Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 viewsActivity 1 - Malubag
Activity 1 - Malubag
Uploaded by
Raxelle MalubagThe Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (BSP) is the central bank of the Philippines. It was established in 1993 to replace the Central Bank of the Philippines. The BSP is responsible for monetary policy and oversees the country's banking system. The banking system includes private banks like commercial banks, thrift banks, and rural banks. It also includes government banks like the Development Bank of the Philippines and Land Bank of the Philippines. Non-bank financial institutions provide banking services without a banking license and include entities like investment houses, financing companies, securities dealers, and insurance companies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Notes On The Revised Corporation CodeDocument34 pagesNotes On The Revised Corporation CodeZuleira Parra100% (10)
- Ch. 8 Financing A BusinessDocument6 pagesCh. 8 Financing A BusinessHANNAH GODBEHERE100% (1)
- A Project Report On Companies Act 2013Document69 pagesA Project Report On Companies Act 2013Bibhuti bhusan maharana63% (8)
- PWC Ifrs Us Gaap Similarities and Differences PDFDocument238 pagesPWC Ifrs Us Gaap Similarities and Differences PDFMu'tashim Al Qoyyim100% (1)
- CHAPTER 2 Financial MarketsDocument17 pagesCHAPTER 2 Financial MarketsAEHYUN YENVYNo ratings yet
- Structure of The Philippine Financial SystemDocument6 pagesStructure of The Philippine Financial SystemJaycel anne ManiboNo ratings yet
- PART I Upload AddendumDocument3 pagesPART I Upload AddendumKaren joy BajoNo ratings yet
- Business Finance PrelimDocument2 pagesBusiness Finance PrelimYna PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Fin MGMT ReportDocument1 pageFin MGMT ReportJERRALYN ALVANo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 and 4Document33 pagesLecture 3 and 4Wei WeiNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets - Chapter 2Document4 pagesFinancial Markets - Chapter 2Jarabata Lai SalveNo ratings yet
- Management of Financial Institutions - BNK604 Power Point Slides Lecture 02Document35 pagesManagement of Financial Institutions - BNK604 Power Point Slides Lecture 02suma100% (5)
- FMI Class - Chap 2Document29 pagesFMI Class - Chap 2ruman mahmoodNo ratings yet
- NBFI'sDocument31 pagesNBFI'sMuhammad Shabahat AhmadNo ratings yet
- AE 18 Financial Market Prelim ExamDocument3 pagesAE 18 Financial Market Prelim ExamWenjunNo ratings yet
- Financial and Regulatory Institutions: Assignment No. 2Document12 pagesFinancial and Regulatory Institutions: Assignment No. 2Saad MajeedNo ratings yet
- FMI - Chap 2Document35 pagesFMI - Chap 2alioNo ratings yet
- Financial Institution MarketDocument20 pagesFinancial Institution MarketryanNo ratings yet
- Financial Intermediaries and Players Philippines Financial Intermediaries and PlayersDocument9 pagesFinancial Intermediaries and Players Philippines Financial Intermediaries and PlayersLeo-Alyssa Gregorio-CorporalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 in Financial MarketDocument16 pagesChapter 6 in Financial MarketMariel RascoNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 - M2 WRDocument8 pagesChap 1 - M2 WRClover JeonNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Cap MarketDocument8 pagesChapter Three Cap MarketpsychowriterrrrrNo ratings yet
- Local Media6085112185595323389Document2 pagesLocal Media6085112185595323389Frecilla SanchezNo ratings yet
- Management of Financial Institutions - BNK604 Power Point Slides Lecture 02Document31 pagesManagement of Financial Institutions - BNK604 Power Point Slides Lecture 02aimanbatool24No ratings yet
- Business Finance Q3 Module 5.Document13 pagesBusiness Finance Q3 Module 5.alishareixdxdNo ratings yet
- Capital Markets Module 1 ReviewerDocument5 pagesCapital Markets Module 1 RevieweritsthlhzlNo ratings yet
- Brown Creative Company Profile Presentation 3Document20 pagesBrown Creative Company Profile Presentation 3Florence Joy AbkilanNo ratings yet
- Financial InstitutionsDocument17 pagesFinancial InstitutionsNuahs MagahatNo ratings yet
- Financial InsitutionsDocument14 pagesFinancial Insitutionscatprep2023No ratings yet
- Ch. 1 Introduction To Financial InstitutionsDocument35 pagesCh. 1 Introduction To Financial Institutionsteshome dagne100% (4)
- Chapter 5 and 6 Financial SystemDocument7 pagesChapter 5 and 6 Financial SystemRemar22No ratings yet
- Philippine Banking SystemDocument9 pagesPhilippine Banking SystemJungkookie Bae100% (3)
- Finance 7 Part 4Document26 pagesFinance 7 Part 4Alyssa AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Business Math NotesDocument14 pagesBusiness Math NotesBeatrice Anne CanapiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Banks & Other Financial Intermediaries: 19 PersonsDocument4 pagesChapter 1 - Banks & Other Financial Intermediaries: 19 PersonsMary.Rose RosalesNo ratings yet
- Notes Inc Module 2Document6 pagesNotes Inc Module 2Euneze LucasNo ratings yet
