Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is CDS
What Is CDS
Uploaded by
Prashant LandgeCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Garrett Birkhoff, Gian-Carlo Rota Ordinary Differential Equations 1989 PDFDocument409 pagesGarrett Birkhoff, Gian-Carlo Rota Ordinary Differential Equations 1989 PDFPrashant Landge88% (8)
- ITTSD - BA Written Test PDFDocument2 pagesITTSD - BA Written Test PDFPrashant Landge0% (2)
- Nomura CDS Primer 12may04Document12 pagesNomura CDS Primer 12may04Ethan Sun100% (1)
- Functioning of CDS PDFDocument5 pagesFunctioning of CDS PDFKeval ShahNo ratings yet
- Inside Job TermsDocument8 pagesInside Job TermsKavita SinghNo ratings yet
- Electrosteel Case: Manufacturing Strategy - MG 635Document4 pagesElectrosteel Case: Manufacturing Strategy - MG 635Prashant LandgeNo ratings yet
- Not InsuranceDocument3 pagesNot InsuranceKritiNo ratings yet
- Credit Default Swaps: Project On Financial Management IiDocument27 pagesCredit Default Swaps: Project On Financial Management IiPratik ReshamwalaNo ratings yet
- Foreclosure Fraud Securitization ProcessDocument5 pagesForeclosure Fraud Securitization ProcessRoseNo ratings yet
- Credit Default Swaps 1712042033Document14 pagesCredit Default Swaps 1712042033anuphome87No ratings yet
- Credit Derivatives: An Overview: David MengleDocument24 pagesCredit Derivatives: An Overview: David MengleMonica HoffmanNo ratings yet
- Credit Default SwapDocument38 pagesCredit Default Swapbrian3442No ratings yet
- Krishna Mohan Maurya F2-13: Prepared byDocument19 pagesKrishna Mohan Maurya F2-13: Prepared byPurnima Bhartia BankaNo ratings yet
- The Cds - A Quick ContextDocument1 pageThe Cds - A Quick ContextTsiori RasamiarisoaNo ratings yet
- Credit Default Swaps and GFC-C2D2Document5 pagesCredit Default Swaps and GFC-C2D2michnhiNo ratings yet
- Credit Default SwapsDocument4 pagesCredit Default Swapsza_gabyNo ratings yet
- Credit Default SwapDocument23 pagesCredit Default SwapSreedev PeringaraNo ratings yet
- CDSDocument21 pagesCDSVishwanathNo ratings yet
- Credit DerivativesDocument21 pagesCredit Derivativesprachiz1No ratings yet
- 11-12 1st MFI Credit DerivativesDocument22 pages11-12 1st MFI Credit DerivativesChris LauNo ratings yet
- Thesis Credit Default SwapsDocument7 pagesThesis Credit Default Swapsjessicaoatisneworleans100% (2)
- 1.4 Credit Risk Transfer Mechanisms-1607079978449Document22 pages1.4 Credit Risk Transfer Mechanisms-1607079978449ashutosh malhotraNo ratings yet
- Credit DerivativesDocument37 pagesCredit DerivativesshehzadshroffNo ratings yet
- Financial Derivatives: A Perceived ValueDocument20 pagesFinancial Derivatives: A Perceived ValueIvan MendesNo ratings yet
- Credit Default SwapDocument6 pagesCredit Default SwapCai YunmengNo ratings yet
- Credit DerivativeDocument5 pagesCredit DerivativedomomwambiNo ratings yet
- Credit Default SwapsDocument7 pagesCredit Default SwapsMạnh ViệtNo ratings yet
- RiskMgt Chap12Document30 pagesRiskMgt Chap12Sidra JamilNo ratings yet
- Credit Default SwapsDocument18 pagesCredit Default SwapsBhawin PatelNo ratings yet
- The Credit Hedging Agency Model Vs Credit Default SwapsDocument3 pagesThe Credit Hedging Agency Model Vs Credit Default SwapsJasvinder JosenNo ratings yet
- BCG CaseDocument2 pagesBCG Caseorigami87No ratings yet
- Credit Derivatives - Basic Concepts Golaka C NathDocument19 pagesCredit Derivatives - Basic Concepts Golaka C NathGolaka NathNo ratings yet
- Credit Default SwapsDocument4 pagesCredit Default SwapsAbhijeit BhosaleNo ratings yet
- Financial Derivatives and Credit DerivativesDocument7 pagesFinancial Derivatives and Credit DerivativesmariamaaloufnasrNo ratings yet
