Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 11
Lesson 11
Uploaded by
Cath Detoperez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views19 pagesATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the major energy currency of cells. It provides energy for most energy-consuming cellular activities through the breaking of its high-energy phosphate bonds. ATP is regenerated through processes like glycolysis and cellular respiration to replenish the cell's supply, as it is constantly hydrolyzed during energy-requiring reactions. The regeneration of ATP is important because cells use up ATP molecules rapidly and rely on a constant production of new ATP to meet their energy demands.
Original Description:
Original Title
LESSON-11
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the major energy currency of cells. It provides energy for most energy-consuming cellular activities through the breaking of its high-energy phosphate bonds. ATP is regenerated through processes like glycolysis and cellular respiration to replenish the cell's supply, as it is constantly hydrolyzed during energy-requiring reactions. The regeneration of ATP is important because cells use up ATP molecules rapidly and rely on a constant production of new ATP to meet their energy demands.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views19 pagesLesson 11
Lesson 11
Uploaded by
Cath DetoperezATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the major energy currency of cells. It provides energy for most energy-consuming cellular activities through the breaking of its high-energy phosphate bonds. ATP is regenerated through processes like glycolysis and cellular respiration to replenish the cell's supply, as it is constantly hydrolyzed during energy-requiring reactions. The regeneration of ATP is important because cells use up ATP molecules rapidly and rely on a constant production of new ATP to meet their energy demands.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 19
1
Anne Gelli L. Lauron, LFT, LPT
Special Science Teacher I
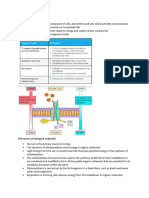
Adenosine Triphospate
• It is the major energy currency of
the cell
• Provides the energy for most of the
energy-consuming activities of the
• cell
• Regulates many biochemical
pathways.
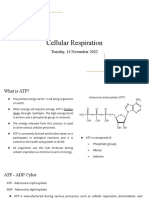
• It is composed of the nitrogen
base ADENINE, the pentose (5C)
sugar RIBOSE, and three
PHOSPHATE groups
• The LAST phosphate group is
bonded with a HIGH ENERGY
chemical bond
• This bond can be BROKEN to
release ENERGY for CELLS to
use
Is ATP a
nucleotide?
an appreciable amount of energy
is released when one of the
phosphate bonds of ATP is
broken in a hydrolysis (water-
mediated breakdown) reaction.
The energy released by
hydrolysis (breakdown) of ATP
is used to power many energy-
requiring cellular reactions.
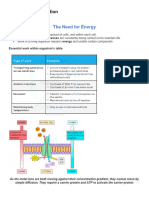
ATP powers most energy-consuming activities of
cells, such as:
• joining transfer RNAs to amino acids for
assembly into proteins
• synthesis of nucleoside triphosphates for
assembly into DNA and RNA
• synthesis of polysaccharides
• synthesis of fats
• active transport of molecules and ions
ATP powers most energy-consuming activities of
cells, such as:
• conduction of nerve impulses
• maintenance of cell volume by osmosis
• addition of phosphate groups
(phosphorylation) to different proteins (e.g., to
alter their activity in cell signaling)
• muscle contraction
• beating of cilia and flagella (including sperm)
• bioluminescence
Is ATP a
renewable
resource?
ATP-ADP CYCLE
Why is
regeneration of
ATP important?
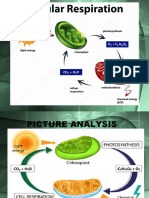
• occurs in the cytosol by
glycolysis
• occurs in mitochondria by
cellular respiration
• occurs in chloroplasts by
photosynthesis
• Energy+ADP + Pi → ATP + H2O
• requires energy: 7.3 kcal/mole
Regeneration of ATP is
important because cells tend to
use up (hydrolyze) ATP
molecules very quickly and rely
on replacement ATP being
constantly produced.
