Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eals ACT2 Valdez
Eals ACT2 Valdez
Uploaded by
Micaella Valdez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views4 pagesThe document summarizes the six levels of structural organization in the human body from simplest to most complex: chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, system, and organism. It then lists and describes the 11 major organ systems of the human body and their functions. These include the integumentary, skeletal, nervous, lymphatic, endocrine, respiratory, muscular, digestive, cardiovascular, reproductive, and urinary systems. The document provides an overview of the hierarchical structure of the human body and the roles of its main components.
Original Description:
eme activity
Original Title
Eals_ACT2_Valdez
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the six levels of structural organization in the human body from simplest to most complex: chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, system, and organism. It then lists and describes the 11 major organ systems of the human body and their functions. These include the integumentary, skeletal, nervous, lymphatic, endocrine, respiratory, muscular, digestive, cardiovascular, reproductive, and urinary systems. The document provides an overview of the hierarchical structure of the human body and the roles of its main components.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views4 pagesEals ACT2 Valdez
Eals ACT2 Valdez
Uploaded by
Micaella ValdezThe document summarizes the six levels of structural organization in the human body from simplest to most complex: chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, system, and organism. It then lists and describes the 11 major organ systems of the human body and their functions. These include the integumentary, skeletal, nervous, lymphatic, endocrine, respiratory, muscular, digestive, cardiovascular, reproductive, and urinary systems. The document provides an overview of the hierarchical structure of the human body and the roles of its main components.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
Micaella Joy Valdez
12- Sodalite
● Name the six different levels of structural organization in the human body and
explain their relationships.
Chemical Level Chemical elements are the building block of
life. They make up the staggering variety of
molecules that are combined to form DNA,
cellular organelles, cells, tissues, and organs.
Cellular Level All living things, from microorganisms to
humans, are built and run by cells.They are
regarded by scientists as the smallest living
thing.The biological machinery that makes the
proteins, chemicals, and signals that control
everything in our bodies are made in cells.
Tissue Level The tissue level of organization consists of a
group of cells that work together to
accomplish one or more specific functions.
Organ Level Organ are the next level of organization of
the human body. An organ is a structure that
consists of two or more types of tissues that
work together to do the same job. Examples
of human organs include the brain, heart,
lungs, skin, and kidneys.
System Level To accomplish a common goal, one or more
organs cooperate.For instance, blood vessels
and the heart collaborate to circulate blood
throughout the body in order to supply cells
with oxygen and nutrients.The integumentary,
skeletal, nervous, muscular, endocrine,
respiratory, lymphatic, digestive, urinary, and
reproductive systems are the other organ
systems of the body in addition to the
cardiovascular system.
Organism Level The highest level of organization is the
organismal level.It is the cooperation of all
structural levels as a whole.Simply put, it
refers to the human species as a whole.
● List 11 organ system of the human body and explain their major functions.
Integumentary System Its main function is to act as a barrier to
protect the body from the outside world. It
also functions to retain body fluids, protect
against disease, eliminate waste products, and
regulate body temperature.(skin,hair,nails and
more)
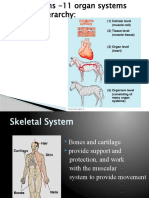
Skeletal System The skeletal system works as a support
structure for your body. It gives the body its
shape, allows movement, makes blood cells,
provides protection for organs and stores
minerals
Nervous System The nervous system transmits signals between
the brain and the rest of the body, including
internal organs.
Lympatic System To return excess tissue fluid to the blood
vascular system via the lymphatic vessels.
Endocrine System Endocrine glands release hormones into the
bloodstream. This lets the hormones travel to
cells in other parts of the body. The endocrine
hormones help control mood, growth and
development, the way our organs work,
metabolism , and reproduction.
Respiratory System The respiratory system is the network of
organs and tissues that help you breathe. It
includes your airways, lungs and blood
vessels.
Muscular System Muscles allow a person to move, speak, and
chew. They control heartbeat, breathing, and
digestion. Other seemingly unrelated
functions, including temperature regulation
and vision, also rely on the muscular system.
Digestive System The digestive system breaks down food into
nutrients such as carbohydrates, fats and
proteins. They can then be absorbed into the
bloodstream so the body can use them for
energy, growth and repair.
Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system delivers oxygen,
nutrients, hormones, and other important
substances to cells and organs in the body.
Reproductive System The human reproductive system functions to
produce human offspring, with the male
providing sperm and the female providing the
ovum
Urinary System The purpose of Urinary system is to eliminate
wastes from the body, regulate blood volume
and pressure, control levels of electrolytes and
metabolites, and regulate blood pH.
— Check your Understanding
1. In the hierarchy, at which level of structural organization would an immunologist’s
field of study be considered? Why?
