ProblemsDocument33 pagesPsychrometry Problems19R21A0334 MATTA SHASHANKNo ratings yet
- E681-09 (2015) Standard Test Method For Concentration Limits of Flammability of Chemicals (Vapors and Gases)Document12 pagesE681-09 (2015) Standard Test Method For Concentration Limits of Flammability of Chemicals (Vapors and Gases)MohamedNo ratings yet