Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EE 419 BEE Lec Module 4
EE 419 BEE Lec Module 4
Uploaded by
Jhun Lucky SadsadCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 2nd Puc Maths Sulalitha Exam Practice Guide Eng Version 2020-21 by ChikkaballapuraDocument101 pages2nd Puc Maths Sulalitha Exam Practice Guide Eng Version 2020-21 by Chikkaballapurabot insaan82% (90)
- EE 424 Module 3Document45 pagesEE 424 Module 3Johnjoseph VeraNo ratings yet
- XII Electronics HSC Board PapersDocument20 pagesXII Electronics HSC Board PapersVidyasagar Academy0% (2)
- Solved Find Vo in Fig E821 Using Mesh Analysisfigure E821 CheggcomDocument5 pagesSolved Find Vo in Fig E821 Using Mesh Analysisfigure E821 Cheggcom20280110No ratings yet
- DC Circuits 9 SibuloDocument9 pagesDC Circuits 9 Sibulonoah.sibulo2014No ratings yet
- Ec-101 - Final PDFDocument2 pagesEc-101 - Final PDFarjunv_14No ratings yet
- Untitled PresentationDocument35 pagesUntitled Presentationmohamedabdelrazek1513No ratings yet
- Ci Ia Li1 Circuit Analysis 1: Chapter # 2 Resistive CircuitsDocument12 pagesCi Ia Li1 Circuit Analysis 1: Chapter # 2 Resistive CircuitssalmanshahidkhanNo ratings yet
- chp03 Bej10303Document37 pageschp03 Bej10303dharwinNo ratings yet
- Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering North-Eastern Hill University, Shillong - 793 022Document2 pagesDepartment of Electronics & Communication Engineering North-Eastern Hill University, Shillong - 793 022Joyprakash LairenlakpamNo ratings yet
- Maths Question-1Document2 pagesMaths Question-1megha raniNo ratings yet
- CE EEE 1203 E-2016 Final QuestionDocument3 pagesCE EEE 1203 E-2016 Final QuestionTA MI MNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical DiscussionDocument157 pagesBasic Electrical Discussionseul jichuNo ratings yet
- ELE1IEL_Assignment_2Document15 pagesELE1IEL_Assignment_2Jai SharmaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals Part - 003Document10 pagesFundamentals Part - 003Ashirvad RathNo ratings yet
- Circuit 3Document5 pagesCircuit 3richy launcherNo ratings yet
- Elecs Compilation 1Document42 pagesElecs Compilation 1Raine LopezNo ratings yet
- Quiz 0n Electrical CircuitsDocument3 pagesQuiz 0n Electrical CircuitsAsdcxzNo ratings yet
- 212 EE203 Chapter4Document104 pages212 EE203 Chapter4Ammar AlmobyiedNo ratings yet
- EE1000Document2 pagesEE1000Swastik LenkaNo ratings yet
- Kirchhoff Current Law: One of The Fundamental Conservation Principles in Electrical EngineeringDocument22 pagesKirchhoff Current Law: One of The Fundamental Conservation Principles in Electrical EngineeringHasnat AhmadNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuit Analysis II 2 QuestioDocument8 pagesElectrical Circuit Analysis II 2 Questioc.madhumanoNo ratings yet
- BJT Device Equations and Small-Signal ModelsDocument16 pagesBJT Device Equations and Small-Signal ModelsC_RojasNo ratings yet
- Mock Test Paper-1920-CBSE-C-XII-Set-II-PHY-AnswersDocument10 pagesMock Test Paper-1920-CBSE-C-XII-Set-II-PHY-AnswersHimansu MookherjeeNo ratings yet
- Drttit - Gvet.edu - in Drttit - Gvet.edu - in Drttit - Gvet.edu - in Drttit - Gvet.edu - inDocument4 pagesDrttit - Gvet.edu - in Drttit - Gvet.edu - in Drttit - Gvet.edu - in Drttit - Gvet.edu - inrama KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits (EEE-141) : Source ConversionsDocument10 pagesElectrical Circuits (EEE-141) : Source ConversionsLittle WizardNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 AnswersDocument2 pagesTutorial 1 AnswersAkash VermaNo ratings yet
