Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3135-Making Piston Rings
3135-Making Piston Rings
Uploaded by
Fajar kurniaThe document discusses four methods for making piston rings for engines, including machining rings of uniform thickness, making eccentric rings of varying thickness, using a strut to compress a ring into a circular shape, and hammering rings to fit a matrix for uniform outward thrust when compressed. Proper fitting of rings is important for efficiency, as gaps or reduced outward thrust in certain areas can cause blow-by and increased friction. Lapping rings can improve the fit but should be done carefully to avoid stretching the rings.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Manitowoc 4600 S4 Parts Manual PDFDocument108 pagesManitowoc 4600 S4 Parts Manual PDFnamduong36850% (2)
- Manual Pulidora RaytechDocument37 pagesManual Pulidora RaytechWarner BenavidesNo ratings yet
- Vitotronic Data Points: V200KW2/KW1Document11 pagesVitotronic Data Points: V200KW2/KW1Cyril PerezNo ratings yet
- Quorn: Tool and D Cutter GrinderDocument5 pagesQuorn: Tool and D Cutter GrinderDan HendersonNo ratings yet
- More Tricks With The: "Quorn"Document5 pagesMore Tricks With The: "Quorn"Dan HendersonNo ratings yet
- Mini Tube BenderDocument4 pagesMini Tube BenderMartin OngNo ratings yet
- Quorn: Tool and Cutter GrinderDocument5 pagesQuorn: Tool and Cutter GrinderDan HendersonNo ratings yet
- Mini Dobrador de Tubos DIYDocument4 pagesMini Dobrador de Tubos DIYw4rh4ck3r-scribdNo ratings yet
- 2965-Lapping Tapers & Seatings #7Document1 page2965-Lapping Tapers & Seatings #7syllavethyjimNo ratings yet
- Precision PressDocument4 pagesPrecision PressFrenchwolf4200% (1)
- Model Elbow EngineDocument5 pagesModel Elbow EngineJim100% (3)
- Quorn: Tool and Cutter GrinderDocument3 pagesQuorn: Tool and Cutter GrinderDan HendersonNo ratings yet
- Lathe-Milling AttachmentDocument4 pagesLathe-Milling AttachmentFrenchwolf420No ratings yet
- Quorn: Tool and Cutter GrinderDocument2 pagesQuorn: Tool and Cutter GrinderDan HendersonNo ratings yet
- Quorn: Tool and Cutter GrinderDocument4 pagesQuorn: Tool and Cutter GrinderDan HendersonNo ratings yet
- V Po-To 3Document60 pagesV Po-To 3Pierre799es100% (1)
- 2873-Cotters & Wedges PDFDocument1 page2873-Cotters & Wedges PDFsyllavethyjimNo ratings yet
- Simple Boring BarDocument3 pagesSimple Boring BarMike Nichlos100% (1)
- 2877-Roller Chain & Sprockets PDFDocument1 page2877-Roller Chain & Sprockets PDFsyllavethyjimNo ratings yet
- Quorn: Tool and Cutter GrinderDocument4 pagesQuorn: Tool and Cutter GrinderDan HendersonNo ratings yet
- 2886-Stud Fitting & Removal PDFDocument1 page2886-Stud Fitting & Removal PDFsyllavethyjimNo ratings yet
- Motor A Vapor (Vapeur - Vertical Steam Engine)Document16 pagesMotor A Vapor (Vapeur - Vertical Steam Engine)migss1074No ratings yet
- Quorn: Tool and Cutter GrinderDocument4 pagesQuorn: Tool and Cutter GrinderDan HendersonNo ratings yet
- Types of Nuts and BoltsDocument19 pagesTypes of Nuts and BoltsSri Ram VikasNo ratings yet
- 2927-Connecting Rod AlignmentDocument1 page2927-Connecting Rod AlignmentCr250r100% (1)
- Plywood ScooterDocument7 pagesPlywood ScooterJim100% (4)
- 2847-Keys & Driving PinsDocument1 page2847-Keys & Driving PinssyllavethyjimNo ratings yet
