Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4 Subcutaneous-Mycoses
4 Subcutaneous-Mycoses
Uploaded by
Mariz MartinezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
4 Subcutaneous-Mycoses
4 Subcutaneous-Mycoses
Uploaded by
Mariz MartinezCopyright:
Available Formats
MYCOVIRO| MYCOLOGY AND VIROLOGY March 24, 2022
(Unified Synchronous Discussion)
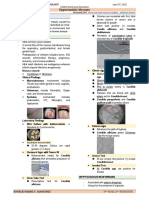
Subcutaneous Mycoses
Discussion/PPT Notes from other trances/readings Additional notes**
Subcutaneous Mycoses
- Subcutaneous mycoses involve the dermis of
the skin extending to the subcutaneous tissues
(muscles and fascia) and can also extend up to
the epidermis to cause skin surface lesions.
- They are acquired from soil, vegetation, and
decaying woods.
- The mode of transmission is usually through - Laboratory Diagnosis
traumatic implantation of foreign objects into • Specimen:
the deep layers of the skin. ◼ Exudate or pus material from the
nodule.
SPOROTRICHOSIS ◼ Tissue biopsy
◼ Respiratory secretions
- Disease associated with gardening particularly
with exposure with rose thorns and sphagnum • Direct microscopy using KOH Mount from
moss. Blood Culture:
- Other names ◼ Sporonthrix schenckii is a dimorphic
fungus
• Rose Gardeners’ Disease
◼ Cigar shaped yeast cells
• Pose Pickers’ Disease
◼ Rosette-like patterned mold (conidia)
• Rose Handler’s Disease
• H&E staining of the Skin biopsy
- Causative agent
◼ Asteroid bodies
• Sporothrix shenckii
- Clinical Findings:
• Can present as Lymphocutaneous CHROMOBLASTOMYCOSIS
sporotrichosis characterized by nodular
and ulcerative lesions along the lymph - Chronic mycosis of the skin and subcutaneous
channels that drain the primary site of tissue.
inoculation - Other names:
• Verrrucous dermatitidis
Chromomycosis
- Causative agents:
• Fosecaea pedrosoi
• Phialophora verrucose
• Can also present as Osteoartivular
sporotrichosis that is characterized by • Cladosporium carrionii
arthritis and can manifest as a form of • Fonsecaea compacta
osteomyelitis. • Rhinocladiela aquaspersa
- Can present as Pulmonary sporotrichosis that
has non-specific signs and symptoms of - Clinical Findings:
coughing accompanied with sputum or • Painless, scaly, papule on the skin that
hemoptysis. develops into warty, crusted nodules
ANGELEI MARIZ C. MARTINEZ 3RD YEAR; 2ND SEMESTER
MYCOVIRO| MYCOLOGY AND VIROLOGY March 24, 2022
(Unified Synchronous Discussion)
Subcutaneous Mycoses
Discussion/PPT Notes from other trances/readings Additional notes**
“cauliflower-like” with micro abscess RHINOSPORIDIOSIS
formation.
- A mycotic element that is not viable. Means the
fungus that can’t be cultured so then is just
exhibited through microscopic examination.
- Causative Agent: Rhinosporidium seeberi
- Clinical Findings:
• A granulomatous nodule that affects the
- Laboratory Diagnosis:
nose, conjunctiva, and other
• Specimen:
mucocutaneous crevices.
◼ Exudate or pus material from the
• Starts with granuloma formation, formation
nodule
of polyp, and then obtains seropurulent
◼ Tissue biopsy
discharge.
◼ Respiratory secretions
• Direct microscopy using KOH Mount from
Blood Culture:
◼ Formation of sclerotic bodies
• Skin Biopsy
◼ Copper pennies of muniform/ sclerotic - Laboratory Diagnosis
cells → copper colored, non-budding • Specimen:
structures occurring in singly or in ◼ Mucosal scrapings and nasal
clusters. discharge.