- Integumentary System because immunologist specially trained to diagnose, treat and
manage allergies, asthma and immunologic disorders including primary
immunodeficiency disorders.
2. What is the correct structural order of the following terms: atom, organ, cell,
organism, tissue?
- Atom, Cell, Tissue , Organ , Organism
3. Which organ system includes the heart and blood vessels? Which organ system
includes the kidneys?
- Circulatory System and Urinary System
4. List the order of the levels of organization in biological life forms from simplest to
most complex and give an example of something from each level of the scale.
Word Bank: Tissue, Organelle , Organ , Cell , Organism, Organ System
Biological Level of Organization Example
Tissue Connective Tissue, Epithelial tissue,Muscle
tissue and Nervous Tissue
Organelle Cell Membrane, Lysosomes, Mitochondria
Organ Heart, Kidney , Liver , Brain
Cell Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cell
Organism Plant, Fungi , Animal , Protist,Monera
Organ System Respiratory System, Nervous System ,
Digestive system, Urinary System,
Cardiovascular System
You might also like
- Human Body: How Is The Human Body Similar To A Well-Tuned Machine?Document9 pagesHuman Body: How Is The Human Body Similar To A Well-Tuned Machine?Montse GilNo ratings yet
- AnaphyDocument2 pagesAnaphynaomimarielleNo ratings yet
- Human Being Are Complex Multicellular OrganismsDocument9 pagesHuman Being Are Complex Multicellular OrganismsWilliam WongNo ratings yet
- CelllllDocument9 pagesCelllllbasman1212No ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument19 pagesAnaphy ReviewerGian Paolo P. CHAVEZNo ratings yet
- Hbs Unite 1 Summary FinalDocument45 pagesHbs Unite 1 Summary Finalapi-277775953No ratings yet
- Human BodyDocument3 pagesHuman Bodyjavier andres martinez100% (1)
- Body Systems Chart System Illustration Structures Function: DigestiveDocument3 pagesBody Systems Chart System Illustration Structures Function: DigestiveMicaela DNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 - Module 7 - Earth and Life ScienceDocument8 pagesQuarter 2 - Module 7 - Earth and Life ScienceKristine Alcordo100% (1)
- From Cell To Organism: Levels of OrganizationDocument26 pagesFrom Cell To Organism: Levels of OrganizationIan ELNo ratings yet
- Modules in Earth ScienceDocument22 pagesModules in Earth ScienceAlpha100% (1)
- System Structure Purpose Interaction With Other SystemDocument1 pageSystem Structure Purpose Interaction With Other SystemLianne LagromaNo ratings yet
- Systems Generalities Functions Cardiovascular System: Luis Daniel Mendez García C.I. 26.051.086 Sección 5Document3 pagesSystems Generalities Functions Cardiovascular System: Luis Daniel Mendez García C.I. 26.051.086 Sección 5Luis Daniel Méndez GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - Ch1 To Ch6Document30 pagesReviewer - Ch1 To Ch6cpagente01No ratings yet
- Physiology 1 IntroductionDocument101 pagesPhysiology 1 IntroductionBrian KipchumbaNo ratings yet
- Cell To Organism WorksheetDocument7 pagesCell To Organism WorksheetSehasa PathiranaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyCheese KekNo ratings yet
- 3-HANDOUT - Understanding The Human BodyDocument5 pages3-HANDOUT - Understanding The Human BodySabrina PorcoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Anatomy and Physiology (Transes)Document9 pagesIntroduction To Human Anatomy and Physiology (Transes)Kathleen BalauagNo ratings yet
- The Human Body: Anatomy and Physiology: Part ADocument60 pagesThe Human Body: Anatomy and Physiology: Part AbeckhamderuloNo ratings yet
- Anatomy: PATHFIT 1-Movement EnhancementDocument21 pagesAnatomy: PATHFIT 1-Movement EnhancementClint BalaNo ratings yet
- The Incredible Human BodyDocument15 pagesThe Incredible Human BodyArki TorniNo ratings yet
- Sistem Kontrol Saraf Dan Endokrin: Departemen Fisiologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sumatera UtaraDocument26 pagesSistem Kontrol Saraf Dan Endokrin: Departemen Fisiologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sumatera UtaraLoshseniNo ratings yet
- The Human Body: Gross /macroscopic AnatomyDocument8 pagesThe Human Body: Gross /macroscopic AnatomyMuhamad Hafiz Bin Mohd BakriNo ratings yet