- Handouts in BusfinDocument2 pagesHandouts in BusfinAimelenne Jay AninionNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Self AssessmentDocument2 pagesLesson 2 Self AssessmentRimuruNo ratings yet
- Special Financial InstitutionsDocument11 pagesSpecial Financial InstitutionsSenelwa Anaya100% (3)
- Financial InstitutionsDocument2 pagesFinancial InstitutionsWilsonNo ratings yet
- BFI Topic 1 2 3Document17 pagesBFI Topic 1 2 3Arnold LuayonNo ratings yet
- FINANCE SYSTEM ReviewerDocument2 pagesFINANCE SYSTEM ReviewerChen-chen NecesarioNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions (Coleen) : Term Funds For The Economy. These Institutions Provide A Variety of FinancialDocument4 pagesFinancial Institutions (Coleen) : Term Funds For The Economy. These Institutions Provide A Variety of Financialsheinamae quelnatNo ratings yet
- PFM AnswersDocument48 pagesPFM Answershinowal388No ratings yet
- Non-Bank Financial InstitutionsDocument11 pagesNon-Bank Financial InstitutionsCristineNo ratings yet
- Branches of Finance: Financial Markets & Financial InstitutionsDocument6 pagesBranches of Finance: Financial Markets & Financial InstitutionsBernadette D. PagulayanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document16 pagesUnit 1Shivam YadavNo ratings yet
- Ch. 1 Introduction To Financial InstitutionsDocument45 pagesCh. 1 Introduction To Financial InstitutionsSofoniyas GashawNo ratings yet
- Financial InstitutionsDocument76 pagesFinancial InstitutionsGaurav Rathaur100% (1)
- Banking and Financial Institution 1ST Term MT ReviewerDocument16 pagesBanking and Financial Institution 1ST Term MT ReviewerAly JoNo ratings yet
- Banking and Financial InstitutionDocument25 pagesBanking and Financial InstitutionAlgie PlondayaNo ratings yet
- Debre Markos Universty College of Post-Graduate Studies Department of Accounting and FinanceDocument14 pagesDebre Markos Universty College of Post-Graduate Studies Department of Accounting and FinanceMikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- Engaging Activity Unit 4 Financial InstitutionDocument2 pagesEngaging Activity Unit 4 Financial InstitutionMary Justine ManaloNo ratings yet
- Business Finance ReviewerDocument3 pagesBusiness Finance ReviewerEmelita abagatNo ratings yet
- 116 - English For Business - Unit 14. Banking-Text & HandoutDocument4 pages116 - English For Business - Unit 14. Banking-Text & Handoutana azarashviliNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document54 pagesChap 2Yeshiwork GirmaNo ratings yet
- Week 1-2 - BF (Revised)Document9 pagesWeek 1-2 - BF (Revised)ELLEN JOY PENIERONo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and InstitutionsDocument31 pagesFinancial Markets and Institutionsqueen estevesNo ratings yet
- Structure of Indian Financial SystemDocument24 pagesStructure of Indian Financial SystemRaj SodhaNo ratings yet
- Finance ReviewerDocument6 pagesFinance Reviewerlun3l1ght18No ratings yet
- Non Banking Financial InstitutionsDocument10 pagesNon Banking Financial InstitutionsPal MarfatiaNo ratings yet
- Private Banking InstitutionsDocument4 pagesPrivate Banking InstitutionsKristel FieldsNo ratings yet
- bstract-Thesis-Defense-Presentation 20240217 070252 0000Document15 pagesbstract-Thesis-Defense-Presentation 20240217 070252 0000roxanneestopaNo ratings yet
- 9-16-Excellent GrammarDocument4 pages9-16-Excellent GrammarRaxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Statement of The Problem-Mgt 406Document1 pageStatement of The Problem-Mgt 406Raxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Group 6-Film View-Scientism-Human FlourishingDocument2 pagesGroup 6-Film View-Scientism-Human FlourishingRaxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Opt From YtDocument14 pagesOpt From YtRaxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Nature's Number Synthesis-MALUBAG, RAXELLEDocument4 pagesNature's Number Synthesis-MALUBAG, RAXELLERaxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Decision CriteriaDocument2 pagesDecision CriteriaRaxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Contempo Reviewer 1Document9 pagesContempo Reviewer 1Raxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Part IV-Decision Criteria & Alternative Solutions-Negligence of EmployeesDocument3 pagesPart IV-Decision Criteria & Alternative Solutions-Negligence of EmployeesRaxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Flat World vs. Multi-DomesticDocument2 pagesFlat World vs. Multi-DomesticRaxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Activity About Functions, Relations and Binary OperationsDocument2 pagesActivity About Functions, Relations and Binary OperationsRaxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Semestral Project-Measures of DispersionDocument13 pagesSemestral Project-Measures of DispersionRaxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Problem AB CompanyDocument1 pageProblem AB CompanyRaxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Excellent GrammarDocument1 pageExcellent GrammarRaxelle Malubag67% (3)
