Professional Documents
Culture Documents
On Implementation of RTI Act 2005: Government's Initiatives: Department of Personnel and Training November 4, 2008, Delhi
On Implementation of RTI Act 2005: Government's Initiatives: Department of Personnel and Training November 4, 2008, Delhi
Uploaded by
Parulekar SonaliCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Mekb Module 13Document31 pagesMekb Module 13hs_hrmNo ratings yet
- Step 7Document9 pagesStep 7Abu Yussif AlaboodiNo ratings yet
- Erik L Walter, Lake County ESC CandidateDocument2 pagesErik L Walter, Lake County ESC CandidateThe News-HeraldNo ratings yet
- MGM Sjmsom Iitb RtiDocument16 pagesMGM Sjmsom Iitb RtiViz PrezNo ratings yet
- State Advisory Panel & Interagency Coordinating Council: Results Driven AccountabilityDocument24 pagesState Advisory Panel & Interagency Coordinating Council: Results Driven AccountabilityterryboothNo ratings yet
- India RTIDocument3 pagesIndia RTIMahesh PatidarNo ratings yet
- RTI Methodology PWC DOPTDocument24 pagesRTI Methodology PWC DOPTrtiNo ratings yet
- Session 9 - Presentation - MONITORING REPORT FOR THE OECD COUNCIL - Jon Blondal (OECD)Document6 pagesSession 9 - Presentation - MONITORING REPORT FOR THE OECD COUNCIL - Jon Blondal (OECD)untukduniamayaNo ratings yet
- ESAMI - Budget TrackingDocument34 pagesESAMI - Budget TrackingRonnie WilliamNo ratings yet
- Auditor General: Case Study at Ethiopian Public SectorsDocument6 pagesAuditor General: Case Study at Ethiopian Public SectorsGizaw KebedeNo ratings yet
- Final Report: Workforce Training Needs Analysis Project HRDC Contract U780193Document10 pagesFinal Report: Workforce Training Needs Analysis Project HRDC Contract U780193ArohilaNo ratings yet
- ICODECON 2018 - Odysseas KopsidasDocument36 pagesICODECON 2018 - Odysseas KopsidasAnonymous YnuwUEfNo ratings yet
- Conducting Surveys: Office of The Auditor General of CanadaDocument46 pagesConducting Surveys: Office of The Auditor General of CanadaalcarNo ratings yet
- Result Based M&EDocument20 pagesResult Based M&EMutaawe MMarkNo ratings yet
- Performance Audit Methods and Examples 091115 - For AESDocument38 pagesPerformance Audit Methods and Examples 091115 - For AESجعلاب سميرNo ratings yet
- Supreme Audit Institution Performance Measurement Framework (SAI PMF)Document39 pagesSupreme Audit Institution Performance Measurement Framework (SAI PMF)International Consortium on Governmental Financial Management100% (1)
- Presentation1 of Public Sector ManagementDocument25 pagesPresentation1 of Public Sector ManagementZahid UsmanNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Communication For DevelopmentDocument21 pagesEvaluating Communication For DevelopmentAikoGonzalesCastroNo ratings yet
- Implementation ManualDocument69 pagesImplementation Manualخاک نشینNo ratings yet
- Day 1 RMNCH EthiopiaDocument11 pagesDay 1 RMNCH EthiopiaOmer HussenNo ratings yet
- Dilla University (Only For Presentation)Document35 pagesDilla University (Only For Presentation)Habtamu WondyifrawNo ratings yet
- Putting Data To Work Brief 11-10Document16 pagesPutting Data To Work Brief 11-10Valerie F. LeonardNo ratings yet
- Citizen Satisfaction Survey Overview ReportDocument29 pagesCitizen Satisfaction Survey Overview ReportGladys LunaNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument20 pagesNotessatyam2800rNo ratings yet
- Information Systems PlanningDocument10 pagesInformation Systems PlanningRachit Puri100% (4)
- NORDC Progress ReportDocument9 pagesNORDC Progress ReportAdvocateOnlineNo ratings yet
- Stat 226 - Chapter 1 & 2Document20 pagesStat 226 - Chapter 1 & 2Owusu Pearl KakrabaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Compliance: Making The Pieces FitDocument3 pagesModule 1 Compliance: Making The Pieces FitBlaire NelsonNo ratings yet