- A Fine Vertical Steam Engine - Hobbies - Apr 1931Document8 pagesA Fine Vertical Steam Engine - Hobbies - Apr 1931dsdffgfgfssfdgsfgdNo ratings yet
- L Li I I L I: Rimless Cartridge ExtractorsDocument12 pagesL Li I I L I: Rimless Cartridge Extractorss rNo ratings yet
- Metalwork and Machining Hints and Tips for Home Machinists: 101 Plans and DrawingsFrom EverandMetalwork and Machining Hints and Tips for Home Machinists: 101 Plans and DrawingsNo ratings yet
- Alternator Frame: Turbine DiameterDocument4 pagesAlternator Frame: Turbine DiameterDennyHalim.com50% (2)
- .Au Agnet Make Piston RingsDocument6 pages.Au Agnet Make Piston Ringsashishgoel102No ratings yet
- 9 BoltPosiConeRepair30Nov04Document5 pages9 BoltPosiConeRepair30Nov04stefan svenssonNo ratings yet
- Lathe Modelling2Document2 pagesLathe Modelling2Marian DimaNo ratings yet
- Universal Tool and Cutter Grinder Manual Low ResDocument16 pagesUniversal Tool and Cutter Grinder Manual Low ResDale Wade100% (1)
- ReamersDocument1 pageReamersvikash kumarNo ratings yet
- RC Airplane Engine PlansDocument8 pagesRC Airplane Engine PlansLacramioara Veronica Malael100% (1)
- CN Maintenance Practices IIDocument10 pagesCN Maintenance Practices IIavijayakumar_1964No ratings yet
- Improvements To An X2 Mill: Neil Wyatt Upgrades His Milling MachineDocument7 pagesImprovements To An X2 Mill: Neil Wyatt Upgrades His Milling MachineYoel PatiñoNo ratings yet
- 149-Workshop Hints & Tips PDFDocument1 page149-Workshop Hints & Tips PDFsyllavethyjimNo ratings yet
- Design of Nut & BoltDocument4 pagesDesign of Nut & BoltJyoti Kale0% (1)
- Small Workshop CompressorDocument2 pagesSmall Workshop Compressorw4rh4ck3r-scribdNo ratings yet
- Worm MeshDocument5 pagesWorm MeshBabalola SundayNo ratings yet
- Cardboard ClockDocument5 pagesCardboard ClockleongfoowingNo ratings yet
- 2950-Patterns With Fins & FlangesDocument1 page2950-Patterns With Fins & FlangesSandra Barnett CrossanNo ratings yet
- 2845-Bending & FormingDocument1 page2845-Bending & FormingJim MarnochNo ratings yet
- How To Make A Tool Post GrinderDocument5 pagesHow To Make A Tool Post Grinderozland9No ratings yet
- Resharpening & Inspection Cutting Tools PDFDocument10 pagesResharpening & Inspection Cutting Tools PDFHeineken Ya PraneetpongrungNo ratings yet
- Steam EngineDocument4 pagesSteam EngineimgopalNo ratings yet
- Building: LatheDocument60 pagesBuilding: LathePierre799es86% (7)
- 2858-How To Use Scrapers PDFDocument1 page2858-How To Use Scrapers PDFsyllavethyjimNo ratings yet
- Foot-Powered Scroll SawDocument8 pagesFoot-Powered Scroll SawJan Steinman100% (1)
- (Diy) - Metalworking - Model Engineer Aug53' - Surface Grinding & Milling MachineDocument6 pages(Diy) - Metalworking - Model Engineer Aug53' - Surface Grinding & Milling MachineFernanda Duarte100% (4)
- Cylinder TechnologyDocument4 pagesCylinder TechnologyHady SundayanaNo ratings yet
- Air Cooled Hot Air EngineDocument6 pagesAir Cooled Hot Air EngineJim50% (2)
- Watch Repairing, Cleaning and Adjusting - A Practical HandbookFrom EverandWatch Repairing, Cleaning and Adjusting - A Practical HandbookNo ratings yet
- The Art of Watch Repair - Including Descriptions of the Watch Movement, Parts of the Watch, and Common Stoppages of Wrist WatchesFrom EverandThe Art of Watch Repair - Including Descriptions of the Watch Movement, Parts of the Watch, and Common Stoppages of Wrist WatchesNo ratings yet
