Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Math9 q3 Wk1 Las2
Math9 q3 Wk1 Las2
Uploaded by
SHEILA MAE CABASAGCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- DLL Math 9Document3 pagesDLL Math 9SHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy Statistics Midterms - Hypothesis TestingDocument41 pagesPharmacy Statistics Midterms - Hypothesis TestingKaguraNo ratings yet
- API 650-Annex PDocument8 pagesAPI 650-Annex PSachinNo ratings yet
- You'Re On Consulting For Peak Performance-ManteshDocument272 pagesYou'Re On Consulting For Peak Performance-ManteshtaeBoNo ratings yet
- Chinese ATS YsuyangDocument16 pagesChinese ATS YsuyangLeo Burns100% (8)
- Math 9-Q3-Module-1Document11 pagesMath 9-Q3-Module-1Jeanette Agumbay AgunosNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 3rd QuarterDocument13 pagesGrade 9 3rd QuarterElija Fernan De JesusNo ratings yet
- Topic F. Angles and Construction of DiagramsDocument18 pagesTopic F. Angles and Construction of Diagramslikad9730No ratings yet
- G8 Math Q3 Module-2Document18 pagesG8 Math Q3 Module-2Elijah Shamir A. RefugioNo ratings yet
- Angles and Constructions: SampleDocument21 pagesAngles and Constructions: SamplePooja SharmaNo ratings yet
- What Are You Going To Learn?: Parallelograms. Those Parallelograms Have Equal Forms and SizesDocument6 pagesWhat Are You Going To Learn?: Parallelograms. Those Parallelograms Have Equal Forms and SizesF X AGUS SISWANTONo ratings yet
- Nebre Mathematics 9 Monthly Third QuarterDocument3 pagesNebre Mathematics 9 Monthly Third QuarterChristian nebreNo ratings yet
- Items Object Name Draw: Is It A Parallelogram Yes / NoDocument21 pagesItems Object Name Draw: Is It A Parallelogram Yes / NoErika PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Polygon Vocabulary. Triangle VocabularyDocument7 pagesPolygon Vocabulary. Triangle VocabularyBill LauloNo ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument18 pagesMathematicsSkyler MontalvoNo ratings yet
- SimilarityDocument20 pagesSimilarityK.s.AarvindSundarNo ratings yet
- SimilarityDocument20 pagesSimilarityK.s.AarvindSundar100% (1)
- ParallelogramsDocument4 pagesParallelogramsYurizkaMeliaSariNo ratings yet
- Lines and Angles - Definitions & PropertiesDocument7 pagesLines and Angles - Definitions & PropertiesArijit DeyNo ratings yet
- GRADE9 - MATH-0417 - Solve Problem On QuadrilateralDocument17 pagesGRADE9 - MATH-0417 - Solve Problem On QuadrilateralJea HestiaNo ratings yet
- Math - Lesson1 - Parallelogram and Its PropertiesDocument9 pagesMath - Lesson1 - Parallelogram and Its PropertiesFree TemplatesNo ratings yet
- Math 7 Quarter 3 Week 2Document6 pagesMath 7 Quarter 3 Week 2Lots KieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 and 8Document52 pagesChapter 7 and 8api-385932886No ratings yet
- 9Document14 pages9api-332361871No ratings yet
- My Honeybunchsugarplumplumwalangmakakapantaysayosweetiecutiepie NotebookDocument18 pagesMy Honeybunchsugarplumplumwalangmakakapantaysayosweetiecutiepie NotebookJhayNo ratings yet
- 3 SimilarityDocument18 pages3 SimilarityLEOGIE LAMUJERNo ratings yet
- Math 7 - Q3 - Week 2 - Module 2 - Relationships of Geometric Figures - For Reproduction - Rev2021Document18 pagesMath 7 - Q3 - Week 2 - Module 2 - Relationships of Geometric Figures - For Reproduction - Rev2021V.G. Lopez Aspirin100% (1)
- G9 Math Q3 - Week 6 - Similarity FiguresDocument21 pagesG9 Math Q3 - Week 6 - Similarity FiguresDivina BattadNo ratings yet
- Parallel Secant and Perpendicular LinesDocument9 pagesParallel Secant and Perpendicular LinesScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Key Concept Overview: Grade 8 - Module 3 - Topic B - Lessons 8-12Document2 pagesKey Concept Overview: Grade 8 - Module 3 - Topic B - Lessons 8-12api-421158925No ratings yet
- Parallel and Perpendicular LinesDocument47 pagesParallel and Perpendicular LinesLilian YusayNo ratings yet
- Ed Neil O. Maratas: Instructor Jrmsu - Main CampusDocument15 pagesEd Neil O. Maratas: Instructor Jrmsu - Main Campusedniel maratasNo ratings yet