You might also like
- Energy and Respiration-1Document25 pagesEnergy and Respiration-1Rohan PaneruNo ratings yet
- Flow of Energy Part 1Document18 pagesFlow of Energy Part 1nancie8No ratings yet
- Atp Adp CycleDocument18 pagesAtp Adp CycleLyn Dela Cruz Fontila100% (1)
- The Functions of ATP: Synthesis of New Chemical CompoundsDocument5 pagesThe Functions of ATP: Synthesis of New Chemical CompoundsMohini BajajNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: 5.1 The Need For Energy in Living OrganismsDocument12 pagesCellular Respiration: 5.1 The Need For Energy in Living OrganismsaamandaNo ratings yet
- Professor K.O. SOETAN Department of Veterinary Physiology and Biochemistry, University of Ibadan, IbadanDocument25 pagesProfessor K.O. SOETAN Department of Veterinary Physiology and Biochemistry, University of Ibadan, Ibadanolawandeilo123No ratings yet
- ATP - ADP CycleDocument13 pagesATP - ADP CycleDanessa Mina BalboaNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNA MetabolismDocument27 pagesDNA and RNA Metabolismazka shahidNo ratings yet
- Energy and ATPDocument5 pagesEnergy and ATPMilka Rahman100% (1)
- Unit 5 Energy TransformationsDocument49 pagesUnit 5 Energy TransformationsFiguracion, Zhass Naye D.No ratings yet
- ATP PPTDocument14 pagesATP PPTagotsolania5No ratings yet
- 2-Energy and RespirationDocument34 pages2-Energy and RespirationLisa DentonNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & MetabolismDocument9 pagesCell Structure & MetabolismChami VillaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Key PointsDocument6 pagesCellular Respiration Key PointsKathleen RamiloNo ratings yet
- Atp Production & Consumption: Ian A. Tolomia Jonel V ParagasDocument12 pagesAtp Production & Consumption: Ian A. Tolomia Jonel V ParagasIan AusejoNo ratings yet
- PE Report - Output - Villanueva 1Document3 pagesPE Report - Output - Villanueva 1Rico Yan CanoNo ratings yet
- Atp: Universal Currency of Cellular Energy: - Aditya Sunil Nair - Class XI D - Roll No: 22Document10 pagesAtp: Universal Currency of Cellular Energy: - Aditya Sunil Nair - Class XI D - Roll No: 22Aditya Sunil NairNo ratings yet
- ATP and Its Role in Living OrganismsDocument2 pagesATP and Its Role in Living OrganismsHayze Jones50% (2)
- Biology NotesDocument214 pagesBiology NotesbloomNo ratings yet
- Energy TransformationDocument19 pagesEnergy TransformationRicardo ErioNo ratings yet
- 9.1. Energy and LifeDocument19 pages9.1. Energy and Lifehanatabbal19No ratings yet
- Bioenergetic: Atp CycleDocument28 pagesBioenergetic: Atp CycleRahmad HidayatNo ratings yet
- A Level Biology: Alevelbiology - Co.ukDocument11 pagesA Level Biology: Alevelbiology - Co.ukg8yd7q9cnmNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio - Second GradingDocument7 pagesGen Bio - Second GradingCasey PedrayaNo ratings yet
- Portal For CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and TricksDocument4 pagesPortal For CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and TricksSHRAVYA K REDDYNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: Your Easy Guide To Understanding A Very Complex Process!Document16 pagesPhotosynthesis: Your Easy Guide To Understanding A Very Complex Process!Alacran Mishina MiguelaNo ratings yet
- Energy and RespirationDocument11 pagesEnergy and Respirationririrachma fitriahNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisDocument41 pagesCellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisCarissa MarchanNo ratings yet
- 1.bioenergeticsDocument38 pages1.bioenergeticsberreozbayraktarNo ratings yet
- Microbial Metabolism 052124Document89 pagesMicrobial Metabolism 052124Marina Abd CebrianNo ratings yet
- Cell RespirationDocument6 pagesCell RespirationDave BoocNo ratings yet
- lesson-4-Role-of-ATP-in-Energy-Coupling-and-Transfer (1) EnergyDocument10 pageslesson-4-Role-of-ATP-in-Energy-Coupling-and-Transfer (1) EnergyKivo ZoshikoroNo ratings yet
- Cell RespiratiionDocument6 pagesCell RespiratiionDave BoocNo ratings yet
- Biologic Oxidation (New)Document71 pagesBiologic Oxidation (New)Muhammad Nur DelaphanEnamNo ratings yet
- 2.8 - Cell RespirationDocument16 pages2.8 - Cell RespirationpjhaveNo ratings yet
- Transes Biochem Cellular MetabolismDocument5 pagesTranses Biochem Cellular MetabolismPia LouiseNo ratings yet
- 2238 Unit 4 Microbial Metabolic PathwaysDocument24 pages2238 Unit 4 Microbial Metabolic PathwaystitojhezielanneNo ratings yet
