Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Toaz - Info Statistics and Probability Week 2 DLL PR
Toaz - Info Statistics and Probability Week 2 DLL PR
Uploaded by
Christian Prudenciano0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views6 pagesThe daily lesson log outlines the teacher's objectives and lesson plan for a week of statistics and probability lessons. The objectives are for students to understand key concepts of random variables and probability distributions, and apply appropriate random variables to real-life problems. Over the week, students will illustrate and construct probability distributions of discrete random variables, calculate mean and variance, and interpret these measures. The lessons will cover probability distributions, the mean of distributions, and variance and standard deviation.
Original Description:
Original Title
toaz.info-statistics-and-probability-week-2-dll-pr_5488087123a0d7bc581ab436febca447
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe daily lesson log outlines the teacher's objectives and lesson plan for a week of statistics and probability lessons. The objectives are for students to understand key concepts of random variables and probability distributions, and apply appropriate random variables to real-life problems. Over the week, students will illustrate and construct probability distributions of discrete random variables, calculate mean and variance, and interpret these measures. The lessons will cover probability distributions, the mean of distributions, and variance and standard deviation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views6 pagesToaz - Info Statistics and Probability Week 2 DLL PR
Toaz - Info Statistics and Probability Week 2 DLL PR
Uploaded by
Christian PrudencianoThe daily lesson log outlines the teacher's objectives and lesson plan for a week of statistics and probability lessons. The objectives are for students to understand key concepts of random variables and probability distributions, and apply appropriate random variables to real-life problems. Over the week, students will illustrate and construct probability distributions of discrete random variables, calculate mean and variance, and interpret these measures. The lessons will cover probability distributions, the mean of distributions, and variance and standard deviation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
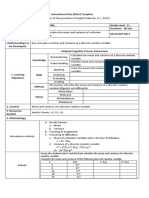
School MARCELO H.
DEL PILAR NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL Grade Level 11
Teacher Learning Area STATISTICS AND
DAILY LESSON LOG PROBABILITY
Teaching Dates & Time Week 2 Quarter 3RD Quarter
Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4
Objectives must be met over the week and connected to the curriculum standards. To meet the objectives, necessary procedures must be followed and if needed, additional lessons, exercises and if remedial
I. OBJECTIVES activities may be done for developing content knowledge and competencies. These are assessed using Formative Assessment strategies. Valuing objectives support the learning content and competencies and
enable children to find significance and joy in learning the lessons. Weekly objectives shall be derived from the curriculum guides.
A. Content Standards The learner demonstrates understanding of key concepts of random variables and probability distributions.
B. Performance Standards The learner is able to apply an appropriate random variable for a given real-life problem (such as in decision making and games of chance).
The learner … The learner … The learner … The learner …
4. illustrates a probability 4. illustrates a probability 7. illustrates the mean and 7. illustrates the mean and
distribution for a discrete distribution for a discrete variance of a discrete random variance of a discrete random
random variable and its random variable and its variable. (M11/12SP-IIIb- variable. (M11/12SP-IIIb-
C. Learning Competencies/Objectives properties. (M11/12SP-IIIa- properties. (M11/12SP-IIIa- 1) 1)
(Write LC code for each area) 4) 4) 8. calculates the mean and the 8. calculates the mean and the
5. constructs the probability 5. constructs the probability variance of a discrete random variance of a discrete random
mass function of a discrete mass function of a discrete variable. (M11/12SP-IIIb-2) variable. (M11/12SP-IIIb-2)
random variable and its random variable and its 9. interprets the mean and the 9. interprets the mean and the
corresponding histogram. corresponding histogram. variance of a discrete random variance of a discrete random
(M11/12SP-IIIa-5) (M11/12SP-IIIa-5) variable. (M11/12SP-IIIb- variable. (M11/12SP-IIIb-
3) 3)
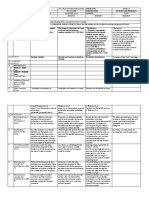
Content is what the lesson is all about. It pertains to the subject matter that the teacher aims to teach in the CG, the content can be tackled in a week or two.