- Third Quarter Examination Grade 9 - Mathematics NAME: - DATE: - SCORE: - General RulesDocument3 pagesThird Quarter Examination Grade 9 - Mathematics NAME: - DATE: - SCORE: - General RulesJeo HuminisNo ratings yet
- G-9 QuadrilateralsNotesDocument23 pagesG-9 QuadrilateralsNotesNysee Tamayo FerrerNo ratings yet
- Geom 7-2Document14 pagesGeom 7-2Ahmed MohamedNo ratings yet
- Quant - Geometry (Level 2) - English - 1635297533Document39 pagesQuant - Geometry (Level 2) - English - 1635297533NathiyashyamNo ratings yet
- Parallelograms TheoremsDocument42 pagesParallelograms TheoremsEstepanie GopetNo ratings yet
- Unit 6Document43 pagesUnit 6Game GeeksNo ratings yet
- CH-22 Geometrical Vocabulary and Constructions (Answers)Document3 pagesCH-22 Geometrical Vocabulary and Constructions (Answers)Divleen KaurNo ratings yet
- G 9 QuadrilateralsNotesDocument42 pagesG 9 QuadrilateralsNotesHomer SotoNo ratings yet
- Classification of QuadrilateralDocument5 pagesClassification of QuadrilateralPatricia SamsonNo ratings yet
- 10 Parallel LinesDocument75 pages10 Parallel Linesbg558697No ratings yet
- DLP g10 Math 2nd QTR Week 7 FinalDocument13 pagesDLP g10 Math 2nd QTR Week 7 FinalCei-Cei100% (1)
- G7-Q3-4-Angle PairsDocument5 pagesG7-Q3-4-Angle PairsLowela Joy SalemNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 1Document18 pagesMathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 1Menchie Morales Villamosada SolasNo ratings yet
- Shape 4 MathsDocument2 pagesShape 4 Mathstranthihuong205No ratings yet
- Yr12 Maths in Focus 2U HSCDocument412 pagesYr12 Maths in Focus 2U HSCRichard Yang93% (14)
- Greetings: Teacher'S Activity A. Preparatory ActivitiesDocument13 pagesGreetings: Teacher'S Activity A. Preparatory ActivitiesAllyza S. MarohomNo ratings yet
- Eucledan GeometryDocument39 pagesEucledan GeometryUrsula VersterNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION GEOMETRY ch4Document24 pagesINTRODUCTION GEOMETRY ch4Jama abdi ibraahim100% (1)
- Perpendicular and Parallel Lines Worksheet 1Document8 pagesPerpendicular and Parallel Lines Worksheet 1eelaine kohNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2015Document10 pagesPresentation 2015api-255819814No ratings yet
- Triangle SimilaritiesDocument44 pagesTriangle Similaritiesworldoftanks.blitzloverNo ratings yet
- Math 7 TQDocument7 pagesMath 7 TQAPPLE JOY YONSONNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesLesson PlanLa MuérteNo ratings yet
- Geometry Midterm ModuleDocument8 pagesGeometry Midterm Modulesarah miinggNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument29 pagesGeometrykhushivanshNo ratings yet
- Similarity Congr Uence Activity ThreeDocument2 pagesSimilarity Congr Uence Activity ThreeRahul ManwatkarNo ratings yet
- LAS Q3 Weeks 3 To 4Document16 pagesLAS Q3 Weeks 3 To 4Miel GaboniNo ratings yet
- Triangle Congruence M2Document29 pagesTriangle Congruence M2Joel BulawanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics (2 Unit) : Based On 1983 Syllabus, Written in 2004Document16 pagesMathematics (2 Unit) : Based On 1983 Syllabus, Written in 2004PaulNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other PolygonsFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other PolygonsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Blaze Through the GRE 120 Quantitative Exercises and ExplanationsFrom EverandBlaze Through the GRE 120 Quantitative Exercises and ExplanationsNo ratings yet
- Travel and Pakyaw Agreement For 2023Document4 pagesTravel and Pakyaw Agreement For 2023SHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Hands-On PolygonDocument36 pagesHands-On PolygonSHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Math9 q3 Wk1 Las3Document1 pageMath9 q3 Wk1 Las3SHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- INSET Completion ReportDocument31 pagesINSET Completion ReportSHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Torqueza - Math - Q2 - Commutative Property of MultiplicationDocument5 pagesTorqueza - Math - Q2 - Commutative Property of MultiplicationSHEILA MAE CABASAG100% (2)