- AtpDocument10 pagesAtpSheba HernandezNo ratings yet
- The Cell (Energy)Document15 pagesThe Cell (Energy)Luka IvanovicNo ratings yet
- Metabolism: Marcus Cueno, RNDocument15 pagesMetabolism: Marcus Cueno, RNMarcus, RN100% (2)
- Gen Bio 1 Second QTR Module RevisedDocument37 pagesGen Bio 1 Second QTR Module RevisedMichaela CasabaNo ratings yet
- ATP-ADP Cycle Lesson 1Document33 pagesATP-ADP Cycle Lesson 1mayzel14No ratings yet
- What Is ATPDocument15 pagesWhat Is ATPEira LeyNo ratings yet
- Cellular - Respiration Lecture KoDocument60 pagesCellular - Respiration Lecture KoEvangelene Esquillo SanaNo ratings yet
- Bio CellDocument102 pagesBio Cellcheryl tayasNo ratings yet
- Role of Atp In-Wps OfficeDocument14 pagesRole of Atp In-Wps OfficeElsa Barrientos BatasNo ratings yet
- Biology Reporting FinaleDocument54 pagesBiology Reporting FinaleJohn Carlo RelosaNo ratings yet
- 4 Energy Metabolism and Metabolic RateDocument56 pages4 Energy Metabolism and Metabolic RateShafici CqadirNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: Amelia Putri Nariya Astri Yohana Putri Gabriellia Oktaviani P. Muhammad Fauzan Safina ZahiraDocument43 pagesCellular Respiration: Amelia Putri Nariya Astri Yohana Putri Gabriellia Oktaviani P. Muhammad Fauzan Safina ZahirasafinazahiraNo ratings yet
- Coupled Reactions and Importance of Chloropyll and Other PigmentsDocument8 pagesCoupled Reactions and Importance of Chloropyll and Other PigmentsPerlyn Del Pilar OduyaNo ratings yet
- Respiration Part 1Document35 pagesRespiration Part 1Ashley JohnsNo ratings yet
- A2 Biology Notes Cellular RespirationDocument19 pagesA2 Biology Notes Cellular RespirationKajana Sivarasa ShenthanNo ratings yet
- METABOLISM Unit 1Document12 pagesMETABOLISM Unit 1Siddhant MazumderNo ratings yet
- Chap 12 Energy and RespirationDocument34 pagesChap 12 Energy and RespirationGeorge ApidiNo ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument17 pagesGeneral Biologydwightballes9No ratings yet
- A2 Biology Notes 2016Document252 pagesA2 Biology Notes 2016MohammedKamelNo ratings yet
- Biology Reporting FinaleDocument29 pagesBiology Reporting FinaleJohn Carlo RelosaNo ratings yet
- 044BIO11-14 Respiration in Plants (Study Notes)Document13 pages044BIO11-14 Respiration in Plants (Study Notes)Zen FredyNo ratings yet
- GenbioDocument5 pagesGenbioYkhay ElfanteNo ratings yet
- The Physiology of Cell Energy Production: CPTIPS.COM MonographsFrom EverandThe Physiology of Cell Energy Production: CPTIPS.COM MonographsNo ratings yet
- Asthenosphere Upper Mantle: Mohorovicic DiscontinuityDocument1 pageAsthenosphere Upper Mantle: Mohorovicic DiscontinuityCath DetoperezNo ratings yet
- Group 7 (EAPP)Document40 pagesGroup 7 (EAPP)Cath DetoperezNo ratings yet
- BROCHUREDocument2 pagesBROCHURECath DetoperezNo ratings yet
- The Last Leaf SummaryDocument1 pageThe Last Leaf SummaryCath DetoperezNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 Reviewer 2NDDocument4 pagesPractical Research 2 Reviewer 2NDCath DetoperezNo ratings yet
- Ely and AriesDocument26 pagesEly and AriesCath DetoperezNo ratings yet
- BIO1 Lesson-12 PhotosynthesisDocument36 pagesBIO1 Lesson-12 PhotosynthesisCath Detoperez100% (1)
- 113 DigestionDocument22 pages113 DigestionCath DetoperezNo ratings yet
- E-Portfolio (Performance Task)Document27 pagesE-Portfolio (Performance Task)Cath DetoperezNo ratings yet
- BROCHUREDocument2 pagesBROCHURECath DetoperezNo ratings yet
- The Last LeafDocument2 pagesThe Last LeafCath DetoperezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Butterfly Plea.Document4 pagesChapter 3 Butterfly Plea.Cath DetoperezNo ratings yet
- Performance Task in EAPPDocument16 pagesPerformance Task in EAPPCath DetoperezNo ratings yet
- Philosophy ReviewerDocument4 pagesPhilosophy ReviewerCath DetoperezNo ratings yet
- AiceeDocument1 pageAiceeCath DetoperezNo ratings yet
- Bio1 LabRep3 Group6Document11 pagesBio1 LabRep3 Group6Cath DetoperezNo ratings yet
- The Last Leaf SummaryDocument1 pageThe Last Leaf SummaryCath DetoperezNo ratings yet
- Free Fall Due To Gravity Practice QuestionsDocument1 pageFree Fall Due To Gravity Practice QuestionsCath DetoperezNo ratings yet
- 1ST QuarterDocument28 pages1ST QuarterCath DetoperezNo ratings yet
- Yukot, ChungDocument18 pagesYukot, ChungCath DetoperezNo ratings yet