- The Time Value of MoneyDocument18 pagesThe Time Value of MoneyRaxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- BIR Form ExplanationDocument8 pagesBIR Form ExplanationRaxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Employment ConditionDocument5 pagesEmployment ConditionRaxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Income Tax ReviewerDocument19 pagesIncome Tax ReviewerRaxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Continuation-NotesDocument3 pagesChapter 3 Continuation-NotesRaxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Financial MarketsDocument2 pagesFundamentals of Financial MarketsRaxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Leases, Debt and ValueDocument57 pagesLeases, Debt and ValueGaurav ThakurNo ratings yet
- Contents Gyan Ganga TallyDocument9 pagesContents Gyan Ganga Tallyaslam844No ratings yet
- Audit of Capital and ReservesDocument24 pagesAudit of Capital and Reserveseequals mcsquaredNo ratings yet
- FIN630 Short Notes For Lecture 23-45 by Humaira PDFDocument45 pagesFIN630 Short Notes For Lecture 23-45 by Humaira PDFsohaib shahidNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Mercantile Law - Bar Exams 2022Document9 pagesSyllabus - Mercantile Law - Bar Exams 2022NoemiNo ratings yet
- 2019 Level I Mock C (PM) QuestionsDocument21 pages2019 Level I Mock C (PM) QuestionsshNo ratings yet
- Final Copy of Conso FS - FEUDocument133 pagesFinal Copy of Conso FS - FEUjoachimjackNo ratings yet
- Sol. Man. - Chapter 6 - Business Transactions and Their AnalysisDocument18 pagesSol. Man. - Chapter 6 - Business Transactions and Their AnalysisAmie Jane MirandaNo ratings yet
- Rfbt102 CorpoDocument13 pagesRfbt102 CorpoNathalie GetinoNo ratings yet
- 4.a.b (MM) Monthly Fund Focus ListDocument13 pages4.a.b (MM) Monthly Fund Focus Listmark.qianNo ratings yet
- Takeover Handbook PDFDocument68 pagesTakeover Handbook PDFPhill NamaraNo ratings yet
- CFA Level III Mock Exam 2 June, 2018 Revision 1Document33 pagesCFA Level III Mock Exam 2 June, 2018 Revision 1Munkhbaatar SanjaasurenNo ratings yet
- BEC Study NotesDocument4 pagesBEC Study NotesCPA ChessNo ratings yet
- AF 316 - Audit of Financial Income ItemsDocument13 pagesAF 316 - Audit of Financial Income Itemsgregory georgeNo ratings yet
- Financial Management For EntrepreneursDocument40 pagesFinancial Management For EntrepreneursHerald TheHorrorNo ratings yet
- Matrimony IPODocument476 pagesMatrimony IPOvicr100No ratings yet
- From The Basel Iii Compliance Professionals Association (Biiicpa)Document4 pagesFrom The Basel Iii Compliance Professionals Association (Biiicpa)Vinay SonkhiyaNo ratings yet
- Fabm1 q3 Mod8 Postingtransactionsintheledger FinalDocument32 pagesFabm1 q3 Mod8 Postingtransactionsintheledger FinalAdonis Zoleta Aranillo33% (3)
- Kasambahay DeskDocument2 pagesKasambahay DeskJohn Gabriel Pascua RicaforNo ratings yet
- Working Capital Management and Profitability: A Study On Cement Industry in BangladeshDocument12 pagesWorking Capital Management and Profitability: A Study On Cement Industry in BangladeshSudip BaruaNo ratings yet
- Multinational Business Finance 12th Edition Slides Chapter 02Document36 pagesMultinational Business Finance 12th Edition Slides Chapter 02Alli TobbaNo ratings yet
- Format For Preparing Cash Flow Statement - Start With PBT: (4) Reclassify Interest Paid Under Financing Activities +Document2 pagesFormat For Preparing Cash Flow Statement - Start With PBT: (4) Reclassify Interest Paid Under Financing Activities +shidupk5 pkNo ratings yet
- Delta Beverage Group Inc. Case: Executive SummaryDocument5 pagesDelta Beverage Group Inc. Case: Executive SummaryTanisha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Handouts Updates: Reo Taxation: List of Changes by The Create LawDocument3 pagesHandouts Updates: Reo Taxation: List of Changes by The Create LawRandhel SorianoNo ratings yet
- Ex-08 - Comprehensive Review 2.0Document14 pagesEx-08 - Comprehensive Review 2.0Jedidiah Smith0% (1)
- CHKD FABM1 - Q3 - LA 22. Comprehensive Example Using T-AccountsDocument1 pageCHKD FABM1 - Q3 - LA 22. Comprehensive Example Using T-AccountsGladys Angela ValdemoroNo ratings yet
Activity 1 - Malubag
Activity 1 - Malubag
Uploaded by
Raxelle Malubag0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views4 pagesThe Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (BSP) is the central bank of the Philippines. It was established in 1993 to replace the Central Bank of the Philippines. The BSP is responsible for monetary policy and oversees the country's banking system. The banking system includes private banks like commercial banks, thrift banks, and rural banks. It also includes government banks like the Development Bank of the Philippines and Land Bank of the Philippines. Non-bank financial institutions provide banking services without a banking license and include entities like investment houses, financing companies, securities dealers, and insurance companies.
