Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 viewsAlcohol Met
Alcohol Met
Uploaded by
Milkoo sabaAlcohol is metabolized primarily in the liver via two pathways: (1) the major pathway converts alcohol to acetate via alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase, and (2) the minor pathway converts it to acetaldehyde via microsomal cytochrome P450. Chronic alcoholism can lead to metabolic alterations like increased lactate and fatty liver due to a high NADH/NAD+ ratio during alcohol metabolism. Effects of long term alcohol abuse include cirrhosis of the liver, neurological changes, and heart damage.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Leap 3 Chapter 5 VocabularyDocument2 pagesLeap 3 Chapter 5 Vocabularyiamfine253No ratings yet
- Alcohol MetabolismDocument6 pagesAlcohol MetabolismPhoebe O. TumammanNo ratings yet
- Alcohol MetabolismDocument16 pagesAlcohol MetabolismVrinda NarulaNo ratings yet
- DR SkieDocument12 pagesDR SkieDaksh SabharwalNo ratings yet
- Alcoholic KetoacidosisDocument19 pagesAlcoholic KetoacidosisPraveenya NunnaNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Metabolism LectureDocument52 pagesAlcohol Metabolism LectureHassan HarunaNo ratings yet
- Why To Study Alcohols in Pharmacology?Document4 pagesWhy To Study Alcohols in Pharmacology?Ronald DarwinNo ratings yet
- ABC of Alcohol - Alcohol in The BodyDocument8 pagesABC of Alcohol - Alcohol in The BodySomya MishraNo ratings yet
- Alcoholic Liver DiseaseDocument56 pagesAlcoholic Liver DiseaseVishal KalyaniNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Pharmacology Siju Prakash Assistant ProfessorDocument29 pagesAlcohol Pharmacology Siju Prakash Assistant ProfessorFuckyouNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - Chronic Alcoholism and Fatty LiverDocument37 pagesTopic 3 - Chronic Alcoholism and Fatty LiverBrenna de RamosNo ratings yet
- Pharma Katzung - AlcoholsDocument5 pagesPharma Katzung - AlcoholsJoshua RemonNo ratings yet
- Ethanol and Fructose MetabolismDocument24 pagesEthanol and Fructose MetabolismpiriyalakanNo ratings yet
- Dr. Hisham Zein Elabdin: Alcohols Ethyl Alcohol (Ethanol)Document11 pagesDr. Hisham Zein Elabdin: Alcohols Ethyl Alcohol (Ethanol)Asia AlhkeemNo ratings yet
- The AlcoholsDocument22 pagesThe Alcoholsdr.ramyaravichandarNo ratings yet
- Alcohol MetabolismDocument12 pagesAlcohol Metabolismjames100% (1)
- Alcohol and Its Effects On MetabolismDocument50 pagesAlcohol and Its Effects On MetabolismLeonard BowenNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Assignment CompleteDocument5 pagesAlcohol Assignment Completeapi-278392762No ratings yet
- PBPN - Topic3 - Alcohol Metabolism - April2019 - StuDocument17 pagesPBPN - Topic3 - Alcohol Metabolism - April2019 - StuRaysonChooNo ratings yet
- V. AlcoholDocument17 pagesV. AlcoholGeorge TsangNo ratings yet
- Basic Pharmacology of EthanolDocument7 pagesBasic Pharmacology of EthanoltemitopeNo ratings yet
- Alcohols & Glycols: Prepared By: Rawan ShamsDocument41 pagesAlcohols & Glycols: Prepared By: Rawan ShamsAhmad AltarefeNo ratings yet
- Alcoholic Liver DiseaseDocument5 pagesAlcoholic Liver Diseaseamt12202No ratings yet
- Alcohol INFO For PilotsDocument6 pagesAlcohol INFO For PilotsmartinNo ratings yet
- Alcohol IntroductionDocument2 pagesAlcohol IntroductionPrerana PawarNo ratings yet
- Alcohol MetabolismDocument2 pagesAlcohol MetabolismVincent MwirigiNo ratings yet