Probability Distributions of Probability Distributions Mean of the Probability Variance and standard
II. CONTENT Discrete Random Variables of Discrete Random Distributions of deviation of the
– Constructing Histogram Variables Discrete Random Probability
– QUIZ Variables Distributions of
Discrete Random
Variables
A. References
1. Teacher’s Guide pages Pages: 117 – 129 Pages: 117 – 129 Pages: 117 – 129 Pages: 117 – 129
2. Learner’s Material pages
3. Textbook pages RBS Statistics and RBS Statistics and RBS Statistics and RBS Statistics and
Probability Probability Probability Probability
Author: R. Belecina, et. Al. Author: R. Belecina, et. Author: R. Belecina, et. Author: R. Belecina, et.
Pages: Al. Pages: Al. Pages: Al. Pages:
4. Additional Materials from
Learning Resources (LR) portal
B. Other Learning Resources
These steps should be done across the week. Spread out the activities appropriately so that the students will learn well. Always be guided by demonstration of learning of the students which can be inferring from
III. PROCEDURE formative assessment activities. Sustain learning systematically by providing students with multiple ways to learn new thing, practice their learning, question their learning processes, and draw conclusions about
what they learned in relation to their life experiences and previous knowledge. Indicate the time allotment to each step.
A. Reviewing previous lessons or Recall the following: Recall the following: How to construct a discrete probability What was discussed yesterday?
presenting the new lesson Random variables ant types Random variables ant types distribution? Histogram? (Mean)
Getting the value of the Getting the value of the What is a mean?
random variable random variable How can we compute for the mean of
Discrete probability Discrete probability a discrete probability distribution?
distribution/ Probability Mass distribution/ Probability Mass
Function Function
Constructing the Discrete Constructing the Discrete
Probability Distribution (give Probability Distribution (give
another example, say, tossing another example, say,
a coin twice) tossing a coin twice)
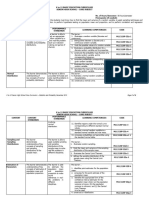
B. Establishing a purpose for the • Illustrate the probability distribution • Illustrate the probability distribution • Illustrate and Compute for the mean • Illustrate and calculate the variance
lesson for discrete random variables and its for discrete random variables and its of the discrete probability distribution and standard deviation of a discrete
properties properties • Interpret the mean of a discrete random variable
• Compute probabilities • Compute probabilities random variable • Interpret the variance and standard
corresponding to a given discrete corresponding to a given discrete • Solve problems involving the mean deviation of a discrete random variable
random variable random variable of probability distributions • Solve problems involving variance
• Construct the probability mass • Construct the probability mass and standard deviation of probability
function of a discrete random variable function of a discrete random distributions
and its corresponding histogram variable and its corresponding
histogram
C. Presenting example/instances Introduce the histogram. (Define) A. Given the values of the variables X Motivation:
of the new lesson and Y, evaluate the following Measuring the height of dogs
summations.
𝑋1 = 4 𝑋2 = 2 𝑋3 = 5 𝑋4 = 1
𝑌1 = 2 𝑌2 = 1 𝑌3 = 0 𝑌4 = 2
1. ∑ 𝑋
2. ∑ 𝑌
3. ∑ 𝑋𝑌 The heights (at the shoulder) are:
4. ∑(𝑋 + 𝑌) 600mm, 470mm, 170mm, 430mm,
5. ∑ 4𝑋𝑌 and 300mm. What is the mean
height of the dogs?
Get the difference of the height of
dogs to the average height. To
measure the amount of variation of
the height of the dogs, square
each difference, then get the
average. (variance)
Get the square root of the variance
(Standard deviation)
All dogs that has a height within
the two blue lines are considered
normal. Those above or below are
considered tall or short.
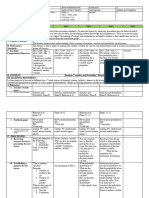
D. Discussing new concepts and Differentiate Histogram and Bar Ask the students what they know Define and discuss variance and
practicing new skills #1 graph about the mean standard deviation.
Consider a rolling die. What is the
average number of spots that would
appear?
