Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 viewsIntroduction To Organic Compounds (For Demo)
Introduction To Organic Compounds (For Demo)
Uploaded by
Shalou Beth FlorendoThe document discusses several functional groups that contain a carbon atom singly bonded to an electronegative atom such as a halogen, oxygen, or nitrogen. These functional groups include alkyl halides, alcohols, ethers, and amines. The carbonyl group is also discussed as being present in many biological and organic compounds.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Polymer Handbook (4th Edition) - Wiley-Blackwell (1999) PDFDocument2,366 pagesPolymer Handbook (4th Edition) - Wiley-Blackwell (1999) PDFLuis Fernando Quiñónez Cadena67% (3)
- 6242 01 Que 20060118Document12 pages6242 01 Que 20060118UncleBulgariaNo ratings yet
- ch16 TEST BANK SOLOMONSDocument110 pagesch16 TEST BANK SOLOMONSPatrick Malcolm Santos0% (1)
- Organic ChemistryDocument55 pagesOrganic ChemistryKim Taeha BTSNo ratings yet
- Alkane NomenclatureDocument1 pageAlkane NomenclatureRhian Geena VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Saturated Hydrocarbons - FactsDocument12 pagesSaturated Hydrocarbons - FactsAlshaimaa SolimanNo ratings yet
- Organic-Chemistry HydrocarbonsDocument4 pagesOrganic-Chemistry Hydrocarbonsxyrruschloe06No ratings yet
- Nouman (CHEM 11)Document6 pagesNouman (CHEM 11)Junaid AkhtarNo ratings yet
- PHARM 122 6 AlkanesDocument38 pagesPHARM 122 6 AlkanesTrixie Anne FelicitasNo ratings yet
- Manual 1 Nomenclature of HydrocarbonsDocument5 pagesManual 1 Nomenclature of HydrocarbonsNathaniel UbaNo ratings yet
- CA Lesson 2 AlkanesDocument31 pagesCA Lesson 2 AlkanesAlbaraaAliNo ratings yet
- (8.1) Learning MaterialDocument41 pages(8.1) Learning MaterialLuna VasquezNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument7 pagesCarbon and Its CompoundsVijeyNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: Saturated and Unsaturated HydrocarbonsDocument44 pagesOrganic Chemistry: Saturated and Unsaturated HydrocarbonsSam LoveNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document3 pagesChapter 4Jonathan SaydeNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons.2Document45 pagesHydrocarbons.2pasatiemporoseanneNo ratings yet
- Organic 23 24Document18 pagesOrganic 23 24VigneshNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons: ObjectivesDocument29 pagesHydrocarbons: Objectivesjohn ryan piolNo ratings yet
- 5-Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument35 pages5-Introduction To Organic ChemistrysamNo ratings yet
- Bonding of Hydrocarbons: Presented by Rina Mae Manceras Benjamin BagayanDocument33 pagesBonding of Hydrocarbons: Presented by Rina Mae Manceras Benjamin BagayanIce BearNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon S: Group 3: Leader: Angela Dela Cruz Daphne Sy Sofia Anne Caoagas Alen Gem Red Christian Faith ColisDocument16 pagesHydrocarbon S: Group 3: Leader: Angela Dela Cruz Daphne Sy Sofia Anne Caoagas Alen Gem Red Christian Faith ColisDaphne SyNo ratings yet
- Naming of Organic CompoundsDocument30 pagesNaming of Organic CompoundsCARLOS FALCASSANo ratings yet
- Naming Organic MoleculesDocument38 pagesNaming Organic MoleculesDale Miko SanchezNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument7 pagesOrganic Chemistryespiritumikhailehayah28No ratings yet
- Alkanes and Cycloalkanes - PPTX 2Document57 pagesAlkanes and Cycloalkanes - PPTX 2eysabelagwenNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonsDocument35 pagesHydrocarbonsCherine NoueihedNo ratings yet
- Naming of Alkanes, Alkenes and AlkynesDocument34 pagesNaming of Alkanes, Alkenes and AlkynesArt Caresosa-FernandoNo ratings yet
- 14-04-20 - Nomenclature - Alkanes, AlkenesmamDocument21 pages14-04-20 - Nomenclature - Alkanes, AlkenesmamArthiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry AssignmentDocument5 pagesChemistry AssignmentBettina Rose GallardoNo ratings yet
- Alkane Alkene Alkyne David VillanuevaDocument39 pagesAlkane Alkene Alkyne David VillanuevacrystaljanelletabsingNo ratings yet
- ALKANESDocument4 pagesALKANESLiezel VillaruzNo ratings yet
- Organic Compounds 1Document74 pagesOrganic Compounds 1angel.abaoNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Organic CompoundsDocument20 pagesAn Introduction To Organic CompoundsJotillnaimNo ratings yet
- Organic NomenclatureDocument11 pagesOrganic NomenclatureAmalia SillerNo ratings yet
- Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Their Stereochemistry: John E. McmurryDocument56 pagesOrganic Compounds: Alkanes and Their Stereochemistry: John E. McmurryKaren SimeonNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons - AlkanesDocument16 pagesHydrocarbons - Alkanesdichosohubert548No ratings yet
- UNIT 10 Organic ChemistryDocument51 pagesUNIT 10 Organic ChemistryTristan PereyNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: (Part One)Document104 pagesOrganic Chemistry: (Part One)eltoumNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature Organic IUPAC RulesDocument9 pagesNomenclature Organic IUPAC RulesSkyla DavisNo ratings yet
- Org Chem U 2-1Document29 pagesOrg Chem U 2-1Cina YemataNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem U-2Document19 pagesOrganic Chem U-2sinte beyuNo ratings yet
- NSSCAS Chemistry Theme 4 Topic 4.1 - TsumebDocument91 pagesNSSCAS Chemistry Theme 4 Topic 4.1 - Tsumebsikereteromanus9No ratings yet
- ch04 AlkanesDocument20 pagesch04 AlkanesSİNEM GÜVENNo ratings yet
- IUPAC NomenclatureDocument4 pagesIUPAC NomenclatureNitesha MadhuNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem NotesDocument21 pagesOrganic Chem NotesVeer PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature 1Document35 pagesNomenclature 1Anchal ChadhaNo ratings yet
- IUPAC RulesDocument14 pagesIUPAC RulesIce BoyNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Hydrocarbon Alkanes Alkenes AlkynesDocument67 pagesWeek 3 Hydrocarbon Alkanes Alkenes AlkynesNikol BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Alkanes and Their StereochemistryDocument75 pagesAlkanes and Their Stereochemistry110003551 110ANo ratings yet
- Alkanes (Paraffins)Document17 pagesAlkanes (Paraffins)Ahmed AmirNo ratings yet
- Alkanes and Cycloalkanes: Hybridized and Tetrahedral, With All Bond Angles of 109.5°Document5 pagesAlkanes and Cycloalkanes: Hybridized and Tetrahedral, With All Bond Angles of 109.5°Alecs Elinor AmoguisNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature JDDocument4 pagesNomenclature JDBose LogoNo ratings yet
- Structural Theory in Organic Chemistry: Functional Groups and Chemical BondingDocument49 pagesStructural Theory in Organic Chemistry: Functional Groups and Chemical BondingMaria Claudia MartinezNo ratings yet
- Alkanes and CycloalkanesDocument8 pagesAlkanes and CycloalkanesasenmitcheNo ratings yet
- FPISA0 Week 7Document37 pagesFPISA0 Week 7sassy2202018No ratings yet
- OrganicChemistry NoteDocument16 pagesOrganicChemistry NotetacocatNo ratings yet
- Bahan Belajar KimDasDocument16 pagesBahan Belajar KimDasfebriNo ratings yet
- Alkanes PDFDocument16 pagesAlkanes PDFfumerojr5164No ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes - HJMDocument78 pagesChapter - 4 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes - HJMMarisol AcostaNo ratings yet
- Intro To Organic Chemistry 2022 Sep 9Document59 pagesIntro To Organic Chemistry 2022 Sep 9SanaaNo ratings yet
- Alkanes 1-1Document22 pagesAlkanes 1-1Benjamen FolarinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemistryMoya-Dean Walcott100% (2)
- Why Are Chemicals Not Named John? Naming Chemical Compounds 6th Grade | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandWhy Are Chemicals Not Named John? Naming Chemical Compounds 6th Grade | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Activity Plan Podcast 2021Document7 pagesActivity Plan Podcast 2021Shalou Beth FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Task 3 - Florendo Shalou Beth No. 1Document3 pagesTask 3 - Florendo Shalou Beth No. 1Shalou Beth FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Excuse Letter ResearchDocument1 pageExcuse Letter ResearchShalou Beth FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Registration Student Consent Promissory FormDocument2 pagesRegistration Student Consent Promissory FormShalou Beth FlorendoNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature Module 5,6,7&8 - Shalou Beth M. Florendo 11 - GuavaDocument3 pages21st Century Literature Module 5,6,7&8 - Shalou Beth M. Florendo 11 - GuavaShalou Beth FlorendoNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature Module 1 - Shalou Beth M. Florendo 11 - GuavaDocument1 page21st Century Literature Module 1 - Shalou Beth M. Florendo 11 - GuavaShalou Beth FlorendoNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature Shalou Beth M. Florendo 11 - GuavaDocument2 pages21st Century Literature Shalou Beth M. Florendo 11 - GuavaShalou Beth FlorendoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Quarter 