• Tissue biopsy and Direct microscopy of
nasal discharge:
◼ Presence of spherules (large
sporandia or sac-like structure)
MYCETOMA
- Chronic granulomatous infection of the
subcutaneous tissues and bone.
- 2 types: LOBOMYCOSIS
• Eumycotic Mycetoma
◼ Other Names: Maduromycosis or - Associated with aquatic habitats and is acquired
Madura foot via traumatic implantations like arthropod stings,
◼ Causative Agent: snake bite, ray sting or wounds obtained while
Madurella mycetomatis cutting vegetables phoretic with Lacazia loboi.
Madurella grisea - Other names:
Pseudallescheria boydii • Keloidal Blastomycoses
Exophialla jeanselmei • Lobo’s Disease
• Lacaziosis
- Causative Agent
• Lacazia loboi
• Loboa loboi
- Clinical Findings
• Actinomycotic Mycetoma • Verrucoid or nodular lesions
◼ Another name: Actinomycetoma
◼ Causative agent: Bacteria
(actinomyces, streptomyces, etc.)
ANGELEI MARIZ C. MARTINEZ 3RD YEAR; 2ND SEMESTER
MYCOVIRO| MYCOLOGY AND VIROLOGY March 24, 2022
(Unified Synchronous Discussion)
Subcutaneous Mycoses
Discussion/PPT Notes from other trances/readings Additional notes**
SUBCUTANEOUS PHAEOHYPOMYCOSIS
- Mycotic disease caused by darkly pigmented
fungi or fungi that have melanin in their cell
walls.
- Causative agent
• Exophiala spp.
• Bipolaros spp.
• Curoularia spp.
• Exserohilum spp.
- Clinical Findings
• Associated with Chromoblastomycosis and
Madurella
ZYGOMYCETOMA
- Most species are saprobes, living of decaying
organic material; a few are parasites.
- Generally, are super rare.
- 2 types
• Entomophthoromycosis
◼ Causative agent
Basidiobolus ranarum
Conidiobolus coronatus
◼ Clinical findings
May affect immunocompetent
patients.
• Mucormycosis
◼ Causative agent
Rhizopus
Mucor
Cunninghamella
Saksenaea
Rhizomucor
Absidia
Lichtheimia
◼ Clinical findings
Although considered to be a rare
infection, mucormycosis
(zygomycosis) has emerged as
the second most common
invasive mould infection. Despite
the advent of newer antifungal
agents, mortality rate of
mucormycosis remains
exceedingly high. However,
mucormycosis is not always
amenable to cure.
ANGELEI MARIZ C. MARTINEZ 3RD YEAR; 2ND SEMESTER
You might also like
- Post Cataract EndophthalmitisDocument55 pagesPost Cataract Endophthalmitisdr samreen arifNo ratings yet
- Subcutaneous Mycoses Hand-OutsDocument5 pagesSubcutaneous Mycoses Hand-OutsKristine BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Systemic Mycoses: BlastomycosisDocument4 pagesSystemic Mycoses: BlastomycosisMary ChristelleNo ratings yet
- Subcutaneous MycosesDocument23 pagesSubcutaneous Mycosessarguss14100% (1)
- 5 Systemic-MycosesDocument2 pages5 Systemic-MycosesMariz MartinezNo ratings yet
- 4 Subutaneous MycosesDocument17 pages4 Subutaneous MycosesAngge Aquino OfficialNo ratings yet
- Systemic Mycoses: Blastomyces DermatitidisDocument12 pagesSystemic Mycoses: Blastomyces Dermatitidisredz_ekg619No ratings yet
- Subcutaneous MycosesDocument14 pagesSubcutaneous MycosesanonacadsNo ratings yet
- Subcutaneous 06122022Document61 pagesSubcutaneous 06122022Stephano LabiaNo ratings yet
- SubcutaneousDocument2 pagesSubcutaneousMary ChristelleNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MycologyDocument46 pagesIntroduction To MycologyAastha SinhaNo ratings yet
- Subcutaneous Mycosis 06-07Document16 pagesSubcutaneous Mycosis 06-07api-3699361100% (1)
