Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Auca1 DLP Medical Surgical 3 Bito Adam Sealtiel Pasay
Auca1 DLP Medical Surgical 3 Bito Adam Sealtiel Pasay
Uploaded by
YoungbloodCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Anatomy Past Papers 2009-2019Document12 pagesAnatomy Past Papers 2009-2019Kashar SaeedNo ratings yet
- The Best Exercise You'Ve Never Heard ofDocument71 pagesThe Best Exercise You'Ve Never Heard ofDI HartmanNo ratings yet
- Arthritis MagazineDocument5 pagesArthritis MagazineAdrian Euan Gonzales RañaNo ratings yet
- Osce Orthopedic Year 4Document3 pagesOsce Orthopedic Year 4Mazia Nadia Khairudin100% (9)
- Osteoarthritis PDFDocument15 pagesOsteoarthritis PDFعبدالرحمن علىNo ratings yet
- Arthritis ProjectDocument17 pagesArthritis ProjectGaurishi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument10 pagesAnatomyapi-3845840No ratings yet
- Arthritis PDFDocument4 pagesArthritis PDFArchana MoreyNo ratings yet
- ArthritisDocument30 pagesArthritisprasherpratik1984No ratings yet
- Arthritis Joint Pain ReliefDocument14 pagesArthritis Joint Pain ReliefSam CookNo ratings yet
- By: Azela Marie Barba Tesha Mae UyDocument12 pagesBy: Azela Marie Barba Tesha Mae UyAzelaMarieJanagapBarbaNo ratings yet
- Blaylock Arthritis 25Document12 pagesBlaylock Arthritis 25mohanp71No ratings yet
- 1 OsteoarthritisDocument61 pages1 OsteoarthritisARYAN THAPANo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument10 pagesOsteoarthritisMogtaba M HilalNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Joint Disease Study GuideDocument18 pagesRheumatic Joint Disease Study Guidechalinsammy1No ratings yet
- Physiotherapy in Portage La Prairie and Emerald Park For FootDocument11 pagesPhysiotherapy in Portage La Prairie and Emerald Park For Footdrrabe3No ratings yet
- Radiological Imaging of Osteoarthritis.: DR/ Abd Allah Nazeer. MDDocument75 pagesRadiological Imaging of Osteoarthritis.: DR/ Abd Allah Nazeer. MDKarthickNo ratings yet
- CVEC Spring 2011Document8 pagesCVEC Spring 2011griffinjayNo ratings yet
- Knee Osteoarthritis PDFDocument4 pagesKnee Osteoarthritis PDFDhan Singh RathoreNo ratings yet
- Arthritis AdviceDocument8 pagesArthritis AdviceInternational Business TimesNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument3 pagesOsteoarthritisVanessa Da CruzNo ratings yet
- Joint DisordersDocument39 pagesJoint DisordersangelaNo ratings yet
- Chapter VI - Bone Pathology: Arthritis & GoutDocument4 pagesChapter VI - Bone Pathology: Arthritis & GoutIndranil SinhaNo ratings yet
- Common Causes of Severe Knee PainDocument8 pagesCommon Causes of Severe Knee PainRatnaPrasadNalamNo ratings yet
- Knee Arthritis - Johns HopkinsDocument4 pagesKnee Arthritis - Johns HopkinsCarmel HarelNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument5 pagesOsteoarthritisprincess0fdeathNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument8 pagesOsteoarthritisNianurmayanti983278No ratings yet
- PSN PresentationDocument14 pagesPSN PresentationJaysie Rose DionesNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument6 pagesOsteoarthritisKristine ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Submitted To DR Iqra Naz 70063678 Habiba Jameel DPT 10 Semester. Topic: ArthritisDocument10 pagesAssignment Submitted To DR Iqra Naz 70063678 Habiba Jameel DPT 10 Semester. Topic: ArthritisMuiz SaddozaiNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis: Done By: Shameem Faheem Group 6Document32 pagesOsteoarthritis: Done By: Shameem Faheem Group 6Alisha ShamsNo ratings yet
- 31 - Surgery For Arthritis in The Hip and KneeDocument77 pages31 - Surgery For Arthritis in The Hip and KneelmaNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis: Applied Medicine BY: Dr. Kinza IftikharDocument16 pagesOsteoarthritis: Applied Medicine BY: Dr. Kinza IftikharsabaamjadNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis and Fibromyalgia: by Tamara MitchellDocument13 pagesOsteoarthritis and Fibromyalgia: by Tamara MitchellmailbabuNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis - Dont EraseDocument3 pagesOsteoarthritis - Dont EraseLynlyn AlforqueNo ratings yet
