Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sheet Exercise 2 - WEP - S-1 1668526290886
Sheet Exercise 2 - WEP - S-1 1668526290886
Uploaded by
Gaurav KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- PAPER+ +Collapse+of+Soil+in+Pile+Bore+and+Its+Stabilisation+Using+Bentonite+SuspensionDocument9 pagesPAPER+ +Collapse+of+Soil+in+Pile+Bore+and+Its+Stabilisation+Using+Bentonite+SuspensionPrashanth Seshamani Iyer100% (1)
- General Physics 1 Newtons-Law-of-MotionDocument87 pagesGeneral Physics 1 Newtons-Law-of-MotionPortia Egken100% (1)
- TB Chapter7 PDFDocument24 pagesTB Chapter7 PDFAsmaa AhmedNo ratings yet
- BY Referral Coode - : Praveen Kumar PachauriDocument38 pagesBY Referral Coode - : Praveen Kumar PachauriSouvik MondalNo ratings yet
- Exercise (S-1) : HCV Worked Out Examples (Chapter No. 8 - 1,4,6,7)Document31 pagesExercise (S-1) : HCV Worked Out Examples (Chapter No. 8 - 1,4,6,7)Aaryan KeshanNo ratings yet
- Work Energy Power 1Document4 pagesWork Energy Power 1Gaming baseNo ratings yet
- Work, Power & Energy (Question)Document4 pagesWork, Power & Energy (Question)Harika NKNo ratings yet
- Impo. WpeDocument24 pagesImpo. WpeChirayu SharmaNo ratings yet
- WORK POWER ENERGY-05-Subjective UnSolvedDocument7 pagesWORK POWER ENERGY-05-Subjective UnSolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Exercise For Final Test Physics Is FUNDocument4 pagesExercise For Final Test Physics Is FUNFarrel AmroeNo ratings yet
- WPE AssignmentDocument14 pagesWPE AssignmentSuraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Work Power Energy Sindh Academy McqsDocument6 pagesWork Power Energy Sindh Academy McqsAnusha HussainNo ratings yet
- Level - 0: CPP - WpeDocument15 pagesLevel - 0: CPP - Wpechaitanya goyalNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 18 Sept 2022Document6 pagesAdobe Scan 18 Sept 2022Ajay AroraNo ratings yet
- WEP AssignmentsDocument11 pagesWEP AssignmentsShubh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 3: Work, Energy and Power Home Assignment-PhysicsDocument2 pagesAssignment # 3: Work, Energy and Power Home Assignment-PhysicsAtulNo ratings yet
- USTH B1 Exercise Part3 QuestionDocument7 pagesUSTH B1 Exercise Part3 Questionbình minh trầnNo ratings yet
- Ch6. Work and Energy Work Done by A Constant ForceDocument93 pagesCh6. Work and Energy Work Done by A Constant ForceKtel R MacarioNo ratings yet
- Trabajo y EnergíaDocument5 pagesTrabajo y EnergíaEve ParedesNo ratings yet
- Work Power EnergyDocument9 pagesWork Power EnergySanmati Jain100% (1)
- Mechanics Exercise B1 Chapter4Document6 pagesMechanics Exercise B1 Chapter4Trần Hoàng ViệtNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4 Work Energy and PowerDocument29 pagesUnit - 4 Work Energy and PowerAnju MohtaNo ratings yet
- Assignment - WORK POWER & ENERGYDocument6 pagesAssignment - WORK POWER & ENERGYChetanNo ratings yet
- DPP WpeDocument6 pagesDPP WpeMohammed Aftab AhmedNo ratings yet
- Newtons Laws ApplicationsDocument17 pagesNewtons Laws ApplicationsFernando AvenirNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet G9 Unit 3&4Document2 pagesWork Sheet G9 Unit 3&4Amarch BahiluNo ratings yet
- Particle Dynamics (11th JK) WADocument48 pagesParticle Dynamics (11th JK) WAParijat SutradharNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy, and PowerDocument13 pagesWork, Energy, and Powerrajputabdullah187No ratings yet
- s.6 Math 2 Holiday Work Day 6 2023Document2 pagess.6 Math 2 Holiday Work Day 6 2023kinene richardNo ratings yet
- Wpe &circular MotionDocument5 pagesWpe &circular MotionSaatvik RaiNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3Document3 pagesExercise 3Banny SaiNo ratings yet
- Wk&EnergyDocument4 pagesWk&EnergyNicolas Patrick OntiverosNo ratings yet
- Ch4 - WEPDocument26 pagesCh4 - WEPALIF SYAKIR SATARNo ratings yet
- JR Iit StarDocument18 pagesJR Iit Star2pwxanqt8aNo ratings yet
- USTH B1 ExerciseMechanics Part3 SolutionDocument10 pagesUSTH B1 ExerciseMechanics Part3 Solutionabcvn67No ratings yet
- Sheet Exercise 1 - WEP - Single Correct L-1 1668526261681Document11 pagesSheet Exercise 1 - WEP - Single Correct L-1 1668526261681Gaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- (Newtons Law Force & Friction) Exercise-I: A B C ////////////////////////////////////////////// F 16NDocument5 pages(Newtons Law Force & Friction) Exercise-I: A B C ////////////////////////////////////////////// F 16NDeepak BaliyanNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion & Work Power Energy (11th) WADocument23 pagesCircular Motion & Work Power Energy (11th) WASwarnlata MishraNo ratings yet
- WPE in One ShotDocument51 pagesWPE in One Shotrahilarahila047No ratings yet
