Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Se
Se
Uploaded by
Shubham Yadav0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views3 pagesThis document contains a question bank that seems to be testing knowledge of software engineering processes and methodologies. It includes 22 multiple choice questions related to topics like the software development life cycle, documentation like requirements specifications and design documents, process models like the waterfall model and agile development, diagramming notations, and project phases. The questions are at a level that would be appropriate for an introductory software engineering course.
Original Description:
Original Title
se
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains a question bank that seems to be testing knowledge of software engineering processes and methodologies. It includes 22 multiple choice questions related to topics like the software development life cycle, documentation like requirements specifications and design documents, process models like the waterfall model and agile development, diagramming notations, and project phases. The questions are at a level that would be appropriate for an introductory software engineering course.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views3 pagesSe
Se
Uploaded by
Shubham YadavThis document contains a question bank that seems to be testing knowledge of software engineering processes and methodologies. It includes 22 multiple choice questions related to topics like the software development life cycle, documentation like requirements specifications and design documents, process models like the waterfall model and agile development, diagramming notations, and project phases. The questions are at a level that would be appropriate for an introductory software engineering course.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
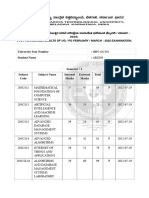
SE QUESTION BANK
1. The application of a systematic, disciplined, quantifiable approach to the development, operation, and
maintenance of software; is called .
(a) Software Engineering (b) Generic Process Model
(c) Software Process (d) None of These
2. Following diagram has fork and join
(a) Activity Diagram (b) Class Diagram
(c) Sequence Diagram (d) Use Case Diagram
3. is a kind of message that represents the invocation of
message of the same lifeline.
(a) Self Message (b) Destroy Message
(c) Recursive Message (d) Call Message
4. The quick design focuses on the representation of those aspects of the
software that will be visible to the customer
(a) Prototyping Model (b) Iterative Model
(c) Agile Model (d) Incremental Model
5. The customer indicates that changes in requirements must be made, the
modeling activity moves from the .
(a) inactive state (b) under development state
(c) awaiting changes state (d) Under review
6. A diagram is the most commonly used interaction diagram.
(a) Deployment (b) State Transtition
(c) Collaboration (d) Sequence
7. The purpose of the phase is to analyze the requirements and
necessary architecture of the system.
(a) Elaboration (b) Construction
(c) Inception (d) Transition
8. The was the first software process model to be introduced.
(a) RAD Model (b) Proto-Typing Model
(c) Iterative Model (d) Waterfall Model
9. Describes the "what" of the system to be produced and not "how." In this
phase, a large document called document
(a) SDD (b) SDS
(c) SRS (d) None of These
10. A is a collection of activities, actions, and tasks that are performed
when some work product is to be created.
(a) Software Engineering (b) Generic Process Model
(c) Software Process (d) None of These
11. A approach to software engineering is based around separate
development stages with the outputs to be produced at each of these stages
planned in advance.
.
(a) plan-driven (b) Extreme programming
(c) Agile development (d) None of These
12. Describes the "what" of the system to be produced and not "how." In this
phase, a large document called document
(a) SDD (b) SDS
(c) SRS (d) None of These
13. in this area process business or technical data in a way that
facilitates business operations or management/technical decision making.
(a) Embedded (b) Application
(c) System Software (d) Product -Line
14. SRS is when every stated requirement has only one
interpretation.
(a) Complete (b) Traceable
(c) Unambiguous (d) Consistent
15. These usually contain mockups, wireframes, and even production-quality UI
prototypes.
(a) MRD (b) FRD
(c) UIRD (d) PRD
16. Identifies Scope of the project using use-case model allowing managers to
estimate costs and time required.
(a) Elaboration (b) Construction
(c) Inception (d) Transition
17. It always happens that a customer defines a set of general objectives for
software but does not identify detailed input, processing, or output
requirements.
