Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1and5.microscopes, Specializedstem Cells, Homeostasis - Answer Key
1and5.microscopes, Specializedstem Cells, Homeostasis - Answer Key
Uploaded by
MCarmen López CastroOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1and5.microscopes, Specializedstem Cells, Homeostasis - Answer Key
1and5.microscopes, Specializedstem Cells, Homeostasis - Answer Key
Uploaded by
MCarmen López CastroCopyright:
Available Formats
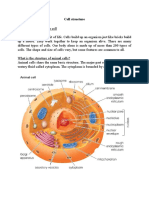
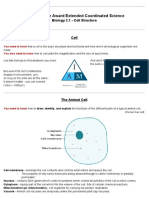
MICROSCOPES
1. What is the size of an eukaryotic cell?
Cells vary in shape from about 5 µm to 120 µm.
2. Compare the light microscope and the electron microscope in terms of their
magnifying power.
Light microscopes can magnify objects about 1,500 times (1,500 x), while electron
microscopes can magnify objects by 1 million times (1,000,000 x).
3. Based on their magnifying power how tall would you look if a life-sized image of
you was observed through a light microscope? And an electron microscope?
To work this out, you must multiply your height by the magnification, which is 1500
for a light microscope and 106 for an electron microscope. For example, if your height
is 1.65m, with the light microscope it will be: 1.65 m x 1,500 = 2,475 m and with the
electron microscope: 1.65 m x 106 = 1,650,000 m (1,650 km)
4. The real diameter of a cell is 0.03 mm. When represented in a picture its
diameter is 90 mm. What degree of magnification must have been used to obtain
the image in the picture?
The image in the picture is 90 mm in diameter. To calculate the magnification, you
should perform the following operation: 90 / 0.03 = magnification of 3,000 x
SPECIALIZED CELLS
5. What are the characteristics of a specialized cell?
- It performs a specific task
- It has a characteristic appearance
- Its cytoplasm is modified. These modifications are related to the specific activities
of the various organelles within the cell.
6. How are stem cells different from specialized cells?
Most specialized cells lose their ability to reproduce. Stem cells or unspecialized cells
handle this task when the need arises.
7. Describe the two basic types of stem cells.
Embryonic stem cells: Can differentiate into any cell type in the organism
Adult stem cells: Are more limited and can only differentiate into certain cell types in
order to repair or regenerate certain tissues.
HOMEOSTASIS
8. Define homeostasis
Homeostasis a property by which our body reacts to environmental changes and is
constantly working to maintain internal conditions within the ranges that best suits
life.
9. Watch the video “A cell´s external environment” and tell four mechanisms to
maintain homeostasis in our body.
Thermoregulation – negative feedback, shiver, sweat
Contractions – positive feedback
Fever positive to get your body work better
Excretory system – negative feedback
Immune system – negative feedback
Respiration – Negative feedback .
You might also like
- Bank Management and Financial Services PDFDocument750 pagesBank Management and Financial Services PDFMCarmen López Castro33% (3)
- Student Exploration: Cell Types: Vocabulary: ATP, Bacteria, Carbon Dioxide (CODocument5 pagesStudent Exploration: Cell Types: Vocabulary: ATP, Bacteria, Carbon Dioxide (COPablo44% (16)
- Selection and Speciation POGILDocument9 pagesSelection and Speciation POGILRyan Liou20% (5)
- The Characteristics of Living ThingsDocument11 pagesThe Characteristics of Living ThingsArthanayaka NandikaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1-1 Introduction To CellsDocument50 pagesTopic 1-1 Introduction To CellsjeffNo ratings yet
- 1.1 An Introduction To CellsDocument15 pages1.1 An Introduction To CellsMukhammadaminkhon AnvarkhonovNo ratings yet