- Klinis Dan Diagnosa Laboratorium Jamur 10,11Document36 pagesKlinis Dan Diagnosa Laboratorium Jamur 10,11H PNo ratings yet
- Intro MycologyDocument62 pagesIntro Mycologyriturajrastogibpt22-26No ratings yet
- Mycovi1 L1Document3 pagesMycovi1 L1MHEKAELLA SAMSONNo ratings yet
- Bacterial InfectionDocument122 pagesBacterial InfectionElga MuralidharanNo ratings yet
- Jamur Pada Traktus Respiratorius Asaad Aaa 06 012Document58 pagesJamur Pada Traktus Respiratorius Asaad Aaa 06 012Muhammad Satir SayatiNo ratings yet
- Subcut Mycoses 2012Document32 pagesSubcut Mycoses 2012gailNo ratings yet
- Table of Sytemic MycosesDocument1 pageTable of Sytemic MycosesLexie BulanNo ratings yet
- Fungal Infection - 1Document87 pagesFungal Infection - 1ParamitaNo ratings yet
- Myco ViroDocument12 pagesMyco ViroRapada, Rowelyn S.No ratings yet
- Name: de Los Santos, Faith Joy T. Section: 3MT01 Date:03142017Document5 pagesName: de Los Santos, Faith Joy T. Section: 3MT01 Date:03142017Mary Rose SJ JimenezNo ratings yet
- Fungi Causing Superficial MycosesDocument41 pagesFungi Causing Superficial MycosesdiniNo ratings yet
- Mycology: Florence Joan S. Te, RMT, EMT, MSMT © College of Nursing Micro-Para UC-BaniladDocument29 pagesMycology: Florence Joan S. Te, RMT, EMT, MSMT © College of Nursing Micro-Para UC-BaniladMary Grace RiveraNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Subcutaneous MycosesDocument75 pagesLecture On Subcutaneous Mycosesmiguel cuevasNo ratings yet
- بلاستومايكوززDocument29 pagesبلاستومايكوززNational Sport for all viewers مشاهدة الأحداث حصرياNo ratings yet
- 03 Cutaneous MycosesDocument30 pages03 Cutaneous MycosesFelix AyornuNo ratings yet
- 2 2020 07 25!06 48 39 PMDocument37 pages2 2020 07 25!06 48 39 PMraul sinatoNo ratings yet
- Dimorphic Fungi: Prabin Shah BSCMLT, MSC (Biochemistry)Document49 pagesDimorphic Fungi: Prabin Shah BSCMLT, MSC (Biochemistry)banteng wibisonoNo ratings yet
- Mycv Week 5Document5 pagesMycv Week 5Janine Alicia VargasNo ratings yet
- Subcutaneous MycosesDocument34 pagesSubcutaneous MycosesNUBWA MEDUGUNo ratings yet
- Week 4. Subcutaneous MycosesDocument59 pagesWeek 4. Subcutaneous MycosesAsdfghjklNo ratings yet
- Subcutaneous MycosesDocument34 pagesSubcutaneous MycosesIvy Jan OcateNo ratings yet
- MycologyDocument68 pagesMycologyANCHELANo ratings yet
- Microbiology Lecture 10 - Subcutaneous Mycoses (Palindrome)Document3 pagesMicrobiology Lecture 10 - Subcutaneous Mycoses (Palindrome)miguel cuevas100% (1)
- Superficial and Cutaneous Mycoses: 2. Disease CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesSuperficial and Cutaneous Mycoses: 2. Disease CharacteristicsMA. ANGELI DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Endemic MycosesDocument9 pagesEndemic MycosesjrbvxfvjhjNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document20 pagesChapter 15Xander LibanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MycologyDocument39 pagesIntroduction To MycologyElena ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Classifying Nodular Lesions of Oral CavityDocument3 pagesClassifying Nodular Lesions of Oral CavitySkAliHassanNo ratings yet
- Mycology For DentistryDocument35 pagesMycology For DentistryErizka RivaniNo ratings yet
- Tan 2018Document8 pagesTan 2018Bagus Putra KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Skin InfectionsDocument9 pagesBacterial Skin InfectionskateverdadNo ratings yet