- 133BK112018Document4 pages133BK112018Chintapalli Ramesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 750913A02101 Electrical CircuitsDocument2 pages750913A02101 Electrical CircuitsKURAKULA VIMAL KUMARNo ratings yet
- Reading 5aDocument23 pagesReading 5ashafyvonommyNo ratings yet
- Drttit - Gvet.edu - in Drttit - Gvet.edu - in Drttit - Gvet.edu - in Drttit - Gvet.edu - inDocument2 pagesDrttit - Gvet.edu - in Drttit - Gvet.edu - in Drttit - Gvet.edu - in Drttit - Gvet.edu - inrama KrishnaNo ratings yet
- MATH15-1: Graphic OrganizerDocument1 pageMATH15-1: Graphic OrganizerRold BaldsNo ratings yet
- Final 05Document8 pagesFinal 05Taha EtemNo ratings yet
- Ap Ipe 2023 4Document15 pagesAp Ipe 2023 4kotapadma1212No ratings yet
- End Sem 2022 ECEDocument18 pagesEnd Sem 2022 ECEgupta.abhi2687No ratings yet
- Det10013 & Electrical Technology: DC Equivalent Circuit & Network TheoremDocument87 pagesDet10013 & Electrical Technology: DC Equivalent Circuit & Network TheoremF1090 ALIF IKHWANNo ratings yet
- CQPPTest-2MainsSoloutions-1679900088565Document38 pagesCQPPTest-2MainsSoloutions-1679900088565Tarun RajputNo ratings yet
- TD Sheet 2 MATH005Document3 pagesTD Sheet 2 MATH005sentia almqNo ratings yet
- DL 541Document3 pagesDL 541Gagan SLNo ratings yet
- hw6 Sol PDFDocument39 pageshw6 Sol PDFLatifNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Sem 2 2014 - 2015Document10 pagesMid Term Sem 2 2014 - 2015FARAZ ABDUL BASITNo ratings yet
- Faculty Recruitment: Time: 1 Hour Total No. of Questions: 30 Maximum Marks: 60Document6 pagesFaculty Recruitment: Time: 1 Hour Total No. of Questions: 30 Maximum Marks: 60Suresh AmalorpavarajNo ratings yet
- Eksdee Boiii!Document18 pagesEksdee Boiii!;(No ratings yet
- NAS (3rd) May2019Document3 pagesNAS (3rd) May2019SANJAY SHARMANo ratings yet
- EE100 Midsem Oct 2014 Question PaperDocument4 pagesEE100 Midsem Oct 2014 Question PaperVachist WangelNo ratings yet
- Answer Scheme Tutorial Sk025: Chapter 3.0: ElectrochemistryDocument18 pagesAnswer Scheme Tutorial Sk025: Chapter 3.0: ElectrochemistryHaikal AminNo ratings yet
- Math Problems Quest Paper bsc1Document2 pagesMath Problems Quest Paper bsc1JaZz SFNo ratings yet
- ElecDocument4 pagesElecJj JumawanNo ratings yet
- (JEE Main 2023 - 25th JAN SHIFT 2 - Paper SolutionsDocument87 pages(JEE Main 2023 - 25th JAN SHIFT 2 - Paper Solutionswifoh66629No ratings yet
- Use E-Papers, Save Trees: Above Line Hide When Print OutDocument101 pagesUse E-Papers, Save Trees: Above Line Hide When Print OutPRUTHVI100% (2)
- Ee-10002 (Sas Nov Mid 22)Document2 pagesEe-10002 (Sas Nov Mid 22)dhruv goraiNo ratings yet
- ϕ ϕ = - - - - - - - 5. Lastly, solve for the unknown distance y - Answer: y = - - - - - - mDocument1 pageϕ ϕ = - - - - - - - 5. Lastly, solve for the unknown distance y - Answer: y = - - - - - - mDerick John RoselNo ratings yet
- Det1013 - Electrical Technology: DC Equivalent Circuit & Network TheoremDocument97 pagesDet1013 - Electrical Technology: DC Equivalent Circuit & Network TheoremSuhaila SharifNo ratings yet
- ENGG 325 - Electric Circuits and Systems: Midterm ExaminationDocument9 pagesENGG 325 - Electric Circuits and Systems: Midterm ExaminationTaha EtemNo ratings yet
