Professional Documents
Culture Documents
U1L7 Student Guide (1) - 1
U1L7 Student Guide (1) - 1
Uploaded by
jonahCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Pediatric Mock Resuscitation ScenariosDocument6 pagesPediatric Mock Resuscitation ScenariosdinkytinkNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Activity SheetDocument3 pagesNervous System Activity SheetTonyC.Reyes100% (3)
- Brain Breakthroughs MASTERCLASSDocument15 pagesBrain Breakthroughs MASTERCLASSRenee NasserNo ratings yet
- QUIZ 1 "Plants and Human As Organism"Document2 pagesQUIZ 1 "Plants and Human As Organism"Yohanna Silalahi100% (2)
- Nervous System WorksheetDocument2 pagesNervous System WorksheetMcLargoNo ratings yet
- Biocare IE 101 & IE 300Document82 pagesBiocare IE 101 & IE 300Mohammed ShabanNo ratings yet
- Esaote P8000 - User ManualDocument58 pagesEsaote P8000 - User ManualJosé Luis Pérez Contreras100% (3)
- ACLS Pre-TestDocument24 pagesACLS Pre-TestBaltej Sidhu80% (10)
- ABC ACLS Checklist Online CY2020 21Document8 pagesABC ACLS Checklist Online CY2020 21Anastasya Gishella RorongNo ratings yet
- Student Guide: Unit 2: Brain Maintenance Lesson 2Document3 pagesStudent Guide: Unit 2: Brain Maintenance Lesson 2ria wuNo ratings yet
- U1L6 Student Guide - 2Document2 pagesU1L6 Student Guide - 2jonahNo ratings yet
- U1L4 Student GuideDocument3 pagesU1L4 Student GuidetheoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Body Coordination: Form 4 ScienceDocument28 pagesChapter 2: Body Coordination: Form 4 ScienceSudhan NairNo ratings yet
- " The Nervous System, Part 1: Crash Course A&P #8 ":: Longest Shortest CAN CannotDocument7 pages" The Nervous System, Part 1: Crash Course A&P #8 ":: Longest Shortest CAN CannotNargess OsmanNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 RevisionDocument3 pagesGrade 5 RevisionshamshadNo ratings yet
- U1L9 Student Guide (1) - 1Document4 pagesU1L9 Student Guide (1) - 1jonahNo ratings yet
- Level - 1 I. Fill in The BlanksDocument5 pagesLevel - 1 I. Fill in The BlanksKesanam SpNo ratings yet
- Human Nervous System WorksheetDocument3 pagesHuman Nervous System WorksheetWai HponeNo ratings yet
- Nervous System ESSENTIAL QUESTIONSDocument8 pagesNervous System ESSENTIAL QUESTIONSAmanuelNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Science Elective: Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesGrade 8 Science Elective: Nervous SystemVincqNo ratings yet
- Nervous System QuizDocument1 pageNervous System QuizHolly May MontejoNo ratings yet
- Grade 3Document4 pagesGrade 3nullka100% (3)
- U2L3 Student GuideDocument6 pagesU2L3 Student GuideMemee MememmNo ratings yet
- 2 Organ SystemsDocument5 pages2 Organ SystemsBeaNo ratings yet
- Q2 Summative Test 1 ScienceDocument2 pagesQ2 Summative Test 1 ScienceHERRENELLE DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Exploring Health CareersDocument6 pagesExploring Health Careersapi-263127781No ratings yet
- U1L8 Student Guide - 2Document5 pagesU1L8 Student Guide - 2jonahNo ratings yet
- 3RD Summative Exam in Science 6Document6 pages3RD Summative Exam in Science 6Maricris Palermo Sancio100% (1)
- Human Body System NotesDocument5 pagesHuman Body System NotesShannon BandyNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 9 Q1 WK1 2 The Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsDocument42 pagesSCIENCE 9 Q1 WK1 2 The Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsDanielle SibayNo ratings yet