- Dissertation On Credit Default SwapDocument6 pagesDissertation On Credit Default SwapBuyingPaperCanada100% (1)
- Securitization SubprimeCrisisDocument5 pagesSecuritization SubprimeCrisisNiraj MohanNo ratings yet
- Securitization SubprimeCrisisDocument5 pagesSecuritization SubprimeCrisisNiraj MohanNo ratings yet
- Markit Credit Indices PrimerDocument63 pagesMarkit Credit Indices Primersa.vivek1522No ratings yet
- Credit Default Swaps (CDS) SimplifiedDocument11 pagesCredit Default Swaps (CDS) Simplifiedvpotdar6865No ratings yet
- Credit Risk - Credit DerivativesDocument20 pagesCredit Risk - Credit DerivativeskerenkangNo ratings yet
- Sovereign Financial Guarantees: by Tomas Magnusson Director and General Counsel The Swedish National Debt OfficeDocument15 pagesSovereign Financial Guarantees: by Tomas Magnusson Director and General Counsel The Swedish National Debt OfficeKHALID SHAMIMNo ratings yet
- Derivative (Finance) : Collateralised Debt ObligationDocument28 pagesDerivative (Finance) : Collateralised Debt ObligationvaniNo ratings yet
- Credit Default Swaps and Their Application: DR Ewelina Sokołowska, DR Justyna Łapi SkaDocument7 pagesCredit Default Swaps and Their Application: DR Ewelina Sokołowska, DR Justyna Łapi SkaSimon AltkornNo ratings yet
- Finshastra January 2011 Volume 1Document17 pagesFinshastra January 2011 Volume 1Sarthak ParnamiNo ratings yet
- Credit Derivatives CDS CDO CLO 1709821374Document5 pagesCredit Derivatives CDS CDO CLO 1709821374walid.ncirNo ratings yet
- Credit Default SwapsDocument7 pagesCredit Default Swapsrameshg1960No ratings yet
- Financial RisksDocument3 pagesFinancial RisksViz PrezNo ratings yet
- Synthetic CDODocument9 pagesSynthetic CDObrian3442No ratings yet
- Group 6: by - Garvit Agarwal Gyan Prakash Karan Gupta Ravikumar Soni Sahil SinglaDocument21 pagesGroup 6: by - Garvit Agarwal Gyan Prakash Karan Gupta Ravikumar Soni Sahil SinglaSahil SinglaNo ratings yet
- Financial Products Refer To Instruments That Help You Save, Invest, GetDocument2 pagesFinancial Products Refer To Instruments That Help You Save, Invest, GetArshad ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Krassimir Petrov - Intto To Credit Default SwapsDocument13 pagesKrassimir Petrov - Intto To Credit Default SwapsAntonio Luis SantosNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five Mortgage MarketDocument41 pagesChapter Five Mortgage MarketBantamkak FikaduNo ratings yet
- Retail BankingDocument9 pagesRetail BankingMohan KottuNo ratings yet
- Counter Party Risk IntermediationDocument12 pagesCounter Party Risk IntermediationGunpreet ChahalNo ratings yet
- Sesi 11 - FI-D & ABSDocument37 pagesSesi 11 - FI-D & ABSMuhibbuddin NoorNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketDocument8 pagesFinancial Marketshahid3454No ratings yet
- Basics of Securitisation of AssetsDocument2 pagesBasics of Securitisation of Assetslapogk100% (1)
- The Great Recession: The burst of the property bubble and the excesses of speculationFrom EverandThe Great Recession: The burst of the property bubble and the excesses of speculationNo ratings yet
- Fixed Income Securities: A Beginner's Guide to Understand, Invest and Evaluate Fixed Income Securities: Investment series, #2From EverandFixed Income Securities: A Beginner's Guide to Understand, Invest and Evaluate Fixed Income Securities: Investment series, #2No ratings yet
- From Dream to Deal: Navigating Creative Financing in Real Estate for the Beginning InvestorFrom EverandFrom Dream to Deal: Navigating Creative Financing in Real Estate for the Beginning InvestorNo ratings yet
- What Is A Interest Rate SwapDocument1 pageWhat Is A Interest Rate SwapPrashant LandgeNo ratings yet
