Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Peptide Bonds
Peptide Bonds
Uploaded by
Soorya SureshOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Peptide Bonds
Peptide Bonds
Uploaded by
Soorya SureshCopyright:
Available Formats
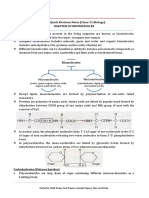
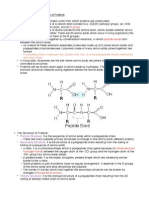
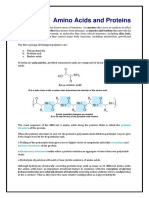
PEPTIDE BONDS
In proteins, amino acids are linked by a peptide bond which is formed when the carboxyl (-COOH)
group of one amino acid reacts with the amino (-NH2) group of the next amino acid with the
elimination of a water moiety (dehydration).
While hydrogen bonds are relatively weak, most biological materials including proteins, sugars, fats,
and nucleic acids are composed of molecules in which the constituent atoms are linked together by
covalent bonds. In covalent bonds, two electrons are shared between the bonding orbitals of the
joined atoms. These bonds range in enthalpic energy from about 250 to 400 kJ/mol with the exact
value depending on the atoms involved. For example, carbon-carbon bonds have an average energy
of 348 kJ/mol, while carbon-nitrogen bonds and carbon-oxygen bonds have energies of 293 kJ/mol
and 358 kJ/mol, respectively. Several specially named covalent bonds have achieved this recognition
in the biological sciences because of their biological importance. However, no other covalent bond
has received the attention of that which joins the amino acid monomers that comprise the
polymeric structures known as peptides and proteins. The basis for the extensive study of covalence
in protein structure lies in the fact that proteins are primarily responsible for catalysing the
innumerable array of chemical reactions that maintain life. Thus, we should begin our consideration
of biological molecules with the study of the amino acids and the peptide bond, which is the
specially named bond that links amino acids into covalent polymeric structures. These structures
include small peptide hormones with fewer than 10 amino acids, up to commonly encountered
proteins with an amino acid content ranging from several hundred to more than one thousand. With
the 20 different amino acids having an average molecular weight (M.W.) of 120 Daltons (Da), the
later values correspond to approximate molecular weights of 1200 Da for a 10 amino acid peptide
and 60,000 Da for a 500 amino acid protein. One of the largest proteins discovered is titin, a muscle
cell protein comprised of 27,000 amino acids with a corresponding M.W. of about 3.2! 106 Da
You might also like
- Ib Biology With Cheryl HickmanDocument3 pagesIb Biology With Cheryl HickmanEric Issel ThomasNo ratings yet
- Biology Lab - Biuret TestDocument7 pagesBiology Lab - Biuret TestZoe Bradshaw0% (1)
- Amino Acids and Their Structure: Cooh-Ch-Nh2 - RDocument12 pagesAmino Acids and Their Structure: Cooh-Ch-Nh2 - RRica NorcioNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry NotesDocument21 pagesBiochemistry NotestariqabuothmanNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION MergedDocument12 pagesINTRODUCTION MergedSoorya SureshNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-01-07 at 1.34.05 PMDocument25 pagesScreenshot 2022-01-07 at 1.34.05 PMPaolaNo ratings yet
- Indira Gandhi National Tribal University Amarkantak, M.P. 484886Document41 pagesIndira Gandhi National Tribal University Amarkantak, M.P. 484886Akanksha LangiwarNo ratings yet
- MolBiol HL (2.1, 2.2,2.3.2.4,7.3) BookletDocument37 pagesMolBiol HL (2.1, 2.2,2.3.2.4,7.3) BookletSeo Young YOONNo ratings yet
- Metabolism Life Life Sciences Botany Medicine Cells: Kim Janxent P. Berlon Grade 9 STE-Platinum (CMT)Document4 pagesMetabolism Life Life Sciences Botany Medicine Cells: Kim Janxent P. Berlon Grade 9 STE-Platinum (CMT)Ronnel Mendoza VasquezNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six, GeneticsDocument10 pagesChapter Six, GeneticsHashim GhazoNo ratings yet
- Biology For The IB Diploma Chapter 2 SummaryDocument8 pagesBiology For The IB Diploma Chapter 2 SummaryJulian WolfgangNo ratings yet
- Chemical Compositions of Protein and CarbohydratesDocument21 pagesChemical Compositions of Protein and CarbohydratesADETOYINBO ADAM ADEWALENo ratings yet
- AP Biology Study GuideDocument69 pagesAP Biology Study GuideEllie GriffinNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lecture 2Document14 pagesBiochemistry Lecture 2Izhan AhmedNo ratings yet
- ProteinsDocument8 pagesProteins10m29satyamsinhaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Biochemistry - Course Notes 1Document8 pagesIntroduction To Biochemistry - Course Notes 1jefov39379No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument84 pagesUntitledTài Nguyễn XuânNo ratings yet
- Tun e Ni.Document9 pagesTun e Ni.LLORITO Cristell Joy M.No ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes Grade 12Document1 pageChemistry Notes Grade 12Hitman KillerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 The Structure and Function of Large Biological MoleculesDocument20 pagesChapter 5 The Structure and Function of Large Biological Moleculesjosue868No ratings yet
- ProteinsDocument43 pagesProteinsBilalNo ratings yet
- Amino AcidsDocument7 pagesAmino Acidsrida khanNo ratings yet
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-09 BiomoleculesDocument5 pagesCBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-09 BiomoleculesSIDHARTH SBNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument10 pagesLab ManualozlemNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 ProteinsDocument140 pagesUnit 7 ProteinsJan Ariel AficialNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3-ProteinsDocument9 pagesLecture 3-ProteinsOminousCroakNo ratings yet