- Revision For Test 1 (SET 1) : Answer All Question Within 1 Hour. Total Marks Is 40 MarksDocument8 pagesRevision For Test 1 (SET 1) : Answer All Question Within 1 Hour. Total Marks Is 40 MarkshadassahhadidNo ratings yet
- Physics - Textbook - Cambridge 6th Edition 2014.pdf - ExtractDocument2 pagesPhysics - Textbook - Cambridge 6th Edition 2014.pdf - ExtractTheodore KimNo ratings yet
- Myungsung Medical College - Ass I 2022Document6 pagesMyungsung Medical College - Ass I 2022YordanosNo ratings yet
- Wa0010.Document3 pagesWa0010.BxkxnzixbNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Newtons LawsDocument11 pagesModule 5 - Newtons LawsKrizel CalasaraNo ratings yet
- Work Energy PowerDocument11 pagesWork Energy PowerManjusha JadhavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7. Kinetic Energy and WorkDocument26 pagesChapter 7. Kinetic Energy and WorkRetno IstighfariniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Newton's Laws of MotionDocument61 pagesChapter 4 Newton's Laws of MotionMUHAMMAD MAHMMOUD EL-QUDAFFYNo ratings yet
- Exercise # 01 CompleteDocument26 pagesExercise # 01 CompleteRehan QureshiNo ratings yet
- Phys1 Ch3 Workenergy NewDocument58 pagesPhys1 Ch3 Workenergy NewDuy ĐỗNo ratings yet
- Trialstpm 2023 YUHUApaper 1 QuestionDocument6 pagesTrialstpm 2023 YUHUApaper 1 QuestionMathew Cheng Yu HaoNo ratings yet
- 07 NLM-Exercise PDFDocument32 pages07 NLM-Exercise PDFDeepak LakharaNo ratings yet
- Sheet Exercise 2 - WEP - S-2 1683019532469Document6 pagesSheet Exercise 2 - WEP - S-2 1683019532469SAHIL KUMAWATNo ratings yet
- CE RefDocument3 pagesCE Refcat buenafeNo ratings yet
- Newtons Law Force & Friction WA (English)Document19 pagesNewtons Law Force & Friction WA (English)Swarnlata MishraNo ratings yet
- Practice Sheet WPEDocument9 pagesPractice Sheet WPENaveen JaferNo ratings yet
- STPM 2018 Term 1 Trial MHSDocument13 pagesSTPM 2018 Term 1 Trial MHSchoichiangNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy&Power (Nitin M Sir)Document6 pagesWork, Energy&Power (Nitin M Sir)Kenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Work Energy PowerDocument12 pagesWork Energy PowerdrpigaNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresFrom EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Sheet Exercise 1 - Circular Motion - Single Correct L-1 1668503280848Document5 pagesSheet Exercise 1 - Circular Motion - Single Correct L-1 1668503280848Gaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Sheet Exercise 1 - WEP - Single Correct L-1 1668526261681Document11 pagesSheet Exercise 1 - WEP - Single Correct L-1 1668526261681Gaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Sheet Exercise 1 - Circular Motion - Single Correct L-2 1668503324009Document3 pagesSheet Exercise 1 - Circular Motion - Single Correct L-2 1668503324009Gaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Sheet Exercise 2 - Circular Motion - S - L-1 1668503345455Document5 pagesSheet Exercise 2 - Circular Motion - S - L-1 1668503345455Gaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Straight Lines Enhancement Assignment 2 1665546133021Document6 pagesStraight Lines Enhancement Assignment 2 1665546133021Gaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Straight Lines Enhancement Assignment 1 1665296690381Document11 pagesStraight Lines Enhancement Assignment 1 1665296690381Gaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Straight Line Assignment 1 1665296680455Document2 pagesStraight Line Assignment 1 1665296680455Gaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Work Energy PowerDocument26 pagesWork Energy PowernyumnamNo ratings yet
- FDN Engg Chapter 7Document39 pagesFDN Engg Chapter 7Jelminda AlfaroNo ratings yet
- A Method To Derive Friction and Rolling Power Loss Formulae For Mixed EHLDocument12 pagesA Method To Derive Friction and Rolling Power Loss Formulae For Mixed EHLJose Ancasi EspinalNo ratings yet
- Simple Machines, Work, Force, Energy, and Newton'S Three Laws of Motion What Is A Simple Machine?Document11 pagesSimple Machines, Work, Force, Energy, and Newton'S Three Laws of Motion What Is A Simple Machine?Spoorthy KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Bionanomachines in ActionDocument32 pagesBionanomachines in Actiondebarpitasahoo73No ratings yet
- SUBMERSIBLE PUMP SelectionDocument6 pagesSUBMERSIBLE PUMP SelectionSyed Muztuza AliNo ratings yet
- Pile Capacity APIDocument30 pagesPile Capacity APIsitti.a100% (1)
- PROBLEM 8.41: M For WhichDocument11 pagesPROBLEM 8.41: M For WhichWilliam HendersonNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Theory: Transfer Function of Physical SystemsDocument108 pagesControl Systems Theory: Transfer Function of Physical SystemsMelanieNo ratings yet
- EP7 3.2.1 Glass Containers For Pharmaceutical Use PDFDocument5 pagesEP7 3.2.1 Glass Containers For Pharmaceutical Use PDFRany Bana100% (1)
