Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 viewsMotor Generator
Motor Generator
Uploaded by
Princes JuatThis document describes the basic components and operation of electric generators and motors. It discusses:
1) How generators work by converting mechanical energy (from sources like falling water, wind, or steam) into electrical energy using electromagnetic induction principles. The main components are a rotor, stator, and commutator.
2) The differences between AC and DC generators and their uses. AC generators produce alternating current and are used for small applications while DC generators produce direct current and power large motors.
3) How electric motors operate using electromagnetic principles to convert electrical energy into rotational mechanical motion. The main components are a rotor, stator, and commutator.
4) Applications of generators include backup household power
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- ASTON Kartika GrogolDocument2 pagesASTON Kartika GrogolAngga Ciro Bams100% (1)
- Energy Systems Phet WorksheetDocument5 pagesEnergy Systems Phet Worksheetapi-203432401No ratings yet
- Final Exam Engineering MechanicsDocument9 pagesFinal Exam Engineering MechanicsjohnjabarajNo ratings yet
- 04 La3cna TeDocument22 pages04 La3cna Tegibson marvalNo ratings yet
- Leah Hartsock: Gravitational-Potential WorkDocument3 pagesLeah Hartsock: Gravitational-Potential WorkRHEAMAE GALLEGONo ratings yet
- Lesson Plans-Grade 11 PhysicsDocument1 pageLesson Plans-Grade 11 Physicsian joseph100% (1)
- Magnetic Induction Lesson Plan A2av6 1Document2 pagesMagnetic Induction Lesson Plan A2av6 1api-313158624100% (1)
- CBSE Class 10 Physics Electricity Worksheet Set ADocument2 pagesCBSE Class 10 Physics Electricity Worksheet Set AlalitNo ratings yet
- Cot g9Document5 pagesCot g9Rince RioNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Electromagnetic InductionDocument3 pagesLesson Plan - Electromagnetic InductionRakotoarison Louis Frederick100% (1)
- Mechanical EnergyDocument10 pagesMechanical Energyapi-320478846No ratings yet
- Q4-WEEK 3-Momentum and ImpulseDocument32 pagesQ4-WEEK 3-Momentum and ImpulseAdonis SanielNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 BondingDocument13 pagesTopic 4 Bondinglobna masadehNo ratings yet
- Stirling Engine ProposalDocument8 pagesStirling Engine ProposalSaibhargavi BkNo ratings yet
- Semi Det. Geothermal 9 DaaDocument5 pagesSemi Det. Geothermal 9 DaaRjane CañeteNo ratings yet
- Theoretical 3 Tornado SolutionDocument7 pagesTheoretical 3 Tornado Solutionjas dwanNo ratings yet
- PDF - Geothermal Power PlantDocument43 pagesPDF - Geothermal Power PlantTrinity MarieNo ratings yet
- Detailed Science Lesson Plan: Grade Level Quarter / Domain Week & Day No. Page NoDocument3 pagesDetailed Science Lesson Plan: Grade Level Quarter / Domain Week & Day No. Page Noaiza larrozaNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan: Student Teacher Grade Level Teaching Date Learning Area Teaching Time Quarter I. ObjectivesDocument7 pagesDaily Lesson Plan: Student Teacher Grade Level Teaching Date Learning Area Teaching Time Quarter I. ObjectivesHazel LiwanagNo ratings yet
- DLL chemNOV15Document5 pagesDLL chemNOV15Rosallie Caaya-NuezNo ratings yet
- School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Time & Dates Quarter I. ObjectivesDocument4 pagesSchool Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Time & Dates Quarter I. ObjectivesRiztine Rachel RaineNo ratings yet
- Potential and Kinetic Energy WorksheetDocument2 pagesPotential and Kinetic Energy WorksheetJorge ArguelloNo ratings yet
- L6 U3 SNC1D NotesDocument6 pagesL6 U3 SNC1D NotesabhieNo ratings yet
- FARADAY's LawDocument27 pagesFARADAY's LawMary Liezl Pilapil50% (4)
- Chap23 PDFDocument26 pagesChap23 PDFsafdar lashariNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Q3 COTDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Q3 COTCharmen PabilonaNo ratings yet
- 7 E Model Lesson PlanDocument7 pages7 E Model Lesson Plangloria tolentinoNo ratings yet
- DLP em Equation Vhien CahipeDocument4 pagesDLP em Equation Vhien CahipeGABRIEL ADONANo ratings yet
- RAISEPlus GRADE 9 Impulse and MomentumDocument2 pagesRAISEPlus GRADE 9 Impulse and Momentumpj oroscoNo ratings yet
