Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Magnetism 10
Magnetism 10
Uploaded by
C.Madan KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Ship Magnetism and the Magnetic Compass: The Commonwealth and International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Liberal Studies: Navigation and Nautical CoursesFrom EverandShip Magnetism and the Magnetic Compass: The Commonwealth and International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Liberal Studies: Navigation and Nautical CoursesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Magnetism and Matter - Short Notes - Yakeen NEET 2.0 2025 (Legend)Document2 pagesMagnetism and Matter - Short Notes - Yakeen NEET 2.0 2025 (Legend)pathansami1796No ratings yet
- Magnetism and Matter: Important Terms Hysteresis LoopDocument2 pagesMagnetism and Matter: Important Terms Hysteresis LoopChinmay .VNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 AKDocument4 pagesChapter 5 AKSan jayNo ratings yet
- IIT Physics - Magnatism Formula SheetDocument9 pagesIIT Physics - Magnatism Formula SheetParas Thakur100% (1)
- 07-02-24 XPL 2.0 Module Exam 5 SolutionsDocument8 pages07-02-24 XPL 2.0 Module Exam 5 Solutionsrathika1882007No ratings yet
- Magnetism: C Mbsin M BDocument3 pagesMagnetism: C Mbsin M Bmalanga.bangaNo ratings yet
- MAGNETISM AND MATTER ModuleDocument24 pagesMAGNETISM AND MATTER Modulehydr0gen001No ratings yet
- 5 Magnetisms and MatterDocument6 pages5 Magnetisms and MatterSharmaNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and Matter Arihant CBSE CHAPTERWISEDocument16 pagesMagnetism and Matter Arihant CBSE CHAPTERWISEChandNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and MatterDocument15 pagesMagnetism and MatterJinshy VinodNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and Matter Class 12 Short NotesDocument6 pagesMagnetism and Matter Class 12 Short Notesprakhichar1316No ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument19 pagesMagnetismAkash Kumar UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Tangent Law: Category: JEE Main & AdvancedDocument13 pagesTangent Law: Category: JEE Main & AdvancedTanmay HazraNo ratings yet
- 4 MagnetismDocument17 pages4 MagnetismThinkershub11No ratings yet
- BKM - MagnetismDocument26 pagesBKM - Magnetismdny001No ratings yet
- Magnetism and Matter IpeDocument39 pagesMagnetism and Matter IpechennareddyvarshithreddyNo ratings yet
- CH 5 Magnetism & MatterDocument12 pagesCH 5 Magnetism & MatterAkash KoulNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS CHAPTER5 - Cbse Board ProblemsDocument10 pagesPHYSICS CHAPTER5 - Cbse Board ProblemsBharath Kaushik SoundarrajanNo ratings yet
- Chap 05 MagnetismandmatterxiiphysicsncertsolDocument26 pagesChap 05 MagnetismandmatterxiiphysicsncertsolANMOLNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and MatterDocument4 pagesMagnetism and MatterPranshu PatelNo ratings yet
- Revision Tips MagnetismDocument2 pagesRevision Tips Magnetismpadma princessNo ratings yet
- WWW - Magnetostatic AskiitiansDocument12 pagesWWW - Magnetostatic Askiitiansthiripura sundariNo ratings yet
- Moving Charges and MagnetismDocument5 pagesMoving Charges and Magnetismkpmhydro10No ratings yet
- Magnetism NcBNa95Document19 pagesMagnetism NcBNa95caiogabrielNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Properties of MatterDocument28 pagesMagnetic Properties of MatterNikunj BhartiNo ratings yet
- Dia, Para, Ferro, Ferri MagnetikDocument21 pagesDia, Para, Ferro, Ferri Magnetikdyah setyowatiNo ratings yet
- Created by C. Mani, Principal, K V No.1, AFS, Jalahalli West, BangaloreDocument21 pagesCreated by C. Mani, Principal, K V No.1, AFS, Jalahalli West, BangaloreAnaya SajilalNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and Matter Notes by Amit SirDocument7 pagesMagnetism and Matter Notes by Amit SirSarjit PooniaNo ratings yet
- Iit Jee Set BDocument18 pagesIit Jee Set BnehachaudharykauriharNo ratings yet
- 4 Magnetism PDFDocument9 pages4 Magnetism PDFsoumengoswami10No ratings yet
- CHEM442 Lecture37Document29 pagesCHEM442 Lecture37fathur fikranNo ratings yet