- EquityDocument1 pageEquityPrashant LandgeNo ratings yet
- MAS OTC ReportingDocument1 pageMAS OTC ReportingPrashant LandgeNo ratings yet
- Recommended Daily Intake of Vitamins and MineralsDocument4 pagesRecommended Daily Intake of Vitamins and MineralsPrashant LandgeNo ratings yet
- Trade Life CycleDocument1 pageTrade Life CyclePrashant LandgeNo ratings yet
- CFTC RegulationDocument1 pageCFTC RegulationPrashant LandgeNo ratings yet
- Valuation of BondsDocument1 pageValuation of BondsPrashant LandgeNo ratings yet
- Cessna Aircraft One Is To One Scale ModelDocument1 pageCessna Aircraft One Is To One Scale ModelPrashant LandgeNo ratings yet
- Interest Rate Swap ValuationDocument1 pageInterest Rate Swap ValuationPrashant LandgeNo ratings yet
- A Companion To Analysis - Solutions, Korner PDFDocument406 pagesA Companion To Analysis - Solutions, Korner PDFPrashant LandgeNo ratings yet
- George Polya, Gabor Szegö, C.E. Billigheimer Problems and Theorems in Analysis II 2004 PDFDocument412 pagesGeorge Polya, Gabor Szegö, C.E. Billigheimer Problems and Theorems in Analysis II 2004 PDFPrashant LandgeNo ratings yet
What Is CDS
What Is CDS
Uploaded by
Prashant LandgeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is CDS
What Is CDS
Uploaded by
Prashant LandgeCopyright:
Available Formats
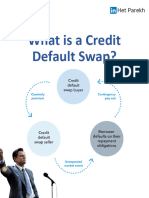
CDS stands for Credit Default Swap, which is a type of financial derivative that allows
investors to protect themselves against the risk of default on a bond or other type of
debt. A CDS contract involves two parties: the buyer of the CDS, who is typically looking
to protect themselves against default risk, and the seller of the CDS, who is typically
looking to earn a fee for taking on that risk.
In a CDS, the buyer pays a fee to the seller in exchange for the right to receive a
payment if a specific credit event occurs, such as a default on the underlying debt. If a
credit event occurs, the seller of the CDS is obligated to pay the buyer the face value of
the underlying debt, minus the recovery value. In other words, the CDS acts as a type of
insurance policy against the risk of default.
CDS contracts are widely used in the financial industry to manage credit risk exposure,
particularly in the market for corporate and sovereign bonds. However, they have been
criticized for their role in the 2008 financial crisis, as some market participants used
CDS to speculate on the risk of default without actually owning the underlying debt. This
led to a proliferation of CDS contracts that were not backed by actual debt, which
contributed to the instability of the financial system.
You might also like
- Garrett Birkhoff, Gian-Carlo Rota Ordinary Differential Equations 1989 PDFDocument409 pagesGarrett Birkhoff, Gian-Carlo Rota Ordinary Differential Equations 1989 PDFPrashant Landge88% (8)
- ITTSD - BA Written Test PDFDocument2 pagesITTSD - BA Written Test PDFPrashant Landge0% (2)
- Nomura CDS Primer 12may04Document12 pagesNomura CDS Primer 12may04Ethan Sun100% (1)
- Functioning of CDS PDFDocument5 pagesFunctioning of CDS PDFKeval ShahNo ratings yet
- Inside Job TermsDocument8 pagesInside Job TermsKavita SinghNo ratings yet
- Electrosteel Case: Manufacturing Strategy - MG 635Document4 pagesElectrosteel Case: Manufacturing Strategy - MG 635Prashant LandgeNo ratings yet
- Not InsuranceDocument3 pagesNot InsuranceKritiNo ratings yet
- Credit Default Swaps: Project On Financial Management IiDocument27 pagesCredit Default Swaps: Project On Financial Management IiPratik ReshamwalaNo ratings yet
- Foreclosure Fraud Securitization ProcessDocument5 pagesForeclosure Fraud Securitization ProcessRoseNo ratings yet