3 Week 1 2Document5 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Quarter 3 Week 1 2Shalou Beth FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Q1 21ST CENTURY LITERATURE Diagnostic TestDocument4 pagesQ1 21ST CENTURY LITERATURE Diagnostic TestShalou Beth FlorendoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 Quarter 2 Weeks 6Document6 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 Quarter 2 Weeks 6Shalou Beth FlorendoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 Quarter 2 Weeks 2 and 3Document17 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 Quarter 2 Weeks 2 and 3Shalou Beth FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Lehman OOC4e Experiment CorrelationsDocument7 pagesLehman OOC4e Experiment CorrelationsPreeti Gunthey DiwanNo ratings yet
- Name ReactionDocument15 pagesName Reactiontrishansarkar07No ratings yet
- Assignment: BiomoleculesDocument6 pagesAssignment: BiomoleculesI AndYouNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry Revision Notes For Chapter 5 - Surface ChemistryDocument10 pagesClass 12 Chemistry Revision Notes For Chapter 5 - Surface ChemistryPrashant Kore100% (1)
- Rings Acids and Amines QuestionsDocument51 pagesRings Acids and Amines QuestionsSuraj DavdraNo ratings yet
- Polymers: Pre-Medical: Chemistry AllenDocument5 pagesPolymers: Pre-Medical: Chemistry AllenAmbesh JhaNo ratings yet
- MaterialsDocument5 pagesMaterialsEgregorLucic100% (1)
- Malonic Acid Derivatives On Duty As Electron-Withdrawing Units in Push-Pull MoleculesDocument16 pagesMalonic Acid Derivatives On Duty As Electron-Withdrawing Units in Push-Pull MoleculesDavid DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Electrophilic Aromatic ReactionsDocument124 pagesElectrophilic Aromatic ReactionsAllan DNo ratings yet
- K00933 - 20181107122127 - Topic 10 - IsomerismDocument41 pagesK00933 - 20181107122127 - Topic 10 - Isomerismmuhammad syahmiNo ratings yet
- CH 03Document34 pagesCH 03Paulo Sérgio100% (1)
- Mmmartin Cm134-1l SyllabusDocument11 pagesMmmartin Cm134-1l SyllabusOliver MendozaNo ratings yet
- Polymer Mcqs 1Document8 pagesPolymer Mcqs 1Para DiseNo ratings yet
- Formal Report. Experiment 7: Classification Test For HydrocarbonsDocument6 pagesFormal Report. Experiment 7: Classification Test For Hydrocarbonsdemichosantos100% (6)
- (HEMA) Technical Data Sheet BisomerDocument2 pages(HEMA) Technical Data Sheet BisomerOsmar ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Library Search Results - Nontarget Hits With DetailsDocument650 pagesLibrary Search Results - Nontarget Hits With DetailsAnh VânNo ratings yet
- Unit-V: Reactions of Synthetic Importance Bp401T: Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry-Iii Metal Hydride Reduction (Nabh 4 and Lialh 4)Document15 pagesUnit-V: Reactions of Synthetic Importance Bp401T: Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry-Iii Metal Hydride Reduction (Nabh 4 and Lialh 4)Kartik RajpootNo ratings yet
- Proline PDFDocument52 pagesProline PDFRathinNo ratings yet
- GC Column Selection For USP MethodsDocument1 pageGC Column Selection For USP Methodsrnd labNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document45 pagesLecture 1Creative ThinkerNo ratings yet
- S CHEM011 Inorganic and Organic Chemistry TraditionalDocument10 pagesS CHEM011 Inorganic and Organic Chemistry TraditionalJasmine CatanaNo ratings yet
- 4.8, 4.9 TestDocument12 pages4.8, 4.9 TestVinh HoangNo ratings yet
- Sample Solution: PROBLEM 4.20Document8 pagesSample Solution: PROBLEM 4.20Nacho Araneda0% (1)
- 2020 JPJC H2 Chemistry Prelim P3 AnswersDocument24 pages2020 JPJC H2 Chemistry Prelim P3 Answersclarissa yeoNo ratings yet
- Grignard Reagent TheoryDocument7 pagesGrignard Reagent Theorylabib120513No ratings yet
- Synthesis of Amino Acids and Peptide BondsDocument26 pagesSynthesis of Amino Acids and Peptide BondsDaniellaNo ratings yet
- 5 HeterocyclicDocument26 pages5 HeterocyclicSaman FatimaNo ratings yet
Introduction To Organic Compounds (For Demo)
Introduction To Organic Compounds (For Demo)
Uploaded by
Shalou Beth Florendo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views36 pagesThe document discusses several functional groups that contain a carbon atom singly bonded to an electronegative atom such as a halogen, oxygen, or nitrogen. These functional groups include alkyl halides, alcohols, ethers, and amines. The carbonyl group is also discussed as being present in many biological and organic compounds.