- Solus Component CatalogDocument216 pagesSolus Component Catalognama saya kikoNo ratings yet
- Characteristic Behaviour of Aluminium Metal Matrix Composites A ReviewDocument9 pagesCharacteristic Behaviour of Aluminium Metal Matrix Composites A ReviewEditor IJTSRD100% (1)
- Solution MidTerm 2 Dynamics 20142Document5 pagesSolution MidTerm 2 Dynamics 20142yettiNo ratings yet
- NASA SP8063 Lube & Wear PDFDocument79 pagesNASA SP8063 Lube & Wear PDFYannou_breizhNo ratings yet
- Chain CalculationDocument16 pagesChain CalculationGabriela Pricope100% (1)
- SPE/IADC-184611-MS Improving Torque and Drag Prediction Using The Advanced Spline Curves Borehole TrajectoryDocument29 pagesSPE/IADC-184611-MS Improving Torque and Drag Prediction Using The Advanced Spline Curves Borehole TrajectoryLeticia Bueno NogueiraNo ratings yet
- Pile Load Capacity Calculation - Single Pile and Group PileDocument3 pagesPile Load Capacity Calculation - Single Pile and Group PilelaikienfuiNo ratings yet
- 2marks With AnswerDocument17 pages2marks With AnswerMECH HODNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Tasks - Essential Questions Group 3Document12 pagesChapter 4 Tasks - Essential Questions Group 3Sofiah Marshialyn PepitoNo ratings yet
- UNIT IV: Worksheet 1Document2 pagesUNIT IV: Worksheet 1sandrakristikNo ratings yet
- Physics Ch7 - Work and EnergyDocument3 pagesPhysics Ch7 - Work and EnergymkinnetxNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology-MizoramDocument6 pagesNational Institute of Technology-MizoramLITTLE RIDERSNo ratings yet
- Local Acceleration Due To Gravity Lab ReportDocument6 pagesLocal Acceleration Due To Gravity Lab ReportHenry Lion ZhangNo ratings yet
- Helicoil Tangfree GB 0150Document10 pagesHelicoil Tangfree GB 0150WK SinnNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Problem..Document2 pagesMechanics Problem..Krissa Marie BuniagNo ratings yet
- The Necessity of A Plateaued Cylinder Wall FinishDocument28 pagesThe Necessity of A Plateaued Cylinder Wall FinishguguimirandaNo ratings yet
- Geogrids Isochronous CurvesDocument12 pagesGeogrids Isochronous Curveslimara65No ratings yet
- Matrikulasi Mekanika: Universitas Ahmad DahlanDocument24 pagesMatrikulasi Mekanika: Universitas Ahmad DahlanNurul FitriNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Design and Manufacturing Question Paper Of.Document40 pagesFundamentals of Design and Manufacturing Question Paper Of.Amaresh MishraNo ratings yet
Sheet Exercise 2 - WEP - S-1 1668526290886
Sheet Exercise 2 - WEP - S-1 1668526290886
Uploaded by
Gaurav KumarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sheet Exercise 2 - WEP - S-1 1668526290886
Sheet Exercise 2 - WEP - S-1 1668526290886
Uploaded by
Gaurav KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
Physicsaholics
Exercise
Work Energy & Power
(Physicsaholics)
Physicsaholics.com Unacademy
Exercise-2
(Subjective Type: Level - 1)
Kota Sheets refined by Physicsaholics Team. 1
Physicsaholics
Q 1. The figure shows a smooth circular path of radius R in the vertical plane which subtends an
angle at O. A block of mass m is taken from position A to B under the action of a constant
2
horizontal force F.
O
B
F
A
(a) Find the work done by this gravity
(b) In previous problem if the block is being pulled by a force F which is always tangential to
the surface, find the work done by the force F between A and B.
Q 2. A body of mass 2 kg initially at rest moves under the action of an applied horizontal force of
7 N on a table with coefficient of kinetic friction = 0.1. Compute the
(a) work done by the applied force in 10 s,
(b) work done by friction in 10 s,
(c) work done by the net force on the body in 10 s,
(d) change in kinetic energy of the body in 10 s, and interpret your results.
Q 3. A person pulls a 6 kg block by a distance of s = 12 m along a horizontal surface at a
constant speed. If the coefficient of kinetic friction is = 0.2 and the cord pulling the block is
at an angle of 45° with the horizontal,then calculate the work done by the person. (take g =
10 m/s2)
Q 4. A particle of mass 2kg moves on a smooth horizontal plane under the action of a single force
F = (3iˆ+ 4 ˆj) Newton. Under this force it is displaced from (0,0) to (–1m, 1m). Find the
work done by F (in Joule)
Q 5. A point mass of 0.5 kg is moving along x-axis as x = t2 + 2t, where, x is in meters and t is in
seconds. Find the work done (in J) by all the forces acting on the body during the time
interval
[0, 2s]
Q 6. A body of mass m is pushed with the initial velocity v0 up an inclined plane set at an angle θ
to the horizontal. The friction coefficient is equal to k. What distance will the body cover
before it stops and what work do the friction forces perform over this distance ?