E. Discussing new concepts and Construct the histogram in tossing a Present the following steps in Present the following steps in
Practicing new skills #2 coin twice computing for the mean of the discrete computing for the variance and
probability distribution: standard deviation of the discrete
1. Probability Distribution probability distribution:
Construct a probability 1. Construct a probability
Distribution for the random distribution.
variable. Convert the probability 2. Find the mean of the probability
into decimal. distribution.
2. Multiply 3. Subtract the mean from each
Multiply the value of the random value of the random variable.
variable to the corresponding 4. Square ALL the results obtained
probability. in step 3.
3. Sum up! 5. Multiply the results obtained in
Add the result in step 2, then step 4 by the corresponding
divide it to the total number of probability.
the sample space in the 6. Add the results in step 5
probability distribution. Standard Deviation can be obtained by
getting the square root of the
variance.
F. Developing Mastery Two balls are drawn in succession The probabilities that a customer will Two balls are drawn in succession
without replacement from a box buy 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5 items in a without replacement from a box
containing 5 red balls and 6 blue grocery
1 1
store
2
are 3 containing 5 red balls and 6 blue balls.
3
balls. Let Z be the random variable , , , , 𝑎𝑛𝑑 respectively. Let Z be the random variable
10 10 10 10 10
representing the number of blue What is the average number of items representing the number of blue balls.
balls. Construct the probability Construct the probability distribution of
that a customer will buy?
distribution of the random variable Z the random variable Z
The probabilities that a surgeon
operates on 3, 4, 5, 6, or 7 patients
in any day are 0.15, 0.10, 0.20,
0.25, and 0.30 respectively. Find the
average number of patients that a
surgeon operates on a day.
G. Finding practical applications of (Mastery and Quiz) (Quiz) Two balls are drawn in succession Two balls are drawn in succession
concepts and skills in daily living without replacement from a box without replacement from a box
containing 5 red balls and 6 blue balls. containing 5 red balls and 6 blue balls.
Let Z be the random variable Let Z be the random variable
representing the number of blue balls. representing the number of blue balls.
Construct the probability distribution of Construct the probability distribution of
the random variable Z the random variable Z
H. Making generalizations and What is the difference between a What is a mean?
Abstractions about the lessons histogram and a bar graph? How can we compute for the mean of
What do we consider in constructing a discrete probability distribution?
the histogram? (random variable and
probability)
I. Evaluating Learning The debate society has 8 members Complete the table below and find the
who were qualified to participate the mean of the probability Distribution
incoming interschool debate. The
adviser needed to choose three
members out of the 8 qualified to
represent the school in the said
event.
a. Identify all the possible
outcomes in selecting 3
members out of 8 Find the mean of the probability
b. Compute for the probabilities distribution of the random variable X,
of each outcome which can take only the values 1, 2,
c. Construct the discrete 10
and 3, given that P(1) = 33 , 𝑃(2) =
probability distribution 12
1
d. Construct the histogram , 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑃(3) =
3 33
J. Additional activities for
application or remediation
V. REMARKS
Reflect on your teaching and assess yourself as a teacher. Think about your students’ progress this week. What works? What else needs to be done to help the students learn? Identify what help your instructional
VI. REFLECTION supervisors can provide for you so when you meet them, you can ask them relevant questions.
A. No. of learners who earned 80% in
the evaluation.
B. No. of learners who require
additional activities remediation.
C. Did the remedial lessons work? No. of
learners who caught up with the
lesson.
D. No. of learners who continue to
require remediation
E. Which of my teaching strategies
worked well? Why did these work?
F. What difficulties did I encounter
which my principal or supervisor can
help me solve?
G. What innovation or localization
materials did I use/discover which I
wish to share with other teachers?