- Ifsp OutcomesintegrationworksheetDocument4 pagesIfsp Outcomesintegrationworksheetapi-286077776No ratings yet
- M3.1 PPTCitizen's CharterDocument11 pagesM3.1 PPTCitizen's Charterutkarsh100% (1)
- Lecture 10 - E-Government Case StudiesDocument9 pagesLecture 10 - E-Government Case StudiesPraise NehumambiNo ratings yet
- White Internal Control SystemsDocument16 pagesWhite Internal Control SystemsAlexandru VasileNo ratings yet
- PEFA Better Understanding Trends - Wescott - EnGDocument12 pagesPEFA Better Understanding Trends - Wescott - EnGInternational Consortium on Governmental Financial ManagementNo ratings yet
- Transparency of The Ministry of Internal AffairsDocument44 pagesTransparency of The Ministry of Internal AffairsTIGeorgiaNo ratings yet
- Launch of UNICEF Reports On Birth Registration: Main Findings and Programmatic ImplicationsDocument36 pagesLaunch of UNICEF Reports On Birth Registration: Main Findings and Programmatic ImplicationsRahul RajpalNo ratings yet
- Questionsaboutocrreport 1Document1 pageQuestionsaboutocrreport 1api-341428932No ratings yet
- Comprehensive M&E Systems: Identifying Resources To Support Monitoring & Evaluation Plans For National TB ProgramsDocument18 pagesComprehensive M&E Systems: Identifying Resources To Support Monitoring & Evaluation Plans For National TB ProgramsMariam JahanzebNo ratings yet
- Programme Evaluation in IndiaDocument26 pagesProgramme Evaluation in Indiabob10012001No ratings yet
- E-Recruitment: The Revolution in How We Find TalentDocument31 pagesE-Recruitment: The Revolution in How We Find TalentRagini SinghNo ratings yet
- Public Policy and Program Implementation: Introduction To Public AdministrationDocument11 pagesPublic Policy and Program Implementation: Introduction To Public Administrationbull jackNo ratings yet
- A Study On Customer Satisfaction of Airtel in Sankarankovil TalukDocument62 pagesA Study On Customer Satisfaction of Airtel in Sankarankovil TalukAish WaryaNo ratings yet
- Monitoring & EvaluationDocument12 pagesMonitoring & Evaluationmbiwott100% (1)
- Deciding What To Monitor and Evaluate: SectionDocument36 pagesDeciding What To Monitor and Evaluate: SectionbqdianzNo ratings yet
- State Advisory Panel & Interagency Coordinating Council: Involvement in OSEP's SPP/APR ProcessDocument23 pagesState Advisory Panel & Interagency Coordinating Council: Involvement in OSEP's SPP/APR ProcessterryboothNo ratings yet
- Research Proposa1Document3 pagesResearch Proposa1Nida MusheerNo ratings yet
- Mca-Assignment Presentation: Presented by Shahid MoosaDocument11 pagesMca-Assignment Presentation: Presented by Shahid MoosaShahid MoosaNo ratings yet
- Ocsd Sis AuditDocument26 pagesOcsd Sis AuditKurt W. WanfriedNo ratings yet
- Brief On Use of Administrative Data For Statistical Purposes5Document7 pagesBrief On Use of Administrative Data For Statistical Purposes5ahmad ragabNo ratings yet
- UFRTI Survey ResultsDocument4 pagesUFRTI Survey ResultsRahul RamakrishnaNo ratings yet
- Role and Purpose of The EIA Review ProcessDocument8 pagesRole and Purpose of The EIA Review Processvishnu mohan (Vichu)No ratings yet
- Fernandez Power PointDocument18 pagesFernandez Power Pointbenueson237No ratings yet
- Master Thesis Presentation, Abdulai AminaDocument20 pagesMaster Thesis Presentation, Abdulai AminaZak StoophNo ratings yet
- 3 Basics of Economy 3pdf Lyst1044Document29 pages3 Basics of Economy 3pdf Lyst1044harshilkrishnamittapalliNo ratings yet
- 1 6 Essential Elements of A Proposal For Research FundingDocument28 pages1 6 Essential Elements of A Proposal For Research FundingNilanjana ChakrabartyNo ratings yet
- Kathryn NewcomerDocument19 pagesKathryn NewcomerEnvironmental Evaluators NetworkNo ratings yet