Q 7. A particle of mass m is taken from position A to position B along the circular path by a force
F , where magnitude of F is constant (| F |) & is always directed towards point B. What will
be the work done by the force F ? Here radius of track is R.
Kota Sheets refined by Physicsaholics Team. 2
Physicsaholics R B
90°
F
m
Q 8. Two cylindrical vessels of equal cross-sectional area A contain water upto heights h1 and h2.
The vessels are interconnected so that the levels in them become equal. Calculate the work
done by the force of gravity during the process. The density of water is .
Q 9. A body of mass 2 kg is kept on a rough horizontal surface as shown in the figure. Find the
work done by frictional force in the time interval t = 0 to t = 5 sec.
10N
10N
30°
2 kg
=0.5
Q 10. A particle is subject to a force Fx that varies with position as in figure. Find the work done by
the force on the body as it moves
Fx (N)
3
2
1
x(m)
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
(a) from x = 0 to x = 5.00 m,
(b) from x = 5.00 m to x = 10.0 m, and
(c) from x = 10.0 m to x = 15.0 m.
(d) What is the total work done by the force over the distance x = 0 to x = 15.0 m?
Q 11. A spring, which is initially in its unstretched condition, is first stretched by a length x and
then again by a further length x. The work done in the first case is W1 and in the second case
W2
is W2. Find .
W1
Q 12. A force given by the relation F = 8t (N/s) acts on a body of mass 2 kg initially at rest on a
smooth surface where t is in seconds. Find the work done by this force on the body during
first 2 seconds of its motion. Assume direction of force remain constant and body moves in
the direction of force.
Q 13. An automobile of mass ‘m’ accelerates starting from rest, while the engine supplies constant
power P show that
Kota Sheets refined by Physicsaholics Team. 3
Physicsaholics
(a) The velocity is given as a function of time by v = (2Pt/m)1/2
(b) The position is given as a function of time by s = (8P/9m)1/2t3/2.
Q 14. Position-time graph of a particle of mass 2 kg is shown in figure. Total work done on the
particle from t = 0 to t = 4s is
x(m)
t(s)
0 2 4 6
Q 15. A point object of mass 2 kg is moved from point A to point B very slowly on a curved path by
applying a tangential force on a curved path as shown in figure. Then find the work done by
external force in moving the body. Given that s = 0.3, k = 0.1. [g = 10 m/s2]
20m
A 10m 5m B
h h
200m
Q 16. An object is attached to a vertical spring and slowly lowered to its equilibrium position. This
stretches the spring by an amount d. If the same object is attached to the same vertical
spring but permitted to fall instead, through what distance does it stretch the spring ?
Q 17. The elevator E has a mass of 3000 kg when fully loaded and is connected as shown to a
counterweight W of mass 1000 kg. Determine the power in kilowatts delivered by the motor
W
E
M
(a) when the elevator is moving down at a constant speed of 3 m/s,
(b) when it has an upward velocity of 3 m/s and a deceleration of 0.5 m/s2.
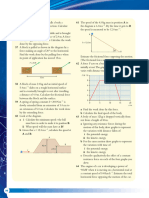
Q 18. A block is released from rest from top of a rough curved track as shown in figure. It comes to
rest at some point on the horizontal part. If its mass is 200 gm, calculate negative of work by
friction is joules.
2m
Q 19. Power applied to a particle varies with time as P = (3t2 – 2t +1) watt, where t is in second.
Find the change in its kinetic energy between time t = 2 s and t = 4 s.
Kota Sheets refined by Physicsaholics Team. 4
Q 20.
Physicsaholics
A person is pulling a mass m slowly from ground on a rough hemispherical fixed surface upto
the top of the hemisphere with the help of a light inextensible string as shown in the figure.
The radius of the hemisphere is R. Find the work done by the tension in the string.
R
m
Q 21. A block of mass 2.0 kg is given an initial speed along the floor towards a spring as shown. The
coefficient of kinetic friction between the floor and the block is 0.4 and force constant of the
spring is 5.6×103 N/m. The block compresses the spring by 10 cm before it stops for a
moment. What is the initial speed (m/s) of the block?
90 cm.
Q 22. A stone with weight W is thrown vertically upwards into the air with initial speed v0. If a
constant force f due to air drag acts on the stone throughout its flight.
v 02
(a) Show that the maximum height reached by the stone is h =
2g1 + ( f / w )
1/ 2
w−f
(b) Show that the speed of the stone upon impact with the ground is v = v 0
w+f
Q 23. A particle is moving with kinetic energy E, straight up an inclined plane with angle , the
coefficient of friction being . The work done against friction before the particle comes
down to rest is
Q 24. A pendulum bob of mass m is suspended at rest. A constant horizontal force F = mg start
acting on it. Find
(a)The maximum angular deflection of the string.
(b)The maximum possible tension in the string.
Q 25. A block placed on a smooth horizontal floor is connected to a spring as shown. Initially an
external force of 100 N keeps it stretched by 1 cm beyond natural length in equilibrium. This
force is now removed and another force F is applied on this block, which slowly moves it
from this position to a position where the spring is finally compressed by 3cm. Find the work
done by this force F (in joules).
