Professional Documents
Culture Documents
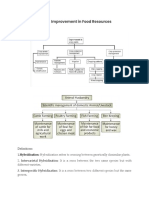
CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources Important Questions 2022-23
CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources Important Questions 2022-23
Uploaded by
abhishek singhOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources Important Questions 2022-23
CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources Important Questions 2022-23
Uploaded by
abhishek singhCopyright:
Available Formats
Important Questions for Class 9
Science
Chapter 15-Improvement in Food Resources
Very Short Answer Type Questions 2 Marks
1. What do we get from cereals, pulses, fruits and vegetables?
Ans: Cereals provide carbohydrates, pulses provide proteins, while fruits and
vegetables provide vitamins and minerals.
2. What factors may be responsible for losses of grains during storage?
Ans: Both biotic and abiotic factors may be responsible for losses of grains during
storage are:
Humidity and temperature of the environment and moisture content of grains
are the abiotic factors.
Biotic factors include organisms such as rodents, bacteria, fungi, and some
insects that feed on grains.
3. What are weeds? Give two examples.
Ans: Weeds are undesired plants that grow in fields. Common weeds include
Amaranthus and Chenopodium.
4. What is crop rotation?
Ans: Crop rotation is the technique of alternately cultivating various crops in the
same land in a pre-planned succession.
Class IX Science www.vedantu.com 1
5. What are drones?
Ans: Drones are airborne devices that are used in agriculture to improve crop
output and to track crop growth.
They assist farmers in developing agricultural field systems for using water,
fertilisers, herbicides, and seeds. These tools have revolutionised agriculture by
allowing farmers to save significant amounts of money while also increasing
efficiency and profitability.
6. What is pasturage and how is it important?
Ans: Crop rotation is the practise of farming a variety of crops in a pre- determined
order on the same piece of land.
7. What is a layer and a broiler? What are the differences between the two?
Ans: The egg-laying poultry bird is known as an egg layer, whereas the meat-
producing poultry bird is known as a chicken or broiler.
Housing (shelter), food, and environmental requirements differ from layer
requirements. Broiler feed is protein- and vitamin-rich, with an acceptable fat
content.
8. Arrange the following statements in correct sequence of preparation of
green manure
(a) Green plants are decomposed in soil
(b) Green plants are cultivated for preparing manure or crop plant parts are
used
(c) Plants are ploughed and mixed into soil
(d) After decomposition it becomes green manure.
Ans:
Class IX Science www.vedantu.com 2
(b) Green plants are cultivated for preparing manure or crop plant parts are used
(c) Plants are ploughed and mixed into soil
(a) Green plants are decomposed in soil
(d) After decomposition it becomes green manure.
9. What are the benefits of poultry farming over cattle farming?
Ans: The advantages of chicken farming over cattle rearing include the following:
a) The amount of money required is little.
b) The amount of space required is minimal.
c) It is simple to maintain.
d) Returns are processed quickly.
10. Define inter – cropping Mention its advantages.
Ans:Intercropping is the practise of cultivating two or more crops on the same field
in rows at the same time.
Added benefits –
1) Productivity is higher.
2) It saves space and time by farming two or more crops at the same time.
3) It aids in the preservation of soil fertility.
11. What are the advantages of organic farming?
Ans: Organic farming has the following advantages:
a) It does not disrupt the natural environment.
Class IX Science www.vedantu.com 3
b) It preserves soil fertility.
c) Chemicals have no harmful impact on living organisms; d) Pollution of the air,
water, and soil does not occur.
12. Differentiate between mixed cropping and Intercropping.
Ans: The difference between mixed cropping and intercropping are as follows:
Mixed Cropping Inter-Cropping
Goal is to reduce the crop failure Goal to boost productivity per square
foot
Before sowing , component crop seeds Before sowing , component crop seeds
are blended together. are blended together.
Sowing do not take place in rows Sowing is done in precise arrangement
in rows
13. Give a difference between Rabi and kharif crops?
Ans: The difference between Rabi and Kharif crop are as follows:
Rabi Crop Kharif crop
This crop is sown during the winter The summer (kharif) season is when it is
season. sown.
It necessitates a chilly, dry climate. It necessitates a hot, humid atmosphere.
Class IX Science www.vedantu.com 4
14. What is hybridization?
Ans: The crossing of genetically distinct plants is referred to as hybridization. In
this strategy, two crop varieties are chosen, each with at least one desirable trait,
such as high yield or disease resistance.
15. List the various methods of weed control.
Ans: Weed control methods include:
a) Mechanical means - Weeds are pulled out by hand or with the use of a khurpa
(trowel) or a hoe.
b) Cultural approaches — cultural methods include seed bed preparation, timely
seed sowing, intercropping, and appropriate rotation.
c) Chemical techniques — compounds such as 2,4,-D can be used to manage
weeds.