Original Description:
Original Title
Introduction to Organic Compounds (for Demo).Pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses several functional groups that contain a carbon atom singly bonded to an electronegative atom such as a halogen, oxygen, or nitrogen. These functional groups include alkyl halides, alcohols, ethers, and amines. The carbonyl group is also discussed as being present in many biological and organic compounds.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views36 pagesIntroduction To Organic Compounds (For Demo)
Introduction To Organic Compounds (For Demo)
Uploaded by
Shalou Beth FlorendoThe document discusses several functional groups that contain a carbon atom singly bonded to an electronegative atom such as a halogen, oxygen, or nitrogen. These functional groups include alkyl halides, alcohols, ethers, and amines. The carbonyl group is also discussed as being present in many biological and organic compounds.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 36
Functional Groups with Carbon Singly
Bonded to an Electronegative Atom
Alkyl halides, alcohols, ethers, amines all have a
carbon singly bonded to an electronegative atom –
halogen (chlorine, fluorine, etc.), oxygen or nitrogen.
Functional Groups with Carbon Singly
Bonded to an Electronegative Atom
Alkyl halides, alcohols, ethers, amines all have a
carbon singly bonded to an electronegative atom –
halogen (chlorine, fluorine, etc.), oxygen or nitrogen.
Functional Groups with Carbon Singly
Bonded to an Electronegative Atom
Alkyl halides, alcohols, ethers, amines all have a
carbon singly bonded to an electronegative atom –
halogen (chlorine, fluorine, etc.), oxygen or nitrogen.
Functional Groups with Carbon Singly
Bonded to an Electronegative Atom
Alkyl halides, alcohols, ethers, amines all have a
carbon singly bonded to an electronegative atom –
halogen (chlorine, fluorine, etc.), oxygen or nitrogen.
Functional Groups with Carbon Singly
Bonded to an Electronegative Atom
Alkyl halides, alcohols, ethers, amines all have a
carbon singly bonded to an electronegative atom –
halogen (chlorine, fluorine, etc.), oxygen or nitrogen.
Functional Groups with Carbon Singly
Bonded to an Electronegative Atom
Alkyl halides, alcohols, ethers, amines all have a
carbon singly bonded to an electronegative atom –
halogen (chlorine, fluorine, etc.), oxygen or nitrogen.
Functional Groups with Carbon Singly
Bonded to an Electronegative Atom
Alkyl halides, alcohols, ethers, amines all have a
carbon singly bonded to an electronegative atom –
halogen (chlorine, fluorine, etc.), oxygen or nitrogen.
Functional Groups with Carbon-Oxygen
Double Bond (Carbonyl Groups)
The carbonyl group is present in a large majority of
organic compounds and in practically all biological
molecules. These compounds behave similarly in many
respects but differ depending on the identity of the
atoms bonded to carbonyl-group carbon.
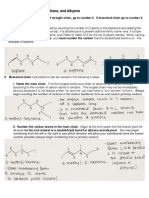
Alkanes and Alkane Isomers
•
Alkanes and Alkane Isomers
Straight-chain alkanes are named according to the
number of carbon atoms they contain. The alkanes are
named based on Greek numbers. The suffix –ane is
added to the end of each name to indicate that the
molecule identified is an alkane.