100N
1cm
Kota Sheets refined by Physicsaholics Team. 5
Q 26.
Physicsaholics
Two blocks of different masses are hanging on two ends of a string passing over a frictionless
pulley. The heavier block has a mass twice as that of the lighter one. The tension in the
string is 60 N. Find the decrease in potential energy during the first second after the system
is released.
Q 27. A 1 kg block situated on a rough incline is connected to a spring of spring constant 100 N m–1
as shown in figure. The block is released from rest with the spring in the unstretched
position. The block moves 10 cm down the incline before coming to rest. Find the coefficient
of friction between the block and the incline. Assume that the spring has a negligible mass
and the pulley is frictionless.
k=100 N/m
1 kg
37°
Q 28. A block of mass m is held at rest on a smooth horizontal floor. A light frictionless, small
pulley is fixed at a height of 6 m from the floor. A light inextensible string of length 16 m,
connected with A passes over the pulley and another identical block B is hung from the
string. Initial height of B is 5m from the floor as shown in Fig. When the system is released
from rest, B starts to move vertically downwards and A slides on the floor towards right.
B
6m
A 5m
(i) If at an instant string makes an angle with horizontal, calculate relation between
velocity u of A and v of B.
(ii) Calculate v when B strikes the floor.
Q 29. For what minimum value of m1 the block of mass m will just leave the contact with surface ?
m1
K
Q 30. A uniform chain of length and mass m overhangs a smooth table with its two third part
lying on the table. Find the kinetic energy of the chain as it completely slips off the table.
Q 31. A block of mass 1 kg is attached to a spring with a force constant 100 N/m and rests on a
rough horizontal ground as shown in the figure. Initial displacement of block from
Kota Sheets refined by Physicsaholics Team. 6
Physicsaholics
equilibrium position is 50 cm. The total distance covered by the block if coefficient of friction
between block & ground is 0.05.[g =10m/s2]
k=100 N/m =0.05
Q 32. A mass m slides from rest at height h down a smooth curved surface which becomes
horizontal at zero height (see figure). A spring is fixed horizontally on the level part of the
surface. The spring constant is k N/m. When the mass encounters the spring it compresses it
by an amount
x = h/10. If m = 1 kg, h = 5m then find k /100.
m
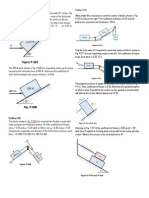
Q 33. A sleeve of mass m = 10 kg can slide on a straight vertical smooth rod. The sleeve is
connected to a spring of spring constant k = 1000 N/m, whose other end is connected to a
fixed support as shown in figure. The sleeve is released when the spring is horizontal and
relaxed. Find the speed in SI units of the sleeve when it descends a distance of 40 cm. (Use g
= 10m/s2)
30 cm.
Q 34. A rod of mass m and length is kept on a smooth wedge of mass M as shown in the figure. If
the system is released when the rod is at the top of the wedge, find the speed of the wedge
when the rod hits the ground level. Neglecting friction between all surfaces in contact.
H
M
Q 35. In the figure shown, pulley and spring are ideal. Find the potential energy stored in the
spring (m1 > m2).
Kota Sheets refined by Physicsaholics Team. 7
Physicsaholics
k
m2
m1
Q 36. The potential energy (in joules) function of a particle in a region of space is given as:
U = (2x2 + 3y3 + 2z) Here x, y and z are in metres. Find the magnitude of x component of
force (in Newton) acting on the particle at point P (1m, 2m, 3m).
Q 37. The potential function for a conservative force is given by U = k(x + y). Find the work done by
the conservative force in moving a particle from the point A (1, 1) to point B (2, 3).
Q 38. The P.E. of a particle oscillating on x-axis is given as U = 20 + (x – 2)2 here U is in Joules & x is
in meters. Total mechanical energy of particle is 36 J
(i) Find the mean position
(ii) Find the max. K.E. of the particle
Q 39. A particle is given a certain velocity v at point P as shown on a hemispherical smooth
surface. The value of v in m/s, such that particle when reaches Q the normal reaction of
surface is equal to particle's weight, is [R = 1.6 m, g = 10 m/s2]
v Q
P R
60°
Q 40. A skier starts from rest at the top of a hill. The skier coasts down the hill and up a second hill,
as the drawing illustrates. The crest of the second hill is circular, with a radius of r = 36 m.
Neglect friction and air resistance. What must be the height h(in m) of the first hill so that
the skier just loses contact with the snow at the crest of the second hill?
Q 41. A ball is attached to a horizontal cord of length L whose other end is fixed, (a) If the ball is
released, what will be its speed at the lowest point of its path? (b) A peg is located a distance
Kota Sheets refined by Physicsaholics Team. 8
Physicsaholics
h directly below the point of attachment of the cord. If h = 0.75 L, what will be the speed of
the ball when it reaches the top of its circular path about the peg?
14
Q 42. One end of a string of length l = m is fixed and a mass of 1 kg is tied to the other end.
9
The ball is given a velocity 2 gl at the bottom most point as shown in figure. The string is
cut when the ball becomes horizontal. Find the distance (in m) travelled till it stop for the 1st
22
time (Take = ).