- Mathematics and Science Faculty Makassar State University 2013-2014Document6 pagesMathematics and Science Faculty Makassar State University 2013-2014Embunku Dan PagimuNo ratings yet
- Proteins: Proteins Are Large Biomolecules, or Macromolecules, Consisting of One orDocument15 pagesProteins: Proteins Are Large Biomolecules, or Macromolecules, Consisting of One orKaleem KhanNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Notebook PDFDocument105 pagesAP Biology Notebook PDFعمر gamerNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Carbon CompoundsDocument10 pagesBiochemistry: Carbon Compoundsapi-464344582No ratings yet
- Intro. BiochemistryDocument34 pagesIntro. BiochemistrymerikoNo ratings yet
- 02 BCH101 Lecture 2 ProteinDocument37 pages02 BCH101 Lecture 2 Proteinsharkar1059No ratings yet
- BiochimieDocument11 pagesBiochimieecosysNo ratings yet
- BIO 101 Macromolecules (0) - 091744Document24 pagesBIO 101 Macromolecules (0) - 091744babatundemoyo05No ratings yet
- Chemical BondsDocument12 pagesChemical BondsjillianneramoranNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 Biomolecules Revision Notes1Document42 pagesCBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 Biomolecules Revision Notes1skumarkushwaha504No ratings yet
- NondisjunctionDocument3 pagesNondisjunctionhurainsahar21No ratings yet
- ProteinDocument49 pagesProteinsima mhammedNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 ShortDocument16 pagesChapter - 2 ShortNadeem ArainNo ratings yet
- CarbohydrateDocument45 pagesCarbohydratescropion_78No ratings yet
- Why Study Chemistry? Why Study Chemistry?Document11 pagesWhy Study Chemistry? Why Study Chemistry?mg99997100% (1)
- Amino Acids are linked by peptide bonds to form formed by linking the α-carboxyl group of one amino acid to the α-amino group of another amino acid with a peptide bond (also called an amide bond)Document2 pagesAmino Acids are linked by peptide bonds to form formed by linking the α-carboxyl group of one amino acid to the α-amino group of another amino acid with a peptide bond (also called an amide bond)Noviemae TuandaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions Part II: Week 7: Organic ChemistryDocument24 pagesChemical Reactions Part II: Week 7: Organic Chemistrymia kris quiatchonNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry ProteinDocument71 pagesBiochemistry Proteinurooj ilyasNo ratings yet
- Nutrients of Human MetabolismDocument8 pagesNutrients of Human MetabolismJust meNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory Project: EnzymesDocument7 pagesBiology Investigatory Project: EnzymesTejal NarvekarNo ratings yet
- Functional GroupsDocument39 pagesFunctional GroupstrudyNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport ChainDocument19 pagesElectron Transport Chaingaurav saxenaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in BiochemDocument11 pagesReviewer in BiochemLile RajabaNo ratings yet
- BasicDocument2 pagesBasicapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Biomolecules Notes XIDocument7 pagesBiomolecules Notes XImadam photonNo ratings yet
- Protein Nuclic AcidsDocument30 pagesProtein Nuclic AcidsAlisha TiwariNo ratings yet
- Agricultural University of Georgia Durmishidze Institute of Biochemistry and BiotechnologyDocument63 pagesAgricultural University of Georgia Durmishidze Institute of Biochemistry and BiotechnologyZainab Jamal SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of The Cell The Importance of Carbon Water and Membranes Best Ch022005f 090428000448 Phpapp02Document15 pagesThe Chemistry of The Cell The Importance of Carbon Water and Membranes Best Ch022005f 090428000448 Phpapp02AC QueuNo ratings yet
- PROTEINSDocument17 pagesPROTEINSAbhijat Jha100% (1)
- Biomolecules: MacromoleculesDocument5 pagesBiomolecules: MacromoleculesPaulaNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULESDocument6 pagesBIOMOLECULESzoyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document10 pagesChapter 7AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology for Students: A College Level Study Guide for Life Science and Allied Health MajorsFrom EverandAnatomy and Physiology for Students: A College Level Study Guide for Life Science and Allied Health MajorsNo ratings yet
- Building, Dwelling, Thinking-Critical SummayDocument3 pagesBuilding, Dwelling, Thinking-Critical SummaySoorya SureshNo ratings yet
- Being HumanDocument2 pagesBeing HumanSoorya SureshNo ratings yet
- LCA Calculator IDEMAT 2021Document625 pagesLCA Calculator IDEMAT 2021Soorya SureshNo ratings yet
- BiomimicryDocument2 pagesBiomimicrySoorya SureshNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION MergedDocument12 pagesINTRODUCTION MergedSoorya SureshNo ratings yet
- PolysaccharidesDocument1 pagePolysaccharidesSoorya SureshNo ratings yet
- PROTEINSDocument1 pagePROTEINSSoorya SureshNo ratings yet
- Glycosidic BondsDocument1 pageGlycosidic BondsSoorya SureshNo ratings yet
- LIPIDSDocument1 pageLIPIDSSoorya SureshNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTIONDocument2 pagesINTRODUCTIONSoorya SureshNo ratings yet
- Fatty AcidsDocument1 pageFatty AcidsSoorya SureshNo ratings yet
- NUCLEOTIDESDocument3 pagesNUCLEOTIDESSoorya SureshNo ratings yet
- Amino AcidsDocument1 pageAmino AcidsSoorya SureshNo ratings yet