You might also like
- Project Report On Cyber SecurityDocument60 pagesProject Report On Cyber SecurityHaritha63% (16)
- Statistics and Probability Week 1 DLLDocument4 pagesStatistics and Probability Week 1 DLLJobelle Mostoles86% (7)
- M11 12SP IIIb 2Document2 pagesM11 12SP IIIb 2bethNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability Week 2 DLLDocument5 pagesStatistics and Probability Week 2 DLLJobelle Mostoles67% (3)
- Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4: I. ObjectivesDocument4 pagesDay 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4: I. Objectivesariel a. ortizNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability Week 2 DLL - CompressDocument6 pagesStatistics and Probability Week 2 DLL - CompressHermit BelanoNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability Week 1 DLLDocument4 pagesStatistics and Probability Week 1 DLLGuro TVNo ratings yet
- Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4: I. ObjectivesDocument3 pagesDay 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4: I. Objectivesariel a. ortizNo ratings yet
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: I. ObjectivesDocument7 pagesMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: I. Objectivesjun del rosarioNo ratings yet
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: I. ObjectivesDocument6 pagesMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: I. Objectivesjun del rosarioNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Stat and Prob DLLDocument3 pagesWeek 3 Stat and Prob DLLronald bantuganNo ratings yet
- DLL Stat&prob Q3 Week1Document2 pagesDLL Stat&prob Q3 Week1Angelica Paler SupasNo ratings yet
- First Week Statistics and ProbabilityDocument2 pagesFirst Week Statistics and ProbabilityChona Vidal BontigaoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Statistics Week 1Document14 pagesLesson Plan in Statistics Week 1Marvin MacanNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document14 pagesWeek 1Kimberly GayosaNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability November 7-11-2016Document5 pagesStatistics and Probability November 7-11-2016Edal SantosNo ratings yet
- Dll-Stat-Week 2Document3 pagesDll-Stat-Week 2Deborah BandahalaNo ratings yet
- Stat W2Document4 pagesStat W2Melody De VeraNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document22 pagesWeek 1wilhelmina romanNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1-Mathematics - Secondary-JhsDocument14 pagesWEEK 1-Mathematics - Secondary-JhsJunior FelipzNo ratings yet
- Stat&Prob 3rd Week 2Document3 pagesStat&Prob 3rd Week 2Mark Lenon VerdaderoNo ratings yet
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday ThursdayDocument6 pagesMonday Tuesday Wednesday ThursdayAnn Manuel BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Statstics and Probability WEEK 1Document14 pagesStatstics and Probability WEEK 1Elvin Pretencio0% (1)
- Stat 5Document20 pagesStat 5denizsaday100% (1)
- Stat&probab Q3 Week 1 DLLDocument13 pagesStat&probab Q3 Week 1 DLLKILVEN MASIONNo ratings yet
- I. ObjectivesDocument3 pagesI. ObjectivesFRECY MARZANNo ratings yet
- 3rd WeekDocument4 pages3rd WeekArtemist FowlNo ratings yet
- 2nd WeekDocument4 pages2nd WeekArtemist FowlNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document14 pagesWeek 1Jay Jay h. JantarNo ratings yet
- Week 1 StatisticsDocument3 pagesWeek 1 StatisticsMichaelle BunaoNo ratings yet
- DLL NewDocument43 pagesDLL NewMary Jane TambisNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document6 pagesWeek 1Christine Faith TablandoNo ratings yet
- SHS Core - Statistics and Probability CGDocument11 pagesSHS Core - Statistics and Probability CGCarol Zamora100% (1)
- Stat&Prob 3rd Week 3Document3 pagesStat&Prob 3rd Week 3Mark Lenon VerdaderoNo ratings yet