- PAU1 - S2 L3 - Crash Course 3 - The Chemical Mind - QuestionsDocument3 pagesPAU1 - S2 L3 - Crash Course 3 - The Chemical Mind - QuestionsHiểu AnhNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Science Weeks 1-4 Worksheets - Term 1Document25 pagesGrade 5 Science Weeks 1-4 Worksheets - Term 1darrengotta8No ratings yet
- Reviewer HOPE12Document2 pagesReviewer HOPE12Xin LouNo ratings yet
- Basic Respiratory WebquestDocument8 pagesBasic Respiratory WebquestWidjaya HS TeacherNo ratings yet
- Chapt10 Study OutlineDocument11 pagesChapt10 Study Outlinekombat13_708353334No ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab ManualDocument9 pagesAnaphy Lab ManualKen KanekiNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Concept MapDocument12 pagesNervous System Concept MapJo BrackenNo ratings yet
- Brain Breakthroughs MASTERCLASS Private WorkbookDocument15 pagesBrain Breakthroughs MASTERCLASS Private WorkbookRida ArifNo ratings yet
- Simple Present Other Verbs MedicineDocument8 pagesSimple Present Other Verbs MedicineFernanda VigilNo ratings yet
- Bio ObjectivesDocument110 pagesBio ObjectivesRishiPanduNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesCirculatory SystemAlba CubilloNo ratings yet
- T2 HealthDocument1 pageT2 HealthShirley LauNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 1Document2 pagesLaboratory Activity 1Samantha sanchezNo ratings yet
- The Most Transformative Thing You Can Do For Your Brain TodayDocument1 pageThe Most Transformative Thing You Can Do For Your Brain TodayAnna ZalewaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Anatomy and Physiology NotesDocument6 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Anatomy and Physiology Notesapi-305436791No ratings yet
- 9e CH 7Document19 pages9e CH 7Aeren RhosenNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesLesson 4 Nervous SystemMohammad FalkayNo ratings yet
- 2a. HPW CHP 1 Packet KEYDocument9 pages2a. HPW CHP 1 Packet KEYDiane TorajaNo ratings yet
- Exercises (Basic Human Anatomy and Medical Terminologies)Document7 pagesExercises (Basic Human Anatomy and Medical Terminologies)tomaNo ratings yet
- Study Guide 12 SleepDocument4 pagesStudy Guide 12 SleepSofia Loreen Melo GarciaNo ratings yet
- 9th Grade Nervous System WorksheetDocument2 pages9th Grade Nervous System WorksheetRICKAYLA HAMILTONNo ratings yet
- U2L3 Student GuideDocument6 pagesU2L3 Student GuidethomasNo ratings yet
- Questions:: Activity Sheet No.1Document14 pagesQuestions:: Activity Sheet No.1Raniey MayolNo ratings yet
- Answer Key PDFDocument7 pagesAnswer Key PDFSamantha Bernardo UndaNo ratings yet
- SCRIPTDocument4 pagesSCRIPTTarash JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Reading and Writing AssignmentDocument3 pagesChapter 10 - Reading and Writing Assignmentteemo no JutsuNo ratings yet
- Human Body Focused Notes 2023Document9 pagesHuman Body Focused Notes 2023pickles.squad11No ratings yet
- Bill Nye RespirationDocument1 pageBill Nye RespirationJoseeNo ratings yet
- Science 6 NerveDocument1 pageScience 6 NerveIvan joseph MarianoNo ratings yet
- PE and Health 12 - Module 1Document39 pagesPE and Health 12 - Module 1Stephen Lorenzo A. Doria100% (1)
- VE EFN1 Tests ProgressTest03Document3 pagesVE EFN1 Tests ProgressTest03ivan.n.stanimirovicNo ratings yet
- Progress Test 3 (Units 5-6) : Name: - Date: - Section 1: VocabularyDocument3 pagesProgress Test 3 (Units 5-6) : Name: - Date: - Section 1: VocabularyPaulina CardinaleNo ratings yet
- P6 ScienceDocument3 pagesP6 ScienceJulie Ann LacanilaoNo ratings yet