Original Description:
Original Title
Activity 1- Malubag
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (BSP) is the central bank of the Philippines. It was established in 1993 to replace the Central Bank of the Philippines. The BSP is responsible for monetary policy and oversees the country's banking system. The banking system includes private banks like commercial banks, thrift banks, and rural banks. It also includes government banks like the Development Bank of the Philippines and Land Bank of the Philippines. Non-bank financial institutions provide banking services without a banking license and include entities like investment houses, financing companies, securities dealers, and insurance companies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views4 pagesActivity 1 - Malubag
Activity 1 - Malubag
Uploaded by
Raxelle MalubagThe Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (BSP) is the central bank of the Philippines. It was established in 1993 to replace the Central Bank of the Philippines. The BSP is responsible for monetary policy and oversees the country's banking system. The banking system includes private banks like commercial banks, thrift banks, and rural banks. It also includes government banks like the Development Bank of the Philippines and Land Bank of the Philippines. Non-bank financial institutions provide banking services without a banking license and include entities like investment houses, financing companies, securities dealers, and insurance companies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
Malubag, Raxelle M.
BSA 4201
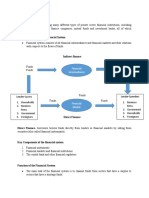
Activity 1 - STRUCTURE OF THE PHILIPPINES FINANCIAL SYSTEM
a. BANGKO SENTRAL NG PILIPINAS
The Republic of the Philippines' central bank is known as Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas
(BSP). In accordance with the 1987 Philippine Constitution's requirements and the
1993's New Central Bank Act, it was founded on July 3, 1993. The BSP replaced the
Central Bank of the Philippines, which had been in place since 3 January 1949 as the
nation's primary monetary authority. The BSP is free to carry out its prescribed duties
without interference from the National Government in terms of finances and
administration.
https://www.devex.com/organizations/bangko-sentral-ng-pilipinas-bsp-69634
b. BANKING INSTITUTIONS
An institution that deals with money and its alternatives as well as other financial
services. A bank lends money and accepts deposits as part of its function as a financial
middleman. It makes money from the difference between the money it spends on
acquiring and maintaining deposits (including interest payments) and the money it
makes from interest payments to borrowers or from securities. Numerous banks offer
related services like financial management as well as goods like credit cards and mutual
funds. Some bank liabilities act as money, or as universally recognized forms of trade
and payment. https://www.britannica.com/topic/bank
i. PRIVATE BANKING INSTITUTIONS
Private banking refers to the specialized financial services and goods that retail
banks and other financial institutions provide to their high-net-worth individual
(HNWI) customers. Numerous wealth management services are included, and they
are all offered under one roof. Services offered include trust and estate planning, tax
preparation, insurance, and investment and portfolio management.
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/p/privatebanking.asp
https://www.studocu.com/ph/document/university-of-la-salette/business-
administration/pcoa005-module-2-the-philippine-financial-system/24153618
Expanded Commercial Banks/ Universal Banks (EKB/UB)
- Is any commercial bank, which performs the investment house function in
addition to its commercial banking authority. It may invests in the equities
of allied and non-allied enterprises. Allied enterprises may either be
financial or non-financial.
Commercial Banks or Domestic Bank (KB)
- Is any commercial bank that is confined only to commercial bank
functions such as accepting drafts and issuing letters of credit,
discounting and negotiating promissory notes, drafts and bills of
exchange, and other evidence of debt, accepting or creating demand
deposits, receiving other types of deposits and deposit substitutes, buying
and selling foreign exchange, and gold or silver bullions, acquiring
marketable bonds and other debt securities, and extending credit subject
to such rules that the Monetary Board may promulgate.
Thrift Banks
- A financial services company that focuses on providing people with
savings accounts and mortgage loans is known as a thrift bank, or thrift.