- AirtelDocument17 pagesAirtelVrinda SethiNo ratings yet
- Learning Management System Efficiency Versus Staff ProficiencyFrom EverandLearning Management System Efficiency Versus Staff ProficiencyNo ratings yet
- Tool Kit for Tax Administration Management Information SystemFrom EverandTool Kit for Tax Administration Management Information SystemRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- The QIAT Companion: A Just-in-Time Resource for Implementing the Quality Indicators for Assistive TechnologyFrom EverandThe QIAT Companion: A Just-in-Time Resource for Implementing the Quality Indicators for Assistive TechnologyNo ratings yet
- 1607HNP006Document1 page1607HNP006nextusnewsNo ratings yet
- Malacora vs. CA Case DigestDocument3 pagesMalacora vs. CA Case DigestCharmaine MejiaNo ratings yet
- Telecom Law SyllabusDocument4 pagesTelecom Law Syllabusrmbj94_scribdNo ratings yet
- Corporation Law PaperDocument5 pagesCorporation Law PaperNN DDLNo ratings yet
- USA Constitution Features (Plural Executive)Document4 pagesUSA Constitution Features (Plural Executive)mohammadnafisx666No ratings yet
- Religious Freedom Restoration ActDocument21 pagesReligious Freedom Restoration ActTeaPartyCheer100% (1)
- Disturbance of Public Order: Chapter FiveDocument2 pagesDisturbance of Public Order: Chapter FiveDessa Ruth ReyesNo ratings yet
- Aclu People Rackauckas 20180404 ComplaintDocument40 pagesAclu People Rackauckas 20180404 ComplaintAshley LudwigNo ratings yet
- Allotment of AgentsDocument4 pagesAllotment of AgentstsrajanNo ratings yet
- The End of American History Begins in AmericaDocument4 pagesThe End of American History Begins in AmericaHenry KormanNo ratings yet
- Ancog Vs Tan - Case DigestDocument1 pageAncog Vs Tan - Case DigestOnilyn MolinoNo ratings yet
- Campus Journalism Act of 1991Document9 pagesCampus Journalism Act of 1991Alexis Ailex Villamor Jr.No ratings yet
- Recommendations Were To File A Malversation, Graft and Other Criminal Cases Against HealthDocument2 pagesRecommendations Were To File A Malversation, Graft and Other Criminal Cases Against HealthJerico ManaloNo ratings yet
- Professor: Dr. Shivani Kapoor Name: Aditi AgrawalDocument5 pagesProfessor: Dr. Shivani Kapoor Name: Aditi AgrawalAditi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- UNITED STATES Vs VALERIO MENDIETADocument2 pagesUNITED STATES Vs VALERIO MENDIETAJoyleen HebronNo ratings yet
- A4 PDFDocument29 pagesA4 PDFAradhanaNo ratings yet
- Digest CivproDocument69 pagesDigest CivproRay PiñocoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Nature of International LawDocument23 pagesUnit 1 Nature of International LawChristine Mwambwa-Banda100% (1)
- Algonquin First Nations Press Release Aoo Aip Referendum 2015-06-15 FinalDocument2 pagesAlgonquin First Nations Press Release Aoo Aip Referendum 2015-06-15 FinalRussell DiaboNo ratings yet
- Asian ValuesDocument7 pagesAsian ValuesKateMcDougallNo ratings yet
- F1 2021-2022 L&S Final Term ExamDocument6 pagesF1 2021-2022 L&S Final Term ExamchloeNo ratings yet
- Sopanam E Magazine Vol 4 Issue 5Document38 pagesSopanam E Magazine Vol 4 Issue 5vbkuwaitNo ratings yet
- Maryland Inmate Search Department of Corrections LookupDocument6 pagesMaryland Inmate Search Department of Corrections LookupinmatesearchinfoNo ratings yet
- THE-ENEMY-WITHIN El Enemigo Interno Robert Kennedy en Ingles PDFDocument258 pagesTHE-ENEMY-WITHIN El Enemigo Interno Robert Kennedy en Ingles PDFAndyGarciaNo ratings yet
- Republic of Indonesia Vs VinzonDocument3 pagesRepublic of Indonesia Vs Vinzonrodel_odzNo ratings yet
- GAD Training DesignDocument4 pagesGAD Training DesignLucille TevesNo ratings yet
- Essay 2 CDocument7 pagesEssay 2 Csanjai_syamaprasadNo ratings yet
- Ord. 688 S 2010, 689 S 2010 Child Code & Gender CodeDocument40 pagesOrd. 688 S 2010, 689 S 2010 Child Code & Gender Codeeatshitmanuel100% (1)