- Credit Default Swaps 1712042033Document14 pagesCredit Default Swaps 1712042033anuphome87No ratings yet
- Credit Derivatives: An Overview: David MengleDocument24 pagesCredit Derivatives: An Overview: David MengleMonica HoffmanNo ratings yet
- Credit Default SwapDocument38 pagesCredit Default Swapbrian3442No ratings yet
- Krishna Mohan Maurya F2-13: Prepared byDocument19 pagesKrishna Mohan Maurya F2-13: Prepared byPurnima Bhartia BankaNo ratings yet
- The Cds - A Quick ContextDocument1 pageThe Cds - A Quick ContextTsiori RasamiarisoaNo ratings yet
- Credit Default Swaps and GFC-C2D2Document5 pagesCredit Default Swaps and GFC-C2D2michnhiNo ratings yet
- Credit Default SwapsDocument4 pagesCredit Default Swapsza_gabyNo ratings yet
- Credit Default SwapDocument23 pagesCredit Default SwapSreedev PeringaraNo ratings yet
- CDSDocument21 pagesCDSVishwanathNo ratings yet
- Credit DerivativesDocument21 pagesCredit Derivativesprachiz1No ratings yet
- 11-12 1st MFI Credit DerivativesDocument22 pages11-12 1st MFI Credit DerivativesChris LauNo ratings yet
- Thesis Credit Default SwapsDocument7 pagesThesis Credit Default Swapsjessicaoatisneworleans100% (2)
- 1.4 Credit Risk Transfer Mechanisms-1607079978449Document22 pages1.4 Credit Risk Transfer Mechanisms-1607079978449ashutosh malhotraNo ratings yet
- Credit DerivativesDocument37 pagesCredit DerivativesshehzadshroffNo ratings yet
- Financial Derivatives: A Perceived ValueDocument20 pagesFinancial Derivatives: A Perceived ValueIvan MendesNo ratings yet
- Credit Default SwapDocument6 pagesCredit Default SwapCai YunmengNo ratings yet
- Credit DerivativeDocument5 pagesCredit DerivativedomomwambiNo ratings yet
- Credit Default SwapsDocument7 pagesCredit Default SwapsMạnh ViệtNo ratings yet
- RiskMgt Chap12Document30 pagesRiskMgt Chap12Sidra JamilNo ratings yet
- Credit Default SwapsDocument18 pagesCredit Default SwapsBhawin PatelNo ratings yet
- The Credit Hedging Agency Model Vs Credit Default SwapsDocument3 pagesThe Credit Hedging Agency Model Vs Credit Default SwapsJasvinder JosenNo ratings yet
- BCG CaseDocument2 pagesBCG Caseorigami87No ratings yet
- Credit Derivatives - Basic Concepts Golaka C NathDocument19 pagesCredit Derivatives - Basic Concepts Golaka C NathGolaka NathNo ratings yet
- Credit Default SwapsDocument4 pagesCredit Default SwapsAbhijeit BhosaleNo ratings yet
- Financial Derivatives and Credit DerivativesDocument7 pagesFinancial Derivatives and Credit DerivativesmariamaaloufnasrNo ratings yet
- Dissertation On Credit Default SwapDocument6 pagesDissertation On Credit Default SwapBuyingPaperCanada100% (1)
- Securitization SubprimeCrisisDocument5 pagesSecuritization SubprimeCrisisNiraj MohanNo ratings yet
- Securitization SubprimeCrisisDocument5 pagesSecuritization SubprimeCrisisNiraj MohanNo ratings yet
- Markit Credit Indices PrimerDocument63 pagesMarkit Credit Indices Primersa.vivek1522No ratings yet
- Credit Default Swaps (CDS) SimplifiedDocument11 pagesCredit Default Swaps (CDS) Simplifiedvpotdar6865No ratings yet
- Credit Risk - Credit DerivativesDocument20 pagesCredit Risk - Credit DerivativeskerenkangNo ratings yet
- Sovereign Financial Guarantees: by Tomas Magnusson Director and General Counsel The Swedish National Debt OfficeDocument15 pagesSovereign Financial Guarantees: by Tomas Magnusson Director and General Counsel The Swedish National Debt OfficeKHALID SHAMIMNo ratings yet
- Derivative (Finance) : Collateralised Debt ObligationDocument28 pagesDerivative (Finance) : Collateralised Debt ObligationvaniNo ratings yet