- Arthritis PowerpointDocument25 pagesArthritis PowerpointAnnalesa BarkerNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid Arthritis EmedicineDocument15 pagesRheumatoid Arthritis EmedicineRifki Maulana100% (1)
- YOU Don'T Have To Live With Joint Pain: A Patient'S Guide To The Causes and Treatment of Joint PainDocument18 pagesYOU Don'T Have To Live With Joint Pain: A Patient'S Guide To The Causes and Treatment of Joint PainbaboosabNo ratings yet
- EtoricoxibfinalasprintedDocument4 pagesEtoricoxibfinalasprintedFarah ShaniaNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritsDocument34 pagesOsteoarthritssamiul bashirNo ratings yet
- English What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis?Document5 pagesEnglish What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis?Mabel CampoNo ratings yet
- Written Report 2Document8 pagesWritten Report 2IsaacNo ratings yet
- Special Issue SeniorsDocument2 pagesSpecial Issue Seniorsapi-668116703No ratings yet
- An Assignment On ArthritisDocument10 pagesAn Assignment On ArthritisRajib RuhanNo ratings yet
- ArthritisDocument6 pagesArthritisChristel Mariz SantellaNo ratings yet
- A Review of Arthritis and Its ManagementDocument19 pagesA Review of Arthritis and Its ManagementPavithra GNo ratings yet
- Arthritis: Osteoarthritis (OA or Degenerative Arthritis) Osteoarthritis FactsDocument6 pagesArthritis: Osteoarthritis (OA or Degenerative Arthritis) Osteoarthritis FactsFelisitas FellNo ratings yet
- OSTEOARTHRITISDocument61 pagesOSTEOARTHRITISARYAN THAPANo ratings yet
- Erbil Polytechnic University Erbil Health Technical College Physiotherapy Department Study Year 2020-2021Document13 pagesErbil Polytechnic University Erbil Health Technical College Physiotherapy Department Study Year 2020-2021Muhamad SdeqNo ratings yet
- Arthritic Shoulder Exercise GuideDocument24 pagesArthritic Shoulder Exercise GuideFeriz100% (1)
- ArthritisDocument54 pagesArthritisPeby M. Ramdhan100% (1)
- Osteoarthritis, Gouty Arthritis, and Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument37 pagesOsteoarthritis, Gouty Arthritis, and Rheumatoid ArthritisDianaNo ratings yet
- Lateral and Medial Epicondylitis-1Document21 pagesLateral and Medial Epicondylitis-1Jalil AhmadNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument23 pagesOsteoarthritisGoutham VGouthamNo ratings yet
- Cotul Reumatic EnglezaDocument7 pagesCotul Reumatic EnglezaElena GaneaNo ratings yet
- Total Hip ReplacementDocument13 pagesTotal Hip ReplacementrezkyagustineNo ratings yet
- Arthritis: Group 6Document24 pagesArthritis: Group 6Jenneth Marquez JoloNo ratings yet
- ARTHRITISrevieweditedDocument26 pagesARTHRITISrevieweditedFelix Morales PerezNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis PocDocument4 pagesOsteoarthritis PocIrene Joy GomezNo ratings yet
- 5417 3 Ankle ArthritisDocument6 pages5417 3 Ankle ArthritisHuzaif KhatibNo ratings yet
- UnderstandingGout Brochure PDFDocument12 pagesUnderstandingGout Brochure PDFGary HoNo ratings yet
- Apyogenous Arthritis: Department of Orthopaedics The First Affiliated Hospital Dalian Medical University Tang KaiDocument131 pagesApyogenous Arthritis: Department of Orthopaedics The First Affiliated Hospital Dalian Medical University Tang KaiFathimathNo ratings yet
- Arthritis Diet: Anti-Inflammatory Dietary Guide On Eliminating ArthritisFrom EverandArthritis Diet: Anti-Inflammatory Dietary Guide On Eliminating ArthritisNo ratings yet
- MACP Referencer ManualDocument167 pagesMACP Referencer ManualHANIF S. MULIANo ratings yet
- Pi Kel 8Document13 pagesPi Kel 8Novelya MarcellinaNo ratings yet