- MDRRMC Reso No. 02-2019Document2 pagesMDRRMC Reso No. 02-2019Jorge MisajonNo ratings yet
On Implementation of RTI Act 2005: Government's Initiatives: Department of Personnel and Training November 4, 2008, Delhi
On Implementation of RTI Act 2005: Government's Initiatives: Department of Personnel and Training November 4, 2008, Delhi
Uploaded by
Parulekar SonaliOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
On Implementation of RTI Act 2005: Government's Initiatives: Department of Personnel and Training November 4, 2008, Delhi
On Implementation of RTI Act 2005: Government's Initiatives: Department of Personnel and Training November 4, 2008, Delhi
Uploaded by
Parulekar SonaliCopyright:
Available Formats
On implementation of RTI Act 2005: Governments initiatives
Department of Personnel and Training November 4, 2008, Delhi
RTI regime in India: facts
RTI Act 2005 operational since October 2005 Information Commissions at the central level as well as at the
state levels (except in J&K) are working
Capacity building of different stakeholders on RTI is in
progress since December 2005
GOI has drawn up program for smooth implementation of the
RTI Act, during 11th Five Year Plans
<footer> Slide 2
RTI Act 2005: looking back to see ahead
Government of India Recognizes the need to remove constraints in early implementation of the RTI Act Is keen to ensure that intended benefits out of RTI regime go to the citizens Wants to know the factors ( institutional, structural, systemic, process related, analytical, etc), that facilitate or hinders implementation of the Act. Launched study on RTI captioned Understanding key issues and constraints in effective implementation of the RTI Act during 2008-09 through an independent agency
Slide 3
<footer>
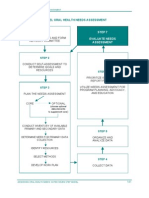
Scope of the Study
Approach and Methodology
Participative Approach to the whole study involving NGOs, CBOs, and Media
Assessment of the current situation
Recommend Changes based on the assessment
Prepare an Implementation Plan
Three Workshops to identify issues and validate the findings
Two Workshops/FGD to discuss the recommendations and Implementation plan
Information Seeker Survey
in five states and central Ministries
Information Provider
Identification of Process
Prepare a detailed action
Gaps based on survey results, observations and case studies
Recommend changes to
plan for implementation of the proposed changes
Survey in five states and Central Ministries
RTI Case Studies RTI successful Practices
plug process gaps
Build in successful
from States
International Benchmarking
with Canada and Mexico
Design of State of
practices into the process
Capacity gaps Infrastructure gaps
Implementation Matrix Design of Issue Identification Framework
Slide 5
Findings of the Study Status on Key Enablers
Key Findings: Compliance
Limited SIC reviews
Out of 5 States, only Andhra Pradesh has established a mechanism for regular review of Public Authorities for RTI Implementation
Low disposal rate of 2nd appeals
79.4% of the appeals received in Maharashtra in 2007 are still pending
Guidelines for Information Providers and Seekers have not been widely disseminated It was observed during one on one discussions with the PIOs that in Assam that they needed comprehensive guidelines for RTI request processing especially related to rejection clauses of the act
Slide 7
Findings: Information Disclosure
PIOs are not aware of the Proactive Disclosure done by their department
77% of the Central PIOs were found to be aware 84% of the PIOs in Andhra Pradesh were found to be aware Only 47% PIOs aware in Maharashtra
SIC reports do not contain the status of Proactive Disclosures done by Public