- Substance Use and Abuse For Students 2018-2019Document50 pagesSubstance Use and Abuse For Students 2018-2019ZauraNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Liver DiseaseDocument7 pagesAlcohol Liver DiseaseRavi ShankarNo ratings yet
- Metabolismo de Alcohol 2005Document35 pagesMetabolismo de Alcohol 2005Ali MontesNo ratings yet
- ALcohol MetabolismDocument17 pagesALcohol MetabolismMaharij NoorNo ratings yet
- Biochem Q.B III Sess Mar 2020Document39 pagesBiochem Q.B III Sess Mar 2020Jinal Jyoti JoshiNo ratings yet
- Alcoholic Liver Disease: DR Anigbo G E Consultant Physician/GastroenterologistDocument50 pagesAlcoholic Liver Disease: DR Anigbo G E Consultant Physician/GastroenterologistEbuka AniNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Oxidation & Ketone BodiesDocument30 pagesFatty Acid Oxidation & Ketone BodiesM.PRASAD NAIDUNo ratings yet
- Complete PaperDocument24 pagesComplete PaperirhammunazatNo ratings yet
- Alcohol in The BodyDocument3 pagesAlcohol in The BodyMarius StancuNo ratings yet
- The Pharmacology of AlcoholDocument8 pagesThe Pharmacology of AlcoholTarii NjNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Alcohol Management of Chronic Alcoholism Treatment of Alcoholic Liver DiseasesDocument41 pagesPharmacology of Alcohol Management of Chronic Alcoholism Treatment of Alcoholic Liver DiseasesVarsha Shende Khobragade100% (2)
- DOPOD Alchohol and Abuse 2023Document12 pagesDOPOD Alchohol and Abuse 2023insyed9No ratings yet
- Alcohol Metabolism ReportDocument25 pagesAlcohol Metabolism ReportRhea Andrea UyNo ratings yet
- EthanolDocument17 pagesEthanoljunaid akbarNo ratings yet
- Alcohol: Ethanol, Methanol and Ethylene GlycolDocument90 pagesAlcohol: Ethanol, Methanol and Ethylene GlycolNisreen Al-share100% (2)
- ALKOHOL - MetabolizamDocument10 pagesALKOHOL - MetabolizamJuoc HrijebarNo ratings yet
- Alcoholism Fatty Liver Liver Cirrhosisg6b1Document48 pagesAlcoholism Fatty Liver Liver Cirrhosisg6b1Franc SalinasNo ratings yet
- A Correlation Between Alcohol Consumption and ObesityDocument15 pagesA Correlation Between Alcohol Consumption and ObesitynikitariNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Toxicity PDFDocument20 pagesAlcohol Toxicity PDFNabila Fatmayday UdiyahNo ratings yet
- Trabajo AlcoholismoDocument7 pagesTrabajo AlcoholismoJavier Andrés HualveNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 ACIDOSIS and ALKALOSISDocument7 pagesLESSON 3 ACIDOSIS and ALKALOSISMaria VistalNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Management For Patient With Diabetic Ketoacidosis (Dka) NCM 118 LectureDocument12 pagesCritical Care Management For Patient With Diabetic Ketoacidosis (Dka) NCM 118 LectureBULONG Darlyn GraceNo ratings yet
- MetabolicDocument23 pagesMetabolicbtidipNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - Lipid MetabolismDocument8 pagesChapter 16 - Lipid MetabolismadambridgerNo ratings yet
- Lipid Metabolism L3+4Document50 pagesLipid Metabolism L3+4bgj9cddvxhNo ratings yet
- Alcohols - Power Point 20-1-2022Document11 pagesAlcohols - Power Point 20-1-2022BenoniNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Topic: Alcohol MetabolismDocument15 pagesBiochemistry: Topic: Alcohol MetabolismMelissa Aina Mohd YusofNo ratings yet
- Alcohol ToxicityDocument81 pagesAlcohol ToxicityKarim RezaNo ratings yet
- Lactic AcidodisDocument27 pagesLactic Acidodisdragab71No ratings yet
- Farmakologi Enterohepatal: Noor WijayahadiDocument134 pagesFarmakologi Enterohepatal: Noor WijayahadiYuni IsmulyatiNo ratings yet