- Week 12Document31 pagesWeek 12Fajar kurniaNo ratings yet
- Chris&Kathleen - Bending Test - 3Document16 pagesChris&Kathleen - Bending Test - 3Fajar kurniaNo ratings yet
- Materials - Properties - 2009 - Beending Test 5aDocument62 pagesMaterials - Properties - 2009 - Beending Test 5aFajar kurniaNo ratings yet
- Formpendaftaran 6Document1 pageFormpendaftaran 6Fajar kurniaNo ratings yet
- Attachment 4Document12 pagesAttachment 4Fajar kurniaNo ratings yet
- Attachment 3Document2 pagesAttachment 3Fajar kurniaNo ratings yet
- Attachment 2Document16 pagesAttachment 2Fajar kurniaNo ratings yet
- D3D-UV PDFDocument4 pagesD3D-UV PDFFajar kurniaNo ratings yet
- WhatsApp Image 2022-07-05 at 14.20.51Document1 pageWhatsApp Image 2022-07-05 at 14.20.51Fajar kurniaNo ratings yet
- Test & Drain Valve Model 1000Document2 pagesTest & Drain Valve Model 1000saifahmed7No ratings yet
- Mahlkoenig X54 Allround Home Grinder Original Instruction Manual ENDocument60 pagesMahlkoenig X54 Allround Home Grinder Original Instruction Manual ENcarlos_alfaro_herreraNo ratings yet
- QE140 Robotrac Screener ManualDocument204 pagesQE140 Robotrac Screener Manualalberto pachonNo ratings yet
- Interpretations ASME B31.3Document338 pagesInterpretations ASME B31.3Claudenir AlvesNo ratings yet
- Saffty Inductions (Igd Hyundai)Document4 pagesSaffty Inductions (Igd Hyundai)bharathostNo ratings yet
- Continuous Cleat Coping Product DetailDocument2 pagesContinuous Cleat Coping Product DetailIrinel CopacinschiNo ratings yet
- Flowserve HPXDocument8 pagesFlowserve HPXcarlos mercadoNo ratings yet
- ISO-10664Document10 pagesISO-10664Daniel Quijada LucarioNo ratings yet
- Wet CoolingDocument1 pageWet CoolingsaeedalipourNo ratings yet
- 500 Litri Dos Sys Item2Document1 page500 Litri Dos Sys Item2Szikzai Alexandru RobertNo ratings yet
- EVIMETALDocument1 pageEVIMETALahmedNo ratings yet
- DDC p2c3 Ug02 Ugs DR Sot 35101 03 Editing1Document40 pagesDDC p2c3 Ug02 Ugs DR Sot 35101 03 Editing1Devesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Mechanic Millwright 433A en TS3Document67 pagesIndustrial Mechanic Millwright 433A en TS3CourseTree LearningNo ratings yet
- Important Questions Bme 201 Unit1-5Document3 pagesImportant Questions Bme 201 Unit1-5Ashish MishraNo ratings yet
- Piaggio X9250Document75 pagesPiaggio X9250Toni MarasovicNo ratings yet
- Ebara 2CDXDocument13 pagesEbara 2CDXDirector Tecnico y Operaciones Baying SASNo ratings yet
- JS4BD-KB Series: Technical SpecificationsDocument12 pagesJS4BD-KB Series: Technical SpecificationsKokoNo ratings yet
- Mikrokator MDocument4 pagesMikrokator Mciber_aristosNo ratings yet
- Lesson - 09 - UG77 - UG120 - Material, Nameplate & Data ReportDocument19 pagesLesson - 09 - UG77 - UG120 - Material, Nameplate & Data Reportmohamed.eldesouky9120No ratings yet
- Steel Tubes For Structural Purposes Conforming To IS 1161 - 1998Document2 pagesSteel Tubes For Structural Purposes Conforming To IS 1161 - 1998Ayush TariyalNo ratings yet
- Potain MCT 205Document21 pagesPotain MCT 205ubeydullah coşkunNo ratings yet
- Parts Manual TB020 PD3 102Z4Document295 pagesParts Manual TB020 PD3 102Z4Nery TojilNo ratings yet