Authorities Out of the 5 States being surveyed, only 2 states (Assam and Andhra Pradesh) SIC reports show the status of proactive disclosure done
There is no monitoring mechanism for Proactive Disclosure in the 4 states
Andhra Pradesh has formed a committee for review of proactive disclosures done by the PAs in the state
Slide 8
Findings: Information Disclosure
Lack of standard dissemination channels for proactive disclosure
Central PAs were found to use internet for dissemination (93.75%) Majority of PAs in Assam used Printed Books for dissemination (83%)
Information Needs of citizens not being captured to improve Proactive
Disclosure None of the PAs in surveyed states have made an effort to capture information needs and reflect them in their Proactive Disclosures
Central and State schemes do not contain RTI specific guidelines for
proactive information disclosure
Slide 9
Findings: Capacity Building
Lack of budget provisions for RTI Implementation at the state
No separate RTI budget provision at state level Budget allocation only for SIC and Training (All four states surveyed)
Ineffective Record Management Systems
Record Management System being cited as the major reason for delay in processing of RTI application (Above 80% in Andhra Pradesh, Assam and Maharashtra)
Low levels of Training among PIOs and AAs 46% PIOs at Central level, 72% PIOs in Assam and 50% of PIOs in Andhra Pradesh have not received training
Slide 10
Key Findings of the Study Challenges faced by Citizen Applicant Side of the Story
Key Findings: Easy Access to Information
Lack of a signage for PIO identification and location at the PA
59% of the respondents said that there was no or little signage present at the PA office for locating the PIO
Lack of easy channel for Information request filing
85% of the respondents said that they had filed their application at the PA office would have preferred more convenient channel
Non standard payment channels for application fee submission Use of treasury challans and court fee stamps inconveniencing the information seekers Also in some cases, used as a means to discourage filing of applications
Slide 12
Key Findings: Easy Access to Information
Multiple visits to the PA office for filing RTI Applications
More than 33% of the respondents said that they had to visit the PA office multiple times for filing a RTI Application Cost of filing an RTI application is estimated at Rs. 150-300 in Urban Areas and Rs. 100-200 in rural areas (Estimates collected, includes cost of lost wages)
PIO attitude when filing a RTI Application
54% of the respondents surveyed said the PIOs has apathetic attitude towards their RTI request Incomplete and incorrect information being provided by the PIOs This was identified as the major reason for dissatisfaction among Information seekers
Lack of Knowledge about RTI among citizens
More than 50% of the respondents surveyed said that they could ask for information about Private enterprises under RTI Act
Slide 13
Key Findings of the Study Challenges faced by Government Staff Other Side of the Story
Identification of Challenges in Government Set-up
State of Implementation Matrix
Objectives
Enabling Strategies Gap Areas
Slide 15
State of Implementation Matrix
State of Implementation being designed to capture objective implementation data from the states. In current situation due non availability of standard data points from across the states, it is difficult to build in qualitative factors into the matrix. Due to the fact that qualitative factors have not been built in, the matrix cannot be used to measure the implementation performance across the states It can only be used as a guiding tool for ascertaining the implementation progress in a particular state over a period of time.