- Biochem B Finals Conference TopicsDocument18 pagesBiochem B Finals Conference TopicsCamille MalilayNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument33 pagesBiochemistryamhhospital0No ratings yet
- Dr. Ali's Uworld Notes For Step 2 CKDocument15 pagesDr. Ali's Uworld Notes For Step 2 CKBoogy WoogyNo ratings yet
- Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis: More Then Just A Mud PileDocument21 pagesAnion Gap Metabolic Acidosis: More Then Just A Mud PileFarah SyazanaNo ratings yet
- 6.digetion of LipidsDocument23 pages6.digetion of LipidsMilkoo sabaNo ratings yet
- Lipo Protein MetDocument32 pagesLipo Protein MetMilkoo sabaNo ratings yet
- Dev't of MuskuloskeletalDocument70 pagesDev't of MuskuloskeletalMilkoo sabaNo ratings yet
- Hist INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM1Document57 pagesHist INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM1Milkoo sabaNo ratings yet
- TransposonsDocument6 pagesTransposonsnikhilsathwikNo ratings yet
- Eon-Duval: Plasmid PurificationDocument9 pagesEon-Duval: Plasmid PurificationYolanda Winarny Eviphanie HutabaratNo ratings yet
- De La Salle Lipa - Integrated School - Senior High School - Science Learning Area - GENERAL BIOLOGY 2Document8 pagesDe La Salle Lipa - Integrated School - Senior High School - Science Learning Area - GENERAL BIOLOGY 2LANCE FREDERICK DIMAANONo ratings yet
- Science Lesson 4Document5 pagesScience Lesson 4Precious EmpedradNo ratings yet
- Gene Transfer in BacteriaDocument46 pagesGene Transfer in BacteriaRenz L. SalumbreNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & DivisionDocument29 pagesCell Structure & DivisionDisaster Management Deptt Rampurhat-I BlockNo ratings yet
- 2009-High Resolution Map of Caenorhabditis Elegans Gap Junction ProteinsDocument15 pages2009-High Resolution Map of Caenorhabditis Elegans Gap Junction ProteinsyicinenNo ratings yet
- Cachexia and Refeeding SyndromeDocument21 pagesCachexia and Refeeding SyndromeCarolina UrbinaNo ratings yet
- Animal BiotechnologyDocument13 pagesAnimal Biotechnologyaisha meharNo ratings yet
- Strategies For Protein PurificationDocument172 pagesStrategies For Protein PurificationBruno MeloNo ratings yet
- Enzymes - Life Sciences Questions and Answers - SanfoundryDocument8 pagesEnzymes - Life Sciences Questions and Answers - SanfoundryHUAWEI HUAWEINo ratings yet
- DNA RepairDocument34 pagesDNA RepairAmit KaushikNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument5 pagesBiochemistryAngeline LimpiadaNo ratings yet
- Bioinformatics Database WorksheetDocument10 pagesBioinformatics Database Worksheetalem010No ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Origins and The ProterozoicDocument81 pagesEukaryotic Origins and The ProterozoicgonzaloNo ratings yet
- Protein SequencingDocument11 pagesProtein SequencingShazia ShoukatNo ratings yet
- Drugs Interaction1Document13 pagesDrugs Interaction1Akshay MandhotraNo ratings yet
- Todaro Et Al 1996Document8 pagesTodaro Et Al 1996Wilbert PerezNo ratings yet
- A Surgeon's Guide To Anaesthesia and Perioperative CareDocument340 pagesA Surgeon's Guide To Anaesthesia and Perioperative CareWALTER GARCÍA TERCERONo ratings yet
- Molecular Diagnostics Fundamentals Methods and Clinical Applications 2nd Edition Buckingham Test BankDocument8 pagesMolecular Diagnostics Fundamentals Methods and Clinical Applications 2nd Edition Buckingham Test Bankhebexuyenod8q100% (33)