- Milling Formulas and DefinitionsDocument10 pagesMilling Formulas and DefinitionsCherish QiuNo ratings yet
- Keystone Figure 777 Electric ActuatorDocument8 pagesKeystone Figure 777 Electric Actuatorrpatelacc74No ratings yet
- 04-APRECO Pressure Reliefe Vent DS-SGV-2021-1.2Document2 pages04-APRECO Pressure Reliefe Vent DS-SGV-2021-1.2Nenad MilenkovicNo ratings yet
- PHQC 3036 - Pull Part Manual 2016 1010Document9 pagesPHQC 3036 - Pull Part Manual 2016 1010VladimirNo ratings yet
- Alignment Training (Presentation) - Apr07Document50 pagesAlignment Training (Presentation) - Apr07Mohamed Belall100% (4)
- Afec Ko204-208-215-315Document1 pageAfec Ko204-208-215-315Andrie AdhynataNo ratings yet
3135-Making Piston Rings
3135-Making Piston Rings
Uploaded by
Fajar kurnia0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageThe document discusses four methods for making piston rings for engines, including machining rings of uniform thickness, making eccentric rings of varying thickness, using a strut to compress a ring into a circular shape, and hammering rings to fit a matrix for uniform outward thrust when compressed. Proper fitting of rings is important for efficiency, as gaps or reduced outward thrust in certain areas can cause blow-by and increased friction. Lapping rings can improve the fit but should be done carefully to avoid stretching the rings.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses four methods for making piston rings for engines, including machining rings of uniform thickness, making eccentric rings of varying thickness, using a strut to compress a ring into a circular shape, and hammering rings to fit a matrix for uniform outward thrust when compressed. Proper fitting of rings is important for efficiency, as gaps or reduced outward thrust in certain areas can cause blow-by and increased friction. Lapping rings can improve the fit but should be done carefully to avoid stretching the rings.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 page3135-Making Piston Rings
3135-Making Piston Rings
Uploaded by
Fajar kurniaThe document discusses four methods for making piston rings for engines, including machining rings of uniform thickness, making eccentric rings of varying thickness, using a strut to compress a ring into a circular shape, and hammering rings to fit a matrix for uniform outward thrust when compressed. Proper fitting of rings is important for efficiency, as gaps or reduced outward thrust in certain areas can cause blow-by and increased friction. Lapping rings can improve the fit but should be done carefully to avoid stretching the rings.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
-
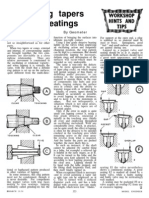
Making PISTON RINGS
T HE REare four ways of making machined on different centres. The
plain piston rings. Two of gap is cut at the point of thinnest
them are straightforward for section.
the model engineer; but with the A third way, which is theoretically
correct. was devised by Dr F. W.
two others reservations must be Lanchester. A ring of uniform section
made, though they would not is machined to fit the cylinder, and
necessarily be impossible for ex- wedged open with a small strut, A3,
perts. which is V-shape each end to touch
A piston ring should fit the cylinder at the line of average section, A4.