16. What are the characteristic features of ideal shelters for cattle?
Ans: The following are characteristics of a shelter:
1) The animals are protected from rain, heat, and cold by a suitably roofed shed.
2) The shed's floor is slanted to make cleaning easier and to keep their sitting area
dry.
3) A plan for safe drinking water is put in place.
4) Excreta disposal is properly arranged in the sheds.
17. What are the hazards of using fertilizers?
Ans: Effects of fertiliser application –
a) Impact on soil quality - fertiliser application leads to a loss of organic matter and
a deterioration of soil structure.
Class IX Science www.vedantu.com 5
b) Eutrophication - Excessive fertiliser application causes nitrate buildup in the
soil.
Rain washes nitrates and phosphates into lakes, ponds, and rivers, where they
encourage algae to develop excessively.
18. How do insect,pest damage crop plants?
Ans: Insect – pests cause damage to plants in the following ways:
a) They hacked away at the root, stem, and leaf.
b) They drink the sap from the cells of diverse plant components.
c) They eat the stems and fruits of plants.
d) They produce galls.
e) They devour grains that have been preserved.
Short Answer Type Questions 3 Marks
1. How do biotic and abiotic factors affect crop production?
Ans: Living organisms such as honey bees and earthworms aid improve crop
output, whereas pests (insects and rodents) and bacteria have a negative impact on
crop production.
Climate conditions and nonliving natural resources such as soil, water, and air are
examples of abiotic factors.They also have an impact on crop productivity, as
favourable temperature, humidity, and mineral nutrition boost crop yield.
2. What are the desirable agronomic characteristics for crop improvements?
Ans: The following are desired agronomic traits for crop improvement:
(i) For cereal crops, dwarfness is a beneficial trait since it allows the plants to use
fewer nutrients.
Class IX Science www.vedantu.com 6
(ii) Tallness and profuse branching are ideal traits for fodder crops so that we can
get more leaves to feed our animals.
3. What are macronutrients and why are they called macronutrients?
Ans: There are sixteen nutrients that are required for plant growth. Six of these
thirteen nutrients are considered macronutrients since they are required in high
amounts.
Nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and sulphur are all
macronutrients.
4. How do plants get nutrients?
Ans: Plants get their nutrients from the air, water, and soil.Nutrients supplied as a
source Carbon in the air, oxygen in the air Hydrogen and oxygen are found in
water.
Soil nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sulphur, iron,
manganese, boron, zinc, copper, molybdenum, chlorine, zinc, manganese,
5. Compare the use of manure and fertilizers in maintaining soil fertility.
Ans: The comparison between use of manure and fertilizers are as follows:
Manure Fertilizers
It is made through the breakdown of animal They are manufactured
excreta and plant waste commercially in factories
It contains a lot of organic matter while also Provides components like nitrogen,
providing tiny amounts of nutrients to the phosphorous, and potassium
soil
Class IX Science www.vedantu.com 7
Helps to increase soil fertility Assures soil fertility in terms of
dose and timing.
6. Why should preventive measures and biological control methods be
preferred for protecting crops?
Ans: It is likewise true for plants that prevention is preferable to treatment.
Herbicides, weedicides, insecticides, pesticides, fungicides, and other chemicals
are sprayed on the crop.
Because their excessive usage can injure crop plants and pollute the environment,
careful seed bed preparation, timely crop sowing, intercropping, and crop rotation
are also recommended.
7. Which method is commonly used for improving cattle breeds and why?
Ans: Cross breeding is a typical technique for developing cow breeds.
For instance, in dairy animals Exotic or foreign breeds (such as Jersey and Brown
Swiss) are bred for lengthy lactation durations, whilst native breeds (such as
RedSindhi and Sahiwal) are bred for disease resistance. The two can be crossed to
produce animals with both desirable traits.
8. Discuss the implications of the following statement:
“It is interesting to note that poultry is India’s most efficient converter of low
fibre food stuff(which is unfit for human consumption) into highly nutritious
animal protein food.”
Ans: Under poultry the birds kept are fed on agricultural waste material and
broken grains etc which are not useful for humans but those birds consuming such
waste provide us with eggs and meat. It is highly nutritious animal protein food
hence the statement made is quite appropriate.
Class IX Science www.vedantu.com 8
9. What management practices are common in dairy and poultry farming?
Ans: Food requirements Proper cleaning and shelter facilities Protection from
unfavourable climatic conditions and diseases are frequent management strategies
in dairy and poultry farms. Protection against pests
10. What are the differences between broilers and layers and in their
management?