Alkanes and Alkane Isomers
Isomers are compounds that have the same numbers
and kinds of atoms but differ in the way the atoms are
arranged. Compounds like butane and isobutane,
whose atoms are connected differently, are called
constitutional isomers.
Alkyl Groups
If you imagine removing a hydrogen atom from an
alkane, the partial structure that remains is called an
alkyl group. Alkyl groups are named by replacing the
–ane ending of the parent alkane with an –yl ending.
Alkyl Groups
Branched alkyl groups are generated by removing a
hydrogen atom from an internal carbon.
Alkyl Groups
One further comment about naming alkyl groups: the
prefixes sec- and tert- used refer to the number of
other carbon atoms attached to the branching carbon
atom. There are four possibilities: primary, secondary,
tertiary, and quaternary. The symbol R is used to
represent an organic group
Alkyl Groups
Alkyl Groups
One further comment about naming alkyl groups: the
prefixes sec- and tert- used refer to the number of
other carbon atoms attached to the branching carbon
atom. There are four possibilities: primary, secondary,
tertiary, and quaternary. The symbol R is used to
represent an organic group
Naming Alkanes
A chemical name typically has four parts in the IUPAC
system of nomenclature: prefix, parent, locant, and
suffix.
Naming Alkanes
STEP 1
Find the parent hydrocarbon.
(a) Find the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms
in the molecule, and use the name of that chain as
the parent name.
Naming Alkanes
(b) If two different chains of equal length are present,
choose the one with the larger number of branch
points as the parent.
Naming Alkanes
STEP 2
Number the atoms in the longest chain.
(a) Beginning at the end nearer the first branch point,
number each carbon atom in the parent chain.
Naming Alkanes
(b) If there is branching an equal distance away from
both ends of the parent chain, begin numbering at the
end nearer the second branch point.
Naming Alkanes
STEP 3
Identify and number the substituents.
(a) Assign a number, or locant, to each substituent to
locate its point of attachment to the parent chain.
Naming Alkanes
(b) If there are two substituents on the same carbon,
give both the same number. There must be many
numbers in the name as there are substituents.
Naming Alkanes
STEP 4
Write the name as a single word. Use hyphens to
separate the different prefixes, and use commas to
separate numbers.
Naming Alkanes
STEP 4
Write the name as a single word. Use hyphens to
separate the different prefixes, and use commas to
separate numbers.
Naming Alkanes
STEP 4
Write the name as a single word. Use hyphens to
separate the different prefixes, and use commas to
separate numbers.
Naming Alkanes
STEP 4
Write the name as a single word. Use hyphens to
separate the different prefixes, and use commas to
separate numbers.
Naming Alkanes
STEP 4
Write the name as a single word. Use hyphens to
separate the different prefixes, and use commas to
separate numbers.
Naming Alkanes
STEP 4
Write the name as a single word. Use hyphens to
separate the different prefixes, and use commas to
separate numbers.
Naming Alkanes
STEP 4
Write the name as a single word. Use hyphens to
separate the different prefixes, and use commas to
separate numbers.
Naming Alkanes
STEP 4
Write the name as a single word. Use hyphens to
separate the different prefixes, and use commas to
separate numbers.
Naming Alkanes
STEP 4
Write the name as a single word. Use hyphens to
separate the different prefixes, and use commas to
separate numbers.
Naming Alkanes
STEP 4
Write the name as a single word. Use hyphens to
separate the different prefixes, and use commas to
separate numbers.
Naming Alkanes
STEP 4
Write the name as a single word. Use hyphens to
separate the different prefixes, and use commas to
separate numbers.
Naming Alkanes
STEP 4
Write the name as a single word. Use hyphens to
separate the different prefixes, and use commas to
separate numbers.