- Biology 30 Unit C - Cell Division, Genetics, and Molecular Genetics - Chapter 18Document165 pagesBiology 30 Unit C - Cell Division, Genetics, and Molecular Genetics - Chapter 18kimmoNo ratings yet
- Enzymes-Biology PresentationDocument52 pagesEnzymes-Biology PresentationAdeenNo ratings yet
- Sveta Chakrabarti: ExperienceDocument4 pagesSveta Chakrabarti: ExperienceNilabja BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Lipid Proteins Carbohydrates 2016Document43 pagesChapter 5 Lipid Proteins Carbohydrates 2016skyscraper 2020No ratings yet
- Biopharma Expression Systems 080926Document340 pagesBiopharma Expression Systems 080926Sungsik ParkNo ratings yet
- 9790 s14 Ms 1Document12 pages9790 s14 Ms 1Kc KanNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type Ii With ComplicationsDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type Ii With ComplicationsEricka Genove100% (1)
- Topic 1.3 Membrane StructureDocument4 pagesTopic 1.3 Membrane Structurejasmine wibawaNo ratings yet
- Anitta Denny IMS12019 Purity and Homogeneity CheckDocument3 pagesAnitta Denny IMS12019 Purity and Homogeneity CheckAnittaDennyNo ratings yet
Alcohol Met
Alcohol Met
Uploaded by
Milkoo saba0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views11 pagesAlcohol is metabolized primarily in the liver via two pathways: (1) the major pathway converts alcohol to acetate via alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase, and (2) the minor pathway converts it to acetaldehyde via microsomal cytochrome P450. Chronic alcoholism can lead to metabolic alterations like increased lactate and fatty liver due to a high NADH/NAD+ ratio during alcohol metabolism. Effects of long term alcohol abuse include cirrhosis of the liver, neurological changes, and heart damage.
Original Description:
Alcohol metabolism
Original Title
18. Alcohol met
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAlcohol is metabolized primarily in the liver via two pathways: (1) the major pathway converts alcohol to acetate via alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase, and (2) the minor pathway converts it to acetaldehyde via microsomal cytochrome P450. Chronic alcoholism can lead to metabolic alterations like increased lactate and fatty liver due to a high NADH/NAD+ ratio during alcohol metabolism. Effects of long term alcohol abuse include cirrhosis of the liver, neurological changes, and heart damage.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views11 pagesAlcohol Met
Alcohol Met
Uploaded by
Milkoo sabaAlcohol is metabolized primarily in the liver via two pathways: (1) the major pathway converts alcohol to acetate via alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase, and (2) the minor pathway converts it to acetaldehyde via microsomal cytochrome P450. Chronic alcoholism can lead to metabolic alterations like increased lactate and fatty liver due to a high NADH/NAD+ ratio during alcohol metabolism. Effects of long term alcohol abuse include cirrhosis of the liver, neurological changes, and heart damage.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 11
ALCOHOL METABOLISM
ALCOHOL METABOLISM
Walker has rightly said
'alcohol can be a food, a
drug or a poison
depending on the dose.
ALCOHOL METABOLISM
Sources
(a)Endogenous Small amounts of alcohol in the
blood may be produced by intestinal flora.
(b) Exogenous Alcohol consumed by pleasure
seekers is absorbed easily all along gastro
intestinal tract and reaches liver.