- Microscopes - Answer KeyDocument1 pageMicroscopes - Answer KeyMCarmen López CastroNo ratings yet
- Cell TheoryDocument22 pagesCell TheoryRahma TahaNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 1Document31 pagesCell Biology 1candyli3788No ratings yet
- Outline The 3 Statements of Cell Theory: However, The Fibres Are Far From Typical, As They Are Much Larger ThanDocument32 pagesOutline The 3 Statements of Cell Theory: However, The Fibres Are Far From Typical, As They Are Much Larger Thanmamo maNo ratings yet
- GCSE CCEA Biology Revison NotesDocument99 pagesGCSE CCEA Biology Revison NotesdanielmcintyreNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument7 pages1.1 Cell Structure and Functionkingsleymakuvaza167No ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Cell Types: Vocabulary: ATP, Bacteria, Carbon Dioxide (CODocument11 pagesStudent Exploration: Cell Types: Vocabulary: ATP, Bacteria, Carbon Dioxide (CODhruti AsharNo ratings yet
- Biology CsDocument84 pagesBiology CsYasmin YehiaNo ratings yet
- sw8 chp04Document23 pagessw8 chp04api-115560904No ratings yet
- Topic 1 - CellsDocument34 pagesTopic 1 - CellsAngela LinNo ratings yet
- Bio Module 12Document45 pagesBio Module 12afeefaNo ratings yet
- Cell Types SeDocument16 pagesCell Types SeKendallNo ratings yet
- Grade 8-CellTypesSE - Adam NasrDocument10 pagesGrade 8-CellTypesSE - Adam Nasradam.nasrNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function - Magnification CalculationDocument17 pagesCell Structure and Function - Magnification CalculationHamza KhanNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument37 pagesCell BiologySapreen KaurNo ratings yet
- Bio For Olevel PDFDocument422 pagesBio For Olevel PDFNalweyiso JoyceNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument19 pagesBiologyAnna ŁajczakNo ratings yet
- Biology BookDocument397 pagesBiology Bookmesh100% (1)
- Lecture 1 - Tissues, Organs, Organ Systems, Organism and Size of SpecimenDocument22 pagesLecture 1 - Tissues, Organs, Organ Systems, Organism and Size of SpecimenAilie Sofyiana SerasaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cells and How We Study ThemDocument56 pagesIntroduction To Cells and How We Study ThemRufaro SadindiNo ratings yet
- Bacte Lab - Laboratory Act 1Document4 pagesBacte Lab - Laboratory Act 1Eloisa LacanilaoNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology NotesDocument547 pagesO Level Biology NotesSsonko Edrine100% (1)
- CellsDocument7 pagesCellsJeremiah CromartieNo ratings yet
- Biology 10-12 Revised Edition 2Document182 pagesBiology 10-12 Revised Edition 2kalubabuleloNo ratings yet
- Cells and Organisation L4 Specialised Cells PowerPointDocument27 pagesCells and Organisation L4 Specialised Cells PowerPointjurymagdi430No ratings yet
- B1 Cell Bio NotesDocument12 pagesB1 Cell Bio Notesmohammedaliaziz15No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Cell BiologyDocument7 pagesUnit 3 Cell BiologyQaran PrintingNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 CellsDocument124 pagesTopic 2 Cellstae gukNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure ASDocument40 pagesCell Structure ASYasmine HadiastrianiNo ratings yet
- Microscope UseDocument7 pagesMicroscope UsebegNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Cells - 241023Document70 pagesUnit 1 Cells - 241023DAN DNANo ratings yet
- B2 CellsDocument47 pagesB2 CellsДилбар ОспановаNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function NotesDocument8 pagesCell Structure and Function NotesShiloh FrederickNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument22 pagesCell BiologyFelionesNo ratings yet
- Unit C-Chapter 8 PowerpointDocument66 pagesUnit C-Chapter 8 Powerpointm_frajman100% (1)