- Neuroathletics Training for Beginners More Coordination, Agility and Concentration Thanks to Improved Neuroathletics - Incl. 10-Week Plan For Training in Everyday Life.From EverandNeuroathletics Training for Beginners More Coordination, Agility and Concentration Thanks to Improved Neuroathletics - Incl. 10-Week Plan For Training in Everyday Life.No ratings yet
- U1L8 Student Guide - 2Document5 pagesU1L8 Student Guide - 2jonahNo ratings yet
- U1L6 Student Guide - 2Document2 pagesU1L6 Student Guide - 2jonahNo ratings yet
- U1L9 Student Guide (1) - 1Document4 pagesU1L9 Student Guide (1) - 1jonahNo ratings yet
- U2L2 How Are Skills Developed Worksheet-2Document2 pagesU2L2 How Are Skills Developed Worksheet-2jonahNo ratings yet
- Aami Ec11Document60 pagesAami Ec11mdd02No ratings yet
- Zoll M Series Defibrillator Manual PDFDocument111 pagesZoll M Series Defibrillator Manual PDFAhmad TanveerNo ratings yet
- 6 - BLS HandoutDocument18 pages6 - BLS HandoutEastern SamarNo ratings yet
- Basic Life SupportDocument54 pagesBasic Life SupportAdrianNo ratings yet
- Lifepak CR2 Data SheetDocument4 pagesLifepak CR2 Data SheetEnerspect Medical SolutionsNo ratings yet
- 170-VDR JRC JCY-1900 Instruct Manual 2-8-2022Document184 pages170-VDR JRC JCY-1900 Instruct Manual 2-8-2022Gilbert GlobalNo ratings yet
- Umass Lowell PCRDocument1 pageUmass Lowell PCRdandude505No ratings yet
- Penggunaan DC Shock Dan AED: Edward Kusuma, DR., M.Kes., SP - An., KICDocument21 pagesPenggunaan DC Shock Dan AED: Edward Kusuma, DR., M.Kes., SP - An., KICNdalemSanguDunia-AkhiratNo ratings yet
- First Aid and Water Safety #3Document30 pagesFirst Aid and Water Safety #3Ezzee YenNo ratings yet
- BeneHeart D3 Operators ManualDocument208 pagesBeneHeart D3 Operators Manualelectromedicina.esNo ratings yet
- Advanced Life Support Algorithm: Version: July 2016Document45 pagesAdvanced Life Support Algorithm: Version: July 2016Dwi RinaNo ratings yet
- GE Dash Responder - Service ManualDocument100 pagesGE Dash Responder - Service ManualРинат ЖахинNo ratings yet
- CPR 2020Document26 pagesCPR 2020Meeta PanditNo ratings yet
- ACLS - Prone PDFDocument2 pagesACLS - Prone PDFArdian WibowoNo ratings yet
- Jss-2250 2500 (E) 7zpjd0624b (Ed02) Installation ManualDocument136 pagesJss-2250 2500 (E) 7zpjd0624b (Ed02) Installation Manualmark.lobianoNo ratings yet
- 2014 Nissan Leaf Service Repair Manual (Front Axle)Document32 pages2014 Nissan Leaf Service Repair Manual (Front Axle)Engr Ko VictorNo ratings yet
- ACLS Practice TestDocument5 pagesACLS Practice Testprettynpink0867% (3)
- CARDIOVERSION Vs DEFIBRILLATIONDocument7 pagesCARDIOVERSION Vs DEFIBRILLATIONjames garciaNo ratings yet
- Bm8601 Dte-1 Question BankDocument8 pagesBm8601 Dte-1 Question BankTamil TskNo ratings yet
- ck88 en Om b0Document80 pagesck88 en Om b0Zlatko OžanićNo ratings yet
- Code Blue Do You Know What To Do .10 PDFDocument6 pagesCode Blue Do You Know What To Do .10 PDFJoy HavsonNo ratings yet
- BLS For TeacherrDocument166 pagesBLS For TeacherrGavinKarl Mianabanatao100% (1)
- Book 1Document209 pagesBook 1Camilo Arturo Suarez Ballesteros100% (1)
- App Expt 8Document2 pagesApp Expt 8Christine LopezNo ratings yet
- Philips HeartStart XL Defibrillator - Service GuidelineDocument3 pagesPhilips HeartStart XL Defibrillator - Service GuidelineLeandro BitencourtNo ratings yet
U1L7 Student Guide (1) - 1
U1L7 Student Guide (1) - 1
Uploaded by
jonahOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
U1L7 Student Guide (1) - 1
U1L7 Student Guide (1) - 1
Uploaded by
jonahCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 1: Introduction to the Brain