- My CologyDocument170 pagesMy CologyVIDHARSHANA JNo ratings yet
- Derma - MTBDocument6 pagesDerma - MTBIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Lec 15mycology SPPDocument35 pagesLec 15mycology SPPbujalkanNo ratings yet
- Systemic Mycoses: A. BlastomycosisDocument3 pagesSystemic Mycoses: A. Blastomycosisbaihern24No ratings yet
- Cns Infections f2022 MeningitisDocument46 pagesCns Infections f2022 MeningitisMadison MillwoodNo ratings yet
- Epithelial and Non-Epithelial Tumor of JawsDocument66 pagesEpithelial and Non-Epithelial Tumor of JawsDinesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Part 3 Episode 1 - Ma'am Magno's LectureDocument8 pagesPart 3 Episode 1 - Ma'am Magno's LectureDennis Aran Tupaz AbrilNo ratings yet
- Subcutaneous MycosesDocument39 pagesSubcutaneous Mycosesdhainey100% (1)
- Medical MycologyDocument84 pagesMedical MycologytenawNo ratings yet
- Granulomatous Reaction PatternDocument63 pagesGranulomatous Reaction Patternahmad syarifNo ratings yet
- Skin Path NotesDocument15 pagesSkin Path NoteszeeathrNo ratings yet
- Fungal InfectionDocument3 pagesFungal InfectionNicole TorralbaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 6 Supplement APRIL 2018 PDFDocument3 pagesMODULE 6 Supplement APRIL 2018 PDFEryll Paolo AleaNo ratings yet
- True Systemic (Endemic) MycosesDocument6 pagesTrue Systemic (Endemic) MycosesKoni Oroceo-SacramedNo ratings yet
- BscNR24 T4 Characteristics of FungiDocument4 pagesBscNR24 T4 Characteristics of Fungiakoeljames8543No ratings yet
- Wonders of the Plant Kingdom: A Microcosm RevealedFrom EverandWonders of the Plant Kingdom: A Microcosm RevealedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Table Stains - HistopathDocument1 pageTable Stains - HistopathMariz MartinezNo ratings yet
- Questions HPLCDocument10 pagesQuestions HPLCMariz MartinezNo ratings yet
- Questions ElisaDocument4 pagesQuestions ElisaMariz MartinezNo ratings yet
- Questions Tissue EngineeringDocument2 pagesQuestions Tissue EngineeringMariz MartinezNo ratings yet
- Questions Molecular CloningDocument4 pagesQuestions Molecular CloningMariz MartinezNo ratings yet
- Questions Bioinformatics An IntroductionDocument3 pagesQuestions Bioinformatics An IntroductionMariz MartinezNo ratings yet
- 6 Opportunistic-MycosesDocument3 pages6 Opportunistic-MycosesMariz MartinezNo ratings yet
- 2 - Specimen Processing in MycologyDocument7 pages2 - Specimen Processing in MycologyMariz MartinezNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction To Medical Mycology Basic Fungal BiologyDocument6 pages1 - Introduction To Medical Mycology Basic Fungal BiologyMariz MartinezNo ratings yet
- 5 Systemic-MycosesDocument2 pages5 Systemic-MycosesMariz MartinezNo ratings yet
- The Evidence Supporting The Revised EORTC-MSGERC Definitions For Invasive Fungal InfectionsDocument2 pagesThe Evidence Supporting The Revised EORTC-MSGERC Definitions For Invasive Fungal Infectionsgwyneth.green.512No ratings yet
- AIDS Related Mycoses Updated Progress and FutureDocument4 pagesAIDS Related Mycoses Updated Progress and Futurelwlolo168No ratings yet
- General Characters and Classification of FungiDocument35 pagesGeneral Characters and Classification of Fungijeonkilovers100% (4)
- POST CHRISTMAS - Glasgow - DTMH - Timetable - 23-24 - 13DEC23Document3 pagesPOST CHRISTMAS - Glasgow - DTMH - Timetable - 23-24 - 13DEC23nathanaellee92No ratings yet