- Practice Question & Worksheet For Chapter 5: Class-12 Magnetism and MatterDocument6 pagesPractice Question & Worksheet For Chapter 5: Class-12 Magnetism and Matterfaizanmiro385No ratings yet
- Electro Magnetic Field (EMF)Document42 pagesElectro Magnetic Field (EMF)d anjilappaNo ratings yet
- Ferromagnetism Weiss Theory Domain ModelDocument10 pagesFerromagnetism Weiss Theory Domain Modellittleartz2024No ratings yet
- Homework 8Document1 pageHomework 8Nicolás KozakNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt 18 19 XII Phy Study Package 6 SET 2 Chapter 5Document24 pagesCLS Aipmt 18 19 XII Phy Study Package 6 SET 2 Chapter 5Bharati PatilNo ratings yet
- Paramagnetic Ions: Brillouin Function and Curie LawDocument3 pagesParamagnetic Ions: Brillouin Function and Curie LawGohar Farooq VanceNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and Matter - DPP 01 (Of Lec-02) - Yakeen 2.0 2024 (Legend)Document3 pagesMagnetism and Matter - DPP 01 (Of Lec-02) - Yakeen 2.0 2024 (Legend)Mohammed AsifNo ratings yet
- Magnetism: Classroom Worksheet Practice WorksheetDocument2 pagesMagnetism: Classroom Worksheet Practice WorksheetDance LoverNo ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument3 pagesMagnetismalvin talaveraNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 13: Ntermediate Lectricity and Agnetism YLE UsseDocument2 pagesProblem Set 13: Ntermediate Lectricity and Agnetism YLE UsseKyle BusseNo ratings yet
- Answer Key: PhysicsDocument24 pagesAnswer Key: PhysicsvardeshNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Magnetostatics 2019 PDFDocument11 pagesLecture 3 Magnetostatics 2019 PDFbazharNo ratings yet
- Magnetism & MatterDocument17 pagesMagnetism & Matterkartiksingh46648No ratings yet
- Key - 2610376 - 2024-03-08 03 - 16 - 57 +0000Document8 pagesKey - 2610376 - 2024-03-08 03 - 16 - 57 +0000kishorekumar20010322No ratings yet
- Magnetism and Matter Practice SheetDocument5 pagesMagnetism and Matter Practice Sheetbusinesswork.ytNo ratings yet
- 6 - Magnetism - Solved Exam. Module-4Document5 pages6 - Magnetism - Solved Exam. Module-4Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Magnetism (Solved Ex. & Exciese)Document22 pagesMagnetism (Solved Ex. & Exciese)Chandradeep MandalNo ratings yet
- Magnetics (Practice Questions)Document23 pagesMagnetics (Practice Questions)SakshamNo ratings yet
- CLS ENG 21 22 XII Phy Target 2 Level 2 Chapter 4Document28 pagesCLS ENG 21 22 XII Phy Target 2 Level 2 Chapter 4hari kroviNo ratings yet
- 20 Magnetism and Matter: SolutionsDocument22 pages20 Magnetism and Matter: Solutionssunaarvind1922No ratings yet
- 5 MagnetismDocument20 pages5 MagnetismAyurvaidyaNo ratings yet
- EMlect 10Document16 pagesEMlect 10AjitBabbanNo ratings yet
- Stern-Gerlach ExperimentDocument18 pagesStern-Gerlach ExperimentTailan SarubiNo ratings yet
- NEET Key - 02Document19 pagesNEET Key - 02oraclepucollegecptNo ratings yet
- YCT Moving Charges & Magnetism NEET JEE Practice QuestionsDocument189 pagesYCT Moving Charges & Magnetism NEET JEE Practice Questionstechnicalfacts31100% (1)
- Aircraft PropulsionDocument3 pagesAircraft PropulsionFahmi AbdillahNo ratings yet
- NEET Magnetic Effects of Current Important QuestionsDocument30 pagesNEET Magnetic Effects of Current Important QuestionsitsnithyahereNo ratings yet
- Geophysical Field Theory and Method, Part B: Electromagnetic Fields IFrom EverandGeophysical Field Theory and Method, Part B: Electromagnetic Fields INo ratings yet
- Gravitation TheoryDocument16 pagesGravitation TheoryC.Madan KumarNo ratings yet
- Oscillations 6Document2 pagesOscillations 6C.Madan KumarNo ratings yet
- Kinematics 2Document3 pagesKinematics 2C.Madan KumarNo ratings yet
- Heat and Thermodynamics-8Document3 pagesHeat and Thermodynamics-8C.Madan KumarNo ratings yet
- Dia, para and Ferro Magnetic SubstancesDocument9 pagesDia, para and Ferro Magnetic SubstancesSridhar NNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and MatterDocument6 pagesMagnetism and MatterGranth SinghNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and Matter Class DiscussionDocument6 pagesMagnetism and Matter Class DiscussionNajilaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Materials and ApplicationsDocument12 pagesMagnetic Materials and Applicationsbodavijayteja007No ratings yet