- 7B1 Cells - L2 Specialised CellsDocument24 pages7B1 Cells - L2 Specialised Cells30bryanwongNo ratings yet
- Charlie Muller CellTypesSEDocument10 pagesCharlie Muller CellTypesSECharles MullerNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Topic 1 Past Paper QuestionsDocument9 pagesBIOLOGY Topic 1 Past Paper QuestionsLoraine NNo ratings yet
- Biology 10-12 Revised Edition 2Document138 pagesBiology 10-12 Revised Edition 2Mwami JayNo ratings yet
- Animal & Plant Cells &&&&&&&&&&&& MyDocument18 pagesAnimal & Plant Cells &&&&&&&&&&&& MyMichelle MusarurwaNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument86 pagesCellsspamiplviewNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Iology Part One 2023-2024Document15 pagesCH 3 Iology Part One 2023-2024D.3s YTNo ratings yet
- GCSE Edexcel Biology Self-Studying TextbookDocument89 pagesGCSE Edexcel Biology Self-Studying TextbookDhuhaa YusufNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY AL - Cell StructureDocument44 pagesBIOLOGY AL - Cell StructureSmile4 UNo ratings yet
- 1 1 Cell TheoryDocument38 pages1 1 Cell TheorySaiam ShahNo ratings yet
- Presentation Cell StructDocument8 pagesPresentation Cell StructWAN MUHAMMAD IRFAN WAN MOHD ZOHARNo ratings yet
- 1 How We Study Cells 2020Document63 pages1 How We Study Cells 2020andiswa21macingwaneNo ratings yet
- M 25 - The CELL - Introduction and Cell Types.Document67 pagesM 25 - The CELL - Introduction and Cell Types.brenda.mboghoNo ratings yet
- Exp 1 Making An Invisible World VisibleDocument13 pagesExp 1 Making An Invisible World VisibleAina HaravataNo ratings yet
- Biology Lab PracticalomgomgDocument215 pagesBiology Lab PracticalomgomgdNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science: Biology 2.1 - Cell StructureDocument4 pagesIGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science: Biology 2.1 - Cell StructureIndah ParamithaNo ratings yet
- General Summary of MicroscopeDocument7 pagesGeneral Summary of Microscopeloycoy008No ratings yet
- Cells and Organisation L4 Specialised Cells PowerPointDocument24 pagesCells and Organisation L4 Specialised Cells PowerPointJhyvril GulacNo ratings yet
- Science NotesDocument15 pagesScience Noteslaramatraji45No ratings yet
- Unit 4Document14 pagesUnit 4Yitbarek TesfayeNo ratings yet
- W09 ApplicationActivityDocument4 pagesW09 ApplicationActivityMCarmen López CastroNo ratings yet
- ArticlesDocument2 pagesArticlesMCarmen López CastroNo ratings yet
- W01 Introduction AssignmentDocument2 pagesW01 Introduction AssignmentMCarmen López CastroNo ratings yet
- Microscopes - Answer KeyDocument1 pageMicroscopes - Answer KeyMCarmen López CastroNo ratings yet
- Personal Pronouns - Object PronounsDocument1 pagePersonal Pronouns - Object PronounsMCarmen López CastroNo ratings yet
- 4.tissue Table - Answer Key Con DibujosDocument2 pages4.tissue Table - Answer Key Con DibujosMCarmen López CastroNo ratings yet
- TR ADMIN 2020 - Eligibility Criteria GridDocument1 pageTR ADMIN 2020 - Eligibility Criteria GridMCarmen López CastroNo ratings yet
- Inomics Handbook 2021Document58 pagesInomics Handbook 2021MCarmen López CastroNo ratings yet
- Cambridge English Preliminary WORKBOOK With Answers Tema 1 4 PDFDocument23 pagesCambridge English Preliminary WORKBOOK With Answers Tema 1 4 PDFMCarmen López CastroNo ratings yet
- A Pie 5,2 Millas, 1 H 44 Min de Nottingham General Cemetery A The Hemlock StoneDocument1 pageA Pie 5,2 Millas, 1 H 44 Min de Nottingham General Cemetery A The Hemlock StoneMCarmen López CastroNo ratings yet
- Psychology and Economics, Evidence From The Field, Della Vigna, PG 315-372Document58 pagesPsychology and Economics, Evidence From The Field, Della Vigna, PG 315-372MCarmen López CastroNo ratings yet