- Jrinter Maths1a Model Paper 6 em PDFDocument2 pagesJrinter Maths1a Model Paper 6 em PDFPrudhvi VudaNo ratings yet
- B.C.A. (Part-III) Examination, 2021: Calculus and GeometryDocument2 pagesB.C.A. (Part-III) Examination, 2021: Calculus and GeometryAk GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ap Ipe 2019Document14 pagesAp Ipe 2019kotapadma1212No ratings yet
- CS End TermDocument10 pagesCS End TermaryanNo ratings yet
- Nodia and Company: Gate Solved Paper Electrical Engineering 2007Document49 pagesNodia and Company: Gate Solved Paper Electrical Engineering 2007pankajNo ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis: 5.1 Kirchoff'S RulesDocument8 pagesCircuit Analysis: 5.1 Kirchoff'S RulesLuqman HakimNo ratings yet
- Sulalitha MathsDocument101 pagesSulalitha MathsNithin R Gowda E RNo ratings yet
- EE 419 BEE Lec Module 8Document3 pagesEE 419 BEE Lec Module 8Jhun Lucky SadsadNo ratings yet
- EE 419 BEE Lec Module 7Document6 pagesEE 419 BEE Lec Module 7Jhun Lucky SadsadNo ratings yet
- (BioE 402) MolBio Lecture 5 Nucleic Acid ChemistryDocument7 pages(BioE 402) MolBio Lecture 5 Nucleic Acid ChemistryJhun Lucky SadsadNo ratings yet
- EE 419 BEE Lec Module 6Document3 pagesEE 419 BEE Lec Module 6Jhun Lucky SadsadNo ratings yet
- EE 419 BEE Lec Module 5Document9 pagesEE 419 BEE Lec Module 5Jhun Lucky SadsadNo ratings yet
- (BioE 402) MolBio Lecture 3 Amino AcidsDocument8 pages(BioE 402) MolBio Lecture 3 Amino AcidsJhun Lucky Sadsad100% (1)
- (BioE 402) MolBio Lecture 4 Protein ChemistryDocument7 pages(BioE 402) MolBio Lecture 4 Protein ChemistryJhun Lucky SadsadNo ratings yet
- (BioE 402) MolBio Lecture 2 LipidsDocument21 pages(BioE 402) MolBio Lecture 2 LipidsJhun Lucky SadsadNo ratings yet
- (BioE 402) MolBIo Lecture 1 CarbohydratesDocument12 pages(BioE 402) MolBIo Lecture 1 CarbohydratesJhun Lucky SadsadNo ratings yet
- SUPERMESH Circuit Analysis (@B)Document4 pagesSUPERMESH Circuit Analysis (@B)shivamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2B Methods of Analysis (DC Circuits)Document24 pagesChapter 2B Methods of Analysis (DC Circuits)Khóa Học MS Word Miễn PhíNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document10 pagesAssignment 5AthreyaNo ratings yet
- 7 Thevenin Theorem PDFDocument18 pages7 Thevenin Theorem PDFMUHAMMAD HASEEB ASHRAF MUHAMMAD ASHRAFNo ratings yet
- BE3252 Notes Ro - by WWW - Easyengineering.net 2Document105 pagesBE3252 Notes Ro - by WWW - Easyengineering.net 2Thirumalai Engineering CollegeNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit Analysis CPE121 Lab Manual: Malik Muhammad Hanzala FA20-BCE-039 BCE-1A Dr. Babar MansoorDocument5 pagesElectric Circuit Analysis CPE121 Lab Manual: Malik Muhammad Hanzala FA20-BCE-039 BCE-1A Dr. Babar Mansoorearn moneyNo ratings yet
- Day 6 Notes Mesh AnalysisDocument11 pagesDay 6 Notes Mesh AnalysisSwaroop RamaswamyNo ratings yet
- 1.ohms Law1Document286 pages1.ohms Law1Joenel AncajasNo ratings yet
- Basic Network AnalysisDocument31 pagesBasic Network AnalysisdaodoquangNo ratings yet
- (PPT) Liner Circuit (20013322-018)Document18 pages(PPT) Liner Circuit (20013322-018)Wasif AliNo ratings yet
- Node and Mesh Analysis by InspectionDocument5 pagesNode and Mesh Analysis by InspectionRodrigoNo ratings yet
- EEA101L Lab Report - VALENTON-E08Document2 pagesEEA101L Lab Report - VALENTON-E08Jan ValentonNo ratings yet