- DLL Week 1 StatDocument4 pagesDLL Week 1 Statwilhelmina romanNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument9 pagesUntitledJESSECA CARPESANONo ratings yet
- Stat and Prob Q1 W2Document4 pagesStat and Prob Q1 W2Nimrod LadianaNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document14 pagesWeek 1Coco LlameraNo ratings yet
- 1st WeekDocument4 pages1st WeekArtemist FowlNo ratings yet
- S&P1Document4 pagesS&P1Rey EcaldreNo ratings yet
- Lesson Exemplar in Statistics and ProbabilityDocument3 pagesLesson Exemplar in Statistics and ProbabilityMay Alvarez Magsino100% (2)
- WLP Statistics&Probability Feb 5 9 2024Document7 pagesWLP Statistics&Probability Feb 5 9 2024cheene.bagosNo ratings yet
- I. ObjectivesDocument3 pagesI. ObjectivesFRECY MARZANNo ratings yet
- I. ObjectivesDocument5 pagesI. ObjectivesFRECY MARZANNo ratings yet
- STATS Week 3 - DLLDocument8 pagesSTATS Week 3 - DLLThess MiraflorNo ratings yet
- 000 BOL StatDocument12 pages000 BOL StatCARLA MAY UYNo ratings yet
- Shs Core Statistics and Probability CGPDFDocument6 pagesShs Core Statistics and Probability CGPDFClyde Elric EsperoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 and 4 Mean Variance and The Normal Random VariableDocument6 pagesLesson 3 and 4 Mean Variance and The Normal Random VariableGeraldine ElisanNo ratings yet
- Stat&Prob DLL Week 1Document7 pagesStat&Prob DLL Week 1HAZEL JOYCE RAMOSNo ratings yet
- Ateneo de Davao University: Welcome To Statistics and Probability Subject!Document13 pagesAteneo de Davao University: Welcome To Statistics and Probability Subject!Kyle BARRIOSNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Teacher's Weekly Instructional Learning Plan For Modular Distance LearningDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Teacher's Weekly Instructional Learning Plan For Modular Distance LearningMark Paul AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Session 1 Session 2 Session 3 Session 4: Statistics AND ProbabilityDocument4 pagesSession 1 Session 2 Session 3 Session 4: Statistics AND ProbabilityEloiza Jane OrdenizaNo ratings yet
- I. ObjectivesDocument3 pagesI. ObjectivesFRECY MARZANNo ratings yet
- DLL Stat&Prob11 - Q3 Wk1Document10 pagesDLL Stat&Prob11 - Q3 Wk1Kristine Lyka CuradaNo ratings yet
- WEEK1SDocument4 pagesWEEK1Sloice crisostomoNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Senior High School Grade Eleven/ Statistics and ProbabilityDocument37 pagesDepartment of Education: Senior High School Grade Eleven/ Statistics and Probabilityoea aoueoNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document5 pagesWeek 2AJ ManialungNo ratings yet
- Stat Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesStat Lesson PlanGrace Magallanes TagadiadNo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Plan 0412 0416Document7 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plan 0412 0416April Joy LascuñaNo ratings yet
- DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS: A Mathematical Analysis for Applied SciencesFrom EverandDIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS: A Mathematical Analysis for Applied SciencesNo ratings yet
- Literature LessonDocument1 pageLiterature LessonChristian PrudencianoNo ratings yet
- Research Lesson Plan - Gas Laws JudeDocument16 pagesResearch Lesson Plan - Gas Laws JudeChristian PrudencianoNo ratings yet
- Pe 2nd Quarter Summative ExamDocument3 pagesPe 2nd Quarter Summative ExamChristian PrudencianoNo ratings yet
- MathDocument13 pagesMathChristian PrudencianoNo ratings yet
- Group 1 RLP - OG - JoeDocument12 pagesGroup 1 RLP - OG - JoeChristian PrudencianoNo ratings yet
- PERDEVDocument7 pagesPERDEVChristian PrudencianoNo ratings yet
- CriteriaDocument2 pagesCriteriaChristian PrudencianoNo ratings yet