- CH 5 Magnetism & MatterDocument12 pagesCH 5 Magnetism & MatterAkash KoulNo ratings yet
- 5-Electromagnetism Multiple Choice Questions PDFDocument18 pages5-Electromagnetism Multiple Choice Questions PDFdagnaw megbaruNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument14 pagesPhysics Projectrgmaran06No ratings yet
- L.J Institute of Engineering and Technology Physics Question BankDocument12 pagesL.J Institute of Engineering and Technology Physics Question BankChacha PatelNo ratings yet
- Superparamagnetism: Neel Relaxation TimeDocument7 pagesSuperparamagnetism: Neel Relaxation TimeYhomn AcerNo ratings yet
- Simulation of FerrimagnetismDocument3 pagesSimulation of FerrimagnetismqdharryNo ratings yet
- Soft and Hard Magnetic MaterialsDocument24 pagesSoft and Hard Magnetic MaterialsVarsha PraburamNo ratings yet
- PHY 103 Practice Problem Set - 8 IITK /ynm May 20, 2021Document2 pagesPHY 103 Practice Problem Set - 8 IITK /ynm May 20, 2021RAJ MEENANo ratings yet
- Solid State Physics Chapter 7 DielectricDocument41 pagesSolid State Physics Chapter 7 DielectricJudy JanaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class-12 Physics Quick Revision Notes Chapter-05: Magnetism and MatterDocument2 pagesCBSE Class-12 Physics Quick Revision Notes Chapter-05: Magnetism and Matter8D Audio TuneNo ratings yet
- Paramagnetic Materials - Google SearchDocument1 pageParamagnetic Materials - Google SearchAddo SakahNo ratings yet
- Magneitism and Hystersis PosterDocument6 pagesMagneitism and Hystersis PosterHet ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Cuet Question Practice Coordination CompoundsDocument11 pagesCuet Question Practice Coordination CompoundsShuttle TrustNo ratings yet
- Magnetic MaterialsDocument73 pagesMagnetic Materialsbb21csb0b07No ratings yet
- 10 Magnetic PropertiesDocument24 pages10 Magnetic PropertieshNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and Matter - Short Notes - Yakeen NEET 2.0 2025 (Legend)Document2 pagesMagnetism and Matter - Short Notes - Yakeen NEET 2.0 2025 (Legend)pathansami1796No ratings yet
- Poster Modelling ExchangeDocument1 pagePoster Modelling Exchangejose.costilla.pNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 4 - ppt-1Document49 pagesUNIT - 4 - ppt-1Neha YarapothuNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between Hard and Soft Magnetic MaterialsDocument2 pagesComparison Between Hard and Soft Magnetic MaterialsUtkarsh [ NIT Aurangabad ]100% (1)
- Magnetism and Matter - 231006 - 224401Document13 pagesMagnetism and Matter - 231006 - 224401patelsur2No ratings yet
- Magnetic MaterialsDocument26 pagesMagnetic MaterialsVinit VikasNo ratings yet
- Ling Zhou Mag SensorsDocument22 pagesLing Zhou Mag SensorsAboDilanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15: Magnetic Properties WHY STUDY The Magnetic Properties of Materials?Document21 pagesChapter 15: Magnetic Properties WHY STUDY The Magnetic Properties of Materials?Thành Phương TấnNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and Matter - 5 (I) Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument8 pagesMagnetism and Matter - 5 (I) Multiple Choice QuestionsFact's FactoryNo ratings yet
- Magnetism in Condensed Matter 1s1okeznovDocument5 pagesMagnetism in Condensed Matter 1s1okeznovivribappsNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Properties: Diamagnetism, Paramagnetism, Ferromagnetism, Antiferromagnetisn and FerrimagnetismDocument29 pagesMagnetic Properties: Diamagnetism, Paramagnetism, Ferromagnetism, Antiferromagnetisn and Ferrimagnetismnimdie jacksonNo ratings yet
Magnetism 10
Magnetism 10
Uploaded by
C.Madan KumarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Magnetism 10
Magnetism 10
Uploaded by
C.Madan KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
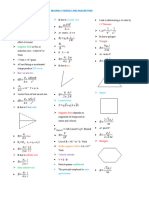
Chapter – 10
MAGNETISM
1. Introduction:
2. Earth’s Magnetic Field and Magnetic Elements:
- Causes of Earth’s magnetism.