- Case Studies (1) .PDF Ayesha MalikDocument20 pagesCase Studies (1) .PDF Ayesha Malikfaizmalik74No ratings yet
- Spondylosis Information LeafletDocument3 pagesSpondylosis Information LeafletAnis Azizah MogilNo ratings yet
- HIP JointDocument15 pagesHIP JointLaiba FaysalNo ratings yet
- Case History and Successful Therapy of Toe WalkingDocument8 pagesCase History and Successful Therapy of Toe WalkingSaraNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Forefoot Disorders. Section 4. Tailor's BunionDocument7 pagesDiagnosis and Treatment of Forefoot Disorders. Section 4. Tailor's BunionbaoNo ratings yet
- Capitulo 8 Crecimiento Craneo FacialDocument32 pagesCapitulo 8 Crecimiento Craneo FacialLady SolarteNo ratings yet
- ISPO Classification System For Congenital Upper Limb ReductionsDocument1 pageISPO Classification System For Congenital Upper Limb ReductionswinNo ratings yet
- Anterior Compartment of Arm & Cubital FossaDocument24 pagesAnterior Compartment of Arm & Cubital FossaShahid MaqboolNo ratings yet
- BBB Nov-Dec 2023 Workout PlanDocument17 pagesBBB Nov-Dec 2023 Workout Planjfiorav6100% (1)
- Anatomy - Anterior Triangle of The Neck PDFDocument6 pagesAnatomy - Anterior Triangle of The Neck PDFAngel KimNo ratings yet
- Sport InjuriesDocument31 pagesSport InjuriesKartika Rizky LimNo ratings yet
- Humeral Nail Tech GuideDocument83 pagesHumeral Nail Tech Guidestv1036No ratings yet
- P.E. 9 - Q1 - Module1bDocument13 pagesP.E. 9 - Q1 - Module1bJay EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Cervical SpondylosisDocument26 pagesCervical SpondylosisAditya Anandito100% (2)
- The Painful Shoulder - Part I. Clinical Evaluation PDFDocument17 pagesThe Painful Shoulder - Part I. Clinical Evaluation PDFOscar FrizziNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb Anatomy PBLDocument3 pagesLower Limb Anatomy PBLFrancesca vitaleNo ratings yet
- Distraction OsteogenesisDocument141 pagesDistraction OsteogenesisJohan Edward Franklin MarpaungNo ratings yet
- G7 - Bones and SkeletonDocument27 pagesG7 - Bones and SkeletonListya RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- An Anatomical Study On Various Types of Suprascapular Notch, Its Relation With Glenoid Cavity and Morphometry of Scapula in South Indian PopulationDocument5 pagesAn Anatomical Study On Various Types of Suprascapular Notch, Its Relation With Glenoid Cavity and Morphometry of Scapula in South Indian PopulationRaviprasanna K HNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy For Artists Comprehensive Handbook of Visual Reference of The Human SkullDocument22 pagesHuman Anatomy For Artists Comprehensive Handbook of Visual Reference of The Human Skullthiago1682No ratings yet
- Penuntun Praktikum Fisiologi Dermatomuskuloskeletal REV 2022 - UNTIRTADocument27 pagesPenuntun Praktikum Fisiologi Dermatomuskuloskeletal REV 2022 - UNTIRTAPhuja Mestika agusmarNo ratings yet
- Facial Muscles - Wikipedia PDFDocument11 pagesFacial Muscles - Wikipedia PDFM Usama HabibNo ratings yet
- Shoulder - LectureDocument82 pagesShoulder - LectureElizabethNo ratings yet
- DB LungeDocument1 pageDB LungeRAM NAIDU CHOPPANo ratings yet
- Checklist For Positioning of PatientsDocument3 pagesChecklist For Positioning of PatientsAngelo Abigania100% (2)
Auca1 DLP Medical Surgical 3 Bito Adam Sealtiel Pasay
Auca1 DLP Medical Surgical 3 Bito Adam Sealtiel Pasay
Uploaded by
YoungbloodOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Auca1 DLP Medical Surgical 3 Bito Adam Sealtiel Pasay
Auca1 DLP Medical Surgical 3 Bito Adam Sealtiel Pasay
Uploaded by
YoungbloodCopyright:
Available Formats
ARELLANO UNIVERSITY
College of Nursing
CAPP – 1 / CA – 1
DLP
MEDICAL-SURGICAL NURSING 3
NAME: BITO, ADAM SEALTIEL G. BRANCH: AU PASAY DATE: 11-09-22
INSTRUCTIONS. Answer the following questions. Write your answers neatly and clearly with complete
citation of reference used (with pages).