- Credit Default Swaps and Their Application: DR Ewelina Sokołowska, DR Justyna Łapi SkaDocument7 pagesCredit Default Swaps and Their Application: DR Ewelina Sokołowska, DR Justyna Łapi SkaSimon AltkornNo ratings yet
- Finshastra January 2011 Volume 1Document17 pagesFinshastra January 2011 Volume 1Sarthak ParnamiNo ratings yet
- Credit Derivatives CDS CDO CLO 1709821374Document5 pagesCredit Derivatives CDS CDO CLO 1709821374walid.ncirNo ratings yet
- Credit Default SwapsDocument7 pagesCredit Default Swapsrameshg1960No ratings yet
- Financial RisksDocument3 pagesFinancial RisksViz PrezNo ratings yet
- Synthetic CDODocument9 pagesSynthetic CDObrian3442No ratings yet
- Group 6: by - Garvit Agarwal Gyan Prakash Karan Gupta Ravikumar Soni Sahil SinglaDocument21 pagesGroup 6: by - Garvit Agarwal Gyan Prakash Karan Gupta Ravikumar Soni Sahil SinglaSahil SinglaNo ratings yet
- Financial Products Refer To Instruments That Help You Save, Invest, GetDocument2 pagesFinancial Products Refer To Instruments That Help You Save, Invest, GetArshad ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Krassimir Petrov - Intto To Credit Default SwapsDocument13 pagesKrassimir Petrov - Intto To Credit Default SwapsAntonio Luis SantosNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five Mortgage MarketDocument41 pagesChapter Five Mortgage MarketBantamkak FikaduNo ratings yet
- Retail BankingDocument9 pagesRetail BankingMohan KottuNo ratings yet
- Counter Party Risk IntermediationDocument12 pagesCounter Party Risk IntermediationGunpreet ChahalNo ratings yet
- Sesi 11 - FI-D & ABSDocument37 pagesSesi 11 - FI-D & ABSMuhibbuddin NoorNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketDocument8 pagesFinancial Marketshahid3454No ratings yet
- Basics of Securitisation of AssetsDocument2 pagesBasics of Securitisation of Assetslapogk100% (1)
- The Great Recession: The burst of the property bubble and the excesses of speculationFrom EverandThe Great Recession: The burst of the property bubble and the excesses of speculationNo ratings yet
- Fixed Income Securities: A Beginner's Guide to Understand, Invest and Evaluate Fixed Income Securities: Investment series, #2From EverandFixed Income Securities: A Beginner's Guide to Understand, Invest and Evaluate Fixed Income Securities: Investment series, #2No ratings yet
- From Dream to Deal: Navigating Creative Financing in Real Estate for the Beginning InvestorFrom EverandFrom Dream to Deal: Navigating Creative Financing in Real Estate for the Beginning InvestorNo ratings yet
- What Is A Interest Rate SwapDocument1 pageWhat Is A Interest Rate SwapPrashant LandgeNo ratings yet
- EquityDocument1 pageEquityPrashant LandgeNo ratings yet
- MAS OTC ReportingDocument1 pageMAS OTC ReportingPrashant LandgeNo ratings yet
- Recommended Daily Intake of Vitamins and MineralsDocument4 pagesRecommended Daily Intake of Vitamins and MineralsPrashant LandgeNo ratings yet
- Trade Life CycleDocument1 pageTrade Life CyclePrashant LandgeNo ratings yet
- CFTC RegulationDocument1 pageCFTC RegulationPrashant LandgeNo ratings yet
- Valuation of BondsDocument1 pageValuation of BondsPrashant LandgeNo ratings yet
- Cessna Aircraft One Is To One Scale ModelDocument1 pageCessna Aircraft One Is To One Scale ModelPrashant LandgeNo ratings yet
- Interest Rate Swap ValuationDocument1 pageInterest Rate Swap ValuationPrashant LandgeNo ratings yet
- A Companion To Analysis - Solutions, Korner PDFDocument406 pagesA Companion To Analysis - Solutions, Korner PDFPrashant LandgeNo ratings yet
- George Polya, Gabor Szegö, C.E. Billigheimer Problems and Theorems in Analysis II 2004 PDFDocument412 pagesGeorge Polya, Gabor Szegö, C.E. Billigheimer Problems and Theorems in Analysis II 2004 PDFPrashant LandgeNo ratings yet