- Loop Mesh AnalysisDocument29 pagesLoop Mesh AnalysisOmkar Kumar JhaNo ratings yet
- CSE 250 Assignment 01Document8 pagesCSE 250 Assignment 01Ziana BhuiyanNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory 1 MidtermDocument101 pagesCircuit Theory 1 MidtermMcHaley HalNo ratings yet
- Electronic Curcuit Chapter 2.Document25 pagesElectronic Curcuit Chapter 2.AbcdNo ratings yet
- Complete DC Circuit NotesDocument59 pagesComplete DC Circuit NotesIsha chandravanshiNo ratings yet
- DC Gen GudDocument234 pagesDC Gen GudMeesixNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 DC CircuitsDocument22 pagesChapter 2 DC CircuitsSolomon AsefaNo ratings yet
- Eca 3Document35 pagesEca 3Ahmed SohailNo ratings yet
- 014 - Network Synthesis, Vol - XIV (1957) (Prof. E. A. Guillemin, Prof. P. M. Lewis II, Dr. M. V. Cerrillo)Document20 pages014 - Network Synthesis, Vol - XIV (1957) (Prof. E. A. Guillemin, Prof. P. M. Lewis II, Dr. M. V. Cerrillo)molly zodiacNo ratings yet
- Esc201: Introduction To Electronics: Shilpi Gupta Dept. of Electrical Engineering Iit KanpurDocument40 pagesEsc201: Introduction To Electronics: Shilpi Gupta Dept. of Electrical Engineering Iit KanpurShreyaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Technology (ESC 101-A) Module 1: DC Circuits Voltage and Current SourcesDocument15 pagesBasic Electrical Technology (ESC 101-A) Module 1: DC Circuits Voltage and Current SourcestusharNo ratings yet
- Mesh and Nodal Analysis ProblemsDocument5 pagesMesh and Nodal Analysis ProblemsSyam Sundar100% (2)
- Control System Analysis New CHP 1 and 2Document109 pagesControl System Analysis New CHP 1 and 2KejeindrranNo ratings yet
- Electrical CircuitDocument81 pagesElectrical CircuitBharat Chandra SahuNo ratings yet
- FCS+Chapter+3 (3 1-3 3)Document11 pagesFCS+Chapter+3 (3 1-3 3)kujong agacerNo ratings yet
- ch2 Raymond Winton Intermediate CircuitsDocument34 pagesch2 Raymond Winton Intermediate CircuitsTyler AnthonyNo ratings yet
EE 419 BEE Lec Module 4
EE 419 BEE Lec Module 4
Uploaded by
Jhun Lucky SadsadOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EE 419 BEE Lec Module 4
EE 419 BEE Lec Module 4
Uploaded by
Jhun Lucky SadsadCopyright:
Available Formats
TRANS / MODULE 4
OUTLINE
I. Maxwell’s Mesh Analysis
a. Figure Examination
II. Maxwell’s Analysis Notes and Procedure
a. Notes
b. Procedure
III. Sample Problem
MAXWELL’S MESH ANALYSIS
- also known as loop analysis or the mesh-current
method.
- It uses Kirchhoff's Law to simplify complex network
- It was proposed by James Clerk Maxwell; it involves MAXWELL’S ANALYSIS NOTES AND PROCEDURE
meshes assigned in an independent loop current. NOTES
Hence, the appropriate resistance was assigned 1. Applicable only for planar network
appropriately when the written arbitrary exist 2. Direction of mesh current
- can be only applied to a planar circuit 3. Number of equation to solve an electrical network
o Planar Circuit- a plane with no branches using mesh analysis
crossing one another PROCEDURE
- It reduces the number of equations that must be solved 1. Identify the total number of meshes
FIGURE EXAMINATION 2. Assign mesh current
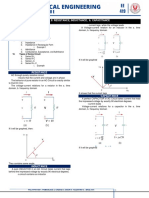
A. Examine the figure below. 3. Develop KVL equation for each mesh
4. Solve for the KVL equation to find the mesh currents
EXAMPLE
EXAMPLE 1 Find the current in each branch.