- LES QUARTERLY SOB 2023 Ron VDocument4 pagesLES QUARTERLY SOB 2023 Ron VSHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Myrna Palomas - Data Gathering Using Forms in MS WordDocument34 pagesMyrna Palomas - Data Gathering Using Forms in MS WordSHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Sample Mid-Year Opcrf Review 2021-2022Document18 pagesSample Mid-Year Opcrf Review 2021-2022SHEILA MAE CABASAG100% (1)
- Jecson Oafallas - Setting Up Office RemoteDocument34 pagesJecson Oafallas - Setting Up Office RemoteSHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 CertificatesDocument7 pagesQuarter 2 CertificatesSHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Aj Sports Price Quotation Liberty National High School FinalDocument1 pageAj Sports Price Quotation Liberty National High School FinalSHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Warren Ambat - Excel in Daily Attendance (Deped Form)Document35 pagesWarren Ambat - Excel in Daily Attendance (Deped Form)SHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Tampakan 1, 2, 3Document9 pagesDepartment of Education: Tampakan 1, 2, 3SHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- AppendixF PMCFDocument1 pageAppendixF PMCFSHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- NV No. 2023 008 HT Iiiiiv SecondaryDocument7 pagesNV No. 2023 008 HT Iiiiiv SecondarySHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Mid Year Program Review and Evaluation MPRE 2016Document4 pagesMid Year Program Review and Evaluation MPRE 2016SHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Community Actio-Wps OfficeDocument20 pagesCommunity Actio-Wps OfficeSHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Enclosure Natg6 Ellna CB Nat12Document22 pagesEnclosure Natg6 Ellna CB Nat12SHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- 1.2 RM CLMD 2023 021 Addendum To RM CLMD 2023 019 Refresher Training Cum Accreditation of 2023 Sraa Meet Technical OfficialsDocument3 pages1.2 RM CLMD 2023 021 Addendum To RM CLMD 2023 019 Refresher Training Cum Accreditation of 2023 Sraa Meet Technical OfficialsSHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- HeaderDocument1 pageHeaderSHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- AppendixE.1 MRF T1-3Document6 pagesAppendixE.1 MRF T1-3SHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Liberty Sped Budget Proposal For Sped Funds For MergeDocument7 pagesLiberty Sped Budget Proposal For Sped Funds For MergeSHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Verified List of Electoral Board For 2022 Nle 1Document21 pagesVerified List of Electoral Board For 2022 Nle 1SHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Class SkedDocument2 pagesClass SkedSHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- School Form 1 (SF 1)Document6 pagesSchool Form 1 (SF 1)SHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- 2021 School Annual Accomplishment ReportDocument312 pages2021 School Annual Accomplishment ReportSHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- School Form 1 (SF 1)Document6 pagesSchool Form 1 (SF 1)SHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesSHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Koronadal Certificate of Non-Availability of Stocks: Product Code Product Description UOM PriceDocument7 pagesKoronadal Certificate of Non-Availability of Stocks: Product Code Product Description UOM PriceSHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- K Ali EntpDocument2 pagesK Ali Entpanim singhNo ratings yet
- BLESSINGS LPT IN THE MAKING TCHR VDocument23 pagesBLESSINGS LPT IN THE MAKING TCHR Vabe BrokenNo ratings yet
- Power Point Math COTDocument39 pagesPower Point Math COTmary jean sumalinogNo ratings yet
- Montessori Nomenclature Solar SystemDocument13 pagesMontessori Nomenclature Solar SystemJulieta NavoneNo ratings yet