- Final Revised Las in Science 9 q3w3Document4 pagesFinal Revised Las in Science 9 q3w3Ma.Kristine Ibarreta JazulNo ratings yet
- DLL Chem Dec02Document4 pagesDLL Chem Dec02Rosallie Caaya-NuezNo ratings yet
- Final Semi Detailed Lesson Plan TemplateDocument10 pagesFinal Semi Detailed Lesson Plan TemplateJessie GernaleNo ratings yet
- LP For 2022 2nd COTDocument6 pagesLP For 2022 2nd COTEmily Tatunay EspejoNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current vs. Direct Current - Lesson For Kids PDFDocument3 pagesAlternating Current vs. Direct Current - Lesson For Kids PDFSatyajit Mishra100% (1)
- Science: Mahay Integrated Secondary SchoolDocument8 pagesScience: Mahay Integrated Secondary Schoollavenia acdalNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesElectricity and Magnetism Lesson PlanNel Pasaiz100% (1)
- Arban, CG. Lesson Plan in Geothermal Energy, 11 - STEMDocument6 pagesArban, CG. Lesson Plan in Geothermal Energy, 11 - STEMCzarina Amor CabilleteNo ratings yet
- HIstory of AtomDocument20 pagesHIstory of AtomIrish Solomon100% (1)
- Unit II Electrical Circuits: Basic Circuit Element and Their CombinationsDocument21 pagesUnit II Electrical Circuits: Basic Circuit Element and Their CombinationsMonte CarloNo ratings yet
- 1 - Electrical+Basics+-+CircuitsDocument36 pages1 - Electrical+Basics+-+Circuitsareina75No ratings yet
- Magnetism (Revised)Document55 pagesMagnetism (Revised)api-275374056100% (1)
- Chap10no1 PDFDocument2 pagesChap10no1 PDFTajiriMollel0% (9)
- Energetics Note 1Document15 pagesEnergetics Note 1shaliniNo ratings yet
- Refraction of Light, From Lens and SlabsDocument90 pagesRefraction of Light, From Lens and Slabsp_k_soni_iit_physicsNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Q2 - W6 - D3Document1 pageScience 10 - Q2 - W6 - D3zenaida a academiaNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN - Subatomic ParticlesDocument2 pagesLESSON PLAN - Subatomic ParticlesCrisanto LlorenteNo ratings yet
- Worksheet MomentumDocument5 pagesWorksheet MomentumSiti RohmahNo ratings yet
- Q1WK1DAY1Document4 pagesQ1WK1DAY1MaricarGabitanNo ratings yet
- 4 Rainbows and DiffractionDocument5 pages4 Rainbows and DiffractionrebbiegNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Document3 pagesGujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19manish_iitrNo ratings yet
- Science 9 q2 Mod2Document16 pagesScience 9 q2 Mod2Prince U KennardNo ratings yet
- Conservation of EnergyDocument5 pagesConservation of Energyapi-281205662No ratings yet
- DLP PHY G10 W8 D1 RevDocument7 pagesDLP PHY G10 W8 D1 RevVincent Paul ReyesNo ratings yet
- Collisions With MomentumDocument6 pagesCollisions With MomentumYilin PangNo ratings yet
- Cambridge English First (FCE) - Part 2Document2 pagesCambridge English First (FCE) - Part 2Catarina AraujoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 5.1Document3 pagesWorksheet 5.1khodijahaminNo ratings yet
- STE - Week 3Document69 pagesSTE - Week 3Anonymous xf4o0AtOTFNo ratings yet
- Activity 1: Atom and Its Subatomic ParticlesDocument1 pageActivity 1: Atom and Its Subatomic ParticlesRenmarie Labor100% (1)
- Electric Motor and GeneratorDocument6 pagesElectric Motor and GeneratorJesell JeanNo ratings yet
- Simple Electric Motor and GeneratorDocument17 pagesSimple Electric Motor and GeneratorAyla BonitaNo ratings yet
- Q2 Module 5 - What's ItDocument6 pagesQ2 Module 5 - What's Itleo markNo ratings yet
- Generato RS: Prepared By: Ms. Clydine Jethna O. SigueDocument33 pagesGenerato RS: Prepared By: Ms. Clydine Jethna O. SigueChamain MarreroNo ratings yet
- Ecological Systems TheoryDocument17 pagesEcological Systems Theorymk soberanoNo ratings yet
- Jan122023 Bscs 05 PDFDocument2 pagesJan122023 Bscs 05 PDFshuvo dassNo ratings yet
- Modal Analysis of A Aeroplane WingDocument20 pagesModal Analysis of A Aeroplane WingPrasanth Inavolu IPNo ratings yet
- Integrated Units A Planning Guide For Teachers: What Is An Integrated Unit?Document18 pagesIntegrated Units A Planning Guide For Teachers: What Is An Integrated Unit?Kim BuiNo ratings yet
- Nut 1661818Document1 pageNut 1661818phantomboyz_aipNo ratings yet
- Radar EquationDocument15 pagesRadar EquationLintang AnggitiadewiNo ratings yet
- QCP Notes1Document39 pagesQCP Notes1Jinendraabhi50% (2)
- Life Coach WorkbookDocument5 pagesLife Coach WorkbookJonathan MooreNo ratings yet