Ans: Differences between broilers and layers are represented in the following
table:
Broilers Layers
Broiler chickens require vitamin-rich Broilers require different
supplements, particularly vitamin A and K, nutritional, environmental, and
for optimal development. housing requirements than egg
layers.
They consume a sufficient amount of protein In comparison to broilers, they
and fat in their diet. They also require don't consume a sufficient
additional care and maintenance to enhance amount of protein and fat in their
their survival probability. diet.
Broilers are bred to provide poultry meat. Layers are bred to produce eggs.
11. How are fish obtained?
Ans: Fishes can be obtained in two ways.
1. Capture fishing: This is a method of collecting fish from natural sources
(rivers, lakes, oceans).
Class IX Science www.vedantu.com 9
2. Cultural fishery: This is also known as fish farming and involves the rearing
and breeding of selected fish.
12. What are the advantages of composite fish culture?
Ans: The following are some of the benefits of composite fish culture:
In such systems, both indigenous and imported fish species can be utilised.
Food accessible in all regions of the water reservoir is exploited due to the non-
competitive nature of selected species.
Increases the amount of fish in the water reservoir (intensive fish farming).
13. What are the desirable characters of bee varieties suitable for honey
production?
Ans: Characteristics of bee types appropriate for honey production include:
Honey harvesting capacity is high. They have to be less stingy.
They should stay in a beehive for a long time and breed prolifically.
14. What is pasturage and how is it related to honey production?
Ans: Pasturage refers to the blooms that bees can collect nectar and pollen from.
The pasturage determines the value or quality of honey. In addition, the type of
flowers present will influence the honey's flavour.
15. For increasing production, what is common in poultry, fisheries and bee-
keeping?
Ans: The following are steps that are commonly used in poultry, fisheries, and
beekeeping to increase production:
Class IX Science www.vedantu.com 10
The best types and breeds are used. Food is supplied that is both nutritional
and tasty.
Cleanliness and hygienic conditions are maintained.
16. What are the benefits of cattle farming?
Ans: Cattle farming provides two advantages:
(i) Draught animals for farm labour (males), i.e. tilling, irrigation, and carting.
(ii) Milch animals (dairy animals) are females who produce milk.
17. How do storage grain losses occur?
Ans: Storage grain losses are caused by a variety of biotic and abiotic factors:
biotic factors include insects, rodents, bacteria, fungi, and other organisms that
feed on grains. Unfavorable humidity and temperature conditions are abiotic
variables.
18. Why are manure and fertilizers used in fields?
Ans: Manure contributes to soil fertility by supplementing it with nutrients and
organic materials. The majority of organic matter in manure aids in soil structure
improvement.
Fertilizers are used to promote healthy vegetative growth (leaves, branches, and
flowers) by supplying specific nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and
potassium.
19. Define
(a) Pisciculture
Ans: Pisciculture is the large-scale rearing and management of fish.
Class IX Science www.vedantu.com 11
(b) hatcheries
Ans: Hatcheries are nurseries where fish eggs or fish seed are placed in freshwater
fisheries.
(c) swarming
Ans: Swarming is the process by which the new queen leaves the old hives and
seeks out a new home for reproduction.
20. What is green manuring? Give examples of green manures.
Ans: Green manure is made from herbaceous plants that are cultivated, ploughed
beneath, and mixed with the soil while they are still green. Green manuring is the
process of ploughing green plants and combining them with the soil.
Sun hemp, cluster bean (guar), lentil (Masur), and cowpea are some of the plants
utilised as green manure (Lobia).
21. Discuss the preventive measures for the storage of grains.
Ans: The preventive measures for the storage of grains are:
a) Drying - For grain storage, the moisture content of the grains should be
decreased to less than 14 percent. This can be accomplished by drying in the sun
and then drying in the shade.
b) Hygiene should be maintained - Godowns and stores should be cleaned
regularly.
Remove any dirt, trash, webs, or debris from the previously kept grains.
Waterproofing and sealing cracks and gaps in the walls, floor, and ceiling are
essential. For storing food grains, new gunny bags should be used. The mouth of
the gunny bag should be tightly sewn once it has been filled.
22. Name three basic scientific approaches for increasing yield of a crop.
Ans: Three scientific approaches for increasing yields of a crop are –
Class IX Science www.vedantu.com 12
(i) Crop production management, which involves correct irrigation and fertiliser
management, is one of three scientific methodologies for enhancing crop yields.
Manure and fertilisers can be used to accomplish this. Crop rotation, intercropping,
and mixed-cropping can all help with nutrient management.Plants require
protection from weeds, insects, pests, and pathogens.
(ii) Crop protection management It can be accomplished through biological,
chemical, or cultural methods.