- Exalco Albio 102 Curtain Wall SystemsDocument92 pagesExalco Albio 102 Curtain Wall SystemsAdmir MatoshiNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document4 pagesWeek 1Czarina RelleveNo ratings yet
- What Makes A Social Practice? Being, Knowing, Doing and LeadingDocument9 pagesWhat Makes A Social Practice? Being, Knowing, Doing and LeadingFabianaNo ratings yet
- MDLM - Pulsar 150-180 Bs III - Pulsar 135, 180 - 220 Ug +bs IVDocument342 pagesMDLM - Pulsar 150-180 Bs III - Pulsar 135, 180 - 220 Ug +bs IVfederico-500hotmail.comNo ratings yet
- Challenges and Opportunities in Practical Training - Perceptions of Clinical EducationDocument10 pagesChallenges and Opportunities in Practical Training - Perceptions of Clinical EducationJaz TagalagNo ratings yet
- Class 1Document15 pagesClass 1eisha123No ratings yet
- EE420 SyllabusDocument1 pageEE420 Syllabussal1980No ratings yet
- MultipLa - A Tool For The Combined Overall Estimation of Various Types of MMHDocument3 pagesMultipLa - A Tool For The Combined Overall Estimation of Various Types of MMHAfirdie FirdausNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Fluids Day 4Document57 pagesReservoir Fluids Day 4Bella cedricNo ratings yet
- Quality Managementy (11-12) RevisiDocument99 pagesQuality Managementy (11-12) Revisimecca fiandraNo ratings yet
- Exam 9Document3 pagesExam 9Schuller TechNo ratings yet
- Literary Reading Through A Biographical ContextDocument1 pageLiterary Reading Through A Biographical ContexthaydeeNo ratings yet
- Letter Writing Business LettersDocument60 pagesLetter Writing Business LettersAvery Jan SilosNo ratings yet
- 295-Article Text-2269-1-10-20210624Document7 pages295-Article Text-2269-1-10-20210624Rahmat AlfajriNo ratings yet
- What Is Employer BrandingDocument3 pagesWhat Is Employer Brandingsageerpa100% (2)
- TCVN 4244-2005Document179 pagesTCVN 4244-2005Toàn ĐinhNo ratings yet
- 1Panel-Data Unit-Root Tests - StataDocument3 pages1Panel-Data Unit-Root Tests - StataHafizAhmadNo ratings yet
- Babylonjs GameDocument112 pagesBabylonjs GameGeorge DeacNo ratings yet
- Awplaybook v4 PDFDocument152 pagesAwplaybook v4 PDFsyalcinkayaNo ratings yet
- Wireless Telecommunications Is The Transfer of Information Between Two or More Points That Are NotDocument3 pagesWireless Telecommunications Is The Transfer of Information Between Two or More Points That Are NotSuperTotie LandritoNo ratings yet
- Dual Mass FlywheelDocument2 pagesDual Mass FlywheelZimekNo ratings yet
- 03-2-Ceramic Form and Function An Ethnographic Search and An Archeological ApplicationDocument14 pages03-2-Ceramic Form and Function An Ethnographic Search and An Archeological ApplicationDante .jpgNo ratings yet
Math9 q3 Wk1 Las2
Math9 q3 Wk1 Las2
Uploaded by
SHEILA MAE CABASAGOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Math9 q3 Wk1 Las2
Math9 q3 Wk1 Las2
Uploaded by
SHEILA MAE CABASAGCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: Grade & Section: Score:
School: Teacher: Subject: Math 9
LAS Writer: GERFLOR T. LAMBINO Content Editor: MA CARAH KEN TAMBUNGALAN
Lesson Topic: Determining the opposite sides, opposite angles, consecutive angles, segments formed by intersecting
diagonals of parallelogram and their measures & relationship (Quarter 3 Wk 1 LAS 2)
Learning Targets: Determines the conditions that make a quadrilateral a parallelogram.
• Illustrates the measure of sides and angles of polygons. (M9GE-IIIa-2)
Reference(s): Merden L. Bryant, et.al., (2014). Mathematics Grade 9 Learner’s Module, First Edition, Vibal Group, Inc.,
pages 312-314
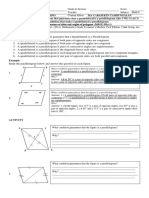
Parallelogram is a quadrilateral with two pairs of opposite sides that are parallel. It also has two pairs of opposite
angles. Two sides of a quadrilateral are called opposite sides if they do not have a common end point. Two angles of a
quadrilateral are called opposite angles if they do not have a common side. Two diagonals can be drawn by connecting
two non-adjacent vertices, and then, two pairs of congruent segments can be formed from each diagonal.