(a) Prototyping (b) Evoluntionary
(c) Spiral (d) Concurrent
18. The customer indicates that changes in requirements must be made, the
modeling activity moves from the .
(a) inactive state (b) under development state
(c)awaiting changes state (d) Under review
19. The waterfall model has last phase as
(a) Requirement and Analysis (b) Implementation and Testing
(c) Operation and Maintenance (d) Software Design
20. is a graphical notation used to construct and visualize object oriented systems
(a) Activity Diagram (b) Class Diagram
(c) Sequence Diagram (d) Use Case Diagram
21. Describes the "what" of the system to be produced and not "how." In this
phase, a large document called document
a. SDD (b) SDS
c. SRS (d) None of These
22. The quick design focuses on the representation of those aspects of the
software that will be visible to the customer
a. Prototyping Model (b) Iterative Model
c. Agile Model (d) Incremental Model
You might also like
- David Lay Linear Algebra 4th Edition Chapter 9Document61 pagesDavid Lay Linear Algebra 4th Edition Chapter 9geko1100% (2)
- Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument3 pagesMultiple Choice QuestionsVanessa Manaoat100% (2)
- ML Training by Custom Yolo v5Document56 pagesML Training by Custom Yolo v5Jone EdenNo ratings yet
- Oose MCQ'SDocument15 pagesOose MCQ'SGuruKPO92% (12)
- Cerinte Negrila NetromDocument1 pageCerinte Negrila NetromToma AdiNo ratings yet
- Bca 602 Software EngineeringDocument19 pagesBca 602 Software EngineeringPatrick Chakanza100% (1)
- MCQ Collection SOFTWARE ENGINEERINGDocument339 pagesMCQ Collection SOFTWARE ENGINEERINGAnurag Yadav100% (1)
- SE Multiple Questions (2019)Document6 pagesSE Multiple Questions (2019)Bomma DineshNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering-Question BankDocument9 pagesSoftware Engineering-Question BankGouthami JukantiNo ratings yet
- Se QuizDocument30 pagesSe QuizSATHYABAMA MADHANKUMARNo ratings yet
- A) B) C) D)Document2 pagesA) B) C) D)Prdella LtdNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document12 pagesUnit 1Deepika SenthilkumarNo ratings yet
- Se Mid1 Online BitsDocument19 pagesSe Mid1 Online Bitsashokanagarani metlapalliNo ratings yet
- Bca 602 Software EngineeringDocument19 pagesBca 602 Software EngineeringMithilesh Vaghela100% (1)
- MCQ Unit123 Software EnggDocument10 pagesMCQ Unit123 Software Engggaganverma141103No ratings yet
- Oomp Unit 4 McqsDocument52 pagesOomp Unit 4 Mcqstest classNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering MCQ Practice QuestionDocument25 pagesSoftware Engineering MCQ Practice QuestionPratik BoseNo ratings yet
- All MCQDocument9 pagesAll MCQaballaibraheemNo ratings yet
- ITSKILL Dcet 2023 MCQDocument4 pagesITSKILL Dcet 2023 MCQHaris C ANo ratings yet
- DCS 214Document8 pagesDCS 214abhaybaranwalNo ratings yet
- This Set of Software Engineering Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument25 pagesThis Set of Software Engineering Multiple Choice QuestionsMehra saabNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions: Ga) Set - of Computer ProgramsDocument597 pagesPractice Questions: Ga) Set - of Computer ProgramsPrashant PoteNo ratings yet
- QB Software TestingDocument28 pagesQB Software Testingahmedalaasobhy2003No ratings yet
- Design and Software ProcessDocument4 pagesDesign and Software ProcesskathiravanNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering MCQDocument63 pagesSoftware Engineering MCQPratyushNo ratings yet