B C
A
It is a nonplanar circuit as it intersects on the
highlighted image. D
F
E
B. Examine the figure below
SOLUTION:
a. Assume that the voltage drop is negative
-[Ia-Ib], -[Ib-Ia]
b. Determine the number of mesh
mesh=2; eq=2
c. KVL @ a,b,e,f
15V – 5Ia – 10(Ia – Ib) – 10 = 0
[(15V – 5Ia – 10Ia + 10Ib – 10) / 5] = 0
3 – 1Ia – 2Ia + 2Ib – 2
1 – 3Ia + 2Ib -------- EQ: 1
It is a nonplanar circuit as it intersects on the d. KVL @ b,c,d,e
highlighted image. It can be turned into a planar circuit when 10 – 10(Ib – Ia) – 6Ib – 4Ib = 0
it is extended. 10 – 10Ib + 10Ia – 6Ib – 4Ib = 0
PALAYPAYON 1. POMAREJOS 2. SADSAD 3. SISON 4. TOLENTINO 5. | BIOE 2101 1
[(10 – 20Ib + 10Ia)/10] = 0 EXAMPLE 3 Find the Mesh Currents
1 – 2Ib + 1Ia = 0
Ia = 2Ib – 1 ------------ EQ: 2
b
e. Sub EQ 2 to EQ 1
1 – 3(2Ib – 1) + 2Ib = 0 a c
1 – 6Ib + 3 + 2Ib = 0
(4 = 4Ib)/4
Ib = 1A Ia Ib
f. Sub Ib to find EQ 2
Ia = 2Ib – 1 f e d
= 2(1) – 1
Ia = 1A
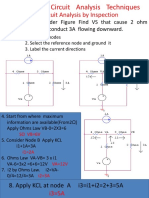
SOLUTION:
g. KCL @ node b a. Finding Ib
I1 = I2 + I3 -Ib = 5A
I3 = I1 – I2 Ib = -5A
I3 = 0
b. KVL @ a,b,e,f
EXAMPLE 2 Find the power delivered to the 4-ohm resistors 10 – 4Ia – 6( Ia – Ib) = 0
10 – 4Ia – 6Ia – 6Ib = 0
10 – 10Ia + 6Ib = 0
a b c 10 – 10Ia + 6(-5) = 0
10 – 10Ia – 30 = 0
(-20 = 10Ia) / 10
Ia = 2A
f d
e
SOLUTION:
a. Find the number of Mesh
m= 2; equations = 2
b. KVL @ a,b,e,f
90 – 6Ia – 10( Ia – Ib) – 4Ia = 0
90 – 6Ia – 10Ia + 10Ib – 4ia = 0
[(90 – 20Ia + 10Ib) / 10] = 0
9 – 2Ia + Ib = 0 ------ EQ 1
c. KVL @ b,c,d,e
-40 – 5Ib – 10(Ib – Ia) – 15Ib = 0
-40 – 5Ib – 10Ib + 10Ia – 15Ib = 0
[(-40 – 30Ib + 10Ia) / 10] = 0
-4 – 3Ib + Ia
Ia = 3Ib + 4------ EQ 2
d. Sub EQ 2 to EQ 1
9 – 2Ia + Ib = 0
9 – 2( 3Ib + 4) + Ib = o
9 – 6Ib – 8 + Ib = 0
(1 = 5Ib) / 5
Ib = 0.2 A
e. Substitute Ib to EQ 2
Ia = 3Ib + 4
Ia = 3(0.2) + 4
Ia = 4.6 A
f. Solve for P
Formula: p=i^2 R
p= (46)^2 (4Ω)
p= 84.64 w
PALAYPAYON 1. POMAREJOS 2. SADSAD 3. SISON 4. TOLENTINO 5. | BIOE 2101 2
You might also like
- 2nd Puc Maths Sulalitha Exam Practice Guide Eng Version 2020-21 by ChikkaballapuraDocument101 pages2nd Puc Maths Sulalitha Exam Practice Guide Eng Version 2020-21 by Chikkaballapurabot insaan82% (90)
- EE 424 Module 3Document45 pagesEE 424 Module 3Johnjoseph VeraNo ratings yet
- XII Electronics HSC Board PapersDocument20 pagesXII Electronics HSC Board PapersVidyasagar Academy0% (2)
- Solved Find Vo in Fig E821 Using Mesh Analysisfigure E821 CheggcomDocument5 pagesSolved Find Vo in Fig E821 Using Mesh Analysisfigure E821 Cheggcom20280110No ratings yet
- DC Circuits 9 SibuloDocument9 pagesDC Circuits 9 Sibulonoah.sibulo2014No ratings yet
- Ec-101 - Final PDFDocument2 pagesEc-101 - Final PDFarjunv_14No ratings yet
- Untitled PresentationDocument35 pagesUntitled Presentationmohamedabdelrazek1513No ratings yet
- Ci Ia Li1 Circuit Analysis 1: Chapter # 2 Resistive CircuitsDocument12 pagesCi Ia Li1 Circuit Analysis 1: Chapter # 2 Resistive CircuitssalmanshahidkhanNo ratings yet
- chp03 Bej10303Document37 pageschp03 Bej10303dharwinNo ratings yet
- Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering North-Eastern Hill University, Shillong - 793 022Document2 pagesDepartment of Electronics & Communication Engineering North-Eastern Hill University, Shillong - 793 022Joyprakash LairenlakpamNo ratings yet
- Maths Question-1Document2 pagesMaths Question-1megha raniNo ratings yet