A D
Example: A
E
Quadrilateral ABCD is a parallelogram.
B C
Using the figure above, complete the table. Use ruler and protractor to measure the quantities of parallelogram indicated
below.
Identify the following: Measurement Are the Measurements equal or not? If not equal
identify their relationship
Pairs of opposite sides AD & BC 3cm & 3cm equal
AB & DC 3cm & 3cm equal
Pairs of opposite angles ∠A &∠C 105° & 105° equal
∠B &∠D 75° & 75° equal
∠A &∠B 105° & 75° Not equal (their sum is 180°- supplementary)
Pairs of consecutive ∠A &∠D 105° & 75° Not equal (their sum is 180°- supplementary)
angles ∠C &∠D 105° & 75° Not equal (their sum is 180°- supplementary)
∠C &∠B 105° & 75° Not equal (their sum is 180°- supplementary)
Pairs of segments AE & EC 1.5cm & 1.5cm equal
formed by intersecting
diagonals BE & ED 2cm & 2cm equal
ACTIVITY
Draw a parallelogram, name it as Rhombus LOVE with G as the intersection of the diagonals. Measure the sides,
angles and segments using a ruler and protractor. Complete the table below. Example above is your guide.
Identify the following: Measurement Are the Measurements equal or not? If not equal
identify their relationship
Pairs of opposite sides
Pairs of opposite angles
Pairs of consecutive angles
Pairs of segments formed
by intersecting diagonals
You might also like
- DLL Math 9Document3 pagesDLL Math 9SHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy Statistics Midterms - Hypothesis TestingDocument41 pagesPharmacy Statistics Midterms - Hypothesis TestingKaguraNo ratings yet
- API 650-Annex PDocument8 pagesAPI 650-Annex PSachinNo ratings yet
- You'Re On Consulting For Peak Performance-ManteshDocument272 pagesYou'Re On Consulting For Peak Performance-ManteshtaeBoNo ratings yet
- Chinese ATS YsuyangDocument16 pagesChinese ATS YsuyangLeo Burns100% (8)
- Math 9-Q3-Module-1Document11 pagesMath 9-Q3-Module-1Jeanette Agumbay AgunosNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 3rd QuarterDocument13 pagesGrade 9 3rd QuarterElija Fernan De JesusNo ratings yet
- Topic F. Angles and Construction of DiagramsDocument18 pagesTopic F. Angles and Construction of Diagramslikad9730No ratings yet
- G8 Math Q3 Module-2Document18 pagesG8 Math Q3 Module-2Elijah Shamir A. RefugioNo ratings yet
- Angles and Constructions: SampleDocument21 pagesAngles and Constructions: SamplePooja SharmaNo ratings yet
- What Are You Going To Learn?: Parallelograms. Those Parallelograms Have Equal Forms and SizesDocument6 pagesWhat Are You Going To Learn?: Parallelograms. Those Parallelograms Have Equal Forms and SizesF X AGUS SISWANTONo ratings yet
- Nebre Mathematics 9 Monthly Third QuarterDocument3 pagesNebre Mathematics 9 Monthly Third QuarterChristian nebreNo ratings yet
- Items Object Name Draw: Is It A Parallelogram Yes / NoDocument21 pagesItems Object Name Draw: Is It A Parallelogram Yes / NoErika PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Polygon Vocabulary. Triangle VocabularyDocument7 pagesPolygon Vocabulary. Triangle VocabularyBill LauloNo ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument18 pagesMathematicsSkyler MontalvoNo ratings yet
- SimilarityDocument20 pagesSimilarityK.s.AarvindSundarNo ratings yet
- SimilarityDocument20 pagesSimilarityK.s.AarvindSundar100% (1)
- ParallelogramsDocument4 pagesParallelogramsYurizkaMeliaSariNo ratings yet
- Lines and Angles - Definitions & PropertiesDocument7 pagesLines and Angles - Definitions & PropertiesArijit DeyNo ratings yet
- GRADE9 - MATH-0417 - Solve Problem On QuadrilateralDocument17 pagesGRADE9 - MATH-0417 - Solve Problem On QuadrilateralJea HestiaNo ratings yet
- Math - Lesson1 - Parallelogram and Its PropertiesDocument9 pagesMath - Lesson1 - Parallelogram and Its PropertiesFree TemplatesNo ratings yet
- Math 7 Quarter 3 Week 2Document6 pagesMath 7 Quarter 3 Week 2Lots KieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 and 8Document52 pagesChapter 7 and 8api-385932886No ratings yet