Others are owned by stockholders, while some are mutually owned, or
owned by their depositors. https://bizfluent.com/info-7757218-meaning-
thrift-bank.html
-
o Savings and Mortgage Banks (SMB) - is any corporation organized for
the purpose of accumulating the savings of depositors and investing
them, together with its capital, in readily marketable bonds and debt
securities.
o Private Development Banks (PDB) – is a bank that exercises all the
powers and assume all the obligations of the savings and mortgage
bank as provided in the General Banking Act except as otherwise
stated
o Stock Savings and Loan Association (SSLA) – is any corporation
engaged in the business of accumulating the savings of its members
or stockholders and using such with its capital for loans and
investment in securities of productive enterprises.
Rural Banks- is any bank authorized by the Central Bank to accept deposits
and make credit available to farmers, businessmen and cottage industries in
the rural areas
Cooperative Banks- are banks established to assists the various cooperatives
by lending those funds at reasonable interest rates
ii. GOVERNMENT BANKING INSTITUTIONS
Development Bank of the Philippines (DBP) - provides loans for
developmental purposes, gives loans to the agricultural sector, commercial
sector and the industrial sector.
Land Bank of the Philippines (LBP) – Is a government bank, which provides
financial support in the implementation of the Agrarian Reform Program
(CARP) of the government.
Philippine Al-Amanah Islamic Investment Bank – R.A. No. 6048 provides for
the charter of the Al-Amanah Islamic Investment Bank which authorizes the
bank to promote and accelerate the socio-economic development of the
Autonomous Region of Muslim Mindanao by performing banking, financing
and investment operations.
c. NON-BANK FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS
Financial institutions that provide a range of banking services without a banking license
are referred to as nonbank financial businesses (NBFCs), often known as nonbank
financial institutions (NBFIs). Typically, the public's readily accessible monies, including
those in checking or savings accounts, cannot be accepted as demand deposits by
these organizations. This restriction keeps them out of the purview of traditional federal
and state financial regulator scrutiny. https://www.investopedia.com/terms/n/nbfcs.asp
i. PRIVATE NON-BANK FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS
Investment House- is any enterprise, which engages in underwriting
securities of other corporations. It also generates income from sale of
investments in securities
Investment Companies- they provide advice to firms issuing stocks and
bonds or considering mergers with other firms. They also engage in
underwriting in which they guarantee a price to a firm issuing stocks or
bonds and then make a profit by selling the stocks or bonds at a higher
price
Financing Companies – is any business enterprise where the primary
purpose is to extend credit to consumers and to industrial, commercial or
agricultural entities.
Securities dealers/brokers – any person or entity engaged in the business
of buying and selling securities for his own or its client’s account thereby
making profit from the difference between the purchase prices and selling
price of securities.
Non-stock savings and loan associations – traditionally served individual
savers and residential and commercial mortgage borrowers, accumulate
the funds of many small savers and then lend this money to home buyers
and other types of borrowers
Building and Loan Associations - Between the 1830s and the 1930s,
cooperatively owned financial organizations (FIs) called building and loan
associations (B&Ls) significantly extended the availability of home loans.
Participants pooled their funds under the auspices of "mutual self-help,"
typically inside small, regional B&Ls, and as a result qualified for
dividends and mortgages.
Pawnshops- refers to persons or entities engaged in the business of
lending money with personal property, jewelry and other durable goods
as collateral for the loans given.
Lending Investors – is any person or entity engaged in the business of
effecting securities transactions, giving loans and earns interest from
them.
Fund Managers- A fund manager is in charge of carrying out the fund's
investing plan and overseeing the trading of its portfolio. The fund may be
run by a sole management, two co-managers, or a group of three or more
people. A percentage of the average assets under management for the
fund is used as the fee that fund managers receive for their services
(AUM). They can be found managing money for hedge funds, mutual
funds, pension funds, and trust funds.
Trust Companies/departments - A trust firm is a business that represents
a person or organization as a fiduciary, agent, or trustee for the
administration, management, and eventual transfer of assets to a
benefitting party. For trusts, estates, custodial arrangements, asset
management, stock transfers, beneficial ownership registration, and other
associated arrangements, the trust firm serves as a custodian.
Insurance Companies - a financial entity that UNDERWRITES the risk of
loss or damage to real and personal property (general insurance), as well
as the danger to life and limb (life and accident insurance). While some
businesses only operate in one of these sectors, others—known as
"composites"—do business in both. Insurance firms issue insurance
policies to cover a number of contingencies (fire, water, breakage, theft,
death, etc.), involving possible financial loss to policy holders or their
dependants in return for regular payments of a premium. The way an
insurance business runs is by spreading out the risk among many
policyholders; premiums are determined by the likelihood that a specific
event will occur and the typical financial loss connected with it.
Venture Capital Corporations- This is funding for venture capital offered to
start-up businesses with a high potential for growth by large firms. A
segment of the total venture capital market, this sort of venture capital.