7
2 g
Q 43. A block of mass 2.0 kg is pulled up on a smooth incline of angle 30º with the horizontal. If
the block moves with an acceleration of 1.0 m/s2, find the power delivered by the pulling
force at a time 4.0 s after the motion starts. What is the average power delivered during the
4.0 s after the motion starts?
Kota Sheets refined by Physicsaholics Team. 9
Physicsaholics
Answer Key
Ans 24. max=90s Tmax = mg[3√2-2]
Ans 1. (a) -mgR (b) FR
2 Ans 25. 4
Ans 2. (a) 882 J; (b) –247 J; (c) 635 J (d) 635 J
Ans 3. 120J Ans 26. 75
Ans 4. 4 1 Ans 27. 0.125
Ans 5. 8
40
Ans 6. v02/2g (sin + k cos ), A = –mv02k / 2 Ans 28. u = v sec , v = m/s
41
(k + tan )
Ans 29. m1 = m/2
Ans 7. FR 2
A Ans 30.
4
mg
Ans 8. (h1 – h2)2g
4 9
Ans 9. zero Ans 31. 25
Ans 10. (a) 7.5 J (b) 15 J (c) 7.5 J (d) 30 J Ans 32. 4
Ans 11. W2 = 3W1 Ans 33. 2
Ans 12. 64 J 2𝑚𝑔𝐻
Ans 34. √
Ans 13. P = mRa, <P> = mrat/2 𝑀+𝑚 𝑡𝑎𝑛2 𝜃
Ans 14. 0 2m12 g 2
Ans 35.
Ans 15. 400 k
Ans 16. 2d Ans 36. 4
Ans 17. (a) –30 kW, 19.5 kW Ans 37. –3k
Ans 18. 4 Ans 38. (i) x= 2, (ii) 16 J
Ans 39. 4
Ans 19. 46
Ans 40. 0.18
Ans 20. mgR (1+ )
Ans 41. 2gL , gL
Ans 21. 6 Ans 42. 4
E cos Ans 43. 47 W, 24 W
Ans 23.
sin + cos
Kota Sheets refined by Physicsaholics Team. 10
You might also like
- PAPER+ +Collapse+of+Soil+in+Pile+Bore+and+Its+Stabilisation+Using+Bentonite+SuspensionDocument9 pagesPAPER+ +Collapse+of+Soil+in+Pile+Bore+and+Its+Stabilisation+Using+Bentonite+SuspensionPrashanth Seshamani Iyer100% (1)
- General Physics 1 Newtons-Law-of-MotionDocument87 pagesGeneral Physics 1 Newtons-Law-of-MotionPortia Egken100% (1)
- TB Chapter7 PDFDocument24 pagesTB Chapter7 PDFAsmaa AhmedNo ratings yet
- BY Referral Coode - : Praveen Kumar PachauriDocument38 pagesBY Referral Coode - : Praveen Kumar PachauriSouvik MondalNo ratings yet
- Exercise (S-1) : HCV Worked Out Examples (Chapter No. 8 - 1,4,6,7)Document31 pagesExercise (S-1) : HCV Worked Out Examples (Chapter No. 8 - 1,4,6,7)Aaryan KeshanNo ratings yet
- Work Energy Power 1Document4 pagesWork Energy Power 1Gaming baseNo ratings yet
- Work, Power & Energy (Question)Document4 pagesWork, Power & Energy (Question)Harika NKNo ratings yet
- Impo. WpeDocument24 pagesImpo. WpeChirayu SharmaNo ratings yet
- WORK POWER ENERGY-05-Subjective UnSolvedDocument7 pagesWORK POWER ENERGY-05-Subjective UnSolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Exercise For Final Test Physics Is FUNDocument4 pagesExercise For Final Test Physics Is FUNFarrel AmroeNo ratings yet
- WPE AssignmentDocument14 pagesWPE AssignmentSuraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Work Power Energy Sindh Academy McqsDocument6 pagesWork Power Energy Sindh Academy McqsAnusha HussainNo ratings yet
- Level - 0: CPP - WpeDocument15 pagesLevel - 0: CPP - Wpechaitanya goyalNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 18 Sept 2022Document6 pagesAdobe Scan 18 Sept 2022Ajay AroraNo ratings yet
- WEP AssignmentsDocument11 pagesWEP AssignmentsShubh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 3: Work, Energy and Power Home Assignment-PhysicsDocument2 pagesAssignment # 3: Work, Energy and Power Home Assignment-PhysicsAtulNo ratings yet
- USTH B1 Exercise Part3 QuestionDocument7 pagesUSTH B1 Exercise Part3 Questionbình minh trầnNo ratings yet
- Ch6. Work and Energy Work Done by A Constant ForceDocument93 pagesCh6. Work and Energy Work Done by A Constant ForceKtel R MacarioNo ratings yet
- Trabajo y EnergíaDocument5 pagesTrabajo y EnergíaEve ParedesNo ratings yet
- Work Power EnergyDocument9 pagesWork Power EnergySanmati Jain100% (1)
- Mechanics Exercise B1 Chapter4Document6 pagesMechanics Exercise B1 Chapter4Trần Hoàng ViệtNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4 Work Energy and PowerDocument29 pagesUnit - 4 Work Energy and PowerAnju MohtaNo ratings yet
- Assignment - WORK POWER & ENERGYDocument6 pagesAssignment - WORK POWER & ENERGYChetanNo ratings yet
- DPP WpeDocument6 pagesDPP WpeMohammed Aftab AhmedNo ratings yet
- Newtons Laws ApplicationsDocument17 pagesNewtons Laws ApplicationsFernando AvenirNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet G9 Unit 3&4Document2 pagesWork Sheet G9 Unit 3&4Amarch BahiluNo ratings yet
- Particle Dynamics (11th JK) WADocument48 pagesParticle Dynamics (11th JK) WAParijat SutradharNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy, and PowerDocument13 pagesWork, Energy, and Powerrajputabdullah187No ratings yet