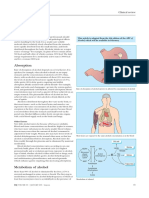
Site
Liver is the major site of alcohol metabolism.
There are two pathways for alcohol degradation.
1. Major pathway
Alcohol is converted to acetate
by the action of two enzymes.
Cytosolic alcohol dehydrogenase
Mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase
Acetyl-CoA may be formed from acetate which
enters TCA cycle or fatty acid biosynthesis.
2. Minor pathway
Alcohol is converted to acetaldehyde
by
Microsomal cytP450-dependent ethanol
oxidizing system.
It is an induceble pathway and become
prominent in chronic alcoholics.
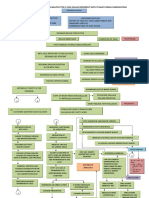
Biochemical changes in alcoholism
The metabolism of alcohol (by both
dehydrogenases) involves the consumption of
NAD+, and consequently a high NADH/NAD+ ratio.
This is mostly responsible for the metabolic
alterations observed in alcoholism.
1. High concentration of NADH favours the
conversion of pyruvate to lactate which may lead
to lactic acidosis.
2. Hypoglycemia due to reduced gluconeogenesis
is observed. This happens as a result of
decreased availability of pyruvate and
oxaloacetate (the latter gets converted to malate
by high NADH).
3. Citric acid cycle is impaired since the
availabilitv of oxaloacetate and NAD+ is
reduced.
As a result, acetyl CoA accumulates which
gets diverted towards ketogenesis,
cholesterologenesis, and fatty acid synthesis.
Accumulation of fats leads to fatty liver and
hyperlipidemia.
4. Increased concentration of serum uric acid
due to its reduced excretion is observed in
alcoholism. This is due to lactic acidosis
5. Acetaldehyde interferes with the functioning
of neurotransmitters, with an overall effect of
neurological depression.
6. Acetaldehyde causes headache, nausea/
tachycardia, reduced blood pressure etc.
Effects of Chronic alcoholism
Cirrhosis Of Liver,
Neurodegenerative Changes,
Cardiomyopathy,
Diuresis,
Impotence etc.
How much alcohol I can
drink?
Alcohol consumption should not exceed
moderate drinking.
Moderation is defined as no more than one
drink per day for women and no more than
two drinks per day for men.
A drink is defined as 1 regular beer,
5 ounces of wine (a little over ¹⁄ cup), or
1.5 ounces of an 80-proof liquor, such as
whiskey.
Pregnant women should drink no alcohol.
Fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS)
The ingestion of alcohol by
pregnant women can result in
Fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS) is marked by
prenatal and postnatal growth
deficiency,
developmental delay, and
craniofacial,limb, and cardiovascular
defects.
You might also like
- Leap 3 Chapter 5 VocabularyDocument2 pagesLeap 3 Chapter 5 Vocabularyiamfine253No ratings yet
- Alcohol MetabolismDocument6 pagesAlcohol MetabolismPhoebe O. TumammanNo ratings yet
- Alcohol MetabolismDocument16 pagesAlcohol MetabolismVrinda NarulaNo ratings yet
- DR SkieDocument12 pagesDR SkieDaksh SabharwalNo ratings yet
- Alcoholic KetoacidosisDocument19 pagesAlcoholic KetoacidosisPraveenya NunnaNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Metabolism LectureDocument52 pagesAlcohol Metabolism LectureHassan HarunaNo ratings yet
- Why To Study Alcohols in Pharmacology?Document4 pagesWhy To Study Alcohols in Pharmacology?Ronald DarwinNo ratings yet
- ABC of Alcohol - Alcohol in The BodyDocument8 pagesABC of Alcohol - Alcohol in The BodySomya MishraNo ratings yet