- Bar Magnets.
- Basic properties of bar magnets.
→ →
2
- Magnetic Moments - Definition [ M = m(2l ) Am ].
- Magnetic Field - Definition.
→
→F N
B=
- Magnetic Induction - Definition [ m m ].
- Magnetic lines of forces [Definition] and its properties.
→ →
- Magnetic Flux - Definition [ φ = B . A ] and Magnetic flux density - Definition.
- Uniform and Non-Uniform magnetic field.
3. Forces between two magnetic poles.
μ m 1 m2
F= N
- Coulomb’s Inverse Square Law: Definition - [ 4 π d2 ].
4. Magnetic Induction at a point along the axial line due to a magnetic dipole (Bar magnet):
μ0 2 M
B= .
[ 4 π d3 ]
5. Magnetic Induction at a point along the equatorial line due to a magnetic dipole of a Bar
μ0 M
magnet: B= .
4 π d3
6. Mapping of magnetic field due to a bar magnet:
- Magnet placed with its north pole facing geographic north:
μ0 M
B= = Bh .
4π 3
2 2 2
( d +l )
- Magnet placed with its south pole facing geographic north:
C.Madan Kumar – CATALYZE CENTER FOR LEARNING Page 1
μ0 2 Md
B= = Bh .
4 π (d 2 −l 2 )2
→ → →
7. Torque on a bar magnet placed in a uniform magnetic field: [ τ = M ×B ].
B1
tan θ =
8. TANGENT LAW: Definition - [ B 2 ].
9. Deflection Magnetometer:
- End-on (or) Tan A Position:
μ0 2 Md
B= = Bh tan θ .
4 π (d 2 −l 2 )2
Comparison of magnetic moments of two bar magnets:
(a) Deflection method:
2 2
M1 d 1−l 1 d 2 tan θ I
= 2 2
M2 d 2−l 2 d 1 tan θ II .
(b) Null deflection Method:
3
M 1 d1
=
M 2 d 32
.
- Broad-Side on (or) Tan B Position:
μ0 M
= Bh tan θ.
4 π d3
Comparison of magnetic moments of two bar magnets:
(a) Deflection method:
3
M1 ( d 21 +l 21 ) 2 tan θ I
=
M2 3 tan θ II
( d 22 +l 22 ) 2 .
(b) Null deflection Method:
M 1 d 31
=
M 2 d 32
.
10. Magnetic Properties of materials:
- Magnetizing field (or) Magnetic Intensity [H] - Definition.
C.Madan Kumar – CATALYZE CENTER FOR LEARNING Page 2
μ B
μr = (or ) μ =
- Magnetic Permeability – Definition [
μ0 H ].
M −1 m
I= Am (or ) I =
- Intensity of magnetization – Definition [ V A ].
- Magnetic Induction – Definition [ B = μ 0 ( H +I ) ].
I
χm = No unit
- Magnetic Susceptibility – Definition [ H ].
- Relation between
χ m and μ r .
11. Classification of Magnetic material:
- Properties of Diamagnetic substances.
- Properties of Paramagnetic substances.
- Properties of Ferromagnetic substances.
12. Hysteresis and Hysteresis loss:
- Uses of Ferromagnetic materials:
(a) Permanent magnets.
(b) Electromagnets.
(c) Core of the transformer.
(d) Magnetic tapes and memory stores.