Usually, funding comes from the corporation's capital budget. These
corporate venture arms either invest in projects because they have a
strategic fit with their company or for financial gain.
ii. GOVERNMENT NON-BANK FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS
Government Service Insurance System (GSIS)- Provides retirement
benefits, housing loans,, personal loans, emergency and calamity loans
to government employees
Social Security Services (SSS) – provides retirement benefits, funeral
benefits, housing loans, personal loans and calamity loans to employees
who are working in private companies
Pag-ibig – provides housing loans to both government and private
employees.
You might also like
- Notes On The Revised Corporation CodeDocument34 pagesNotes On The Revised Corporation CodeZuleira Parra100% (10)
- Ch. 8 Financing A BusinessDocument6 pagesCh. 8 Financing A BusinessHANNAH GODBEHERE100% (1)
- A Project Report On Companies Act 2013Document69 pagesA Project Report On Companies Act 2013Bibhuti bhusan maharana63% (8)
- PWC Ifrs Us Gaap Similarities and Differences PDFDocument238 pagesPWC Ifrs Us Gaap Similarities and Differences PDFMu'tashim Al Qoyyim100% (1)
- CHAPTER 2 Financial MarketsDocument17 pagesCHAPTER 2 Financial MarketsAEHYUN YENVYNo ratings yet
- Structure of The Philippine Financial SystemDocument6 pagesStructure of The Philippine Financial SystemJaycel anne ManiboNo ratings yet
- PART I Upload AddendumDocument3 pagesPART I Upload AddendumKaren joy BajoNo ratings yet
- Business Finance PrelimDocument2 pagesBusiness Finance PrelimYna PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Fin MGMT ReportDocument1 pageFin MGMT ReportJERRALYN ALVANo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 and 4Document33 pagesLecture 3 and 4Wei WeiNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets - Chapter 2Document4 pagesFinancial Markets - Chapter 2Jarabata Lai SalveNo ratings yet
- Management of Financial Institutions - BNK604 Power Point Slides Lecture 02Document35 pagesManagement of Financial Institutions - BNK604 Power Point Slides Lecture 02suma100% (5)
- FMI Class - Chap 2Document29 pagesFMI Class - Chap 2ruman mahmoodNo ratings yet
- NBFI'sDocument31 pagesNBFI'sMuhammad Shabahat AhmadNo ratings yet
- AE 18 Financial Market Prelim ExamDocument3 pagesAE 18 Financial Market Prelim ExamWenjunNo ratings yet
- Financial and Regulatory Institutions: Assignment No. 2Document12 pagesFinancial and Regulatory Institutions: Assignment No. 2Saad MajeedNo ratings yet
- FMI - Chap 2Document35 pagesFMI - Chap 2alioNo ratings yet
- Financial Institution MarketDocument20 pagesFinancial Institution MarketryanNo ratings yet
- Financial Intermediaries and Players Philippines Financial Intermediaries and PlayersDocument9 pagesFinancial Intermediaries and Players Philippines Financial Intermediaries and PlayersLeo-Alyssa Gregorio-CorporalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 in Financial MarketDocument16 pagesChapter 6 in Financial MarketMariel RascoNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 - M2 WRDocument8 pagesChap 1 - M2 WRClover JeonNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Cap MarketDocument8 pagesChapter Three Cap MarketpsychowriterrrrrNo ratings yet
- Local Media6085112185595323389Document2 pagesLocal Media6085112185595323389Frecilla SanchezNo ratings yet
- Management of Financial Institutions - BNK604 Power Point Slides Lecture 02Document31 pagesManagement of Financial Institutions - BNK604 Power Point Slides Lecture 02aimanbatool24No ratings yet
- Business Finance Q3 Module 5.Document13 pagesBusiness Finance Q3 Module 5.alishareixdxdNo ratings yet
- Capital Markets Module 1 ReviewerDocument5 pagesCapital Markets Module 1 RevieweritsthlhzlNo ratings yet
- Brown Creative Company Profile Presentation 3Document20 pagesBrown Creative Company Profile Presentation 3Florence Joy AbkilanNo ratings yet
- Financial InstitutionsDocument17 pagesFinancial InstitutionsNuahs MagahatNo ratings yet
- Financial InsitutionsDocument14 pagesFinancial Insitutionscatprep2023No ratings yet
- Ch. 1 Introduction To Financial InstitutionsDocument35 pagesCh. 1 Introduction To Financial Institutionsteshome dagne100% (4)
- Chapter 5 and 6 Financial SystemDocument7 pagesChapter 5 and 6 Financial SystemRemar22No ratings yet
- Philippine Banking SystemDocument9 pagesPhilippine Banking SystemJungkookie Bae100% (3)
- Finance 7 Part 4Document26 pagesFinance 7 Part 4Alyssa AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Business Math NotesDocument14 pagesBusiness Math NotesBeatrice Anne CanapiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Banks & Other Financial Intermediaries: 19 PersonsDocument4 pagesChapter 1 - Banks & Other Financial Intermediaries: 19 PersonsMary.Rose RosalesNo ratings yet