- Clinical Microbiology-I SEMESTER-IDocument26 pagesClinical Microbiology-I SEMESTER-IAreeba NazNo ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Fitzpatricks Color Atlas and Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology Eighth Edition 8Th Edition PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument53 pages(Download PDF) Fitzpatricks Color Atlas and Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology Eighth Edition 8Th Edition PDF Full Chapter PDFolintoecrin100% (9)
- Microbiology and Pathology Guideline by MSSDocument81 pagesMicrobiology and Pathology Guideline by MSSMuhammad ZamimNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts in MycologyDocument1 pageBasic Concepts in MycologyAngeloMartinNo ratings yet
- Fungi Causing Superficial MycosesDocument41 pagesFungi Causing Superficial MycosesdiniNo ratings yet
- Mycovi1 L1Document3 pagesMycovi1 L1MHEKAELLA SAMSONNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology MidtermDocument27 pagesPharmacology Midtermnaomie manaliliNo ratings yet
- Mycology VirologyDocument23 pagesMycology VirologymikeNo ratings yet
- Secret Superheroes of Saving The PlanetDocument17 pagesSecret Superheroes of Saving The PlanetPriyanka ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Unit - 10 - General Characters and Classification of Fungi by Dr. Kirtika PadaliaDocument38 pagesUnit - 10 - General Characters and Classification of Fungi by Dr. Kirtika PadalianucleophilicmishraNo ratings yet
- NEW BMLT Stream - Syllabus - PDF - 1961275447 - B.SC - MLTTDocument24 pagesNEW BMLT Stream - Syllabus - PDF - 1961275447 - B.SC - MLTTadn paramedicalNo ratings yet
- Best Insight Specialty-Paeds TeamDocument56 pagesBest Insight Specialty-Paeds TeamSaQlain BalochNo ratings yet
- MYCV311LECDocument80 pagesMYCV311LECAljohn VillarinNo ratings yet
- Lecture FUNGI 2022Document52 pagesLecture FUNGI 2022JenniferNo ratings yet
- MYCOVIRODocument184 pagesMYCOVIROprnfbmsdqnNo ratings yet
- Fungal Skin Infections 6Document15 pagesFungal Skin Infections 6h8j5fnyh7dNo ratings yet
- Fungal InfectionsDocument19 pagesFungal InfectionsKasuganti koteshwar raoNo ratings yet
- Fungal Diseases in Animals 2021Document201 pagesFungal Diseases in Animals 2021ANDREA HATSUMI BAZAN YAMADANo ratings yet
- Antifungal Antibiotics - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument16 pagesAntifungal Antibiotics - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfsovalaxNo ratings yet
- Antifungal Drugs: Side Effects and Adverse Reactions of Amphotericin BDocument23 pagesAntifungal Drugs: Side Effects and Adverse Reactions of Amphotericin BElizabeth IdananNo ratings yet
- Micoses Superficiais - GlobalDocument19 pagesMicoses Superficiais - GlobalJosé Paulo Ribeiro JúniorNo ratings yet
- Strigarianz 2nd YearDocument42 pagesStrigarianz 2nd YearKhaleedNo ratings yet
- Rekap JR Ppds DV Update Mei 2023Document75 pagesRekap JR Ppds DV Update Mei 2023Katarina ZhongNo ratings yet
- Medical Technology Assessment Program: Mycology Review NotesDocument6 pagesMedical Technology Assessment Program: Mycology Review NotesMoira Pauline LibroraniaNo ratings yet
- Prelim Myco Trans PPT BasedDocument98 pagesPrelim Myco Trans PPT BasedJohn Vincent TacalNo ratings yet
- HML 316 Notes 2021Document39 pagesHML 316 Notes 2021nessa nimoNo ratings yet