- Alcoholic Liver DiseaseDocument56 pagesAlcoholic Liver DiseaseVishal KalyaniNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Pharmacology Siju Prakash Assistant ProfessorDocument29 pagesAlcohol Pharmacology Siju Prakash Assistant ProfessorFuckyouNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - Chronic Alcoholism and Fatty LiverDocument37 pagesTopic 3 - Chronic Alcoholism and Fatty LiverBrenna de RamosNo ratings yet
- Pharma Katzung - AlcoholsDocument5 pagesPharma Katzung - AlcoholsJoshua RemonNo ratings yet
- Ethanol and Fructose MetabolismDocument24 pagesEthanol and Fructose MetabolismpiriyalakanNo ratings yet
- Dr. Hisham Zein Elabdin: Alcohols Ethyl Alcohol (Ethanol)Document11 pagesDr. Hisham Zein Elabdin: Alcohols Ethyl Alcohol (Ethanol)Asia AlhkeemNo ratings yet
- The AlcoholsDocument22 pagesThe Alcoholsdr.ramyaravichandarNo ratings yet
- Alcohol MetabolismDocument12 pagesAlcohol Metabolismjames100% (1)
- Alcohol and Its Effects On MetabolismDocument50 pagesAlcohol and Its Effects On MetabolismLeonard BowenNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Assignment CompleteDocument5 pagesAlcohol Assignment Completeapi-278392762No ratings yet
- PBPN - Topic3 - Alcohol Metabolism - April2019 - StuDocument17 pagesPBPN - Topic3 - Alcohol Metabolism - April2019 - StuRaysonChooNo ratings yet
- V. AlcoholDocument17 pagesV. AlcoholGeorge TsangNo ratings yet
- Basic Pharmacology of EthanolDocument7 pagesBasic Pharmacology of EthanoltemitopeNo ratings yet
- Alcohols & Glycols: Prepared By: Rawan ShamsDocument41 pagesAlcohols & Glycols: Prepared By: Rawan ShamsAhmad AltarefeNo ratings yet
- Alcoholic Liver DiseaseDocument5 pagesAlcoholic Liver Diseaseamt12202No ratings yet
- Alcohol INFO For PilotsDocument6 pagesAlcohol INFO For PilotsmartinNo ratings yet
- Alcohol IntroductionDocument2 pagesAlcohol IntroductionPrerana PawarNo ratings yet
- Alcohol MetabolismDocument2 pagesAlcohol MetabolismVincent MwirigiNo ratings yet
- Substance Use and Abuse For Students 2018-2019Document50 pagesSubstance Use and Abuse For Students 2018-2019ZauraNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Liver DiseaseDocument7 pagesAlcohol Liver DiseaseRavi ShankarNo ratings yet
- Metabolismo de Alcohol 2005Document35 pagesMetabolismo de Alcohol 2005Ali MontesNo ratings yet
- ALcohol MetabolismDocument17 pagesALcohol MetabolismMaharij NoorNo ratings yet
- Biochem Q.B III Sess Mar 2020Document39 pagesBiochem Q.B III Sess Mar 2020Jinal Jyoti JoshiNo ratings yet
- Alcoholic Liver Disease: DR Anigbo G E Consultant Physician/GastroenterologistDocument50 pagesAlcoholic Liver Disease: DR Anigbo G E Consultant Physician/GastroenterologistEbuka AniNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Oxidation & Ketone BodiesDocument30 pagesFatty Acid Oxidation & Ketone BodiesM.PRASAD NAIDUNo ratings yet
- Complete PaperDocument24 pagesComplete PaperirhammunazatNo ratings yet
- Alcohol in The BodyDocument3 pagesAlcohol in The BodyMarius StancuNo ratings yet
- The Pharmacology of AlcoholDocument8 pagesThe Pharmacology of AlcoholTarii NjNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Alcohol Management of Chronic Alcoholism Treatment of Alcoholic Liver DiseasesDocument41 pagesPharmacology of Alcohol Management of Chronic Alcoholism Treatment of Alcoholic Liver DiseasesVarsha Shende Khobragade100% (2)