- CE EEE 1203 E-2016 Final QuestionDocument3 pagesCE EEE 1203 E-2016 Final QuestionTA MI MNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical DiscussionDocument157 pagesBasic Electrical Discussionseul jichuNo ratings yet
- ELE1IEL_Assignment_2Document15 pagesELE1IEL_Assignment_2Jai SharmaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals Part - 003Document10 pagesFundamentals Part - 003Ashirvad RathNo ratings yet
- Circuit 3Document5 pagesCircuit 3richy launcherNo ratings yet
- Elecs Compilation 1Document42 pagesElecs Compilation 1Raine LopezNo ratings yet
- Quiz 0n Electrical CircuitsDocument3 pagesQuiz 0n Electrical CircuitsAsdcxzNo ratings yet
- 212 EE203 Chapter4Document104 pages212 EE203 Chapter4Ammar AlmobyiedNo ratings yet
- EE1000Document2 pagesEE1000Swastik LenkaNo ratings yet
- Kirchhoff Current Law: One of The Fundamental Conservation Principles in Electrical EngineeringDocument22 pagesKirchhoff Current Law: One of The Fundamental Conservation Principles in Electrical EngineeringHasnat AhmadNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuit Analysis II 2 QuestioDocument8 pagesElectrical Circuit Analysis II 2 Questioc.madhumanoNo ratings yet
- BJT Device Equations and Small-Signal ModelsDocument16 pagesBJT Device Equations and Small-Signal ModelsC_RojasNo ratings yet
- Mock Test Paper-1920-CBSE-C-XII-Set-II-PHY-AnswersDocument10 pagesMock Test Paper-1920-CBSE-C-XII-Set-II-PHY-AnswersHimansu MookherjeeNo ratings yet
- Drttit - Gvet.edu - in Drttit - Gvet.edu - in Drttit - Gvet.edu - in Drttit - Gvet.edu - inDocument4 pagesDrttit - Gvet.edu - in Drttit - Gvet.edu - in Drttit - Gvet.edu - in Drttit - Gvet.edu - inrama KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits (EEE-141) : Source ConversionsDocument10 pagesElectrical Circuits (EEE-141) : Source ConversionsLittle WizardNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 AnswersDocument2 pagesTutorial 1 AnswersAkash VermaNo ratings yet
- 133BK112018Document4 pages133BK112018Chintapalli Ramesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 750913A02101 Electrical CircuitsDocument2 pages750913A02101 Electrical CircuitsKURAKULA VIMAL KUMARNo ratings yet
- Reading 5aDocument23 pagesReading 5ashafyvonommyNo ratings yet
- Drttit - Gvet.edu - in Drttit - Gvet.edu - in Drttit - Gvet.edu - in Drttit - Gvet.edu - inDocument2 pagesDrttit - Gvet.edu - in Drttit - Gvet.edu - in Drttit - Gvet.edu - in Drttit - Gvet.edu - inrama KrishnaNo ratings yet
- MATH15-1: Graphic OrganizerDocument1 pageMATH15-1: Graphic OrganizerRold BaldsNo ratings yet
- Final 05Document8 pagesFinal 05Taha EtemNo ratings yet
- Ap Ipe 2023 4Document15 pagesAp Ipe 2023 4kotapadma1212No ratings yet
- End Sem 2022 ECEDocument18 pagesEnd Sem 2022 ECEgupta.abhi2687No ratings yet
- Det10013 & Electrical Technology: DC Equivalent Circuit & Network TheoremDocument87 pagesDet10013 & Electrical Technology: DC Equivalent Circuit & Network TheoremF1090 ALIF IKHWANNo ratings yet
- CQPPTest-2MainsSoloutions-1679900088565Document38 pagesCQPPTest-2MainsSoloutions-1679900088565Tarun RajputNo ratings yet
- TD Sheet 2 MATH005Document3 pagesTD Sheet 2 MATH005sentia almqNo ratings yet
- DL 541Document3 pagesDL 541Gagan SLNo ratings yet
- hw6 Sol PDFDocument39 pageshw6 Sol PDFLatifNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Sem 2 2014 - 2015Document10 pagesMid Term Sem 2 2014 - 2015FARAZ ABDUL BASITNo ratings yet
- Faculty Recruitment: Time: 1 Hour Total No. of Questions: 30 Maximum Marks: 60Document6 pagesFaculty Recruitment: Time: 1 Hour Total No. of Questions: 30 Maximum Marks: 60Suresh AmalorpavarajNo ratings yet