exactly, which means that, with the From this shape, a cam is made to
ring compressed, its periphery must operate the cross slide of the lathe.
be circular; and it should exert a Then a ring of uniform section is
uniform outward thrust to the cylinder. machined; and with the gap cut, it
For this, it must be slit at one point. compresses circular in the cylinder,
To give the required outward with uniform outward thrust.
thrust, the ring when free has a The fourth way of making rings is
considerable gap, Al, with which it is the commercial method. From the
opened ring, A3, a matrix is made,
and rings of uniform section are
specially hammered to fit it. They,
too, compress circular, with uniform
By GEOMETER outward thrust.
Faulty fitting of a small ring usually
takes the form of a reduction of
outward thrust at two places on its
periphery. They are along arcs W
not circular; it attains this shape and X, Bl. Sometimes there may be
with the small working gap, A2, tiny gaps which can be seen against
when in the cylinder. a strong light. Lapping a ring (or
Simple as the conditions are, they a brief period of use) will show up
are by no means easily ensured in these areas of reduced thrust,. which
practice. Departure from them means may occur even on an eccentric rmg,
loss of efficiency from blow-by of B2.
pressure; and in a small engine there As lapping improves the fit of
may be extra frictional losses which rings, it is recommended, with Brasso
seriously reduce mechanical efficiency. as the abrasive, but not with the rings
If a piston is machined the same on the piston. A holder can be made,
size as the cylinder, it will be circular, C, with a screw in handle and a loose
but will have no outward thrust, plate. Then they can be fitted without
and so will not be efficient. On the stretching. Their gaps should be kept
other hand, if a ring is machined to to a minimum to allow for the increase
a large diameter and a piece is cut with lapping.
out for it to be entered in the cylinder, To lap a ring in making, the set-
it will have outward thrust but will up can be as at D. The lap should
not be circular. By allowing extra be a thou or two larger than the
material on such a ring, it can be cylinder, and run in the chuck. The
machined after the piece is cut out. ring is loose in the holder, so that it
The ring can be clamped on a can expand, hut is gripped opposite
mandrel for turning the outside. its gap with shimstock, Y-Z. Stops
For boring the inside, it can be gripped for the handle-as the ring is moved NDREL
in a recess in a holder. The section to and fro in the revolving lap-are
will be uniform, but that is one way set either side of a bar on the slide.
of making a ring. Diagram E shows a split lap which
A second way is broadly on the lines can be returned to size by filing its
of the first, but the ring is made of faces and reaming its bore; while F
varying section. It is eccentric, with illustrates a typical mandrel on which
the outside and inside diameters rings are turned. ‘b RINGS
10 AUGUST 1961 169 MODEL ENGINEER
You might also like
- Manitowoc 4600 S4 Parts Manual PDFDocument108 pagesManitowoc 4600 S4 Parts Manual PDFnamduong36850% (2)