- Notes Inc Module 2Document6 pagesNotes Inc Module 2Euneze LucasNo ratings yet
- Handouts in BusfinDocument2 pagesHandouts in BusfinAimelenne Jay AninionNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Self AssessmentDocument2 pagesLesson 2 Self AssessmentRimuruNo ratings yet
- Special Financial InstitutionsDocument11 pagesSpecial Financial InstitutionsSenelwa Anaya100% (3)
- Financial InstitutionsDocument2 pagesFinancial InstitutionsWilsonNo ratings yet
- BFI Topic 1 2 3Document17 pagesBFI Topic 1 2 3Arnold LuayonNo ratings yet
- FINANCE SYSTEM ReviewerDocument2 pagesFINANCE SYSTEM ReviewerChen-chen NecesarioNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions (Coleen) : Term Funds For The Economy. These Institutions Provide A Variety of FinancialDocument4 pagesFinancial Institutions (Coleen) : Term Funds For The Economy. These Institutions Provide A Variety of Financialsheinamae quelnatNo ratings yet
- PFM AnswersDocument48 pagesPFM Answershinowal388No ratings yet
- Non-Bank Financial InstitutionsDocument11 pagesNon-Bank Financial InstitutionsCristineNo ratings yet
- Branches of Finance: Financial Markets & Financial InstitutionsDocument6 pagesBranches of Finance: Financial Markets & Financial InstitutionsBernadette D. PagulayanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document16 pagesUnit 1Shivam YadavNo ratings yet
- Ch. 1 Introduction To Financial InstitutionsDocument45 pagesCh. 1 Introduction To Financial InstitutionsSofoniyas GashawNo ratings yet
- Financial InstitutionsDocument76 pagesFinancial InstitutionsGaurav Rathaur100% (1)
- Banking and Financial Institution 1ST Term MT ReviewerDocument16 pagesBanking and Financial Institution 1ST Term MT ReviewerAly JoNo ratings yet
- Banking and Financial InstitutionDocument25 pagesBanking and Financial InstitutionAlgie PlondayaNo ratings yet
- Debre Markos Universty College of Post-Graduate Studies Department of Accounting and FinanceDocument14 pagesDebre Markos Universty College of Post-Graduate Studies Department of Accounting and FinanceMikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- Engaging Activity Unit 4 Financial InstitutionDocument2 pagesEngaging Activity Unit 4 Financial InstitutionMary Justine ManaloNo ratings yet
- Business Finance ReviewerDocument3 pagesBusiness Finance ReviewerEmelita abagatNo ratings yet
- 116 - English For Business - Unit 14. Banking-Text & HandoutDocument4 pages116 - English For Business - Unit 14. Banking-Text & Handoutana azarashviliNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document54 pagesChap 2Yeshiwork GirmaNo ratings yet
- Week 1-2 - BF (Revised)Document9 pagesWeek 1-2 - BF (Revised)ELLEN JOY PENIERONo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and InstitutionsDocument31 pagesFinancial Markets and Institutionsqueen estevesNo ratings yet
- Structure of Indian Financial SystemDocument24 pagesStructure of Indian Financial SystemRaj SodhaNo ratings yet
- Finance ReviewerDocument6 pagesFinance Reviewerlun3l1ght18No ratings yet
- Non Banking Financial InstitutionsDocument10 pagesNon Banking Financial InstitutionsPal MarfatiaNo ratings yet
- Private Banking InstitutionsDocument4 pagesPrivate Banking InstitutionsKristel FieldsNo ratings yet
- bstract-Thesis-Defense-Presentation 20240217 070252 0000Document15 pagesbstract-Thesis-Defense-Presentation 20240217 070252 0000roxanneestopaNo ratings yet
- 9-16-Excellent GrammarDocument4 pages9-16-Excellent GrammarRaxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Statement of The Problem-Mgt 406Document1 pageStatement of The Problem-Mgt 406Raxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Group 6-Film View-Scientism-Human FlourishingDocument2 pagesGroup 6-Film View-Scientism-Human FlourishingRaxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Opt From YtDocument14 pagesOpt From YtRaxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Nature's Number Synthesis-MALUBAG, RAXELLEDocument4 pagesNature's Number Synthesis-MALUBAG, RAXELLERaxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Decision CriteriaDocument2 pagesDecision CriteriaRaxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Contempo Reviewer 1Document9 pagesContempo Reviewer 1Raxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Part IV-Decision Criteria & Alternative Solutions-Negligence of EmployeesDocument3 pagesPart IV-Decision Criteria & Alternative Solutions-Negligence of EmployeesRaxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Flat World vs. Multi-DomesticDocument2 pagesFlat World vs. Multi-DomesticRaxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Activity About Functions, Relations and Binary OperationsDocument2 pagesActivity About Functions, Relations and Binary OperationsRaxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Semestral Project-Measures of DispersionDocument13 pagesSemestral Project-Measures of DispersionRaxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Problem AB CompanyDocument1 pageProblem AB CompanyRaxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Excellent GrammarDocument1 pageExcellent GrammarRaxelle Malubag67% (3)