--oo00oo--
C.Madan Kumar – CATALYZE CENTER FOR LEARNING Page 3
You might also like
- Ship Magnetism and the Magnetic Compass: The Commonwealth and International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Liberal Studies: Navigation and Nautical CoursesFrom EverandShip Magnetism and the Magnetic Compass: The Commonwealth and International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Liberal Studies: Navigation and Nautical CoursesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Magnetism and Matter - Short Notes - Yakeen NEET 2.0 2025 (Legend)Document2 pagesMagnetism and Matter - Short Notes - Yakeen NEET 2.0 2025 (Legend)pathansami1796No ratings yet
- Magnetism and Matter: Important Terms Hysteresis LoopDocument2 pagesMagnetism and Matter: Important Terms Hysteresis LoopChinmay .VNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 AKDocument4 pagesChapter 5 AKSan jayNo ratings yet
- IIT Physics - Magnatism Formula SheetDocument9 pagesIIT Physics - Magnatism Formula SheetParas Thakur100% (1)
- 07-02-24 XPL 2.0 Module Exam 5 SolutionsDocument8 pages07-02-24 XPL 2.0 Module Exam 5 Solutionsrathika1882007No ratings yet
- Magnetism: C Mbsin M BDocument3 pagesMagnetism: C Mbsin M Bmalanga.bangaNo ratings yet
- MAGNETISM AND MATTER ModuleDocument24 pagesMAGNETISM AND MATTER Modulehydr0gen001No ratings yet
- 5 Magnetisms and MatterDocument6 pages5 Magnetisms and MatterSharmaNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and Matter Arihant CBSE CHAPTERWISEDocument16 pagesMagnetism and Matter Arihant CBSE CHAPTERWISEChandNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and MatterDocument15 pagesMagnetism and MatterJinshy VinodNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and Matter Class 12 Short NotesDocument6 pagesMagnetism and Matter Class 12 Short Notesprakhichar1316No ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument19 pagesMagnetismAkash Kumar UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Tangent Law: Category: JEE Main & AdvancedDocument13 pagesTangent Law: Category: JEE Main & AdvancedTanmay HazraNo ratings yet
- 4 MagnetismDocument17 pages4 MagnetismThinkershub11No ratings yet
- BKM - MagnetismDocument26 pagesBKM - Magnetismdny001No ratings yet
- Magnetism and Matter IpeDocument39 pagesMagnetism and Matter IpechennareddyvarshithreddyNo ratings yet
- CH 5 Magnetism & MatterDocument12 pagesCH 5 Magnetism & MatterAkash KoulNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS CHAPTER5 - Cbse Board ProblemsDocument10 pagesPHYSICS CHAPTER5 - Cbse Board ProblemsBharath Kaushik SoundarrajanNo ratings yet
- Chap 05 MagnetismandmatterxiiphysicsncertsolDocument26 pagesChap 05 MagnetismandmatterxiiphysicsncertsolANMOLNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and MatterDocument4 pagesMagnetism and MatterPranshu PatelNo ratings yet
- Revision Tips MagnetismDocument2 pagesRevision Tips Magnetismpadma princessNo ratings yet
- WWW - Magnetostatic AskiitiansDocument12 pagesWWW - Magnetostatic Askiitiansthiripura sundariNo ratings yet
- Moving Charges and MagnetismDocument5 pagesMoving Charges and Magnetismkpmhydro10No ratings yet
- Magnetism NcBNa95Document19 pagesMagnetism NcBNa95caiogabrielNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Properties of MatterDocument28 pagesMagnetic Properties of MatterNikunj BhartiNo ratings yet
- Dia, Para, Ferro, Ferri MagnetikDocument21 pagesDia, Para, Ferro, Ferri Magnetikdyah setyowatiNo ratings yet
- Created by C. Mani, Principal, K V No.1, AFS, Jalahalli West, BangaloreDocument21 pagesCreated by C. Mani, Principal, K V No.1, AFS, Jalahalli West, BangaloreAnaya SajilalNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and Matter Notes by Amit SirDocument7 pagesMagnetism and Matter Notes by Amit SirSarjit PooniaNo ratings yet
- Iit Jee Set BDocument18 pagesIit Jee Set BnehachaudharykauriharNo ratings yet
- 4 Magnetism PDFDocument9 pages4 Magnetism PDFsoumengoswami10No ratings yet