- Manual Pulidora RaytechDocument37 pagesManual Pulidora RaytechWarner BenavidesNo ratings yet
- Vitotronic Data Points: V200KW2/KW1Document11 pagesVitotronic Data Points: V200KW2/KW1Cyril PerezNo ratings yet
- Quorn: Tool and D Cutter GrinderDocument5 pagesQuorn: Tool and D Cutter GrinderDan HendersonNo ratings yet
- More Tricks With The: "Quorn"Document5 pagesMore Tricks With The: "Quorn"Dan HendersonNo ratings yet
- Mini Tube BenderDocument4 pagesMini Tube BenderMartin OngNo ratings yet
- Quorn: Tool and Cutter GrinderDocument5 pagesQuorn: Tool and Cutter GrinderDan HendersonNo ratings yet
- Mini Dobrador de Tubos DIYDocument4 pagesMini Dobrador de Tubos DIYw4rh4ck3r-scribdNo ratings yet
- 2965-Lapping Tapers & Seatings #7Document1 page2965-Lapping Tapers & Seatings #7syllavethyjimNo ratings yet
- Precision PressDocument4 pagesPrecision PressFrenchwolf4200% (1)
- Model Elbow EngineDocument5 pagesModel Elbow EngineJim100% (3)
- Quorn: Tool and Cutter GrinderDocument3 pagesQuorn: Tool and Cutter GrinderDan HendersonNo ratings yet
- Lathe-Milling AttachmentDocument4 pagesLathe-Milling AttachmentFrenchwolf420No ratings yet
- Quorn: Tool and Cutter GrinderDocument2 pagesQuorn: Tool and Cutter GrinderDan HendersonNo ratings yet
- Quorn: Tool and Cutter GrinderDocument4 pagesQuorn: Tool and Cutter GrinderDan HendersonNo ratings yet
- V Po-To 3Document60 pagesV Po-To 3Pierre799es100% (1)
- 2873-Cotters & Wedges PDFDocument1 page2873-Cotters & Wedges PDFsyllavethyjimNo ratings yet
- Simple Boring BarDocument3 pagesSimple Boring BarMike Nichlos100% (1)
- 2877-Roller Chain & Sprockets PDFDocument1 page2877-Roller Chain & Sprockets PDFsyllavethyjimNo ratings yet
- Quorn: Tool and Cutter GrinderDocument4 pagesQuorn: Tool and Cutter GrinderDan HendersonNo ratings yet
- 2886-Stud Fitting & Removal PDFDocument1 page2886-Stud Fitting & Removal PDFsyllavethyjimNo ratings yet
- Motor A Vapor (Vapeur - Vertical Steam Engine)Document16 pagesMotor A Vapor (Vapeur - Vertical Steam Engine)migss1074No ratings yet
- Quorn: Tool and Cutter GrinderDocument4 pagesQuorn: Tool and Cutter GrinderDan HendersonNo ratings yet
- Types of Nuts and BoltsDocument19 pagesTypes of Nuts and BoltsSri Ram VikasNo ratings yet
- 2927-Connecting Rod AlignmentDocument1 page2927-Connecting Rod AlignmentCr250r100% (1)
- Plywood ScooterDocument7 pagesPlywood ScooterJim100% (4)
- 2847-Keys & Driving PinsDocument1 page2847-Keys & Driving PinssyllavethyjimNo ratings yet
- A Fine Vertical Steam Engine - Hobbies - Apr 1931Document8 pagesA Fine Vertical Steam Engine - Hobbies - Apr 1931dsdffgfgfssfdgsfgdNo ratings yet
- L Li I I L I: Rimless Cartridge ExtractorsDocument12 pagesL Li I I L I: Rimless Cartridge Extractorss rNo ratings yet
- Metalwork and Machining Hints and Tips for Home Machinists: 101 Plans and DrawingsFrom EverandMetalwork and Machining Hints and Tips for Home Machinists: 101 Plans and DrawingsNo ratings yet
- Alternator Frame: Turbine DiameterDocument4 pagesAlternator Frame: Turbine DiameterDennyHalim.com50% (2)
- .Au Agnet Make Piston RingsDocument6 pages.Au Agnet Make Piston Ringsashishgoel102No ratings yet
- 9 BoltPosiConeRepair30Nov04Document5 pages9 BoltPosiConeRepair30Nov04stefan svenssonNo ratings yet