Student Guide Lesson 7
1. What are the objectives of today’s lesson?
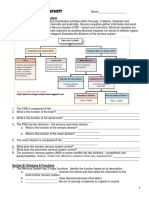
2. What are some of the involuntary actions that occur between the brain and body systems?
Circulatory System:
Digestive System:
Respiratory System:
3. What are some things that are regulated by the brain?
The brain has s________ n________ that detect o______ and c______ d_________
Neurons in the brain tell the heart to s_______ ___ or ______ _______ it adjusts according
to l______ of e_________ and oxygen demand
4. What are the different parts of the nervous system and what do they do?
The Peripheral Nervous System consists of the nerves that radiate out from the c_______
nervous system and take information from the b_____ to the b_____.
The Somatic Nervous System which is a part of the “p_________” nervous system, sends
nerves to c_______ m_________ and receives s_______ i____________ about things such as
touch, pain, itch, etc.
The Autonomic Nervous System controls the o_____ s________; the s___________ part
prepares the body for a f_____ or f______ reaction. The p______________ part r_________
body functions that go on when things are calm.
U1L7 Student Guide 1
5. What are some things your brain is responsible for when it detects a threat? (Refer to Road
Runner and Coyote example)
A____________ heart rate,
Constricting _______ vessels,
Raising blood p_________
Blood sent to m_______ away from the g____
D_________ is inhibited.
6. How does the brain impact digestion?
The brain has a d______ e______ on the stomach
The gut-brain c__________ can be linked to a________
A troubled i________ can s_____ s________ to the brain, just as a troubled b______ can
send signals to the g____
A person’s stomach or intestinal d_________ can be the c_____ or p________ of anxiety,
stress, or depression.
7. Define some of the key heartrate terms.
Target Heart Rate:
Resting Heartrate
Recovery Heart Rate:
8. What is an Automatic External Defibrillator (AED)?
An automated external defibrillator is used to help those experiencing sudden c_______
a_______
It is a sophisticated, yet easy-to-use m______ d______ that can a_________ the h_______
r_________, and if necessary, deliver an e________ s_____, or defibrillation, to help the
heart re-establish an e__________ rhythm.
It can be places on a person’s c_____ to revive the person if the heart ______ beating
N____________ people can use AED’s
U1L7 Student Guide 2
9. Do AED’s replace CPR?
___, _____ is still needed
When a person goes into c_______ a______, CPR keeps b______ f________ to the brain
AED’s c___ be u_____ as a part of CPR
The e________ s_____ of an AED g_______ i__________ the chances of getting the heart to
start p________ again
The A________ R____ C______ includes AED training in many CPR training classes
10. How can CPR save your brain?
According to the American Heart Association, CPR is an e__________ l__________ procedure
performed when the heart s______ b_______
Immediate CPR can d______ or t______ chances of s_________ after cardiac arrest
CPR helps keep b______ flowing to the brain and ________.
11. Why is administering CPR important, and what happens if it’s not administered promptly?
___________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
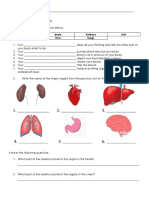
12. Why do cells need oxygen?
Every cell in the body r_______ oxygen to f________
No breathing = No o_______ = No brain function
The brain is the f_____ o_____ to _______ down followed by the heart
U1L7 Student Guide 3
13. What is biofeedback?
The process of r___________ what is going on in your body and bringing the processes under
v_________ control
Biofeedback requires you to ________ on your body and make s______ changes such as
r_________ certain m________ to achieve desired results
It gives you the power to use your thoughts to c______l your b____, often to manage specific
h______ c___________ or physical performance
14. What are some types of biofeedback?
Deep breathing
Progressive muscle relaxation – t__________ then r__________ different muscle groups
Guided imagery – concentrating on a certain _______ to f______ your mind and feel more