- Full Test Bank For Vanders Human Physiology 15Th Edition by Eric Widmaier PDF Docx Full Chapter ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Test Bank For Vanders Human Physiology 15Th Edition by Eric Widmaier PDF Docx Full Chapter Chaptergenevafigueroag9ec100% (15)
- IBM Data Science CapstoneDocument51 pagesIBM Data Science CapstonegeorgebhilaiNo ratings yet
- Viscometer Manual PDFDocument47 pagesViscometer Manual PDFBalqis yasinNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Philo Module 1 (Intro)Document4 pagesReviewer Philo Module 1 (Intro)JhenryNo ratings yet
- MicroGen 说明书Document24 pagesMicroGen 说明书Kailyne WatersNo ratings yet
- ch9 Text Bank Consumer BehaviorDocument60 pagesch9 Text Bank Consumer BehaviorHiba AhmedNo ratings yet
- Process Optimization For Dietary Fiber Production From Cassava Pulp Using Acid TreatmentDocument12 pagesProcess Optimization For Dietary Fiber Production From Cassava Pulp Using Acid TreatmentYanuar PramanaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Speech Delivery: Ezequiel D. QuijanoDocument26 pagesPrinciples of Speech Delivery: Ezequiel D. QuijanotintinNo ratings yet
- 11 - Sarkodie - & Al - 2016 - On A - Multivariate - Analysis - With ElectricityDocument9 pages11 - Sarkodie - & Al - 2016 - On A - Multivariate - Analysis - With Electricitykmlhectorseth94No ratings yet
- Consultant: Project: Designed By: Case: Date: Design of Masonry Retaining WallDocument4 pagesConsultant: Project: Designed By: Case: Date: Design of Masonry Retaining WallSamuel Gezahegn100% (1)
- Concept of C ProgrammingDocument74 pagesConcept of C ProgrammingAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- The Transmission-Line Modeling (TLM) Method in ElectromagneticsDocument132 pagesThe Transmission-Line Modeling (TLM) Method in ElectromagneticsFabio Hugo Souza MatosNo ratings yet
- Basf Masterflow 980 TdsDocument4 pagesBasf Masterflow 980 Tdschopdekar1969_890124No ratings yet
- Week 1 Lesson Plan Math 8Document6 pagesWeek 1 Lesson Plan Math 8Marlon SuazoNo ratings yet
- Conduct of Operations Field Handbook PDFDocument213 pagesConduct of Operations Field Handbook PDFChitu Ionut LaurentiuNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document2 pagesLab 2gregNo ratings yet
- EU - Type Examination Certificate: II 2G Ex Ia IIC T5/T6 GB II 2D Ex Ia IIIC T100°C/T85°C DB IP6XDocument4 pagesEU - Type Examination Certificate: II 2G Ex Ia IIC T5/T6 GB II 2D Ex Ia IIIC T100°C/T85°C DB IP6XHabibulla BavajiNo ratings yet
- Serial Adder Mealy Modelling ProgramDocument22 pagesSerial Adder Mealy Modelling ProgrambcemailidNo ratings yet
- Shashank DMDocument2 pagesShashank DMShashank NemaNo ratings yet
- Paper Airplane LabDocument4 pagesPaper Airplane LabMeg BakerNo ratings yet
Motor Generator
Motor Generator
Uploaded by
Princes Juat0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views3 pagesThis document describes the basic components and operation of electric generators and motors. It discusses:
1) How generators work by converting mechanical energy (from sources like falling water, wind, or steam) into electrical energy using electromagnetic induction principles. The main components are a rotor, stator, and commutator.
2) The differences between AC and DC generators and their uses. AC generators produce alternating current and are used for small applications while DC generators produce direct current and power large motors.
3) How electric motors operate using electromagnetic principles to convert electrical energy into rotational mechanical motion. The main components are a rotor, stator, and commutator.
4) Applications of generators include backup household power
Original Description:
motor generator
Original Title
Motor-generator
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document describes the basic components and operation of electric generators and motors. It discusses:
1) How generators work by converting mechanical energy (from sources like falling water, wind, or steam) into electrical energy using electromagnetic induction principles. The main components are a rotor, stator, and commutator.
2) The differences between AC and DC generators and their uses. AC generators produce alternating current and are used for small applications while DC generators produce direct current and power large motors.