- 9Document14 pages9api-332361871No ratings yet
- My Honeybunchsugarplumplumwalangmakakapantaysayosweetiecutiepie NotebookDocument18 pagesMy Honeybunchsugarplumplumwalangmakakapantaysayosweetiecutiepie NotebookJhayNo ratings yet
- 3 SimilarityDocument18 pages3 SimilarityLEOGIE LAMUJERNo ratings yet
- Math 7 - Q3 - Week 2 - Module 2 - Relationships of Geometric Figures - For Reproduction - Rev2021Document18 pagesMath 7 - Q3 - Week 2 - Module 2 - Relationships of Geometric Figures - For Reproduction - Rev2021V.G. Lopez Aspirin100% (1)
- G9 Math Q3 - Week 6 - Similarity FiguresDocument21 pagesG9 Math Q3 - Week 6 - Similarity FiguresDivina BattadNo ratings yet
- Parallel Secant and Perpendicular LinesDocument9 pagesParallel Secant and Perpendicular LinesScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Key Concept Overview: Grade 8 - Module 3 - Topic B - Lessons 8-12Document2 pagesKey Concept Overview: Grade 8 - Module 3 - Topic B - Lessons 8-12api-421158925No ratings yet
- Parallel and Perpendicular LinesDocument47 pagesParallel and Perpendicular LinesLilian YusayNo ratings yet
- Ed Neil O. Maratas: Instructor Jrmsu - Main CampusDocument15 pagesEd Neil O. Maratas: Instructor Jrmsu - Main Campusedniel maratasNo ratings yet
- Third Quarter Examination Grade 9 - Mathematics NAME: - DATE: - SCORE: - General RulesDocument3 pagesThird Quarter Examination Grade 9 - Mathematics NAME: - DATE: - SCORE: - General RulesJeo HuminisNo ratings yet
- G-9 QuadrilateralsNotesDocument23 pagesG-9 QuadrilateralsNotesNysee Tamayo FerrerNo ratings yet
- Geom 7-2Document14 pagesGeom 7-2Ahmed MohamedNo ratings yet
- Quant - Geometry (Level 2) - English - 1635297533Document39 pagesQuant - Geometry (Level 2) - English - 1635297533NathiyashyamNo ratings yet
- Parallelograms TheoremsDocument42 pagesParallelograms TheoremsEstepanie GopetNo ratings yet
- Unit 6Document43 pagesUnit 6Game GeeksNo ratings yet
- CH-22 Geometrical Vocabulary and Constructions (Answers)Document3 pagesCH-22 Geometrical Vocabulary and Constructions (Answers)Divleen KaurNo ratings yet
- G 9 QuadrilateralsNotesDocument42 pagesG 9 QuadrilateralsNotesHomer SotoNo ratings yet
- Classification of QuadrilateralDocument5 pagesClassification of QuadrilateralPatricia SamsonNo ratings yet
- 10 Parallel LinesDocument75 pages10 Parallel Linesbg558697No ratings yet
- DLP g10 Math 2nd QTR Week 7 FinalDocument13 pagesDLP g10 Math 2nd QTR Week 7 FinalCei-Cei100% (1)
- G7-Q3-4-Angle PairsDocument5 pagesG7-Q3-4-Angle PairsLowela Joy SalemNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 1Document18 pagesMathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 1Menchie Morales Villamosada SolasNo ratings yet
- Shape 4 MathsDocument2 pagesShape 4 Mathstranthihuong205No ratings yet
- Yr12 Maths in Focus 2U HSCDocument412 pagesYr12 Maths in Focus 2U HSCRichard Yang93% (14)
- Greetings: Teacher'S Activity A. Preparatory ActivitiesDocument13 pagesGreetings: Teacher'S Activity A. Preparatory ActivitiesAllyza S. MarohomNo ratings yet
- Eucledan GeometryDocument39 pagesEucledan GeometryUrsula VersterNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION GEOMETRY ch4Document24 pagesINTRODUCTION GEOMETRY ch4Jama abdi ibraahim100% (1)
- Perpendicular and Parallel Lines Worksheet 1Document8 pagesPerpendicular and Parallel Lines Worksheet 1eelaine kohNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2015Document10 pagesPresentation 2015api-255819814No ratings yet
- Triangle SimilaritiesDocument44 pagesTriangle Similaritiesworldoftanks.blitzloverNo ratings yet
- Math 7 TQDocument7 pagesMath 7 TQAPPLE JOY YONSONNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesLesson PlanLa MuérteNo ratings yet
- Geometry Midterm ModuleDocument8 pagesGeometry Midterm Modulesarah miinggNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument29 pagesGeometrykhushivanshNo ratings yet
- Similarity Congr Uence Activity ThreeDocument2 pagesSimilarity Congr Uence Activity ThreeRahul ManwatkarNo ratings yet