relaxed
Meditation- focusing your thoughts and letting go of n_________ e_________
15. What is the summary of today’s lesson?
• The nervous, circulatory, respiratory, and digestive systems work with the brain to sustain the
various i____________ s___________ functions (automatic processes) that occur in the body
• An a_________ ex_______ d__________ (AED), is used to help those experiencing sudden
c________ a______
• ____ is an emergency l_______________ p_________ performed when the heart stops beating
• Administering CPR is incredibly important to your brain because it continues to p________
o_______ to the brain and heart
• All o______ need _________ to survive, but b______ cells are particularly dependent
• B____________ is the process of recognizing what is going on in your body and bringing the
processes under v_______ control
• Biofeedback requires you to focus on your body and make subtle changes such as relaxing a
certain muscle to achieve desired results
U1L7 Student Guide 4
You might also like
- Pediatric Mock Resuscitation ScenariosDocument6 pagesPediatric Mock Resuscitation ScenariosdinkytinkNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Activity SheetDocument3 pagesNervous System Activity SheetTonyC.Reyes100% (3)
- Brain Breakthroughs MASTERCLASSDocument15 pagesBrain Breakthroughs MASTERCLASSRenee NasserNo ratings yet
- QUIZ 1 "Plants and Human As Organism"Document2 pagesQUIZ 1 "Plants and Human As Organism"Yohanna Silalahi100% (2)
- Nervous System WorksheetDocument2 pagesNervous System WorksheetMcLargoNo ratings yet
- Biocare IE 101 & IE 300Document82 pagesBiocare IE 101 & IE 300Mohammed ShabanNo ratings yet
- Esaote P8000 - User ManualDocument58 pagesEsaote P8000 - User ManualJosé Luis Pérez Contreras100% (3)
- ACLS Pre-TestDocument24 pagesACLS Pre-TestBaltej Sidhu80% (10)
- ABC ACLS Checklist Online CY2020 21Document8 pagesABC ACLS Checklist Online CY2020 21Anastasya Gishella RorongNo ratings yet
- Student Guide: Unit 2: Brain Maintenance Lesson 2Document3 pagesStudent Guide: Unit 2: Brain Maintenance Lesson 2ria wuNo ratings yet
- U1L6 Student Guide - 2Document2 pagesU1L6 Student Guide - 2jonahNo ratings yet
- U1L4 Student GuideDocument3 pagesU1L4 Student GuidetheoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Body Coordination: Form 4 ScienceDocument28 pagesChapter 2: Body Coordination: Form 4 ScienceSudhan NairNo ratings yet
- " The Nervous System, Part 1: Crash Course A&P #8 ":: Longest Shortest CAN CannotDocument7 pages" The Nervous System, Part 1: Crash Course A&P #8 ":: Longest Shortest CAN CannotNargess OsmanNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 RevisionDocument3 pagesGrade 5 RevisionshamshadNo ratings yet
- U1L9 Student Guide (1) - 1Document4 pagesU1L9 Student Guide (1) - 1jonahNo ratings yet
- Level - 1 I. Fill in The BlanksDocument5 pagesLevel - 1 I. Fill in The BlanksKesanam SpNo ratings yet
- Human Nervous System WorksheetDocument3 pagesHuman Nervous System WorksheetWai HponeNo ratings yet
- Nervous System ESSENTIAL QUESTIONSDocument8 pagesNervous System ESSENTIAL QUESTIONSAmanuelNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Science Elective: Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesGrade 8 Science Elective: Nervous SystemVincqNo ratings yet
- Nervous System QuizDocument1 pageNervous System QuizHolly May MontejoNo ratings yet
- Grade 3Document4 pagesGrade 3nullka100% (3)
- U2L3 Student GuideDocument6 pagesU2L3 Student GuideMemee MememmNo ratings yet
- 2 Organ SystemsDocument5 pages2 Organ SystemsBeaNo ratings yet
- Q2 Summative Test 1 ScienceDocument2 pagesQ2 Summative Test 1 ScienceHERRENELLE DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Exploring Health CareersDocument6 pagesExploring Health Careersapi-263127781No ratings yet