3) How electric motors operate using electromagnetic principles to convert electrical energy into rotational mechanical motion. The main components are a rotor, stator, and commutator.
4) Applications of generators include backup household power
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views3 pagesMotor Generator
Motor Generator
Uploaded by
Princes JuatThis document describes the basic components and operation of electric generators and motors. It discusses:
1) How generators work by converting mechanical energy (from sources like falling water, wind, or steam) into electrical energy using electromagnetic induction principles. The main components are a rotor, stator, and commutator.
2) The differences between AC and DC generators and their uses. AC generators produce alternating current and are used for small applications while DC generators produce direct current and power large motors.
3) How electric motors operate using electromagnetic principles to convert electrical energy into rotational mechanical motion. The main components are a rotor, stator, and commutator.
4) Applications of generators include backup household power
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
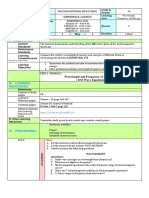
Simple Electric Motor and 3.
Commutator - A commutator works like a rectifier
Generator that changes AC voltage to DC voltage within the
armature winding. It is designed with a copper
What is a generator? segment, and each copper segment is protected from
A generator converts Mechanical Energy to Electrical each other with the help of mica sheets. It is located on
Energy. the shaft of the machine.
4. Brushes – The Brushes are in constant contact with
It produces an electric current when a coil of wire is
the commutator and are attached to the wires leading
wrapped around an iron core and rotated near a
from the generator. The commutator spins while the
magnet.
brushes remain stationary, transferring current from
How does a generator work?
the commutator.
An electric generator is a device that converts 5. Shaft – The shaft transfers mechanical energy to
mechanical energy obtained from an external source the generator and turns the coil
into electrical energy as the output. through the magnetic field. The shaft may be turned by
Principle of Electromagnetic Induction in a turbine that operates with water, steam or air, or by
Generator other means.
Modern generators can be attributed to Michael Difference between the AC Generator and the DC
Faraday’s principle of Generator
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION. Faraday AC generator produces AC electrical power whereas
discovered that when a conductor moves in a DC generator produces DC electrical power
magnetic field, electrical In DC generator the current flows in one direction
charges could be created and directed to create a flow whereas in the AC generators current reverses
of current. periodically.
At its most basic, an electrical generator is nothing In DC generator split rings are used they wear out
more than an electromagnet – moving wire near a quickly in AC generator slip rings are used, so they
magnet to direct the flow of electricity. It’s similar to have high efficiency.
how a pump pushes water through a pipe. AC generators are used for small domestic
It is important to understand that a generator does not applications whereas DC generators used to power
actually “create” electrical energy. Instead, it uses the large motors.
mechanical energy supplied to it to force the movement of What are the top Uses of Generator?
electric charges present in the wire of its windings through Back -Up power for your house
an external electric circuit. Stand-by power for businesses
This flow of electric charges constitutes the output electric Temporary power in a construction site
Permanent power to a farm
current supplied by the generator. This mechanism can be
Helping main source of electricity to supply the total
understood by considering the generator to be similar to a power required
water pump, which causes the flow of water but does not Pop concerts, events, and exhibitions
actually create the water flowing through it. Caravans/Camping in remote locations Outdoor
How water, wind, and steam make electricity catering facilities
through generator? ELECTRIC MOTOR
1. Water – Hydropower plants capture the energy of Anything that changes electricity into motion, meaning
falling water to generate electricity. A turbine converts
electrical energy into mechanical energy is called an electric
motor.
the kinetic energy of the falling water into mechanical
Basic Principles
energy. Then a generator converts the mechanical
Danish physicist HANS CHRISTIAN ØRSTED began a
energy from the turbine into electrical energy.
new scientific era when he discovered that electricity and
2. Wind - The wind turns the blades of the windmill, magnetism are linked. He showed by experiment that an
known as the turbine, which, in turn, spins the shaft
electric current flowing through a wire could move a nearby
that turns the coil inside the magnet, known as the
generator, magnet.
and it produces the electricity. The discovery of ELECTROMAGNETISM set the
3. Fossil Fuel/Steam/Heat - Oil is burned to heat stage for the eventual development of our modern
water which makes steam. Steam technology-based world. How do Electric Motors
moves the turbine blades that turn a shaft inside the work? Motors work through the principles of
generator. The shaft spins the coil of wire inside a ELECTROMAGNETISM. If you run electricity through
magnet in the generator that produces a current of a wire, it creates a magnetic field. If you coil the wire
electricity.
around a rod and run electricity through the wire, it
What are the main components of a DC generator?