- Reading Chart New TestamentDocument1 pageReading Chart New TestamentMCarmen López CastroNo ratings yet
- NuevoDocumento 1Document1 pageNuevoDocumento 1MCarmen López CastroNo ratings yet
- Early Development and Axis Formation in Amphibians and FishDocument3 pagesEarly Development and Axis Formation in Amphibians and FishJohnkevin Noche100% (1)
- 2023 - 1 - Mikrobiologi Umum - Pendahuluan - Taksonomi - Identifikasi - ESR - 13feb PDFDocument106 pages2023 - 1 - Mikrobiologi Umum - Pendahuluan - Taksonomi - Identifikasi - ESR - 13feb PDFRisma Karimah PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Human Biology ATAR Y11 Sample Course Outline WACE 201516 - PDFDocument4 pagesHuman Biology ATAR Y11 Sample Course Outline WACE 201516 - PDFpartyNo ratings yet
- Prachi S Patel Sex/Age: Female / 25 Years: Real Time PCRDocument1 pagePrachi S Patel Sex/Age: Female / 25 Years: Real Time PCRprachi patelNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet in Biology 1: Quarter 1 Week 1Document10 pagesLearning Activity Sheet in Biology 1: Quarter 1 Week 1Ryan NegadNo ratings yet
- SystematicsDocument77 pagesSystematicsVinz MatagayNo ratings yet
- SBL100 Labs - Final Marks, 8-Nov-23 - 3Document14 pagesSBL100 Labs - Final Marks, 8-Nov-23 - 3AnuNo ratings yet
- The Indonesian Archipelago: An Ancient Genetic Highway Linking Asia and The PacificDocument9 pagesThe Indonesian Archipelago: An Ancient Genetic Highway Linking Asia and The PacificMIF VerseNo ratings yet
- 5 Virtual Mitosis and Meiosis Lab (CNY Homework)Document5 pages5 Virtual Mitosis and Meiosis Lab (CNY Homework)yswang0125No ratings yet
- Chapter 21 Reading GuideDocument3 pagesChapter 21 Reading GuideAnonymous RVfQZkvjNo ratings yet
- Response To Tony JosephDocument25 pagesResponse To Tony JosephSudeesh M SNo ratings yet
- Venn Diagram (MP)Document1 pageVenn Diagram (MP)veralynn100% (1)
- MODULE 1 - BioDocument4 pagesMODULE 1 - BioSophie BaromanNo ratings yet
- Written-Report Group#2Document4 pagesWritten-Report Group#2Kyla CabullosNo ratings yet
- JHG 201236Document3 pagesJHG 201236Iva TintiloNo ratings yet
- BIO201L Lab 5 TissuesDocument12 pagesBIO201L Lab 5 Tissuesmyra Thiong'oNo ratings yet
- Previous Board Exam QuestionsDocument9 pagesPrevious Board Exam QuestionsElgie AumanNo ratings yet
- Biology: Genetics & Inheritance III: Genetic Basis For Variation IDocument27 pagesBiology: Genetics & Inheritance III: Genetic Basis For Variation ITimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Gene Mapping in Bacteria and Bacteriophages: Peter J. RussellDocument48 pagesGene Mapping in Bacteria and Bacteriophages: Peter J. Russellhellfire90110% (1)
- 1 s2.0 S0014299903027250 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S0014299903027250 MainZulfiani SyachbaniahNo ratings yet
- Conceptions of Change in The Built EnvironmentDocument14 pagesConceptions of Change in The Built EnvironmentTuğman BüberciNo ratings yet
- Las 1 Q4Document10 pagesLas 1 Q4triplesevenNo ratings yet
- Case Study 18Document38 pagesCase Study 18Akshar JainNo ratings yet
- DNA Modeling Objectives:: ProcedureDocument5 pagesDNA Modeling Objectives:: ProcedureAyesha MhallawiNo ratings yet
- Nature & NurtureDocument2 pagesNature & NurtureSamantha WoiNo ratings yet
- A Polynomial Model For Concrete Compressive Strength Prediction UsingDocument6 pagesA Polynomial Model For Concrete Compressive Strength Prediction UsinglintianananNo ratings yet
- BioChem Formal ReportDocument5 pagesBioChem Formal Reportayracruz_No ratings yet
- Individual Development & IdentityDocument13 pagesIndividual Development & IdentityTHEA LAURENE SUBANo ratings yet
- Voluntary Ethanol Consumption in 22 Inbred Mouse StrainsDocument18 pagesVoluntary Ethanol Consumption in 22 Inbred Mouse StrainsJef_8No ratings yet