- ISAD REVIEWERDocument3 pagesISAD REVIEWERTricia Angel P. BantigueNo ratings yet
- Manual McqsDocument31 pagesManual McqsDr. KarthickeyanNo ratings yet
- Question Paper BTCS-504 SEPMDocument3 pagesQuestion Paper BTCS-504 SEPMDr-Surendra Kumar ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Compiled SE - MCQDocument12 pagesCompiled SE - MCQv.p.patelq12No ratings yet
- Se MCQDocument66 pagesSe MCQzackNo ratings yet
- Sample Questions RevisionDocument3 pagesSample Questions Revisionalmuhtarif.egyptian.yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Information Technology 1Document4 pagesInformation Technology 1Tarun BhardwajNo ratings yet
- System Analysis and DesignDocument11 pagesSystem Analysis and DesignGuruKPO100% (1)
- SE Objective Q Bank U - I & IIDocument13 pagesSE Objective Q Bank U - I & IIpeddaboina yamuna ramNo ratings yet
- Software EngineeringDocument13 pagesSoftware EngineeringAyushNo ratings yet
- Ooad ObjectiveDocument8 pagesOoad ObjectivelakshmiatsNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: C) Software Is Set of Programs, Documentation & Configuration of DataDocument93 pagesUnit 1: C) Software Is Set of Programs, Documentation & Configuration of Datajeffry patelNo ratings yet
- SE SAMPLE MCQ AllDocument30 pagesSE SAMPLE MCQ Allquyen100% (1)
- Summary MCQ ADDocument17 pagesSummary MCQ ADKasun JayaminaNo ratings yet
- MCQ Se&pm 2019-2020 Q & ADocument78 pagesMCQ Se&pm 2019-2020 Q & ASudhisha ZareNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering SYIT SEM-IVDocument7 pagesSoftware Engineering SYIT SEM-IVRohan GhadgeNo ratings yet
- SEPM MCQ - PriyadarshaniDocument20 pagesSEPM MCQ - PriyadarshaniApoorva RodeNo ratings yet
- Project ManagementDocument13 pagesProject ManagementTushar TaleNo ratings yet
- SEPM MCQ - SBJainDocument9 pagesSEPM MCQ - SBJainApoorva RodeNo ratings yet
- BCA 3rd Semester MCQ Question With AnswerDocument4 pagesBCA 3rd Semester MCQ Question With AnswerAakash ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Se MCQ Unit 1Document7 pagesSe MCQ Unit 1MANISH SHARMANo ratings yet
- MCQADocument14 pagesMCQAvenniraselviNo ratings yet
- 15se203-Ct2 Part A Set 1Document2 pages15se203-Ct2 Part A Set 1Deeban Chakravarthy VasudevanNo ratings yet
- C) Radial, Angular: A) WINWIN Spiral ModelDocument13 pagesC) Radial, Angular: A) WINWIN Spiral Modelgovind swamyNo ratings yet
- MCQ For Second YearDocument22 pagesMCQ For Second YearVaishNo ratings yet
- MCQ Practice Software Engineer 1Document6 pagesMCQ Practice Software Engineer 1Nakul BharNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitledCherivirala NikhilNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument4 pagesMCQBodhi ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- MAD MCQs2Document12 pagesMAD MCQs2QADEER AHMADNo ratings yet
- IT Officer Questions For Professional Knowledge SectionDocument5 pagesIT Officer Questions For Professional Knowledge SectionSonali ShreeNo ratings yet
- Ece Os Mid-Ii BitsDocument9 pagesEce Os Mid-Ii BitsVenkata Ramana NaiduNo ratings yet
- It McqsDocument22 pagesIt McqsFlow RiyaNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Software EngineeringDocument77 pagesFundamental of Software EngineeringWaqar HassanNo ratings yet
- Quiz ZZZZDocument40 pagesQuiz ZZZZRana Abdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Se Mid Question PaperDocument3 pagesSe Mid Question Papervarsha reddyNo ratings yet