- U1L8 Student Guide - 2Document5 pagesU1L8 Student Guide - 2jonahNo ratings yet
- 3RD Summative Exam in Science 6Document6 pages3RD Summative Exam in Science 6Maricris Palermo Sancio100% (1)
- Human Body System NotesDocument5 pagesHuman Body System NotesShannon BandyNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 9 Q1 WK1 2 The Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsDocument42 pagesSCIENCE 9 Q1 WK1 2 The Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsDanielle SibayNo ratings yet
- PAU1 - S2 L3 - Crash Course 3 - The Chemical Mind - QuestionsDocument3 pagesPAU1 - S2 L3 - Crash Course 3 - The Chemical Mind - QuestionsHiểu AnhNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Science Weeks 1-4 Worksheets - Term 1Document25 pagesGrade 5 Science Weeks 1-4 Worksheets - Term 1darrengotta8No ratings yet
- Reviewer HOPE12Document2 pagesReviewer HOPE12Xin LouNo ratings yet
- Basic Respiratory WebquestDocument8 pagesBasic Respiratory WebquestWidjaya HS TeacherNo ratings yet
- Chapt10 Study OutlineDocument11 pagesChapt10 Study Outlinekombat13_708353334No ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab ManualDocument9 pagesAnaphy Lab ManualKen KanekiNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Concept MapDocument12 pagesNervous System Concept MapJo BrackenNo ratings yet
- Brain Breakthroughs MASTERCLASS Private WorkbookDocument15 pagesBrain Breakthroughs MASTERCLASS Private WorkbookRida ArifNo ratings yet
- Simple Present Other Verbs MedicineDocument8 pagesSimple Present Other Verbs MedicineFernanda VigilNo ratings yet
- Bio ObjectivesDocument110 pagesBio ObjectivesRishiPanduNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesCirculatory SystemAlba CubilloNo ratings yet
- T2 HealthDocument1 pageT2 HealthShirley LauNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 1Document2 pagesLaboratory Activity 1Samantha sanchezNo ratings yet
- The Most Transformative Thing You Can Do For Your Brain TodayDocument1 pageThe Most Transformative Thing You Can Do For Your Brain TodayAnna ZalewaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Anatomy and Physiology NotesDocument6 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Anatomy and Physiology Notesapi-305436791No ratings yet
- 9e CH 7Document19 pages9e CH 7Aeren RhosenNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesLesson 4 Nervous SystemMohammad FalkayNo ratings yet
- 2a. HPW CHP 1 Packet KEYDocument9 pages2a. HPW CHP 1 Packet KEYDiane TorajaNo ratings yet
- Exercises (Basic Human Anatomy and Medical Terminologies)Document7 pagesExercises (Basic Human Anatomy and Medical Terminologies)tomaNo ratings yet
- Study Guide 12 SleepDocument4 pagesStudy Guide 12 SleepSofia Loreen Melo GarciaNo ratings yet
- 9th Grade Nervous System WorksheetDocument2 pages9th Grade Nervous System WorksheetRICKAYLA HAMILTONNo ratings yet
- U2L3 Student GuideDocument6 pagesU2L3 Student GuidethomasNo ratings yet
- Questions:: Activity Sheet No.1Document14 pagesQuestions:: Activity Sheet No.1Raniey MayolNo ratings yet
- Answer Key PDFDocument7 pagesAnswer Key PDFSamantha Bernardo UndaNo ratings yet
- SCRIPTDocument4 pagesSCRIPTTarash JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Reading and Writing AssignmentDocument3 pagesChapter 10 - Reading and Writing Assignmentteemo no JutsuNo ratings yet
- Human Body Focused Notes 2023Document9 pagesHuman Body Focused Notes 2023pickles.squad11No ratings yet
- Bill Nye RespirationDocument1 pageBill Nye RespirationJoseeNo ratings yet
- Science 6 NerveDocument1 pageScience 6 NerveIvan joseph MarianoNo ratings yet
- PE and Health 12 - Module 1Document39 pagesPE and Health 12 - Module 1Stephen Lorenzo A. Doria100% (1)