- DOPOD Alchohol and Abuse 2023Document12 pagesDOPOD Alchohol and Abuse 2023insyed9No ratings yet
- Alcohol Metabolism ReportDocument25 pagesAlcohol Metabolism ReportRhea Andrea UyNo ratings yet
- EthanolDocument17 pagesEthanoljunaid akbarNo ratings yet
- Alcohol: Ethanol, Methanol and Ethylene GlycolDocument90 pagesAlcohol: Ethanol, Methanol and Ethylene GlycolNisreen Al-share100% (2)
- ALKOHOL - MetabolizamDocument10 pagesALKOHOL - MetabolizamJuoc HrijebarNo ratings yet
- Alcoholism Fatty Liver Liver Cirrhosisg6b1Document48 pagesAlcoholism Fatty Liver Liver Cirrhosisg6b1Franc SalinasNo ratings yet
- A Correlation Between Alcohol Consumption and ObesityDocument15 pagesA Correlation Between Alcohol Consumption and ObesitynikitariNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Toxicity PDFDocument20 pagesAlcohol Toxicity PDFNabila Fatmayday UdiyahNo ratings yet
- Trabajo AlcoholismoDocument7 pagesTrabajo AlcoholismoJavier Andrés HualveNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 ACIDOSIS and ALKALOSISDocument7 pagesLESSON 3 ACIDOSIS and ALKALOSISMaria VistalNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Management For Patient With Diabetic Ketoacidosis (Dka) NCM 118 LectureDocument12 pagesCritical Care Management For Patient With Diabetic Ketoacidosis (Dka) NCM 118 LectureBULONG Darlyn GraceNo ratings yet
- MetabolicDocument23 pagesMetabolicbtidipNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - Lipid MetabolismDocument8 pagesChapter 16 - Lipid MetabolismadambridgerNo ratings yet
- Lipid Metabolism L3+4Document50 pagesLipid Metabolism L3+4bgj9cddvxhNo ratings yet
- Alcohols - Power Point 20-1-2022Document11 pagesAlcohols - Power Point 20-1-2022BenoniNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Topic: Alcohol MetabolismDocument15 pagesBiochemistry: Topic: Alcohol MetabolismMelissa Aina Mohd YusofNo ratings yet
- Alcohol ToxicityDocument81 pagesAlcohol ToxicityKarim RezaNo ratings yet
- Lactic AcidodisDocument27 pagesLactic Acidodisdragab71No ratings yet
- Farmakologi Enterohepatal: Noor WijayahadiDocument134 pagesFarmakologi Enterohepatal: Noor WijayahadiYuni IsmulyatiNo ratings yet
- Biochem B Finals Conference TopicsDocument18 pagesBiochem B Finals Conference TopicsCamille MalilayNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument33 pagesBiochemistryamhhospital0No ratings yet
- Dr. Ali's Uworld Notes For Step 2 CKDocument15 pagesDr. Ali's Uworld Notes For Step 2 CKBoogy WoogyNo ratings yet
- Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis: More Then Just A Mud PileDocument21 pagesAnion Gap Metabolic Acidosis: More Then Just A Mud PileFarah SyazanaNo ratings yet
- 6.digetion of LipidsDocument23 pages6.digetion of LipidsMilkoo sabaNo ratings yet
- Lipo Protein MetDocument32 pagesLipo Protein MetMilkoo sabaNo ratings yet
- Dev't of MuskuloskeletalDocument70 pagesDev't of MuskuloskeletalMilkoo sabaNo ratings yet
- Hist INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM1Document57 pagesHist INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM1Milkoo sabaNo ratings yet
- TransposonsDocument6 pagesTransposonsnikhilsathwikNo ratings yet
- Eon-Duval: Plasmid PurificationDocument9 pagesEon-Duval: Plasmid PurificationYolanda Winarny Eviphanie HutabaratNo ratings yet