A DC generator is an electrical machine which converts creates a magnetic field around the rod. One end of the
mechanical energy into direct current electricity. rod will have a north magnetic pole and the other will
1. Stator - The main function of the stator is to have a south pole. Opposite poles attract one another,
provide magnetic fields where the coil spins. A stator like poles repel. When you surround that rod with
includes two magnets with opposite polarity facing other magnets, the rod will rotate from the attractive
each other. These magnets are located to fit in the and repulsive forces.
region of the rotor.
What are the parts of an electric motor?
2. Rotor - A rotor in a DC machine includes slotted
iron laminations with slots that are stacked to shape a Electric motor designs can vary quite a lot, though in
cylindrical armature core. The function of the general they have three main parts: a rotor, a stator
lamination is to decrease the loss caused due to “Eddy and a commutator. These three parts use the attractive
Current”.
and repulsive forces of electromagnetism, causing the In power stations, it is usually the magnet which is
motor to spin continually as long as it receives a attached to the axel and rotates with the coils
steady flow of electric current. surrounding the magnet. However, the end result is
A. THE STATOR the same. The motor and the generator are almost
Every electric motor has two essential parts; one similar from the construction point of view, as both
stationary, and one that rotates. The stationary part is have stator and rotor.
the stator. Though configurations vary, the stator is Applications of Concave and Convex Mirrors
most often a permanent magnet or row of magnets A mirror is not just flat and plane, a mirror can be
lining the edge of the motor casing, which is usually a curved; convex and concave mirrors. These mirrors are
round plastic drum. collectively called spherical mirrors.
B. THE ROTOR Concave mirror, also known as a converging
Inserted into the stator is the rotor, usually consisting mirror has reflecting surface which collects light inward
of copper wire wound into a coil around an axle. When and focus them to one focal point, this type of mirror is
electric current flows through the coil, the resulting what the dentist used in magnifying the area behind
magnetic field pushes against the field created by the your teeth to check on cavities and tooth decay.
stator, and makes the axle spin For illuminating purposes, you can see concave
C. THE COMMUTATOR mirrors used in headlamps, flashlights and spotlights.
1. BASICS – An electric motor has another important In these devices, the light rays that gathered from a
component, the commutator, small source of the mirror are collected and directed
which sits at one end of the coil. It is a metal ring outward in a beam. Small light source bounded by a
divided into two halves. It reverses the electrical concave mirror flashes a brighter beam.
current in the coil each time the coil rotates half a Convex mirror, also known as diverging mirror, is
turn. The commutator periodically reverses the current another type of spherical mirror which has the outer
between the rotor and the external circuit, or the bulging surface that reflects light instead of the inner
battery. This ensures that the ends of coils do not one. It has a wider view field compared to a concave
move in opposite directions, and ensures that the axle mirror. This makes bigger objects appear to be smaller
spins in one direction. than their original form.
2. MAGNETIC POLES – BRUSHES AND TERMINALS. Uses of Convex Lenses
At one end of the motor are Sometimes called a positive lens, a convex lens is
the brushes and the terminals. They are at the characterized by its bulging surfaces that is directed
opposite end from where the rotor exits the motor outward making it thicker at the center than on its
casing. The brushes send electrical current to the edges. It is also known as converging lens because as
commutator and are typically made of graphite. The light passes through it, its rays bend inward and
terminals are the locations where the battery attaches converge at a spot located beyond the lens known as
to the motor and sends the currents to spin the rotor. the focal point causing the object behind the lens to
Difference between the AC Motor and the DC Motor magnify or to appear bigger than its actual size. Image
In the AC Motor, the source of power is AC mains produced by convex lenses can be a virtual or real
supply whereas in DC motor power is obtained from image. If both sides of the lens are curved inward, then
batteries. that type of convex lens is called biconvex typically
In AC motors no commutators and brushes are used seen in magnifying glasses. If only one side of the lens
whereas in DC motors these play an important part in is curved inward and the other has a flat surface, it is
their operation. called as plano-convex.
In AC motors the armature is stationary and the Concave Lenses and Myopia (nearsightedness)
magnetic field rotates whereas in DC motors it is vice Correction
versa. Concave lenses, such as eyeglasses and contact lenses
AC motors are suitable for large industrial are used in correcting myopia (nearsightedness).
applications whereas DC motors are suitable for Myopia is a condition in which light rays focus in front
domestic applications. of the eye’s retina instead of, on the retina. The result
Comparison of Motor and Generator
of this condition is a makes distant object to appear
A motor and generator perform opposite functions, but
their fundamental structure is the same. Their blurry, while near objects appear normal.
structure is a “coil mounted on an axle within a Meniscus Lenses and Hyperopia (farsightedness)
magnetic field”. An electric motor is used to produce Correction
rotational motion from electrical supply. In a motor, an Hyperopia is the eye condition that enables
electric current is passed through the coil. someone to see distant object clearly but makes nearby
The coil then creates a magnetic field that interacts object seem blurry. This condition is due to the
with the already existing magnetic field. This inability one’s eyes to focus on objects closer to the
interaction forces the coil to rotate. eyes.