- s.6 Math 2 Holiday Work Day 6 2023Document2 pagess.6 Math 2 Holiday Work Day 6 2023kinene richardNo ratings yet
- Wpe &circular MotionDocument5 pagesWpe &circular MotionSaatvik RaiNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3Document3 pagesExercise 3Banny SaiNo ratings yet
- Wk&EnergyDocument4 pagesWk&EnergyNicolas Patrick OntiverosNo ratings yet
- Ch4 - WEPDocument26 pagesCh4 - WEPALIF SYAKIR SATARNo ratings yet
- JR Iit StarDocument18 pagesJR Iit Star2pwxanqt8aNo ratings yet
- USTH B1 ExerciseMechanics Part3 SolutionDocument10 pagesUSTH B1 ExerciseMechanics Part3 Solutionabcvn67No ratings yet
- Sheet Exercise 1 - WEP - Single Correct L-1 1668526261681Document11 pagesSheet Exercise 1 - WEP - Single Correct L-1 1668526261681Gaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- (Newtons Law Force & Friction) Exercise-I: A B C ////////////////////////////////////////////// F 16NDocument5 pages(Newtons Law Force & Friction) Exercise-I: A B C ////////////////////////////////////////////// F 16NDeepak BaliyanNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion & Work Power Energy (11th) WADocument23 pagesCircular Motion & Work Power Energy (11th) WASwarnlata MishraNo ratings yet
- WPE in One ShotDocument51 pagesWPE in One Shotrahilarahila047No ratings yet
- Revision For Test 1 (SET 1) : Answer All Question Within 1 Hour. Total Marks Is 40 MarksDocument8 pagesRevision For Test 1 (SET 1) : Answer All Question Within 1 Hour. Total Marks Is 40 MarkshadassahhadidNo ratings yet
- Physics - Textbook - Cambridge 6th Edition 2014.pdf - ExtractDocument2 pagesPhysics - Textbook - Cambridge 6th Edition 2014.pdf - ExtractTheodore KimNo ratings yet
- Myungsung Medical College - Ass I 2022Document6 pagesMyungsung Medical College - Ass I 2022YordanosNo ratings yet
- Wa0010.Document3 pagesWa0010.BxkxnzixbNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Newtons LawsDocument11 pagesModule 5 - Newtons LawsKrizel CalasaraNo ratings yet
- Work Energy PowerDocument11 pagesWork Energy PowerManjusha JadhavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7. Kinetic Energy and WorkDocument26 pagesChapter 7. Kinetic Energy and WorkRetno IstighfariniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Newton's Laws of MotionDocument61 pagesChapter 4 Newton's Laws of MotionMUHAMMAD MAHMMOUD EL-QUDAFFYNo ratings yet
- Exercise # 01 CompleteDocument26 pagesExercise # 01 CompleteRehan QureshiNo ratings yet
- Phys1 Ch3 Workenergy NewDocument58 pagesPhys1 Ch3 Workenergy NewDuy ĐỗNo ratings yet
- Trialstpm 2023 YUHUApaper 1 QuestionDocument6 pagesTrialstpm 2023 YUHUApaper 1 QuestionMathew Cheng Yu HaoNo ratings yet
- 07 NLM-Exercise PDFDocument32 pages07 NLM-Exercise PDFDeepak LakharaNo ratings yet
- Sheet Exercise 2 - WEP - S-2 1683019532469Document6 pagesSheet Exercise 2 - WEP - S-2 1683019532469SAHIL KUMAWATNo ratings yet
- CE RefDocument3 pagesCE Refcat buenafeNo ratings yet
- Newtons Law Force & Friction WA (English)Document19 pagesNewtons Law Force & Friction WA (English)Swarnlata MishraNo ratings yet
- Practice Sheet WPEDocument9 pagesPractice Sheet WPENaveen JaferNo ratings yet
- STPM 2018 Term 1 Trial MHSDocument13 pagesSTPM 2018 Term 1 Trial MHSchoichiangNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy&Power (Nitin M Sir)Document6 pagesWork, Energy&Power (Nitin M Sir)Kenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Work Energy PowerDocument12 pagesWork Energy PowerdrpigaNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresFrom EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Sheet Exercise 1 - Circular Motion - Single Correct L-1 1668503280848Document5 pagesSheet Exercise 1 - Circular Motion - Single Correct L-1 1668503280848Gaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Sheet Exercise 1 - WEP - Single Correct L-1 1668526261681Document11 pagesSheet Exercise 1 - WEP - Single Correct L-1 1668526261681Gaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Sheet Exercise 1 - Circular Motion - Single Correct L-2 1668503324009Document3 pagesSheet Exercise 1 - Circular Motion - Single Correct L-2 1668503324009Gaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Sheet Exercise 2 - Circular Motion - S - L-1 1668503345455Document5 pagesSheet Exercise 2 - Circular Motion - S - L-1 1668503345455Gaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Straight Lines Enhancement Assignment 2 1665546133021Document6 pagesStraight Lines Enhancement Assignment 2 1665546133021Gaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Straight Lines Enhancement Assignment 1 1665296690381Document11 pagesStraight Lines Enhancement Assignment 1 1665296690381Gaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Straight Line Assignment 1 1665296680455Document2 pagesStraight Line Assignment 1 1665296680455Gaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Work Energy PowerDocument26 pagesWork Energy PowernyumnamNo ratings yet