Slide 16
Immediate future Agenda
Acting upon recommendations of various studies Facilitating easy access to information Strengthening Information Commissions Capacity building Awareness on RTI
Thank You
You might also like
- Mekb Module 13Document31 pagesMekb Module 13hs_hrmNo ratings yet
- Step 7Document9 pagesStep 7Abu Yussif AlaboodiNo ratings yet
- Erik L Walter, Lake County ESC CandidateDocument2 pagesErik L Walter, Lake County ESC CandidateThe News-HeraldNo ratings yet
- MGM Sjmsom Iitb RtiDocument16 pagesMGM Sjmsom Iitb RtiViz PrezNo ratings yet
- State Advisory Panel & Interagency Coordinating Council: Results Driven AccountabilityDocument24 pagesState Advisory Panel & Interagency Coordinating Council: Results Driven AccountabilityterryboothNo ratings yet
- India RTIDocument3 pagesIndia RTIMahesh PatidarNo ratings yet
- RTI Methodology PWC DOPTDocument24 pagesRTI Methodology PWC DOPTrtiNo ratings yet
- Session 9 - Presentation - MONITORING REPORT FOR THE OECD COUNCIL - Jon Blondal (OECD)Document6 pagesSession 9 - Presentation - MONITORING REPORT FOR THE OECD COUNCIL - Jon Blondal (OECD)untukduniamayaNo ratings yet
- ESAMI - Budget TrackingDocument34 pagesESAMI - Budget TrackingRonnie WilliamNo ratings yet
- Auditor General: Case Study at Ethiopian Public SectorsDocument6 pagesAuditor General: Case Study at Ethiopian Public SectorsGizaw KebedeNo ratings yet
- Final Report: Workforce Training Needs Analysis Project HRDC Contract U780193Document10 pagesFinal Report: Workforce Training Needs Analysis Project HRDC Contract U780193ArohilaNo ratings yet
- ICODECON 2018 - Odysseas KopsidasDocument36 pagesICODECON 2018 - Odysseas KopsidasAnonymous YnuwUEfNo ratings yet
- Conducting Surveys: Office of The Auditor General of CanadaDocument46 pagesConducting Surveys: Office of The Auditor General of CanadaalcarNo ratings yet
- Result Based M&EDocument20 pagesResult Based M&EMutaawe MMarkNo ratings yet
- Performance Audit Methods and Examples 091115 - For AESDocument38 pagesPerformance Audit Methods and Examples 091115 - For AESجعلاب سميرNo ratings yet
- Supreme Audit Institution Performance Measurement Framework (SAI PMF)Document39 pagesSupreme Audit Institution Performance Measurement Framework (SAI PMF)International Consortium on Governmental Financial Management100% (1)
- Presentation1 of Public Sector ManagementDocument25 pagesPresentation1 of Public Sector ManagementZahid UsmanNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Communication For DevelopmentDocument21 pagesEvaluating Communication For DevelopmentAikoGonzalesCastroNo ratings yet
- Implementation ManualDocument69 pagesImplementation Manualخاک نشینNo ratings yet
- Day 1 RMNCH EthiopiaDocument11 pagesDay 1 RMNCH EthiopiaOmer HussenNo ratings yet
- Dilla University (Only For Presentation)Document35 pagesDilla University (Only For Presentation)Habtamu WondyifrawNo ratings yet
- Putting Data To Work Brief 11-10Document16 pagesPutting Data To Work Brief 11-10Valerie F. LeonardNo ratings yet
- Citizen Satisfaction Survey Overview ReportDocument29 pagesCitizen Satisfaction Survey Overview ReportGladys LunaNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument20 pagesNotessatyam2800rNo ratings yet
- Information Systems PlanningDocument10 pagesInformation Systems PlanningRachit Puri100% (4)
- NORDC Progress ReportDocument9 pagesNORDC Progress ReportAdvocateOnlineNo ratings yet
- Stat 226 - Chapter 1 & 2Document20 pagesStat 226 - Chapter 1 & 2Owusu Pearl KakrabaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Compliance: Making The Pieces FitDocument3 pagesModule 1 Compliance: Making The Pieces FitBlaire NelsonNo ratings yet
- Ifsp OutcomesintegrationworksheetDocument4 pagesIfsp Outcomesintegrationworksheetapi-286077776No ratings yet