- Physical inacti-WPS Office 4Document2 pagesPhysical inacti-WPS Office 4Christian PrudencianoNo ratings yet
- PE LessonDocument13 pagesPE LessonChristian PrudencianoNo ratings yet
- Jar Nicotine an-WPS Office 2Document1 pageJar Nicotine an-WPS Office 2Christian PrudencianoNo ratings yet
- Heart Rhythm ab-WPS Office 5Document2 pagesHeart Rhythm ab-WPS Office 5Christian PrudencianoNo ratings yet
- PE 2nd Quarter 1st TopicDocument35 pagesPE 2nd Quarter 1st TopicChristian PrudencianoNo ratings yet
- Likewise, Clung-WPS Office 7Document1 pageLikewise, Clung-WPS Office 7Christian PrudencianoNo ratings yet
- 1Document2 pages1Christian PrudencianoNo ratings yet
- List of Companies Having SAPDocument2 pagesList of Companies Having SAPKrushikeshNo ratings yet
- Charusat 6th SemDocument1 pageCharusat 6th SemdhruvilNo ratings yet
- Sardar JokesDocument5 pagesSardar JokesblpsimhaNo ratings yet
- Vendor ListDocument3 pagesVendor ListJohn Son GNo ratings yet
- Somewhere I Have Never TravelledDocument221 pagesSomewhere I Have Never TravelledLucy SummerNo ratings yet
- Final of Small Plowing MachineDocument89 pagesFinal of Small Plowing Machinenigus gereziher75% (4)
- Introduction To Mineral Processing 2010Document24 pagesIntroduction To Mineral Processing 2010elmonemNo ratings yet
- Electronic Reservation Slip (ERS) : 2144543628 11078/jhelum Express Ac 3 Tier Sleeper (3A)Document2 pagesElectronic Reservation Slip (ERS) : 2144543628 11078/jhelum Express Ac 3 Tier Sleeper (3A)nirjra kansalNo ratings yet
- English Unit 9 - Ni Putu Angelika RistyaDocument3 pagesEnglish Unit 9 - Ni Putu Angelika RistyaAngel LikaNo ratings yet
- Laura Su ResumeDocument1 pageLaura Su Resumeapi-280311314No ratings yet
- Idose4 - Whitepaper - Technical - Low Res - PDF Nodeid 8432599&vernum - 2 PDFDocument40 pagesIdose4 - Whitepaper - Technical - Low Res - PDF Nodeid 8432599&vernum - 2 PDFOmarah AbdalqaderNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Accounting For Other LiabilitiesDocument21 pagesChapter 4 - Accounting For Other Liabilitiesjeanette lampitoc0% (1)
- Tutorial TransformerDocument2 pagesTutorial TransformerMohd KhairiNo ratings yet
- In A NutshellDocument3 pagesIn A NutshellJane TuazonNo ratings yet
- Legendary RakshashaDocument24 pagesLegendary RakshashajavandarNo ratings yet
- Best Practices SQL Server For OpenText Content Server 10.5Document44 pagesBest Practices SQL Server For OpenText Content Server 10.5peptaNo ratings yet
- August 12, 2016 Strathmore TimesDocument20 pagesAugust 12, 2016 Strathmore TimesStrathmore TimesNo ratings yet
- Docker Management Design Patterns: Swarm Mode On Amazon Web ServicesDocument1 pageDocker Management Design Patterns: Swarm Mode On Amazon Web ServicesAli AhmadNo ratings yet
- At The AirportDocument6 pagesAt The AirportAlen KuharićNo ratings yet
- Reflection Paper: Chapter 2Document3 pagesReflection Paper: Chapter 2RedgiemarkNo ratings yet
- Guía Express TOEFL iBTDocument21 pagesGuía Express TOEFL iBTJordan Raji JrLcNo ratings yet
- Maja Blanca RecipeDocument5 pagesMaja Blanca RecipeChristopher PadillaNo ratings yet
- 4045tf270 Power Unit For Gen Set (12 24v 1800rpm) Sdmo EngineDocument3 pages4045tf270 Power Unit For Gen Set (12 24v 1800rpm) Sdmo EngineRoberto MoraNo ratings yet
- BM-24 HRM Assignment Brief - 1654313266Document9 pagesBM-24 HRM Assignment Brief - 1654313266aung san0% (1)
- Solution Chapter 4Document11 pagesSolution Chapter 4accounts 3 lifeNo ratings yet
- 3 Thermal LoadsDocument19 pages3 Thermal LoadsJaime Fernando Leon TerrazosNo ratings yet
- What Is Spend AnalysisDocument35 pagesWhat Is Spend AnalysisMahesh NaiduNo ratings yet
- Family Biz BibleDocument26 pagesFamily Biz BibleFrank ParrNo ratings yet
- Homework, References PDFDocument2 pagesHomework, References PDFSeavMeng SengNo ratings yet