- MC100 Human Anatomy and Physiology: The Human Body: Anatomy - Is The Study of The Body's Development AnatomyDocument17 pagesMC100 Human Anatomy and Physiology: The Human Body: Anatomy - Is The Study of The Body's Development AnatomyRikki Mae BuenoNo ratings yet
- Human Biology: Prof. Dr. Ahmed Ali MohammedDocument22 pagesHuman Biology: Prof. Dr. Ahmed Ali MohammedAli HarthNo ratings yet
- 2nd - Human Organ SystemsDocument26 pages2nd - Human Organ SystemsJaeshelle Florendo100% (1)
- ANAPHY REV Chapt 1Document8 pagesANAPHY REV Chapt 1crptzxraffNo ratings yet
- Structure Level Assignment KeanneDocument2 pagesStructure Level Assignment KeanneJerome GaribayNo ratings yet
- Ch. 13 Human Body Final 1Document16 pagesCh. 13 Human Body Final 1RANJAN RAJNo ratings yet
- KnowledgeDocument2 pagesKnowledgeSet FireNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument2 pagesAnaphy ReviewerNarena BoniteNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Reviewer 1 BodyDocument5 pagesAnaphy Reviewer 1 BodyJohn Niño CasuelaNo ratings yet
- TX Bio Ch30Document48 pagesTX Bio Ch30Mario Alberto Mora OrtizNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiologybobadillamarie156No ratings yet
- Body Cells: Skin Cells Red Blood Cells Bones andDocument17 pagesBody Cells: Skin Cells Red Blood Cells Bones andHj LifeNo ratings yet
- Module 8-9Document5 pagesModule 8-9mirriam mag-asoNo ratings yet
- AP Module1 Trans DiazDocument9 pagesAP Module1 Trans DiazJohn Rafael DiazNo ratings yet
- Bio StudyDocument12 pagesBio StudyAs If YoU dOnT kNoW tHe NaMeNo ratings yet
- Activity #1 Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesActivity #1 Anatomy and PhysiologyJenny Sumangil EspejoNo ratings yet
- NOTES ReportingsDocument16 pagesNOTES Reportings2240739No ratings yet
- Organ System 1Document15 pagesOrgan System 1LeoNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To The Human Body: I. CompetenceDocument11 pagesAn Introduction To The Human Body: I. CompetenceMea DolautaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Organ System Overview: Atoms Cell Tissue OrganDocument8 pagesAnatomy Organ System Overview: Atoms Cell Tissue OrganBea PrestoNo ratings yet
- Body OrganizationDocument4 pagesBody OrganizationGlaizel PanalNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Physiology and Biochemistry-Notes For BBA (HA)Document12 pagesIntroduction of Physiology and Biochemistry-Notes For BBA (HA)devNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument12 pagesAnaphy ReviewerRuby Jane LaquihonNo ratings yet
- Document 5Document42 pagesDocument 5mmbakk :0No ratings yet
- Body SystemsDocument2 pagesBody SystemsOlerato NtsimaneNo ratings yet
- Assignment Topic 1Document3 pagesAssignment Topic 1Charlyn CasabalNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Pre LimDocument13 pagesAnaphy Pre LimKyle M. BayangosNo ratings yet
- Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 1Document28 pagesOverview of Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 1Vincent Dajao CimafrancaNo ratings yet
- M. Anatomy Lesson 1Document9 pagesM. Anatomy Lesson 1Lainie ZefiahNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument27 pagesBiology Projectswatipatel200816No ratings yet
- Our BodyDocument4 pagesOur BodyaleyisverycooNo ratings yet
- Revisão de ScienceDocument7 pagesRevisão de Sciencebezin RPNo ratings yet
- Module 1 RAWDocument25 pagesModule 1 RAWCordelia TobinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Body As A Whole: Abdul Quddoos Lecturer SAHARA College of Pharmacy, NarowalDocument23 pagesIntroduction To The Body As A Whole: Abdul Quddoos Lecturer SAHARA College of Pharmacy, NarowalAyeshaNo ratings yet
- Types of Body SystemDocument4 pagesTypes of Body SystemLatowed RemuelNo ratings yet
- Culmi Activity 1Document1 pageCulmi Activity 1Micaella ValdezNo ratings yet
- LS Act03Document5 pagesLS Act03Micaella ValdezNo ratings yet
- Transcend - Valdez - SodaliteDocument1 pageTranscend - Valdez - SodaliteMicaella ValdezNo ratings yet
- The Lucky Plaza (Poetry) Dinah Roma: and I Remember Her Through The Day's Leisure. My Veiled Urgency To Leave The SpotDocument6 pagesThe Lucky Plaza (Poetry) Dinah Roma: and I Remember Her Through The Day's Leisure. My Veiled Urgency To Leave The SpotMicaella ValdezNo ratings yet
- Pie and Pastries - Recasa Hyacinth - SodaliteDocument16 pagesPie and Pastries - Recasa Hyacinth - SodaliteMicaella ValdezNo ratings yet