- M3.1 PPTCitizen's CharterDocument11 pagesM3.1 PPTCitizen's Charterutkarsh100% (1)
- Lecture 10 - E-Government Case StudiesDocument9 pagesLecture 10 - E-Government Case StudiesPraise NehumambiNo ratings yet
- White Internal Control SystemsDocument16 pagesWhite Internal Control SystemsAlexandru VasileNo ratings yet
- PEFA Better Understanding Trends - Wescott - EnGDocument12 pagesPEFA Better Understanding Trends - Wescott - EnGInternational Consortium on Governmental Financial ManagementNo ratings yet
- Transparency of The Ministry of Internal AffairsDocument44 pagesTransparency of The Ministry of Internal AffairsTIGeorgiaNo ratings yet
- Launch of UNICEF Reports On Birth Registration: Main Findings and Programmatic ImplicationsDocument36 pagesLaunch of UNICEF Reports On Birth Registration: Main Findings and Programmatic ImplicationsRahul RajpalNo ratings yet
- Questionsaboutocrreport 1Document1 pageQuestionsaboutocrreport 1api-341428932No ratings yet
- Comprehensive M&E Systems: Identifying Resources To Support Monitoring & Evaluation Plans For National TB ProgramsDocument18 pagesComprehensive M&E Systems: Identifying Resources To Support Monitoring & Evaluation Plans For National TB ProgramsMariam JahanzebNo ratings yet
- Programme Evaluation in IndiaDocument26 pagesProgramme Evaluation in Indiabob10012001No ratings yet
- E-Recruitment: The Revolution in How We Find TalentDocument31 pagesE-Recruitment: The Revolution in How We Find TalentRagini SinghNo ratings yet
- Public Policy and Program Implementation: Introduction To Public AdministrationDocument11 pagesPublic Policy and Program Implementation: Introduction To Public Administrationbull jackNo ratings yet
- A Study On Customer Satisfaction of Airtel in Sankarankovil TalukDocument62 pagesA Study On Customer Satisfaction of Airtel in Sankarankovil TalukAish WaryaNo ratings yet
- Monitoring & EvaluationDocument12 pagesMonitoring & Evaluationmbiwott100% (1)
- Deciding What To Monitor and Evaluate: SectionDocument36 pagesDeciding What To Monitor and Evaluate: SectionbqdianzNo ratings yet
- State Advisory Panel & Interagency Coordinating Council: Involvement in OSEP's SPP/APR ProcessDocument23 pagesState Advisory Panel & Interagency Coordinating Council: Involvement in OSEP's SPP/APR ProcessterryboothNo ratings yet
- Research Proposa1Document3 pagesResearch Proposa1Nida MusheerNo ratings yet
- Mca-Assignment Presentation: Presented by Shahid MoosaDocument11 pagesMca-Assignment Presentation: Presented by Shahid MoosaShahid MoosaNo ratings yet
- Ocsd Sis AuditDocument26 pagesOcsd Sis AuditKurt W. WanfriedNo ratings yet
- Brief On Use of Administrative Data For Statistical Purposes5Document7 pagesBrief On Use of Administrative Data For Statistical Purposes5ahmad ragabNo ratings yet
- UFRTI Survey ResultsDocument4 pagesUFRTI Survey ResultsRahul RamakrishnaNo ratings yet
- Role and Purpose of The EIA Review ProcessDocument8 pagesRole and Purpose of The EIA Review Processvishnu mohan (Vichu)No ratings yet
- Fernandez Power PointDocument18 pagesFernandez Power Pointbenueson237No ratings yet
- Master Thesis Presentation, Abdulai AminaDocument20 pagesMaster Thesis Presentation, Abdulai AminaZak StoophNo ratings yet
- 3 Basics of Economy 3pdf Lyst1044Document29 pages3 Basics of Economy 3pdf Lyst1044harshilkrishnamittapalliNo ratings yet
- 1 6 Essential Elements of A Proposal For Research FundingDocument28 pages1 6 Essential Elements of A Proposal For Research FundingNilanjana ChakrabartyNo ratings yet
- Kathryn NewcomerDocument19 pagesKathryn NewcomerEnvironmental Evaluators NetworkNo ratings yet
- AirtelDocument17 pagesAirtelVrinda SethiNo ratings yet
- Learning Management System Efficiency Versus Staff ProficiencyFrom EverandLearning Management System Efficiency Versus Staff ProficiencyNo ratings yet