- LAS Q3 Weeks 3 To 4Document16 pagesLAS Q3 Weeks 3 To 4Miel GaboniNo ratings yet
- Triangle Congruence M2Document29 pagesTriangle Congruence M2Joel BulawanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics (2 Unit) : Based On 1983 Syllabus, Written in 2004Document16 pagesMathematics (2 Unit) : Based On 1983 Syllabus, Written in 2004PaulNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other PolygonsFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other PolygonsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Blaze Through the GRE 120 Quantitative Exercises and ExplanationsFrom EverandBlaze Through the GRE 120 Quantitative Exercises and ExplanationsNo ratings yet
- Travel and Pakyaw Agreement For 2023Document4 pagesTravel and Pakyaw Agreement For 2023SHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Hands-On PolygonDocument36 pagesHands-On PolygonSHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Math9 q3 Wk1 Las3Document1 pageMath9 q3 Wk1 Las3SHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- INSET Completion ReportDocument31 pagesINSET Completion ReportSHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Torqueza - Math - Q2 - Commutative Property of MultiplicationDocument5 pagesTorqueza - Math - Q2 - Commutative Property of MultiplicationSHEILA MAE CABASAG100% (2)
- LES QUARTERLY SOB 2023 Ron VDocument4 pagesLES QUARTERLY SOB 2023 Ron VSHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Myrna Palomas - Data Gathering Using Forms in MS WordDocument34 pagesMyrna Palomas - Data Gathering Using Forms in MS WordSHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Sample Mid-Year Opcrf Review 2021-2022Document18 pagesSample Mid-Year Opcrf Review 2021-2022SHEILA MAE CABASAG100% (1)
- Jecson Oafallas - Setting Up Office RemoteDocument34 pagesJecson Oafallas - Setting Up Office RemoteSHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 CertificatesDocument7 pagesQuarter 2 CertificatesSHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Aj Sports Price Quotation Liberty National High School FinalDocument1 pageAj Sports Price Quotation Liberty National High School FinalSHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Warren Ambat - Excel in Daily Attendance (Deped Form)Document35 pagesWarren Ambat - Excel in Daily Attendance (Deped Form)SHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Tampakan 1, 2, 3Document9 pagesDepartment of Education: Tampakan 1, 2, 3SHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- AppendixF PMCFDocument1 pageAppendixF PMCFSHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- NV No. 2023 008 HT Iiiiiv SecondaryDocument7 pagesNV No. 2023 008 HT Iiiiiv SecondarySHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Mid Year Program Review and Evaluation MPRE 2016Document4 pagesMid Year Program Review and Evaluation MPRE 2016SHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Community Actio-Wps OfficeDocument20 pagesCommunity Actio-Wps OfficeSHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Enclosure Natg6 Ellna CB Nat12Document22 pagesEnclosure Natg6 Ellna CB Nat12SHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- 1.2 RM CLMD 2023 021 Addendum To RM CLMD 2023 019 Refresher Training Cum Accreditation of 2023 Sraa Meet Technical OfficialsDocument3 pages1.2 RM CLMD 2023 021 Addendum To RM CLMD 2023 019 Refresher Training Cum Accreditation of 2023 Sraa Meet Technical OfficialsSHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- HeaderDocument1 pageHeaderSHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- AppendixE.1 MRF T1-3Document6 pagesAppendixE.1 MRF T1-3SHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Liberty Sped Budget Proposal For Sped Funds For MergeDocument7 pagesLiberty Sped Budget Proposal For Sped Funds For MergeSHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Verified List of Electoral Board For 2022 Nle 1Document21 