For a motor, the input energy is electrical energy Astigmatism
and the useful output The unevenness in the curvature of the lens of the eyeball
energy is mechanical energy. causes astigmatism which results in blurred vision and
The generator is used to produce an electric current headaches. An astigmatic person will see horizontal and
from rotational motion (on large scale power stations a vertical lines not equally distinct and clear. This is usually
“turbine” is used to provide this rotation). In a corrected with cylindrical lenses.
generator, the rotation causes the coil to rotate inside
the magnetic field. This induces an alternating current
in the coil. Real and virtual images
For generator the input energy is mechanical
energy and the useful Real image is formed by the actual intersection of
output energy is electrical energy.
light rays. It can be obtained on a screen. Hence,
projectors form real images.
Virtual image is formed when the light rays
appear to be originating from a point but does not
actually meet. It can be seen by human eyes.
Simple microscope forms virtual images.
Note: Concave lens always form virtual images.
Convex lens may or may not form virtual images.
Converging and Diverging Lens
Converging lens is convex lens whereas diverging
lens is a concave lens. Converging lens converge and
focus the light ray to meet at a single point whereas
diverging lens, diverge the light falling on its surface
and not meet at a single point. Converging and
diverging lens are shown in the figure.
How could you build your periscope to see
behind you?
By creating a forward-looking periscope by facing
the mirrors in opposite directions and by creating
backwards-looking one by facing the mirrors in
the same direction.
You might also like
- ASTON Kartika GrogolDocument2 pagesASTON Kartika GrogolAngga Ciro Bams100% (1)
- Energy Systems Phet WorksheetDocument5 pagesEnergy Systems Phet Worksheetapi-203432401No ratings yet
- Final Exam Engineering MechanicsDocument9 pagesFinal Exam Engineering MechanicsjohnjabarajNo ratings yet
- 04 La3cna TeDocument22 pages04 La3cna Tegibson marvalNo ratings yet
- Leah Hartsock: Gravitational-Potential WorkDocument3 pagesLeah Hartsock: Gravitational-Potential WorkRHEAMAE GALLEGONo ratings yet
- Lesson Plans-Grade 11 PhysicsDocument1 pageLesson Plans-Grade 11 Physicsian joseph100% (1)
- Magnetic Induction Lesson Plan A2av6 1Document2 pagesMagnetic Induction Lesson Plan A2av6 1api-313158624100% (1)
- CBSE Class 10 Physics Electricity Worksheet Set ADocument2 pagesCBSE Class 10 Physics Electricity Worksheet Set AlalitNo ratings yet
- Cot g9Document5 pagesCot g9Rince RioNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Electromagnetic InductionDocument3 pagesLesson Plan - Electromagnetic InductionRakotoarison Louis Frederick100% (1)
- Mechanical EnergyDocument10 pagesMechanical Energyapi-320478846No ratings yet
- Q4-WEEK 3-Momentum and ImpulseDocument32 pagesQ4-WEEK 3-Momentum and ImpulseAdonis SanielNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 BondingDocument13 pagesTopic 4 Bondinglobna masadehNo ratings yet
- Stirling Engine ProposalDocument8 pagesStirling Engine ProposalSaibhargavi BkNo ratings yet
- Semi Det. Geothermal 9 DaaDocument5 pagesSemi Det. Geothermal 9 DaaRjane CañeteNo ratings yet
- Theoretical 3 Tornado SolutionDocument7 pagesTheoretical 3 Tornado Solutionjas dwanNo ratings yet
- PDF - Geothermal Power PlantDocument43 pagesPDF - Geothermal Power PlantTrinity MarieNo ratings yet
- Detailed Science Lesson Plan: Grade Level Quarter / Domain Week & Day No. Page NoDocument3 pagesDetailed Science Lesson Plan: Grade Level Quarter / Domain Week & Day No. Page Noaiza larrozaNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan: Student Teacher Grade Level Teaching Date Learning Area Teaching Time Quarter I. ObjectivesDocument7 pagesDaily Lesson Plan: Student Teacher Grade Level Teaching Date Learning Area Teaching Time Quarter I. ObjectivesHazel LiwanagNo ratings yet
- DLL chemNOV15Document5 pagesDLL chemNOV15Rosallie Caaya-NuezNo ratings yet