You might also like
- Polymer Handbook (4th Edition) - Wiley-Blackwell (1999) PDFDocument2,366 pagesPolymer Handbook (4th Edition) - Wiley-Blackwell (1999) PDFLuis Fernando Quiñónez Cadena67% (3)
- 6242 01 Que 20060118Document12 pages6242 01 Que 20060118UncleBulgariaNo ratings yet
- ch16 TEST BANK SOLOMONSDocument110 pagesch16 TEST BANK SOLOMONSPatrick Malcolm Santos0% (1)
- Organic ChemistryDocument55 pagesOrganic ChemistryKim Taeha BTSNo ratings yet
- Alkane NomenclatureDocument1 pageAlkane NomenclatureRhian Geena VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Saturated Hydrocarbons - FactsDocument12 pagesSaturated Hydrocarbons - FactsAlshaimaa SolimanNo ratings yet
- Organic-Chemistry HydrocarbonsDocument4 pagesOrganic-Chemistry Hydrocarbonsxyrruschloe06No ratings yet
- Nouman (CHEM 11)Document6 pagesNouman (CHEM 11)Junaid AkhtarNo ratings yet
- PHARM 122 6 AlkanesDocument38 pagesPHARM 122 6 AlkanesTrixie Anne FelicitasNo ratings yet
- Manual 1 Nomenclature of HydrocarbonsDocument5 pagesManual 1 Nomenclature of HydrocarbonsNathaniel UbaNo ratings yet
- CA Lesson 2 AlkanesDocument31 pagesCA Lesson 2 AlkanesAlbaraaAliNo ratings yet
- (8.1) Learning MaterialDocument41 pages(8.1) Learning MaterialLuna VasquezNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument7 pagesCarbon and Its CompoundsVijeyNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: Saturated and Unsaturated HydrocarbonsDocument44 pagesOrganic Chemistry: Saturated and Unsaturated HydrocarbonsSam LoveNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document3 pagesChapter 4Jonathan SaydeNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons.2Document45 pagesHydrocarbons.2pasatiemporoseanneNo ratings yet
- Organic 23 24Document18 pagesOrganic 23 24VigneshNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons: ObjectivesDocument29 pagesHydrocarbons: Objectivesjohn ryan piolNo ratings yet
- 5-Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument35 pages5-Introduction To Organic ChemistrysamNo ratings yet
- Bonding of Hydrocarbons: Presented by Rina Mae Manceras Benjamin BagayanDocument33 pagesBonding of Hydrocarbons: Presented by Rina Mae Manceras Benjamin BagayanIce BearNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon S: Group 3: Leader: Angela Dela Cruz Daphne Sy Sofia Anne Caoagas Alen Gem Red Christian Faith ColisDocument16 pagesHydrocarbon S: Group 3: Leader: Angela Dela Cruz Daphne Sy Sofia Anne Caoagas Alen Gem Red Christian Faith ColisDaphne SyNo ratings yet
- Naming of Organic CompoundsDocument30 pagesNaming of Organic CompoundsCARLOS FALCASSANo ratings yet
- Naming Organic MoleculesDocument38 pagesNaming Organic MoleculesDale Miko SanchezNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument7 pagesOrganic Chemistryespiritumikhailehayah28No ratings yet
- Alkanes and Cycloalkanes - PPTX 2Document57 pagesAlkanes and Cycloalkanes - PPTX 2eysabelagwenNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonsDocument35 pagesHydrocarbonsCherine NoueihedNo ratings yet
- Naming of Alkanes, Alkenes and AlkynesDocument34 pagesNaming of Alkanes, Alkenes and AlkynesArt Caresosa-FernandoNo ratings yet
- 14-04-20 - Nomenclature - Alkanes, AlkenesmamDocument21 pages14-04-20 - Nomenclature - Alkanes, AlkenesmamArthiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry AssignmentDocument5 pagesChemistry AssignmentBettina Rose GallardoNo ratings yet
- Alkane Alkene Alkyne David VillanuevaDocument39 pagesAlkane Alkene Alkyne David VillanuevacrystaljanelletabsingNo ratings yet
- ALKANESDocument4 pagesALKANESLiezel VillaruzNo ratings yet
- Organic Compounds 1Document74 pagesOrganic Compounds 1angel.abaoNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Organic CompoundsDocument20 pagesAn Introduction To Organic CompoundsJotillnaimNo ratings yet
- Organic NomenclatureDocument11 pagesOrganic NomenclatureAmalia SillerNo ratings yet
- Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Their Stereochemistry: John E. McmurryDocument56 pagesOrganic Compounds: Alkanes and Their Stereochemistry: John E. McmurryKaren SimeonNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons - AlkanesDocument16 pagesHydrocarbons - Alkanesdichosohubert548No ratings yet