pagesVerified List of Electoral Board For 2022 Nle 1SHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Class SkedDocument2 pagesClass SkedSHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- School Form 1 (SF 1)Document6 pagesSchool Form 1 (SF 1)SHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- 2021 School Annual Accomplishment ReportDocument312 pages2021 School Annual Accomplishment ReportSHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- School Form 1 (SF 1)Document6 pagesSchool Form 1 (SF 1)SHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesSHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- Koronadal Certificate of Non-Availability of Stocks: Product Code Product Description UOM PriceDocument7 pagesKoronadal Certificate of Non-Availability of Stocks: Product Code Product Description UOM PriceSHEILA MAE CABASAGNo ratings yet
- K Ali EntpDocument2 pagesK Ali Entpanim singhNo ratings yet
- BLESSINGS LPT IN THE MAKING TCHR VDocument23 pagesBLESSINGS LPT IN THE MAKING TCHR Vabe BrokenNo ratings yet
- Power Point Math COTDocument39 pagesPower Point Math COTmary jean sumalinogNo ratings yet
- Montessori Nomenclature Solar SystemDocument13 pagesMontessori Nomenclature Solar SystemJulieta NavoneNo ratings yet
- Exalco Albio 102 Curtain Wall SystemsDocument92 pagesExalco Albio 102 Curtain Wall SystemsAdmir MatoshiNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document4 pagesWeek 1Czarina RelleveNo ratings yet
- What Makes A Social Practice? Being, Knowing, Doing and LeadingDocument9 pagesWhat Makes A Social Practice? Being, Knowing, Doing and LeadingFabianaNo ratings yet
- MDLM - Pulsar 150-180 Bs III - Pulsar 135, 180 - 220 Ug +bs IVDocument342 pagesMDLM - Pulsar 150-180 Bs III - Pulsar 135, 180 - 220 Ug +bs IVfederico-500hotmail.comNo ratings yet
- Challenges and Opportunities in Practical Training - Perceptions of Clinical EducationDocument10 pagesChallenges and Opportunities in Practical Training - Perceptions of Clinical EducationJaz TagalagNo ratings yet
- Class 1Document15 pagesClass 1eisha123No ratings yet
- EE420 SyllabusDocument1 pageEE420 Syllabussal1980No ratings yet
- MultipLa - A Tool For The Combined Overall Estimation of Various Types of MMHDocument3 pagesMultipLa - A Tool For The Combined Overall Estimation of Various Types of MMHAfirdie FirdausNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Fluids Day 4Document57 pagesReservoir Fluids Day 4Bella cedricNo ratings yet
- Quality Managementy (11-12) RevisiDocument99 pagesQuality Managementy (11-12) Revisimecca fiandraNo ratings yet
- Exam 9Document3 pagesExam 9Schuller TechNo ratings yet
- Literary Reading Through A Biographical ContextDocument1 pageLiterary Reading Through A Biographical ContexthaydeeNo ratings yet
- Letter Writing Business LettersDocument60 pagesLetter Writing Business LettersAvery Jan SilosNo ratings yet
- 295-Article Text-2269-1-10-20210624Document7 pages295-Article Text-2269-1-10-20210624Rahmat AlfajriNo ratings yet
- What Is Employer BrandingDocument3 pagesWhat Is Employer Brandingsageerpa100% (2)
- TCVN 4244-2005Document179 pagesTCVN 4244-2005Toàn ĐinhNo ratings yet
- 1Panel-Data Unit-Root Tests - StataDocument3 pages1Panel-Data Unit-Root Tests - StataHafizAhmadNo ratings yet
- Babylonjs GameDocument112 pagesBabylonjs GameGeorge DeacNo ratings yet
- Awplaybook v4 PDFDocument152 pagesAwplaybook v4 PDFsyalcinkayaNo ratings yet
- Wireless Telecommunications Is The Transfer of Information Between Two or More Points That Are NotDocument3 pagesWireless Telecommunications Is The Transfer of Information Between Two or More Points That Are NotSuperTotie LandritoNo ratings yet
- Dual Mass FlywheelDocument2 pagesDual Mass FlywheelZimekNo ratings yet
- 03-2-Ceramic Form and Function An Ethnographic Search and An Archeological ApplicationDocument14 pages03-2-Ceramic Form and Function An Ethnographic Search and An Archeological ApplicationDante .jpgNo ratings yet