- School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Time & Dates Quarter I. ObjectivesDocument4 pagesSchool Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Time & Dates Quarter I. ObjectivesRiztine Rachel RaineNo ratings yet
- Potential and Kinetic Energy WorksheetDocument2 pagesPotential and Kinetic Energy WorksheetJorge ArguelloNo ratings yet
- L6 U3 SNC1D NotesDocument6 pagesL6 U3 SNC1D NotesabhieNo ratings yet
- FARADAY's LawDocument27 pagesFARADAY's LawMary Liezl Pilapil50% (4)
- Chap23 PDFDocument26 pagesChap23 PDFsafdar lashariNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Q3 COTDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Q3 COTCharmen PabilonaNo ratings yet
- 7 E Model Lesson PlanDocument7 pages7 E Model Lesson Plangloria tolentinoNo ratings yet
- DLP em Equation Vhien CahipeDocument4 pagesDLP em Equation Vhien CahipeGABRIEL ADONANo ratings yet
- RAISEPlus GRADE 9 Impulse and MomentumDocument2 pagesRAISEPlus GRADE 9 Impulse and Momentumpj oroscoNo ratings yet
- Final Revised Las in Science 9 q3w3Document4 pagesFinal Revised Las in Science 9 q3w3Ma.Kristine Ibarreta JazulNo ratings yet
- DLL Chem Dec02Document4 pagesDLL Chem Dec02Rosallie Caaya-NuezNo ratings yet
- Final Semi Detailed Lesson Plan TemplateDocument10 pagesFinal Semi Detailed Lesson Plan TemplateJessie GernaleNo ratings yet
- LP For 2022 2nd COTDocument6 pagesLP For 2022 2nd COTEmily Tatunay EspejoNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current vs. Direct Current - Lesson For Kids PDFDocument3 pagesAlternating Current vs. Direct Current - Lesson For Kids PDFSatyajit Mishra100% (1)
- Science: Mahay Integrated Secondary SchoolDocument8 pagesScience: Mahay Integrated Secondary Schoollavenia acdalNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesElectricity and Magnetism Lesson PlanNel Pasaiz100% (1)
- Arban, CG. Lesson Plan in Geothermal Energy, 11 - STEMDocument6 pagesArban, CG. Lesson Plan in Geothermal Energy, 11 - STEMCzarina Amor CabilleteNo ratings yet
- HIstory of AtomDocument20 pagesHIstory of AtomIrish Solomon100% (1)
- Unit II Electrical Circuits: Basic Circuit Element and Their CombinationsDocument21 pagesUnit II Electrical Circuits: Basic Circuit Element and Their CombinationsMonte CarloNo ratings yet
- 1 - Electrical+Basics+-+CircuitsDocument36 pages1 - Electrical+Basics+-+Circuitsareina75No ratings yet
- Magnetism (Revised)Document55 pagesMagnetism (Revised)api-275374056100% (1)
- Chap10no1 PDFDocument2 pagesChap10no1 PDFTajiriMollel0% (9)
- Energetics Note 1Document15 pagesEnergetics Note 1shaliniNo ratings yet
- Refraction of Light, From Lens and SlabsDocument90 pagesRefraction of Light, From Lens and Slabsp_k_soni_iit_physicsNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Q2 - W6 - D3Document1 pageScience 10 - Q2 - W6 - D3zenaida a academiaNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN - Subatomic ParticlesDocument2 pagesLESSON PLAN - Subatomic ParticlesCrisanto LlorenteNo ratings yet
- Worksheet MomentumDocument5 pagesWorksheet MomentumSiti RohmahNo ratings yet
- Q1WK1DAY1Document4 pagesQ1WK1DAY1MaricarGabitanNo ratings yet
- 4 Rainbows and DiffractionDocument5 pages4 Rainbows and DiffractionrebbiegNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Document3 pagesGujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19manish_iitrNo ratings yet
- Science 9 q2 Mod2Document16 pagesScience 9 q2 Mod2Prince U KennardNo ratings yet
- Conservation of EnergyDocument5 pagesConservation of Energyapi-281205662No ratings yet
- DLP PHY G10 W8 D1 RevDocument7 pagesDLP PHY G10 W8 D1 RevVincent Paul ReyesNo ratings yet
- Collisions With MomentumDocument6 pagesCollisions With MomentumYilin PangNo ratings yet
- Cambridge English First (FCE) - Part 2Document2 pagesCambridge English First (FCE) - Part 2Catarina AraujoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 5.1Document3 pagesWorksheet 5.1khodijahaminNo ratings yet
- STE - Week 3Document69 pagesSTE - Week 3Anonymous xf4o0AtOTFNo ratings yet