- Lathe Modelling2Document2 pagesLathe Modelling2Marian DimaNo ratings yet
- Universal Tool and Cutter Grinder Manual Low ResDocument16 pagesUniversal Tool and Cutter Grinder Manual Low ResDale Wade100% (1)
- ReamersDocument1 pageReamersvikash kumarNo ratings yet
- RC Airplane Engine PlansDocument8 pagesRC Airplane Engine PlansLacramioara Veronica Malael100% (1)
- CN Maintenance Practices IIDocument10 pagesCN Maintenance Practices IIavijayakumar_1964No ratings yet
- Improvements To An X2 Mill: Neil Wyatt Upgrades His Milling MachineDocument7 pagesImprovements To An X2 Mill: Neil Wyatt Upgrades His Milling MachineYoel PatiñoNo ratings yet
- 149-Workshop Hints & Tips PDFDocument1 page149-Workshop Hints & Tips PDFsyllavethyjimNo ratings yet
- Design of Nut & BoltDocument4 pagesDesign of Nut & BoltJyoti Kale0% (1)
- Small Workshop CompressorDocument2 pagesSmall Workshop Compressorw4rh4ck3r-scribdNo ratings yet
- Worm MeshDocument5 pagesWorm MeshBabalola SundayNo ratings yet
- Cardboard ClockDocument5 pagesCardboard ClockleongfoowingNo ratings yet
- 2950-Patterns With Fins & FlangesDocument1 page2950-Patterns With Fins & FlangesSandra Barnett CrossanNo ratings yet
- 2845-Bending & FormingDocument1 page2845-Bending & FormingJim MarnochNo ratings yet
- How To Make A Tool Post GrinderDocument5 pagesHow To Make A Tool Post Grinderozland9No ratings yet
- Resharpening & Inspection Cutting Tools PDFDocument10 pagesResharpening & Inspection Cutting Tools PDFHeineken Ya PraneetpongrungNo ratings yet
- Steam EngineDocument4 pagesSteam EngineimgopalNo ratings yet
- Building: LatheDocument60 pagesBuilding: LathePierre799es86% (7)
- 2858-How To Use Scrapers PDFDocument1 page2858-How To Use Scrapers PDFsyllavethyjimNo ratings yet
- Foot-Powered Scroll SawDocument8 pagesFoot-Powered Scroll SawJan Steinman100% (1)
- (Diy) - Metalworking - Model Engineer Aug53' - Surface Grinding & Milling MachineDocument6 pages(Diy) - Metalworking - Model Engineer Aug53' - Surface Grinding & Milling MachineFernanda Duarte100% (4)
- Cylinder TechnologyDocument4 pagesCylinder TechnologyHady SundayanaNo ratings yet
- Air Cooled Hot Air EngineDocument6 pagesAir Cooled Hot Air EngineJim50% (2)
- Watch Repairing, Cleaning and Adjusting - A Practical HandbookFrom EverandWatch Repairing, Cleaning and Adjusting - A Practical HandbookNo ratings yet
- The Art of Watch Repair - Including Descriptions of the Watch Movement, Parts of the Watch, and Common Stoppages of Wrist WatchesFrom EverandThe Art of Watch Repair - Including Descriptions of the Watch Movement, Parts of the Watch, and Common Stoppages of Wrist WatchesNo ratings yet
- Week 12Document31 pagesWeek 12Fajar kurniaNo ratings yet
- Chris&Kathleen - Bending Test - 3Document16 pagesChris&Kathleen - Bending Test - 3Fajar kurniaNo ratings yet
- Materials - Properties - 2009 - Beending Test 5aDocument62 pagesMaterials - Properties - 2009 - Beending Test 5aFajar kurniaNo ratings yet
- Formpendaftaran 6Document1 pageFormpendaftaran 6Fajar kurniaNo ratings yet
- Attachment 4Document12 pagesAttachment 4Fajar kurniaNo ratings yet
- Attachment 3Document2 pagesAttachment 3Fajar kurniaNo ratings yet
- Attachment 2Document16 pagesAttachment 2Fajar kurniaNo ratings yet