- Eksdee Boiii!Document18 pagesEksdee Boiii!;(No ratings yet
- NAS (3rd) May2019Document3 pagesNAS (3rd) May2019SANJAY SHARMANo ratings yet
- EE100 Midsem Oct 2014 Question PaperDocument4 pagesEE100 Midsem Oct 2014 Question PaperVachist WangelNo ratings yet
- Answer Scheme Tutorial Sk025: Chapter 3.0: ElectrochemistryDocument18 pagesAnswer Scheme Tutorial Sk025: Chapter 3.0: ElectrochemistryHaikal AminNo ratings yet
- Math Problems Quest Paper bsc1Document2 pagesMath Problems Quest Paper bsc1JaZz SFNo ratings yet
- ElecDocument4 pagesElecJj JumawanNo ratings yet
- (JEE Main 2023 - 25th JAN SHIFT 2 - Paper SolutionsDocument87 pages(JEE Main 2023 - 25th JAN SHIFT 2 - Paper Solutionswifoh66629No ratings yet
- Use E-Papers, Save Trees: Above Line Hide When Print OutDocument101 pagesUse E-Papers, Save Trees: Above Line Hide When Print OutPRUTHVI100% (2)
- Ee-10002 (Sas Nov Mid 22)Document2 pagesEe-10002 (Sas Nov Mid 22)dhruv goraiNo ratings yet
- ϕ ϕ = - - - - - - - 5. Lastly, solve for the unknown distance y - Answer: y = - - - - - - mDocument1 pageϕ ϕ = - - - - - - - 5. Lastly, solve for the unknown distance y - Answer: y = - - - - - - mDerick John RoselNo ratings yet
- Det1013 - Electrical Technology: DC Equivalent Circuit & Network TheoremDocument97 pagesDet1013 - Electrical Technology: DC Equivalent Circuit & Network TheoremSuhaila SharifNo ratings yet
- ENGG 325 - Electric Circuits and Systems: Midterm ExaminationDocument9 pagesENGG 325 - Electric Circuits and Systems: Midterm ExaminationTaha EtemNo ratings yet
- Jrinter Maths1a Model Paper 6 em PDFDocument2 pagesJrinter Maths1a Model Paper 6 em PDFPrudhvi VudaNo ratings yet
- B.C.A. (Part-III) Examination, 2021: Calculus and GeometryDocument2 pagesB.C.A. (Part-III) Examination, 2021: Calculus and GeometryAk GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ap Ipe 2019Document14 pagesAp Ipe 2019kotapadma1212No ratings yet
- CS End TermDocument10 pagesCS End TermaryanNo ratings yet
- Nodia and Company: Gate Solved Paper Electrical Engineering 2007Document49 pagesNodia and Company: Gate Solved Paper Electrical Engineering 2007pankajNo ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis: 5.1 Kirchoff'S RulesDocument8 pagesCircuit Analysis: 5.1 Kirchoff'S RulesLuqman HakimNo ratings yet
- Sulalitha MathsDocument101 pagesSulalitha MathsNithin R Gowda E RNo ratings yet
- EE 419 BEE Lec Module 8Document3 pagesEE 419 BEE Lec Module 8Jhun Lucky SadsadNo ratings yet
- EE 419 BEE Lec Module 7Document6 pagesEE 419 BEE Lec Module 7Jhun Lucky SadsadNo ratings yet
- (BioE 402) MolBio Lecture 5 Nucleic Acid ChemistryDocument7 pages(BioE 402) MolBio Lecture 5 Nucleic Acid ChemistryJhun Lucky SadsadNo ratings yet
- EE 419 BEE Lec Module 6Document3 pagesEE 419 BEE Lec Module 6Jhun Lucky SadsadNo ratings yet
- EE 419 BEE Lec Module 5Document9 pagesEE 419 BEE Lec Module 5Jhun Lucky SadsadNo ratings yet
- (BioE 402) MolBio Lecture 3 Amino AcidsDocument8 pages(BioE 402) MolBio Lecture 3 Amino AcidsJhun Lucky Sadsad100% (1)
- (BioE 402) MolBio Lecture 4 Protein ChemistryDocument7 pages(BioE 402) MolBio Lecture 4 Protein ChemistryJhun Lucky SadsadNo ratings yet
- (BioE 402) MolBio Lecture 2 LipidsDocument21 pages(BioE 402) MolBio Lecture 2 LipidsJhun Lucky SadsadNo ratings yet
- (BioE 402) MolBIo Lecture 1 CarbohydratesDocument12 pages(BioE 402) MolBIo Lecture 1 CarbohydratesJhun Lucky SadsadNo ratings yet