- Activity 1: Atom and Its Subatomic ParticlesDocument1 pageActivity 1: Atom and Its Subatomic ParticlesRenmarie Labor100% (1)
- Electric Motor and GeneratorDocument6 pagesElectric Motor and GeneratorJesell JeanNo ratings yet
- Simple Electric Motor and GeneratorDocument17 pagesSimple Electric Motor and GeneratorAyla BonitaNo ratings yet
- Q2 Module 5 - What's ItDocument6 pagesQ2 Module 5 - What's Itleo markNo ratings yet
- Generato RS: Prepared By: Ms. Clydine Jethna O. SigueDocument33 pagesGenerato RS: Prepared By: Ms. Clydine Jethna O. SigueChamain MarreroNo ratings yet
- Ecological Systems TheoryDocument17 pagesEcological Systems Theorymk soberanoNo ratings yet
- Jan122023 Bscs 05 PDFDocument2 pagesJan122023 Bscs 05 PDFshuvo dassNo ratings yet
- Modal Analysis of A Aeroplane WingDocument20 pagesModal Analysis of A Aeroplane WingPrasanth Inavolu IPNo ratings yet
- Integrated Units A Planning Guide For Teachers: What Is An Integrated Unit?Document18 pagesIntegrated Units A Planning Guide For Teachers: What Is An Integrated Unit?Kim BuiNo ratings yet
- Nut 1661818Document1 pageNut 1661818phantomboyz_aipNo ratings yet
- Radar EquationDocument15 pagesRadar EquationLintang AnggitiadewiNo ratings yet
- QCP Notes1Document39 pagesQCP Notes1Jinendraabhi50% (2)
- Life Coach WorkbookDocument5 pagesLife Coach WorkbookJonathan MooreNo ratings yet
- Full Test Bank For Vanders Human Physiology 15Th Edition by Eric Widmaier PDF Docx Full Chapter ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Test Bank For Vanders Human Physiology 15Th Edition by Eric Widmaier PDF Docx Full Chapter Chaptergenevafigueroag9ec100% (15)
- IBM Data Science CapstoneDocument51 pagesIBM Data Science CapstonegeorgebhilaiNo ratings yet
- Viscometer Manual PDFDocument47 pagesViscometer Manual PDFBalqis yasinNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Philo Module 1 (Intro)Document4 pagesReviewer Philo Module 1 (Intro)JhenryNo ratings yet
- MicroGen 说明书Document24 pagesMicroGen 说明书Kailyne WatersNo ratings yet
- ch9 Text Bank Consumer BehaviorDocument60 pagesch9 Text Bank Consumer BehaviorHiba AhmedNo ratings yet
- Process Optimization For Dietary Fiber Production From Cassava Pulp Using Acid TreatmentDocument12 pagesProcess Optimization For Dietary Fiber Production From Cassava Pulp Using Acid TreatmentYanuar PramanaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Speech Delivery: Ezequiel D. QuijanoDocument26 pagesPrinciples of Speech Delivery: Ezequiel D. QuijanotintinNo ratings yet
- 11 - Sarkodie - & Al - 2016 - On A - Multivariate - Analysis - With ElectricityDocument9 pages11 - Sarkodie - & Al - 2016 - On A - Multivariate - Analysis - With Electricitykmlhectorseth94No ratings yet
- Consultant: Project: Designed By: Case: Date: Design of Masonry Retaining WallDocument4 pagesConsultant: Project: Designed By: Case: Date: Design of Masonry Retaining WallSamuel Gezahegn100% (1)
- Concept of C ProgrammingDocument74 pagesConcept of C ProgrammingAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- The Transmission-Line Modeling (TLM) Method in ElectromagneticsDocument132 pagesThe Transmission-Line Modeling (TLM) Method in ElectromagneticsFabio Hugo Souza MatosNo ratings yet
- Basf Masterflow 980 TdsDocument4 pagesBasf Masterflow 980 Tdschopdekar1969_890124No ratings yet
- Week 1 Lesson Plan Math 8Document6 pagesWeek 1 Lesson Plan Math 8Marlon SuazoNo ratings yet
- Conduct of Operations Field Handbook PDFDocument213 pagesConduct of Operations Field Handbook PDFChitu Ionut LaurentiuNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document2 pagesLab 2gregNo ratings yet
- EU - Type Examination Certificate: II 2G Ex Ia IIC T5/T6 GB II 2D Ex Ia IIIC T100°C/T85°C DB IP6XDocument4 pagesEU - Type Examination Certificate: II 2G Ex Ia IIC T5/T6 GB II 2D Ex Ia IIIC T100°C/T85°C DB IP6XHabibulla BavajiNo ratings yet
- Serial Adder Mealy Modelling ProgramDocument22 pagesSerial Adder Mealy Modelling ProgrambcemailidNo ratings yet
- Shashank DMDocument2 pagesShashank DMShashank NemaNo ratings yet
- Paper Airplane LabDocument4 pagesPaper Airplane LabMeg BakerNo ratings yet