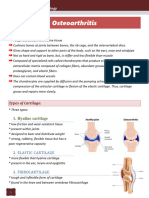
1. Identify and describe 3 common deformities of the spine that are illustrated below
2. Differentiate Osteoarthritis and Gouty arthritis
Osteoarthritis Gouty Arthritis
Definition Millions of people worldwide An outbreak of joint inflammation
suffer from osteoarthritis, the that is typically very painful is
most prevalent kind of arthritis. It brought on by uric acid crystal
happens as a result of deposits in the synovial fluid and
deterioration of the protective joint lining (synovial lining). As
cartilage that cushions the ends white blood cells consume the
of the bones throughout time. uric acid crystals, intense joint
Despite the fact that inflammation develops, resulting
osteoarthritis can harm any joint, in discomfort, heat, and redness
it most frequently affects the of the joint tissues. These
hands, knees, hips, and spine. excruciating arthritis bouts are
frequently referred to as "gout,"
however gouty arthritis is but one
symptom of gout.
Clinical manifestation Joint discomfort and stiffness that
gets worse with activity and
(at least 3) becomes better with rest. While Severe attacks of pain.
stiffness tends to get better
Swelling.
throughout the day, pain usually
gets worse. Redness and tenderness .
Diagnostic procedure Bone spurs, bony protrusions that The most frequent examinations
can develop in the joints as a are for uric acid. When uric acid, a
result of OA, can also be seen on bodily waste product,
an X-ray. Magnesium-based accumulates in the bloodstream
imaging (MRI). Less frequently, and crystallizes in the joints, it
your doctor might request an MRI causes gout. The presence of
to identify osteoarthritis. An MRI, elevated uric acid levels in the
as opposed to a conventional X- blood could support the diagnosis
ray, can detect changes in soft of gout.
tissues, including cartilage.
Give the 4 stages of gout:
1. Stage 1: High Uric Acid Levels
In the early stages of gout, also known as asymptomatic hyperuricemia, uric acid builds up in the
blood and begins to crystallize around joints, most frequently the foot.
2. Stage 2: Acute Gout
At this moment, a midnight episode of gout symptoms could happen suddenly and unexpectedly.
According to Dr. Fields, gout can begin in other joints as well. "This is when the person
experiences pain, redness, and swelling of a joint, most usually in the big toe, the foot, the ankle,
or the knee. "This is the time when the urate crystals are released into the joint fluid and induce
an inflammatory reaction, attracting numerous white blood cells and releasing inflammatory
chemicals that cause the pain, redness, and swelling."
3. Stage 3: Intercritical Gout
According to Dr. Fields, 75% of patients who experience a first gout flare will experience a
second within a year, although some people may go years without experiencing another attack.
According to him, the transitional period is when a person has already experienced a gout flare
but is not now experiencing any joint pain or swelling. Since gout tends to flare up and then
subside for a while before another flare, almost all gout patients will experience this phase.
4. Stage 4: Chronic Gout
Due to the possibility of tophi (uric acid deposits) developing, this stage is also known as
"tophaceous gout." Tophi commonly develop around the elbow or the bunion point of the big
toe. Tophi can develop anywhere in the body, though. According to Dr. Fields, this stage is when
gouty arthritis can cause joint discomfort almost constantly. In most cases, gout does not
progress to this level until it has been uncontrolled for a number of years.