- Typical Q&A - SOftware EngineeringDocument81 pagesTypical Q&A - SOftware EngineeringJafar Khan87% (38)
- Java / J2EE Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedFrom EverandJava / J2EE Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence: Presented By: Er. Shree Ram KhaituDocument19 pagesArtificial Intelligence: Presented By: Er. Shree Ram Khaituganesh dcNo ratings yet
- Implementing Pointnet For Point Cloud Segmentation in The Heritage ContextDocument18 pagesImplementing Pointnet For Point Cloud Segmentation in The Heritage ContextSUBHADHA BATTINA 2270166No ratings yet
- DevSecOps Caretcloud BrochureDocument9 pagesDevSecOps Caretcloud BrochurePhani MathangiNo ratings yet
- Industrial Engineer in New York City Resume Rohit ChatterjiDocument1 pageIndustrial Engineer in New York City Resume Rohit ChatterjiRohitChatterji2No ratings yet
- SMED JournalDocument3 pagesSMED JournalRizki Nurul Fathia100% (1)
- Neural Networks at Your FingertipsDocument4 pagesNeural Networks at Your FingertipsFelix Alfredo Vilchez TupayachiNo ratings yet
- Homework 1 - System TheoryDocument10 pagesHomework 1 - System TheoryAndrei MorosanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: System ModelingDocument55 pagesChapter 5: System Modelingnabaraj negiNo ratings yet
- 1 20302 D A PPT 00 Introduction To Instrumentation Process Control 38s (Lecture Seule)Document19 pages1 20302 D A PPT 00 Introduction To Instrumentation Process Control 38s (Lecture Seule)Morgan SidesoNo ratings yet
- FmeaDocument2 pagesFmeaPradeep RNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Lect. 4 PIDDocument65 pagesControl Systems Lect. 4 PIDhmaymadNo ratings yet
- Oose JugarDocument107 pagesOose JugarAdnan AadiNo ratings yet
- W5 - Model DevelopmentDocument39 pagesW5 - Model DevelopmentIstna Nisa KhasanahNo ratings yet
- Virtual Spring-Based 3D Multi-Agent Group CoordinationDocument8 pagesVirtual Spring-Based 3D Multi-Agent Group CoordinationMwakidNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment #1 - Network Diagram ExerciseDocument8 pagesIndividual Assignment #1 - Network Diagram ExerciseveenajkumarNo ratings yet
- Engg 10Document2 pagesEngg 10Rafi AzamNo ratings yet
- 1st SemDocument2 pages1st Semaarzu qadriNo ratings yet
- Lesson I: Overview of Six Sigma and Organizational GoalsDocument536 pagesLesson I: Overview of Six Sigma and Organizational GoalsShankar Ashok GawareNo ratings yet
- Unit 34 - System Analysis & Design Reworded 2021-MergedDocument65 pagesUnit 34 - System Analysis & Design Reworded 2021-MergedROSHEN ANTHONYNo ratings yet
- Mechanical EngineerDocument2 pagesMechanical Engineerapi-76934684No ratings yet
- Types of Learning Approach: Supervised and Semi-Supervised LearningDocument2 pagesTypes of Learning Approach: Supervised and Semi-Supervised LearningVõ Hoàng ChươngNo ratings yet
- Auto MLDocument15 pagesAuto MLshreyans JainNo ratings yet
- SE171154 SWE201c PE 01-1Document5 pagesSE171154 SWE201c PE 01-1Doan Hoang Dung QP2775No ratings yet
- Deep Learning in Natural Language Processing A State-of-the-Art SurveyDocument6 pagesDeep Learning in Natural Language Processing A State-of-the-Art SurveySmriti Medhi MoralNo ratings yet
- What Are Centralized, Decentralized, and Distributed SystemsDocument7 pagesWhat Are Centralized, Decentralized, and Distributed SystemsClaire MarshallNo ratings yet
- CIM Wheel and ModelDocument43 pagesCIM Wheel and ModelNathanael Aklilu Ejersa100% (2)