- D3D-UV PDFDocument4 pagesD3D-UV PDFFajar kurniaNo ratings yet
- WhatsApp Image 2022-07-05 at 14.20.51Document1 pageWhatsApp Image 2022-07-05 at 14.20.51Fajar kurniaNo ratings yet
- Test & Drain Valve Model 1000Document2 pagesTest & Drain Valve Model 1000saifahmed7No ratings yet
- Mahlkoenig X54 Allround Home Grinder Original Instruction Manual ENDocument60 pagesMahlkoenig X54 Allround Home Grinder Original Instruction Manual ENcarlos_alfaro_herreraNo ratings yet
- QE140 Robotrac Screener ManualDocument204 pagesQE140 Robotrac Screener Manualalberto pachonNo ratings yet
- Interpretations ASME B31.3Document338 pagesInterpretations ASME B31.3Claudenir AlvesNo ratings yet
- Saffty Inductions (Igd Hyundai)Document4 pagesSaffty Inductions (Igd Hyundai)bharathostNo ratings yet
- Continuous Cleat Coping Product DetailDocument2 pagesContinuous Cleat Coping Product DetailIrinel CopacinschiNo ratings yet
- Flowserve HPXDocument8 pagesFlowserve HPXcarlos mercadoNo ratings yet
- ISO-10664Document10 pagesISO-10664Daniel Quijada LucarioNo ratings yet
- Wet CoolingDocument1 pageWet CoolingsaeedalipourNo ratings yet
- 500 Litri Dos Sys Item2Document1 page500 Litri Dos Sys Item2Szikzai Alexandru RobertNo ratings yet
- EVIMETALDocument1 pageEVIMETALahmedNo ratings yet
- DDC p2c3 Ug02 Ugs DR Sot 35101 03 Editing1Document40 pagesDDC p2c3 Ug02 Ugs DR Sot 35101 03 Editing1Devesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Mechanic Millwright 433A en TS3Document67 pagesIndustrial Mechanic Millwright 433A en TS3CourseTree LearningNo ratings yet
- Important Questions Bme 201 Unit1-5Document3 pagesImportant Questions Bme 201 Unit1-5Ashish MishraNo ratings yet
- Piaggio X9250Document75 pagesPiaggio X9250Toni MarasovicNo ratings yet
- Ebara 2CDXDocument13 pagesEbara 2CDXDirector Tecnico y Operaciones Baying SASNo ratings yet
- JS4BD-KB Series: Technical SpecificationsDocument12 pagesJS4BD-KB Series: Technical SpecificationsKokoNo ratings yet
- Mikrokator MDocument4 pagesMikrokator Mciber_aristosNo ratings yet
- Lesson - 09 - UG77 - UG120 - Material, Nameplate & Data ReportDocument19 pagesLesson - 09 - UG77 - UG120 - Material, Nameplate & Data Reportmohamed.eldesouky9120No ratings yet
- Steel Tubes For Structural Purposes Conforming To IS 1161 - 1998Document2 pagesSteel Tubes For Structural Purposes Conforming To IS 1161 - 1998Ayush TariyalNo ratings yet
- Potain MCT 205Document21 pagesPotain MCT 205ubeydullah coşkunNo ratings yet
- Parts Manual TB020 PD3 102Z4Document295 pagesParts Manual TB020 PD3 102Z4Nery TojilNo ratings yet
- Milling Formulas and DefinitionsDocument10 pagesMilling Formulas and DefinitionsCherish QiuNo ratings yet
- Keystone Figure 777 Electric ActuatorDocument8 pagesKeystone Figure 777 Electric Actuatorrpatelacc74No ratings yet
- 04-APRECO Pressure Reliefe Vent DS-SGV-2021-1.2Document2 pages04-APRECO Pressure Reliefe Vent DS-SGV-2021-1.2Nenad MilenkovicNo ratings yet
- PHQC 3036 - Pull Part Manual 2016 1010Document9 pagesPHQC 3036 - Pull Part Manual 2016 1010VladimirNo ratings yet
- Alignment Training (Presentation) - Apr07Document50 pagesAlignment Training (Presentation) - Apr07Mohamed Belall100% (4)
- Afec Ko204-208-215-315Document1 pageAfec Ko204-208-215-315Andrie AdhynataNo ratings yet