- CHEM442 Lecture37Document29 pagesCHEM442 Lecture37fathur fikranNo ratings yet
- Practice Question & Worksheet For Chapter 5: Class-12 Magnetism and MatterDocument6 pagesPractice Question & Worksheet For Chapter 5: Class-12 Magnetism and Matterfaizanmiro385No ratings yet
- Electro Magnetic Field (EMF)Document42 pagesElectro Magnetic Field (EMF)d anjilappaNo ratings yet
- Ferromagnetism Weiss Theory Domain ModelDocument10 pagesFerromagnetism Weiss Theory Domain Modellittleartz2024No ratings yet
- Homework 8Document1 pageHomework 8Nicolás KozakNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt 18 19 XII Phy Study Package 6 SET 2 Chapter 5Document24 pagesCLS Aipmt 18 19 XII Phy Study Package 6 SET 2 Chapter 5Bharati PatilNo ratings yet
- Paramagnetic Ions: Brillouin Function and Curie LawDocument3 pagesParamagnetic Ions: Brillouin Function and Curie LawGohar Farooq VanceNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and Matter - DPP 01 (Of Lec-02) - Yakeen 2.0 2024 (Legend)Document3 pagesMagnetism and Matter - DPP 01 (Of Lec-02) - Yakeen 2.0 2024 (Legend)Mohammed AsifNo ratings yet
- Magnetism: Classroom Worksheet Practice WorksheetDocument2 pagesMagnetism: Classroom Worksheet Practice WorksheetDance LoverNo ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument3 pagesMagnetismalvin talaveraNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 13: Ntermediate Lectricity and Agnetism YLE UsseDocument2 pagesProblem Set 13: Ntermediate Lectricity and Agnetism YLE UsseKyle BusseNo ratings yet
- Answer Key: PhysicsDocument24 pagesAnswer Key: PhysicsvardeshNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Magnetostatics 2019 PDFDocument11 pagesLecture 3 Magnetostatics 2019 PDFbazharNo ratings yet
- Magnetism & MatterDocument17 pagesMagnetism & Matterkartiksingh46648No ratings yet
- Key - 2610376 - 2024-03-08 03 - 16 - 57 +0000Document8 pagesKey - 2610376 - 2024-03-08 03 - 16 - 57 +0000kishorekumar20010322No ratings yet
- Magnetism and Matter Practice SheetDocument5 pagesMagnetism and Matter Practice Sheetbusinesswork.ytNo ratings yet
- 6 - Magnetism - Solved Exam. Module-4Document5 pages6 - Magnetism - Solved Exam. Module-4Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Magnetism (Solved Ex. & Exciese)Document22 pagesMagnetism (Solved Ex. & Exciese)Chandradeep MandalNo ratings yet
- Magnetics (Practice Questions)Document23 pagesMagnetics (Practice Questions)SakshamNo ratings yet
- CLS ENG 21 22 XII Phy Target 2 Level 2 Chapter 4Document28 pagesCLS ENG 21 22 XII Phy Target 2 Level 2 Chapter 4hari kroviNo ratings yet
- 20 Magnetism and Matter: SolutionsDocument22 pages20 Magnetism and Matter: Solutionssunaarvind1922No ratings yet
- 5 MagnetismDocument20 pages5 MagnetismAyurvaidyaNo ratings yet
- EMlect 10Document16 pagesEMlect 10AjitBabbanNo ratings yet
- Stern-Gerlach ExperimentDocument18 pagesStern-Gerlach ExperimentTailan SarubiNo ratings yet
- NEET Key - 02Document19 pagesNEET Key - 02oraclepucollegecptNo ratings yet
- YCT Moving Charges & Magnetism NEET JEE Practice QuestionsDocument189 pagesYCT Moving Charges & Magnetism NEET JEE Practice Questionstechnicalfacts31100% (1)
- Aircraft PropulsionDocument3 pagesAircraft PropulsionFahmi AbdillahNo ratings yet
- NEET Magnetic Effects of Current Important QuestionsDocument30 pagesNEET Magnetic Effects of Current Important QuestionsitsnithyahereNo ratings yet
- Geophysical Field Theory and Method, Part B: Electromagnetic Fields IFrom EverandGeophysical Field Theory and Method, Part B: Electromagnetic Fields INo ratings yet
- Gravitation TheoryDocument16 pagesGravitation TheoryC.Madan KumarNo ratings yet
- Oscillations 6Document2 pagesOscillations 6C.Madan KumarNo ratings yet
- Kinematics 2Document3 pagesKinematics 2C.Madan KumarNo ratings yet
- Heat and Thermodynamics-8Document3 pagesHeat and Thermodynamics-8C.Madan KumarNo ratings yet