- VE EFN1 Tests ProgressTest03Document3 pagesVE EFN1 Tests ProgressTest03ivan.n.stanimirovicNo ratings yet
- Progress Test 3 (Units 5-6) : Name: - Date: - Section 1: VocabularyDocument3 pagesProgress Test 3 (Units 5-6) : Name: - Date: - Section 1: VocabularyPaulina CardinaleNo ratings yet
- P6 ScienceDocument3 pagesP6 ScienceJulie Ann LacanilaoNo ratings yet
- Neuroathletics Training for Beginners More Coordination, Agility and Concentration Thanks to Improved Neuroathletics - Incl. 10-Week Plan For Training in Everyday Life.From EverandNeuroathletics Training for Beginners More Coordination, Agility and Concentration Thanks to Improved Neuroathletics - Incl. 10-Week Plan For Training in Everyday Life.No ratings yet
- U1L8 Student Guide - 2Document5 pagesU1L8 Student Guide - 2jonahNo ratings yet
- U1L6 Student Guide - 2Document2 pagesU1L6 Student Guide - 2jonahNo ratings yet
- U1L9 Student Guide (1) - 1Document4 pagesU1L9 Student Guide (1) - 1jonahNo ratings yet
- U2L2 How Are Skills Developed Worksheet-2Document2 pagesU2L2 How Are Skills Developed Worksheet-2jonahNo ratings yet
- Aami Ec11Document60 pagesAami Ec11mdd02No ratings yet
- Zoll M Series Defibrillator Manual PDFDocument111 pagesZoll M Series Defibrillator Manual PDFAhmad TanveerNo ratings yet
- 6 - BLS HandoutDocument18 pages6 - BLS HandoutEastern SamarNo ratings yet
- Basic Life SupportDocument54 pagesBasic Life SupportAdrianNo ratings yet
- Lifepak CR2 Data SheetDocument4 pagesLifepak CR2 Data SheetEnerspect Medical SolutionsNo ratings yet
- 170-VDR JRC JCY-1900 Instruct Manual 2-8-2022Document184 pages170-VDR JRC JCY-1900 Instruct Manual 2-8-2022Gilbert GlobalNo ratings yet
- Umass Lowell PCRDocument1 pageUmass Lowell PCRdandude505No ratings yet
- Penggunaan DC Shock Dan AED: Edward Kusuma, DR., M.Kes., SP - An., KICDocument21 pagesPenggunaan DC Shock Dan AED: Edward Kusuma, DR., M.Kes., SP - An., KICNdalemSanguDunia-AkhiratNo ratings yet
- First Aid and Water Safety #3Document30 pagesFirst Aid and Water Safety #3Ezzee YenNo ratings yet
- BeneHeart D3 Operators ManualDocument208 pagesBeneHeart D3 Operators Manualelectromedicina.esNo ratings yet
- Advanced Life Support Algorithm: Version: July 2016Document45 pagesAdvanced Life Support Algorithm: Version: July 2016Dwi RinaNo ratings yet
- GE Dash Responder - Service ManualDocument100 pagesGE Dash Responder - Service ManualРинат ЖахинNo ratings yet
- CPR 2020Document26 pagesCPR 2020Meeta PanditNo ratings yet
- ACLS - Prone PDFDocument2 pagesACLS - Prone PDFArdian WibowoNo ratings yet
- Jss-2250 2500 (E) 7zpjd0624b (Ed02) Installation ManualDocument136 pagesJss-2250 2500 (E) 7zpjd0624b (Ed02) Installation Manualmark.lobianoNo ratings yet
- 2014 Nissan Leaf Service Repair Manual (Front Axle)Document32 pages2014 Nissan Leaf Service Repair Manual (Front Axle)Engr Ko VictorNo ratings yet
- ACLS Practice TestDocument5 pagesACLS Practice Testprettynpink0867% (3)
- CARDIOVERSION Vs DEFIBRILLATIONDocument7 pagesCARDIOVERSION Vs DEFIBRILLATIONjames garciaNo ratings yet
- Bm8601 Dte-1 Question BankDocument8 pagesBm8601 Dte-1 Question BankTamil TskNo ratings yet
- ck88 en Om b0Document80 pagesck88 en Om b0Zlatko OžanićNo ratings yet
- Code Blue Do You Know What To Do .10 PDFDocument6 pagesCode Blue Do You Know What To Do .10 PDFJoy HavsonNo ratings yet
- BLS For TeacherrDocument166 pagesBLS For TeacherrGavinKarl Mianabanatao100% (1)
- Book 1Document209 pagesBook 1Camilo Arturo Suarez Ballesteros100% (1)
- App Expt 8Document2 pagesApp Expt 8Christine LopezNo ratings yet
- Philips HeartStart XL Defibrillator - Service GuidelineDocument3 pagesPhilips HeartStart XL Defibrillator - Service GuidelineLeandro BitencourtNo ratings yet