- Tool Kit for Tax Administration Management Information SystemFrom EverandTool Kit for Tax Administration Management Information SystemRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- The QIAT Companion: A Just-in-Time Resource for Implementing the Quality Indicators for Assistive TechnologyFrom EverandThe QIAT Companion: A Just-in-Time Resource for Implementing the Quality Indicators for Assistive TechnologyNo ratings yet
- 1607HNP006Document1 page1607HNP006nextusnewsNo ratings yet
- Malacora vs. CA Case DigestDocument3 pagesMalacora vs. CA Case DigestCharmaine MejiaNo ratings yet
- Telecom Law SyllabusDocument4 pagesTelecom Law Syllabusrmbj94_scribdNo ratings yet
- Corporation Law PaperDocument5 pagesCorporation Law PaperNN DDLNo ratings yet
- USA Constitution Features (Plural Executive)Document4 pagesUSA Constitution Features (Plural Executive)mohammadnafisx666No ratings yet
- Religious Freedom Restoration ActDocument21 pagesReligious Freedom Restoration ActTeaPartyCheer100% (1)
- Disturbance of Public Order: Chapter FiveDocument2 pagesDisturbance of Public Order: Chapter FiveDessa Ruth ReyesNo ratings yet
- Aclu People Rackauckas 20180404 ComplaintDocument40 pagesAclu People Rackauckas 20180404 ComplaintAshley LudwigNo ratings yet
- Allotment of AgentsDocument4 pagesAllotment of AgentstsrajanNo ratings yet
- The End of American History Begins in AmericaDocument4 pagesThe End of American History Begins in AmericaHenry KormanNo ratings yet
- Ancog Vs Tan - Case DigestDocument1 pageAncog Vs Tan - Case DigestOnilyn MolinoNo ratings yet
- Campus Journalism Act of 1991Document9 pagesCampus Journalism Act of 1991Alexis Ailex Villamor Jr.No ratings yet
- Recommendations Were To File A Malversation, Graft and Other Criminal Cases Against HealthDocument2 pagesRecommendations Were To File A Malversation, Graft and Other Criminal Cases Against HealthJerico ManaloNo ratings yet
- Professor: Dr. Shivani Kapoor Name: Aditi AgrawalDocument5 pagesProfessor: Dr. Shivani Kapoor Name: Aditi AgrawalAditi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- UNITED STATES Vs VALERIO MENDIETADocument2 pagesUNITED STATES Vs VALERIO MENDIETAJoyleen HebronNo ratings yet
- A4 PDFDocument29 pagesA4 PDFAradhanaNo ratings yet
- Digest CivproDocument69 pagesDigest CivproRay PiñocoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Nature of International LawDocument23 pagesUnit 1 Nature of International LawChristine Mwambwa-Banda100% (1)
- Algonquin First Nations Press Release Aoo Aip Referendum 2015-06-15 FinalDocument2 pagesAlgonquin First Nations Press Release Aoo Aip Referendum 2015-06-15 FinalRussell DiaboNo ratings yet
- Asian ValuesDocument7 pagesAsian ValuesKateMcDougallNo ratings yet
- F1 2021-2022 L&S Final Term ExamDocument6 pagesF1 2021-2022 L&S Final Term ExamchloeNo ratings yet
- Sopanam E Magazine Vol 4 Issue 5Document38 pagesSopanam E Magazine Vol 4 Issue 5vbkuwaitNo ratings yet
- Maryland Inmate Search Department of Corrections LookupDocument6 pagesMaryland Inmate Search Department of Corrections LookupinmatesearchinfoNo ratings yet
- THE-ENEMY-WITHIN El Enemigo Interno Robert Kennedy en Ingles PDFDocument258 pagesTHE-ENEMY-WITHIN El Enemigo Interno Robert Kennedy en Ingles PDFAndyGarciaNo ratings yet
- Republic of Indonesia Vs VinzonDocument3 pagesRepublic of Indonesia Vs Vinzonrodel_odzNo ratings yet
- GAD Training DesignDocument4 pagesGAD Training DesignLucille TevesNo ratings yet
- Essay 2 CDocument7 pagesEssay 2 Csanjai_syamaprasadNo ratings yet
- Ord. 688 S 2010, 689 S 2010 Child Code & Gender CodeDocument40 pagesOrd. 688 S 2010, 689 S 2010 Child Code & Gender Codeeatshitmanuel100% (1)
- MDRRMC Reso No. 02-2019Document2 pagesMDRRMC Reso No. 02-2019Jorge MisajonNo ratings yet