You might also like
- Anatomy Past Papers 2009-2019Document12 pagesAnatomy Past Papers 2009-2019Kashar SaeedNo ratings yet
- The Best Exercise You'Ve Never Heard ofDocument71 pagesThe Best Exercise You'Ve Never Heard ofDI HartmanNo ratings yet
- Arthritis MagazineDocument5 pagesArthritis MagazineAdrian Euan Gonzales RañaNo ratings yet
- Osce Orthopedic Year 4Document3 pagesOsce Orthopedic Year 4Mazia Nadia Khairudin100% (9)
- Osteoarthritis PDFDocument15 pagesOsteoarthritis PDFعبدالرحمن علىNo ratings yet
- Arthritis ProjectDocument17 pagesArthritis ProjectGaurishi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument10 pagesAnatomyapi-3845840No ratings yet
- Arthritis PDFDocument4 pagesArthritis PDFArchana MoreyNo ratings yet
- ArthritisDocument30 pagesArthritisprasherpratik1984No ratings yet
- Arthritis Joint Pain ReliefDocument14 pagesArthritis Joint Pain ReliefSam CookNo ratings yet
- By: Azela Marie Barba Tesha Mae UyDocument12 pagesBy: Azela Marie Barba Tesha Mae UyAzelaMarieJanagapBarbaNo ratings yet
- Blaylock Arthritis 25Document12 pagesBlaylock Arthritis 25mohanp71No ratings yet
- 1 OsteoarthritisDocument61 pages1 OsteoarthritisARYAN THAPANo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument10 pagesOsteoarthritisMogtaba M HilalNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Joint Disease Study GuideDocument18 pagesRheumatic Joint Disease Study Guidechalinsammy1No ratings yet
- Physiotherapy in Portage La Prairie and Emerald Park For FootDocument11 pagesPhysiotherapy in Portage La Prairie and Emerald Park For Footdrrabe3No ratings yet
- Radiological Imaging of Osteoarthritis.: DR/ Abd Allah Nazeer. MDDocument75 pagesRadiological Imaging of Osteoarthritis.: DR/ Abd Allah Nazeer. MDKarthickNo ratings yet
- CVEC Spring 2011Document8 pagesCVEC Spring 2011griffinjayNo ratings yet
- Knee Osteoarthritis PDFDocument4 pagesKnee Osteoarthritis PDFDhan Singh RathoreNo ratings yet
- Arthritis AdviceDocument8 pagesArthritis AdviceInternational Business TimesNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument3 pagesOsteoarthritisVanessa Da CruzNo ratings yet
- Joint DisordersDocument39 pagesJoint DisordersangelaNo ratings yet
- Chapter VI - Bone Pathology: Arthritis & GoutDocument4 pagesChapter VI - Bone Pathology: Arthritis & GoutIndranil SinhaNo ratings yet
- Common Causes of Severe Knee PainDocument8 pagesCommon Causes of Severe Knee PainRatnaPrasadNalamNo ratings yet
- Knee Arthritis - Johns HopkinsDocument4 pagesKnee Arthritis - Johns HopkinsCarmel HarelNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument5 pagesOsteoarthritisprincess0fdeathNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument8 pagesOsteoarthritisNianurmayanti983278No ratings yet
- PSN PresentationDocument14 pagesPSN PresentationJaysie Rose DionesNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument6 pagesOsteoarthritisKristine ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Submitted To DR Iqra Naz 70063678 Habiba Jameel DPT 10 Semester. Topic: ArthritisDocument10 pagesAssignment Submitted To DR Iqra Naz 70063678 Habiba Jameel DPT 10 Semester. Topic: ArthritisMuiz SaddozaiNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis: Done By: Shameem Faheem Group 6Document32 pagesOsteoarthritis: Done By: Shameem Faheem Group 6Alisha ShamsNo ratings yet