- FDN Engg Chapter 7Document39 pagesFDN Engg Chapter 7Jelminda AlfaroNo ratings yet
- A Method To Derive Friction and Rolling Power Loss Formulae For Mixed EHLDocument12 pagesA Method To Derive Friction and Rolling Power Loss Formulae For Mixed EHLJose Ancasi EspinalNo ratings yet
- Simple Machines, Work, Force, Energy, and Newton'S Three Laws of Motion What Is A Simple Machine?Document11 pagesSimple Machines, Work, Force, Energy, and Newton'S Three Laws of Motion What Is A Simple Machine?Spoorthy KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Bionanomachines in ActionDocument32 pagesBionanomachines in Actiondebarpitasahoo73No ratings yet
- SUBMERSIBLE PUMP SelectionDocument6 pagesSUBMERSIBLE PUMP SelectionSyed Muztuza AliNo ratings yet
- Pile Capacity APIDocument30 pagesPile Capacity APIsitti.a100% (1)
- PROBLEM 8.41: M For WhichDocument11 pagesPROBLEM 8.41: M For WhichWilliam HendersonNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Theory: Transfer Function of Physical SystemsDocument108 pagesControl Systems Theory: Transfer Function of Physical SystemsMelanieNo ratings yet
- EP7 3.2.1 Glass Containers For Pharmaceutical Use PDFDocument5 pagesEP7 3.2.1 Glass Containers For Pharmaceutical Use PDFRany Bana100% (1)
- Solus Component CatalogDocument216 pagesSolus Component Catalognama saya kikoNo ratings yet
- Characteristic Behaviour of Aluminium Metal Matrix Composites A ReviewDocument9 pagesCharacteristic Behaviour of Aluminium Metal Matrix Composites A ReviewEditor IJTSRD100% (1)
- Solution MidTerm 2 Dynamics 20142Document5 pagesSolution MidTerm 2 Dynamics 20142yettiNo ratings yet
- NASA SP8063 Lube & Wear PDFDocument79 pagesNASA SP8063 Lube & Wear PDFYannou_breizhNo ratings yet
- Chain CalculationDocument16 pagesChain CalculationGabriela Pricope100% (1)
- SPE/IADC-184611-MS Improving Torque and Drag Prediction Using The Advanced Spline Curves Borehole TrajectoryDocument29 pagesSPE/IADC-184611-MS Improving Torque and Drag Prediction Using The Advanced Spline Curves Borehole TrajectoryLeticia Bueno NogueiraNo ratings yet
- Pile Load Capacity Calculation - Single Pile and Group PileDocument3 pagesPile Load Capacity Calculation - Single Pile and Group PilelaikienfuiNo ratings yet
- 2marks With AnswerDocument17 pages2marks With AnswerMECH HODNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Tasks - Essential Questions Group 3Document12 pagesChapter 4 Tasks - Essential Questions Group 3Sofiah Marshialyn PepitoNo ratings yet
- UNIT IV: Worksheet 1Document2 pagesUNIT IV: Worksheet 1sandrakristikNo ratings yet
- Physics Ch7 - Work and EnergyDocument3 pagesPhysics Ch7 - Work and EnergymkinnetxNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology-MizoramDocument6 pagesNational Institute of Technology-MizoramLITTLE RIDERSNo ratings yet
- Local Acceleration Due To Gravity Lab ReportDocument6 pagesLocal Acceleration Due To Gravity Lab ReportHenry Lion ZhangNo ratings yet
- Helicoil Tangfree GB 0150Document10 pagesHelicoil Tangfree GB 0150WK SinnNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Problem..Document2 pagesMechanics Problem..Krissa Marie BuniagNo ratings yet
- The Necessity of A Plateaued Cylinder Wall FinishDocument28 pagesThe Necessity of A Plateaued Cylinder Wall FinishguguimirandaNo ratings yet
- Geogrids Isochronous CurvesDocument12 pagesGeogrids Isochronous Curveslimara65No ratings yet
- Matrikulasi Mekanika: Universitas Ahmad DahlanDocument24 pagesMatrikulasi Mekanika: Universitas Ahmad DahlanNurul FitriNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Design and Manufacturing Question Paper Of.Document40 pagesFundamentals of Design and Manufacturing Question Paper Of.Amaresh MishraNo ratings yet