- The Time Value of MoneyDocument18 pagesThe Time Value of MoneyRaxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- BIR Form ExplanationDocument8 pagesBIR Form ExplanationRaxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Employment ConditionDocument5 pagesEmployment ConditionRaxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Income Tax ReviewerDocument19 pagesIncome Tax ReviewerRaxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Continuation-NotesDocument3 pagesChapter 3 Continuation-NotesRaxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Financial MarketsDocument2 pagesFundamentals of Financial MarketsRaxelle MalubagNo ratings yet
- Leases, Debt and ValueDocument57 pagesLeases, Debt and ValueGaurav ThakurNo ratings yet
- Contents Gyan Ganga TallyDocument9 pagesContents Gyan Ganga Tallyaslam844No ratings yet
- Audit of Capital and ReservesDocument24 pagesAudit of Capital and Reserveseequals mcsquaredNo ratings yet
- FIN630 Short Notes For Lecture 23-45 by Humaira PDFDocument45 pagesFIN630 Short Notes For Lecture 23-45 by Humaira PDFsohaib shahidNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Mercantile Law - Bar Exams 2022Document9 pagesSyllabus - Mercantile Law - Bar Exams 2022NoemiNo ratings yet
- 2019 Level I Mock C (PM) QuestionsDocument21 pages2019 Level I Mock C (PM) QuestionsshNo ratings yet
- Final Copy of Conso FS - FEUDocument133 pagesFinal Copy of Conso FS - FEUjoachimjackNo ratings yet
- Sol. Man. - Chapter 6 - Business Transactions and Their AnalysisDocument18 pagesSol. Man. - Chapter 6 - Business Transactions and Their AnalysisAmie Jane MirandaNo ratings yet
- Rfbt102 CorpoDocument13 pagesRfbt102 CorpoNathalie GetinoNo ratings yet
- 4.a.b (MM) Monthly Fund Focus ListDocument13 pages4.a.b (MM) Monthly Fund Focus Listmark.qianNo ratings yet
- Takeover Handbook PDFDocument68 pagesTakeover Handbook PDFPhill NamaraNo ratings yet
- CFA Level III Mock Exam 2 June, 2018 Revision 1Document33 pagesCFA Level III Mock Exam 2 June, 2018 Revision 1Munkhbaatar SanjaasurenNo ratings yet
- BEC Study NotesDocument4 pagesBEC Study NotesCPA ChessNo ratings yet
- AF 316 - Audit of Financial Income ItemsDocument13 pagesAF 316 - Audit of Financial Income Itemsgregory georgeNo ratings yet
- Financial Management For EntrepreneursDocument40 pagesFinancial Management For EntrepreneursHerald TheHorrorNo ratings yet
- Matrimony IPODocument476 pagesMatrimony IPOvicr100No ratings yet
- From The Basel Iii Compliance Professionals Association (Biiicpa)Document4 pagesFrom The Basel Iii Compliance Professionals Association (Biiicpa)Vinay SonkhiyaNo ratings yet
- Fabm1 q3 Mod8 Postingtransactionsintheledger FinalDocument32 pagesFabm1 q3 Mod8 Postingtransactionsintheledger FinalAdonis Zoleta Aranillo33% (3)
- Kasambahay DeskDocument2 pagesKasambahay DeskJohn Gabriel Pascua RicaforNo ratings yet
- Working Capital Management and Profitability: A Study On Cement Industry in BangladeshDocument12 pagesWorking Capital Management and Profitability: A Study On Cement Industry in BangladeshSudip BaruaNo ratings yet
- Multinational Business Finance 12th Edition Slides Chapter 02Document36 pagesMultinational Business Finance 12th Edition Slides Chapter 02Alli TobbaNo ratings yet
- Format For Preparing Cash Flow Statement - Start With PBT: (4) Reclassify Interest Paid Under Financing Activities +Document2 pagesFormat For Preparing Cash Flow Statement - Start With PBT: (4) Reclassify Interest Paid Under Financing Activities +shidupk5 pkNo ratings yet
- Delta Beverage Group Inc. Case: Executive SummaryDocument5 pagesDelta Beverage Group Inc. Case: Executive SummaryTanisha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Handouts Updates: Reo Taxation: List of Changes by The Create LawDocument3 pagesHandouts Updates: Reo Taxation: List of Changes by The Create LawRandhel SorianoNo ratings yet
- Ex-08 - Comprehensive Review 2.0Document14 pagesEx-08 - Comprehensive Review 2.0Jedidiah Smith0% (1)
- CHKD FABM1 - Q3 - LA 22. Comprehensive Example Using T-AccountsDocument1 pageCHKD FABM1 - Q3 - LA 22. Comprehensive Example Using T-AccountsGladys Angela ValdemoroNo ratings yet