- 31 - Surgery For Arthritis in The Hip and KneeDocument77 pages31 - Surgery For Arthritis in The Hip and KneelmaNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis: Applied Medicine BY: Dr. Kinza IftikharDocument16 pagesOsteoarthritis: Applied Medicine BY: Dr. Kinza IftikharsabaamjadNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis and Fibromyalgia: by Tamara MitchellDocument13 pagesOsteoarthritis and Fibromyalgia: by Tamara MitchellmailbabuNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis - Dont EraseDocument3 pagesOsteoarthritis - Dont EraseLynlyn AlforqueNo ratings yet
- Arthritis PowerpointDocument25 pagesArthritis PowerpointAnnalesa BarkerNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid Arthritis EmedicineDocument15 pagesRheumatoid Arthritis EmedicineRifki Maulana100% (1)
- YOU Don'T Have To Live With Joint Pain: A Patient'S Guide To The Causes and Treatment of Joint PainDocument18 pagesYOU Don'T Have To Live With Joint Pain: A Patient'S Guide To The Causes and Treatment of Joint PainbaboosabNo ratings yet
- EtoricoxibfinalasprintedDocument4 pagesEtoricoxibfinalasprintedFarah ShaniaNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritsDocument34 pagesOsteoarthritssamiul bashirNo ratings yet
- English What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis?Document5 pagesEnglish What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis?Mabel CampoNo ratings yet
- Written Report 2Document8 pagesWritten Report 2IsaacNo ratings yet
- Special Issue SeniorsDocument2 pagesSpecial Issue Seniorsapi-668116703No ratings yet
- An Assignment On ArthritisDocument10 pagesAn Assignment On ArthritisRajib RuhanNo ratings yet
- ArthritisDocument6 pagesArthritisChristel Mariz SantellaNo ratings yet
- A Review of Arthritis and Its ManagementDocument19 pagesA Review of Arthritis and Its ManagementPavithra GNo ratings yet
- Arthritis: Osteoarthritis (OA or Degenerative Arthritis) Osteoarthritis FactsDocument6 pagesArthritis: Osteoarthritis (OA or Degenerative Arthritis) Osteoarthritis FactsFelisitas FellNo ratings yet
- OSTEOARTHRITISDocument61 pagesOSTEOARTHRITISARYAN THAPANo ratings yet
- Erbil Polytechnic University Erbil Health Technical College Physiotherapy Department Study Year 2020-2021Document13 pagesErbil Polytechnic University Erbil Health Technical College Physiotherapy Department Study Year 2020-2021Muhamad SdeqNo ratings yet
- Arthritic Shoulder Exercise GuideDocument24 pagesArthritic Shoulder Exercise GuideFeriz100% (1)
- ArthritisDocument54 pagesArthritisPeby M. Ramdhan100% (1)
- Osteoarthritis, Gouty Arthritis, and Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument37 pagesOsteoarthritis, Gouty Arthritis, and Rheumatoid ArthritisDianaNo ratings yet
- Lateral and Medial Epicondylitis-1Document21 pagesLateral and Medial Epicondylitis-1Jalil AhmadNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument23 pagesOsteoarthritisGoutham VGouthamNo ratings yet
- Cotul Reumatic EnglezaDocument7 pagesCotul Reumatic EnglezaElena GaneaNo ratings yet
- Total Hip ReplacementDocument13 pagesTotal Hip ReplacementrezkyagustineNo ratings yet
- Arthritis: Group 6Document24 pagesArthritis: Group 6Jenneth Marquez JoloNo ratings yet
- ARTHRITISrevieweditedDocument26 pagesARTHRITISrevieweditedFelix Morales PerezNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis PocDocument4 pagesOsteoarthritis PocIrene Joy GomezNo ratings yet
- 5417 3 Ankle ArthritisDocument6 pages5417 3 Ankle ArthritisHuzaif KhatibNo ratings yet
- UnderstandingGout Brochure PDFDocument12 pagesUnderstandingGout Brochure PDFGary HoNo ratings yet
- Apyogenous Arthritis: Department of Orthopaedics The First Affiliated Hospital Dalian Medical University Tang KaiDocument131 pagesApyogenous Arthritis: Department of Orthopaedics The First Affiliated Hospital Dalian Medical University Tang KaiFathimathNo ratings yet