- UNIT 10 Organic ChemistryDocument51 pagesUNIT 10 Organic ChemistryTristan PereyNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: (Part One)Document104 pagesOrganic Chemistry: (Part One)eltoumNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature Organic IUPAC RulesDocument9 pagesNomenclature Organic IUPAC RulesSkyla DavisNo ratings yet
- Org Chem U 2-1Document29 pagesOrg Chem U 2-1Cina YemataNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem U-2Document19 pagesOrganic Chem U-2sinte beyuNo ratings yet
- NSSCAS Chemistry Theme 4 Topic 4.1 - TsumebDocument91 pagesNSSCAS Chemistry Theme 4 Topic 4.1 - Tsumebsikereteromanus9No ratings yet
- ch04 AlkanesDocument20 pagesch04 AlkanesSİNEM GÜVENNo ratings yet
- IUPAC NomenclatureDocument4 pagesIUPAC NomenclatureNitesha MadhuNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem NotesDocument21 pagesOrganic Chem NotesVeer PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature 1Document35 pagesNomenclature 1Anchal ChadhaNo ratings yet
- IUPAC RulesDocument14 pagesIUPAC RulesIce BoyNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Hydrocarbon Alkanes Alkenes AlkynesDocument67 pagesWeek 3 Hydrocarbon Alkanes Alkenes AlkynesNikol BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Alkanes and Their StereochemistryDocument75 pagesAlkanes and Their Stereochemistry110003551 110ANo ratings yet
- Alkanes (Paraffins)Document17 pagesAlkanes (Paraffins)Ahmed AmirNo ratings yet
- Alkanes and Cycloalkanes: Hybridized and Tetrahedral, With All Bond Angles of 109.5°Document5 pagesAlkanes and Cycloalkanes: Hybridized and Tetrahedral, With All Bond Angles of 109.5°Alecs Elinor AmoguisNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature JDDocument4 pagesNomenclature JDBose LogoNo ratings yet
- Structural Theory in Organic Chemistry: Functional Groups and Chemical BondingDocument49 pagesStructural Theory in Organic Chemistry: Functional Groups and Chemical BondingMaria Claudia MartinezNo ratings yet
- Alkanes and CycloalkanesDocument8 pagesAlkanes and CycloalkanesasenmitcheNo ratings yet
- FPISA0 Week 7Document37 pagesFPISA0 Week 7sassy2202018No ratings yet
- OrganicChemistry NoteDocument16 pagesOrganicChemistry NotetacocatNo ratings yet
- Bahan Belajar KimDasDocument16 pagesBahan Belajar KimDasfebriNo ratings yet
- Alkanes PDFDocument16 pagesAlkanes PDFfumerojr5164No ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes - HJMDocument78 pagesChapter - 4 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes - HJMMarisol AcostaNo ratings yet
- Intro To Organic Chemistry 2022 Sep 9Document59 pagesIntro To Organic Chemistry 2022 Sep 9SanaaNo ratings yet
- Alkanes 1-1Document22 pagesAlkanes 1-1Benjamen FolarinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemistryMoya-Dean Walcott100% (2)
- Why Are Chemicals Not Named John? Naming Chemical Compounds 6th Grade | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandWhy Are Chemicals Not Named John? Naming Chemical Compounds 6th Grade | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Activity Plan Podcast 2021Document7 pagesActivity Plan Podcast 2021Shalou Beth FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Task 3 - Florendo Shalou Beth No. 1Document3 pagesTask 3 - Florendo Shalou Beth No. 1Shalou Beth FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Excuse Letter ResearchDocument1 pageExcuse Letter ResearchShalou Beth FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Registration Student Consent Promissory FormDocument2 pagesRegistration Student Consent Promissory FormShalou Beth FlorendoNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature Module 5,6,7&8 - Shalou Beth M. Florendo 11 - GuavaDocument3 pages21st Century Literature Module 5,6,7&8 - Shalou Beth M. Florendo 11 - GuavaShalou Beth FlorendoNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature Module 1 - Shalou Beth M. Florendo 11 - GuavaDocument1 page21st Century Literature Module 1 - Shalou Beth M. Florendo 11 - GuavaShalou Beth FlorendoNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature Shalou Beth M. Florendo 11 - GuavaDocument2 pages21st Century Literature Shalou Beth M. Florendo 11 - GuavaShalou Beth FlorendoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Quarter 3 Week 1 2Document5 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Quarter 3 Week 1 2Shalou Beth FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Q1 21ST CENTURY LITERATURE Diagnostic TestDocument4 pagesQ1 21ST CENTURY LITERATURE Diagnostic TestShalou Beth FlorendoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 Quarter 2 Weeks 6Document6 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 Quarter 2 Weeks 6Shalou Beth FlorendoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 Quarter 2 Weeks 2 and 3Document17 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 Quarter 2 Weeks 2 and 3Shalou Beth FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Lehman OOC4e Experiment CorrelationsDocument7 pagesLehman OOC4e Experiment CorrelationsPreeti Gunthey DiwanNo ratings yet
- Name ReactionDocument15 pagesName Reactiontrishansarkar07No ratings yet
- Assignment: BiomoleculesDocument6 pagesAssignment: BiomoleculesI AndYouNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry Revision Notes For Chapter 5 - Surface ChemistryDocument10 pagesClass 12 Chemistry Revision Notes For Chapter 5 - Surface ChemistryPrashant Kore100% (1)
- Rings Acids and Amines QuestionsDocument51 pagesRings Acids and Amines QuestionsSuraj DavdraNo ratings yet
- Polymers: Pre-Medical: Chemistry AllenDocument5 pagesPolymers: Pre-Medical: Chemistry AllenAmbesh JhaNo ratings yet
- MaterialsDocument5 pagesMaterialsEgregorLucic100% (1)
- Malonic Acid Derivatives On Duty As Electron-Withdrawing Units in Push-Pull MoleculesDocument16 pagesMalonic Acid Derivatives On Duty As Electron-Withdrawing Units in Push-Pull MoleculesDavid DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Electrophilic Aromatic ReactionsDocument124 pagesElectrophilic Aromatic ReactionsAllan DNo ratings yet
- K00933 - 20181107122127 - Topic 10 - IsomerismDocument41 pagesK00933 - 20181107122127 - Topic 10 - Isomerismmuhammad syahmiNo ratings yet
- CH 03Document34 pagesCH 03Paulo Sérgio100% (1)
- Mmmartin Cm134-1l SyllabusDocument11 pagesMmmartin Cm134-1l SyllabusOliver MendozaNo ratings yet
- Polymer Mcqs 1Document8 pagesPolymer Mcqs 1Para DiseNo ratings yet
- Formal Report. Experiment 7: Classification Test For HydrocarbonsDocument6 pagesFormal Report. Experiment 7: Classification Test For Hydrocarbonsdemichosantos100% (6)
- (HEMA) Technical Data Sheet BisomerDocument2 pages(HEMA) Technical Data Sheet BisomerOsmar ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Library Search Results - Nontarget Hits With DetailsDocument650 pagesLibrary Search Results - Nontarget Hits With DetailsAnh VânNo ratings yet
- Unit-V: Reactions of Synthetic Importance Bp401T: Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry-Iii Metal Hydride Reduction (Nabh 4 and Lialh 4)Document15 pagesUnit-V: Reactions of Synthetic Importance Bp401T: Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry-Iii Metal Hydride Reduction (Nabh 4 and Lialh 4)Kartik RajpootNo ratings yet
- Proline PDFDocument52 pagesProline PDFRathinNo ratings yet
- GC Column Selection For USP MethodsDocument1 pageGC Column Selection For USP Methodsrnd labNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document45 pagesLecture 1Creative ThinkerNo ratings yet
- S CHEM011 Inorganic and Organic Chemistry TraditionalDocument10 pagesS CHEM011 Inorganic and Organic Chemistry TraditionalJasmine CatanaNo ratings yet
- 4.8, 4.9 TestDocument12 pages4.8, 4.9 TestVinh HoangNo ratings yet
- Sample Solution: PROBLEM 4.20Document8 pagesSample Solution: PROBLEM 4.20Nacho Araneda0% (1)
- 2020 JPJC H2 Chemistry Prelim P3 AnswersDocument24 pages2020 JPJC H2 Chemistry Prelim P3 Answersclarissa yeoNo ratings yet
- Grignard Reagent TheoryDocument7 pagesGrignard Reagent Theorylabib120513No ratings yet
- Synthesis of Amino Acids and Peptide BondsDocument26 pagesSynthesis of Amino Acids and Peptide BondsDaniellaNo ratings yet
- 5 HeterocyclicDocument26 pages5 HeterocyclicSaman FatimaNo ratings yet