- De La Salle Lipa - Integrated School - Senior High School - Science Learning Area - GENERAL BIOLOGY 2Document8 pagesDe La Salle Lipa - Integrated School - Senior High School - Science Learning Area - GENERAL BIOLOGY 2LANCE FREDERICK DIMAANONo ratings yet
- Science Lesson 4Document5 pagesScience Lesson 4Precious EmpedradNo ratings yet
- Gene Transfer in BacteriaDocument46 pagesGene Transfer in BacteriaRenz L. SalumbreNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & DivisionDocument29 pagesCell Structure & DivisionDisaster Management Deptt Rampurhat-I BlockNo ratings yet
- 2009-High Resolution Map of Caenorhabditis Elegans Gap Junction ProteinsDocument15 pages2009-High Resolution Map of Caenorhabditis Elegans Gap Junction ProteinsyicinenNo ratings yet
- Cachexia and Refeeding SyndromeDocument21 pagesCachexia and Refeeding SyndromeCarolina UrbinaNo ratings yet
- Animal BiotechnologyDocument13 pagesAnimal Biotechnologyaisha meharNo ratings yet
- Strategies For Protein PurificationDocument172 pagesStrategies For Protein PurificationBruno MeloNo ratings yet
- Enzymes - Life Sciences Questions and Answers - SanfoundryDocument8 pagesEnzymes - Life Sciences Questions and Answers - SanfoundryHUAWEI HUAWEINo ratings yet
- DNA RepairDocument34 pagesDNA RepairAmit KaushikNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument5 pagesBiochemistryAngeline LimpiadaNo ratings yet
- Bioinformatics Database WorksheetDocument10 pagesBioinformatics Database Worksheetalem010No ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Origins and The ProterozoicDocument81 pagesEukaryotic Origins and The ProterozoicgonzaloNo ratings yet
- Protein SequencingDocument11 pagesProtein SequencingShazia ShoukatNo ratings yet
- Drugs Interaction1Document13 pagesDrugs Interaction1Akshay MandhotraNo ratings yet
- Todaro Et Al 1996Document8 pagesTodaro Et Al 1996Wilbert PerezNo ratings yet
- A Surgeon's Guide To Anaesthesia and Perioperative CareDocument340 pagesA Surgeon's Guide To Anaesthesia and Perioperative CareWALTER GARCÍA TERCERONo ratings yet
- Molecular Diagnostics Fundamentals Methods and Clinical Applications 2nd Edition Buckingham Test BankDocument8 pagesMolecular Diagnostics Fundamentals Methods and Clinical Applications 2nd Edition Buckingham Test Bankhebexuyenod8q100% (33)
- Biology 30 Unit C - Cell Division, Genetics, and Molecular Genetics - Chapter 18Document165 pagesBiology 30 Unit C - Cell Division, Genetics, and Molecular Genetics - Chapter 18kimmoNo ratings yet
- Enzymes-Biology PresentationDocument52 pagesEnzymes-Biology PresentationAdeenNo ratings yet
- Sveta Chakrabarti: ExperienceDocument4 pagesSveta Chakrabarti: ExperienceNilabja BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Lipid Proteins Carbohydrates 2016Document43 pagesChapter 5 Lipid Proteins Carbohydrates 2016skyscraper 2020No ratings yet
- Biopharma Expression Systems 080926Document340 pagesBiopharma Expression Systems 080926Sungsik ParkNo ratings yet
- 9790 s14 Ms 1Document12 pages9790 s14 Ms 1Kc KanNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type Ii With ComplicationsDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type Ii With ComplicationsEricka Genove100% (1)
- Topic 1.3 Membrane StructureDocument4 pagesTopic 1.3 Membrane Structurejasmine wibawaNo ratings yet
- Anitta Denny IMS12019 Purity and Homogeneity CheckDocument3 pagesAnitta Denny IMS12019 Purity and Homogeneity CheckAnittaDennyNo ratings yet