- Dia, para and Ferro Magnetic SubstancesDocument9 pagesDia, para and Ferro Magnetic SubstancesSridhar NNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and MatterDocument6 pagesMagnetism and MatterGranth SinghNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and Matter Class DiscussionDocument6 pagesMagnetism and Matter Class DiscussionNajilaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Materials and ApplicationsDocument12 pagesMagnetic Materials and Applicationsbodavijayteja007No ratings yet
- CH 5 Magnetism & MatterDocument12 pagesCH 5 Magnetism & MatterAkash KoulNo ratings yet
- 5-Electromagnetism Multiple Choice Questions PDFDocument18 pages5-Electromagnetism Multiple Choice Questions PDFdagnaw megbaruNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument14 pagesPhysics Projectrgmaran06No ratings yet
- L.J Institute of Engineering and Technology Physics Question BankDocument12 pagesL.J Institute of Engineering and Technology Physics Question BankChacha PatelNo ratings yet
- Superparamagnetism: Neel Relaxation TimeDocument7 pagesSuperparamagnetism: Neel Relaxation TimeYhomn AcerNo ratings yet
- Simulation of FerrimagnetismDocument3 pagesSimulation of FerrimagnetismqdharryNo ratings yet
- Soft and Hard Magnetic MaterialsDocument24 pagesSoft and Hard Magnetic MaterialsVarsha PraburamNo ratings yet
- PHY 103 Practice Problem Set - 8 IITK /ynm May 20, 2021Document2 pagesPHY 103 Practice Problem Set - 8 IITK /ynm May 20, 2021RAJ MEENANo ratings yet
- Solid State Physics Chapter 7 DielectricDocument41 pagesSolid State Physics Chapter 7 DielectricJudy JanaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class-12 Physics Quick Revision Notes Chapter-05: Magnetism and MatterDocument2 pagesCBSE Class-12 Physics Quick Revision Notes Chapter-05: Magnetism and Matter8D Audio TuneNo ratings yet
- Paramagnetic Materials - Google SearchDocument1 pageParamagnetic Materials - Google SearchAddo SakahNo ratings yet
- Magneitism and Hystersis PosterDocument6 pagesMagneitism and Hystersis PosterHet ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Cuet Question Practice Coordination CompoundsDocument11 pagesCuet Question Practice Coordination CompoundsShuttle TrustNo ratings yet
- Magnetic MaterialsDocument73 pagesMagnetic Materialsbb21csb0b07No ratings yet
- 10 Magnetic PropertiesDocument24 pages10 Magnetic PropertieshNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and Matter - Short Notes - Yakeen NEET 2.0 2025 (Legend)Document2 pagesMagnetism and Matter - Short Notes - Yakeen NEET 2.0 2025 (Legend)pathansami1796No ratings yet
- Poster Modelling ExchangeDocument1 pagePoster Modelling Exchangejose.costilla.pNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 4 - ppt-1Document49 pagesUNIT - 4 - ppt-1Neha YarapothuNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between Hard and Soft Magnetic MaterialsDocument2 pagesComparison Between Hard and Soft Magnetic MaterialsUtkarsh [ NIT Aurangabad ]100% (1)
- Magnetism and Matter - 231006 - 224401Document13 pagesMagnetism and Matter - 231006 - 224401patelsur2No ratings yet
- Magnetic MaterialsDocument26 pagesMagnetic MaterialsVinit VikasNo ratings yet
- Ling Zhou Mag SensorsDocument22 pagesLing Zhou Mag SensorsAboDilanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15: Magnetic Properties WHY STUDY The Magnetic Properties of Materials?Document21 pagesChapter 15: Magnetic Properties WHY STUDY The Magnetic Properties of Materials?Thành Phương TấnNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and Matter - 5 (I) Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument8 pagesMagnetism and Matter - 5 (I) Multiple Choice QuestionsFact's FactoryNo ratings yet
- Magnetism in Condensed Matter 1s1okeznovDocument5 pagesMagnetism in Condensed Matter 1s1okeznovivribappsNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Properties: Diamagnetism, Paramagnetism, Ferromagnetism, Antiferromagnetisn and FerrimagnetismDocument29 pagesMagnetic Properties: Diamagnetism, Paramagnetism, Ferromagnetism, Antiferromagnetisn and Ferrimagnetismnimdie jacksonNo ratings yet