- SUPERMESH Circuit Analysis (@B)Document4 pagesSUPERMESH Circuit Analysis (@B)shivamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2B Methods of Analysis (DC Circuits)Document24 pagesChapter 2B Methods of Analysis (DC Circuits)Khóa Học MS Word Miễn PhíNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document10 pagesAssignment 5AthreyaNo ratings yet
- 7 Thevenin Theorem PDFDocument18 pages7 Thevenin Theorem PDFMUHAMMAD HASEEB ASHRAF MUHAMMAD ASHRAFNo ratings yet
- BE3252 Notes Ro - by WWW - Easyengineering.net 2Document105 pagesBE3252 Notes Ro - by WWW - Easyengineering.net 2Thirumalai Engineering CollegeNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit Analysis CPE121 Lab Manual: Malik Muhammad Hanzala FA20-BCE-039 BCE-1A Dr. Babar MansoorDocument5 pagesElectric Circuit Analysis CPE121 Lab Manual: Malik Muhammad Hanzala FA20-BCE-039 BCE-1A Dr. Babar Mansoorearn moneyNo ratings yet
- Day 6 Notes Mesh AnalysisDocument11 pagesDay 6 Notes Mesh AnalysisSwaroop RamaswamyNo ratings yet
- 1.ohms Law1Document286 pages1.ohms Law1Joenel AncajasNo ratings yet
- Basic Network AnalysisDocument31 pagesBasic Network AnalysisdaodoquangNo ratings yet
- (PPT) Liner Circuit (20013322-018)Document18 pages(PPT) Liner Circuit (20013322-018)Wasif AliNo ratings yet
- Node and Mesh Analysis by InspectionDocument5 pagesNode and Mesh Analysis by InspectionRodrigoNo ratings yet
- EEA101L Lab Report - VALENTON-E08Document2 pagesEEA101L Lab Report - VALENTON-E08Jan ValentonNo ratings yet
- Loop Mesh AnalysisDocument29 pagesLoop Mesh AnalysisOmkar Kumar JhaNo ratings yet
- CSE 250 Assignment 01Document8 pagesCSE 250 Assignment 01Ziana BhuiyanNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory 1 MidtermDocument101 pagesCircuit Theory 1 MidtermMcHaley HalNo ratings yet
- Electronic Curcuit Chapter 2.Document25 pagesElectronic Curcuit Chapter 2.AbcdNo ratings yet
- Complete DC Circuit NotesDocument59 pagesComplete DC Circuit NotesIsha chandravanshiNo ratings yet
- DC Gen GudDocument234 pagesDC Gen GudMeesixNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 DC CircuitsDocument22 pagesChapter 2 DC CircuitsSolomon AsefaNo ratings yet
- Eca 3Document35 pagesEca 3Ahmed SohailNo ratings yet
- 014 - Network Synthesis, Vol - XIV (1957) (Prof. E. A. Guillemin, Prof. P. M. Lewis II, Dr. M. V. Cerrillo)Document20 pages014 - Network Synthesis, Vol - XIV (1957) (Prof. E. A. Guillemin, Prof. P. M. Lewis II, Dr. M. V. Cerrillo)molly zodiacNo ratings yet
- Esc201: Introduction To Electronics: Shilpi Gupta Dept. of Electrical Engineering Iit KanpurDocument40 pagesEsc201: Introduction To Electronics: Shilpi Gupta Dept. of Electrical Engineering Iit KanpurShreyaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Technology (ESC 101-A) Module 1: DC Circuits Voltage and Current SourcesDocument15 pagesBasic Electrical Technology (ESC 101-A) Module 1: DC Circuits Voltage and Current SourcestusharNo ratings yet
- Mesh and Nodal Analysis ProblemsDocument5 pagesMesh and Nodal Analysis ProblemsSyam Sundar100% (2)
- Control System Analysis New CHP 1 and 2Document109 pagesControl System Analysis New CHP 1 and 2KejeindrranNo ratings yet
- Electrical CircuitDocument81 pagesElectrical CircuitBharat Chandra SahuNo ratings yet
- FCS+Chapter+3 (3 1-3 3)Document11 pagesFCS+Chapter+3 (3 1-3 3)kujong agacerNo ratings yet
- ch2 Raymond Winton Intermediate CircuitsDocument34 pagesch2 Raymond Winton Intermediate CircuitsTyler AnthonyNo ratings yet