- Arthritis Diet: Anti-Inflammatory Dietary Guide On Eliminating ArthritisFrom EverandArthritis Diet: Anti-Inflammatory Dietary Guide On Eliminating ArthritisNo ratings yet
- MACP Referencer ManualDocument167 pagesMACP Referencer ManualHANIF S. MULIANo ratings yet
- Pi Kel 8Document13 pagesPi Kel 8Novelya MarcellinaNo ratings yet
- Case Studies (1) .PDF Ayesha MalikDocument20 pagesCase Studies (1) .PDF Ayesha Malikfaizmalik74No ratings yet
- Spondylosis Information LeafletDocument3 pagesSpondylosis Information LeafletAnis Azizah MogilNo ratings yet
- HIP JointDocument15 pagesHIP JointLaiba FaysalNo ratings yet
- Case History and Successful Therapy of Toe WalkingDocument8 pagesCase History and Successful Therapy of Toe WalkingSaraNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Forefoot Disorders. Section 4. Tailor's BunionDocument7 pagesDiagnosis and Treatment of Forefoot Disorders. Section 4. Tailor's BunionbaoNo ratings yet
- Capitulo 8 Crecimiento Craneo FacialDocument32 pagesCapitulo 8 Crecimiento Craneo FacialLady SolarteNo ratings yet
- ISPO Classification System For Congenital Upper Limb ReductionsDocument1 pageISPO Classification System For Congenital Upper Limb ReductionswinNo ratings yet
- Anterior Compartment of Arm & Cubital FossaDocument24 pagesAnterior Compartment of Arm & Cubital FossaShahid MaqboolNo ratings yet
- BBB Nov-Dec 2023 Workout PlanDocument17 pagesBBB Nov-Dec 2023 Workout Planjfiorav6100% (1)
- Anatomy - Anterior Triangle of The Neck PDFDocument6 pagesAnatomy - Anterior Triangle of The Neck PDFAngel KimNo ratings yet
- Sport InjuriesDocument31 pagesSport InjuriesKartika Rizky LimNo ratings yet
- Humeral Nail Tech GuideDocument83 pagesHumeral Nail Tech Guidestv1036No ratings yet
- P.E. 9 - Q1 - Module1bDocument13 pagesP.E. 9 - Q1 - Module1bJay EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Cervical SpondylosisDocument26 pagesCervical SpondylosisAditya Anandito100% (2)
- The Painful Shoulder - Part I. Clinical Evaluation PDFDocument17 pagesThe Painful Shoulder - Part I. Clinical Evaluation PDFOscar FrizziNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb Anatomy PBLDocument3 pagesLower Limb Anatomy PBLFrancesca vitaleNo ratings yet
- Distraction OsteogenesisDocument141 pagesDistraction OsteogenesisJohan Edward Franklin MarpaungNo ratings yet
- G7 - Bones and SkeletonDocument27 pagesG7 - Bones and SkeletonListya RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- An Anatomical Study On Various Types of Suprascapular Notch, Its Relation With Glenoid Cavity and Morphometry of Scapula in South Indian PopulationDocument5 pagesAn Anatomical Study On Various Types of Suprascapular Notch, Its Relation With Glenoid Cavity and Morphometry of Scapula in South Indian PopulationRaviprasanna K HNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy For Artists Comprehensive Handbook of Visual Reference of The Human SkullDocument22 pagesHuman Anatomy For Artists Comprehensive Handbook of Visual Reference of The Human Skullthiago1682No ratings yet
- Penuntun Praktikum Fisiologi Dermatomuskuloskeletal REV 2022 - UNTIRTADocument27 pagesPenuntun Praktikum Fisiologi Dermatomuskuloskeletal REV 2022 - UNTIRTAPhuja Mestika agusmarNo ratings yet
- Facial Muscles - Wikipedia PDFDocument11 pagesFacial Muscles - Wikipedia PDFM Usama HabibNo ratings yet
- Shoulder - LectureDocument82 pagesShoulder - LectureElizabethNo ratings yet
- DB LungeDocument1 pageDB LungeRAM NAIDU CHOPPANo ratings yet
- Checklist For Positioning of PatientsDocument3 pagesChecklist For Positioning of PatientsAngelo Abigania100% (2)