(iii) Crop variety management: Crop variety can be enhanced by hybridization or
transgenic techniques. It is possible to do so in order to get desired plant traits
23. What are the advantages of bee-keeping?
Ans:The following are some of the benefits of beekeeping:
a) It takes minimal investment and offers the farmer additional income.
b) In addition to honey, beekeeping produces wax, royal jelly, and bee venom,
among other things.
c) Cross pollination is aided by bees.
24. Differentiate between capture fishing, aquaculture and mariculture.
Ans: The difference between capture fishing, aquaculture and mariculture is:
a) Capture fishing - Capture fishing is the process of obtaining fish from bodies of
water such as rivers, seas, and oceAns:
b) Aquaculture - Aquaculture is the cultivation of aquatic creatures in fresh or
saltwater.
c) Mariculture - Mariculture is the cultivation of marine fish.
25. List the steps to be taken to prevent and control diseases in animals.
Ans: The following steps should be followed to control diseases:
Class IX Science www.vedantu.com 13
a) Providing adequate shelter.
b) Maintaining animal hygiene and disposing of dead animals and animal wastes
properly.
c) Disease screening of animals on a regular basis, with unhealthy animals being
isolated immediately.
d) Following the advice of a veterinary practitioner, providing a proper diet and
appropriate medications.
e) Handling of all animal products and by product in a sanitary manner.
26. Give the difference between manures and fertilizers.
Ans: The difference between manure and fertilizers are as follows:
Manure Fertilizers
Manure is an organic natural substance that is Fertilizers are inorganic
formed when living materials decompose. compounds that are produced in
factories.
Large amounts of organic materials can be There is no organic substance
found in manure. present in fertilizers.
Manures aren't nutrient-specific at all Fertilizers have nutrient-specific
properties
27. What are the components of cattle feed?
Ans: Roughage and concentrates are present in cattle feed in the form of hay and
grain, as well as a large amount of water.
a)Roughage — Roughage is made up of coarse and fibrous components with poor
nutrient content; animals acquire roughage from hay (cereal straw) and grain,
respectively, as well as a lot of water.
Class IX Science www.vedantu.com 14
b)Cotton seeds, oilseeds, oilcakes, and cereal grains like gramme and bajra are
high in one or more nutrients (such as carbohydrate, lipids, proteins, minerals, and
vitamins) and low in fibres. Cattle are fed green fodder in the winter, primarily
Berseem and Lucerne, and maize, bajra, jowar, and dry fodder in the other seasons.
28. Define the following
(i) White revolution
Ans: The term "white revolution" refers to the increased production of milk. It
required the utilisation of upgraded high-milk-yielding mulch animal crossbreeds.
(ii) Silver revolution
Ans: The term "silver revolution" refers to a massive increase in egg output.
(iii) blue revolution.
Ans: The term "blue revolution" refers to an increase in fish production.
29. What is green manuring? Give an example of green manures?
Ans: Green manure is made from herbaceous plants that have been cultivated,
ploughed under, and mixed with the soil while they are still green. Green manuring
is the term for this process.
Sun hemp, cluster bean (guar), lentil (maser), and cowpea are some of the
plants utilised as green manure (Berseem)
30. What are the main practices involved in keeping animals or animal
husbandry?
Ans: Animal husbandry day involves the following main practises.
a) Breeding - This is done to get animals with specific traits. Animals with high
milk yields and meat yields can be developed through breeding.
Class IX Science www.vedantu.com 15
b) Feeding – This is the study of the right food (called feed), as well as the mode
and timing of feeding of various animals.
c) Weeding - This is the process of eliminating animals that are not economically
viable.
31. Name the abiotic and biotic factors which affect stored grains and how?
Ans: Insects, birds, rodents, mites, fungi, and bacteria are examples of biotic
forces.
a)Moisture, temperature, and the storage container's material are all abiotic
variables. As a result of the aforementioned conditions, cereal grains become
infested with insects and microorganisms.
b) Quality deterioration
c) Weight reduction.
b) Poor grain germination potential
e) Produce discoloration
32. What is the need for crop improvement? What are the desirable
agronomic characteristics for crop improvement?
Ans: Crop enhancement entails creating superior plants with the following
characteristics:
a) High-yielding
b) Varieties with higher-quality produce.
b) Disease-resistant cultivars
d) Plants have beneficial agronomic traits, such as
(i) Dwarfness is required in cereals, which consumes less nutrients.
(ii) Plants for fodder crops that are tall and have a lot of branching.
Class IX Science www.vedantu.com 16
33. Define
(i) Draught breeds
Ans: Draught cattle, sometimes known as bullocks, are cattle that are employed for
labour.
(ii) Dual purpose breeds
Ans: Dual-purpose breeds are those that have females for milk and men for work.
(iii) Dairy breeds
Ans: Dairy animals are breeds that are solely used for milk production.
34. What are the symptoms of diseased animals?
Ans: The symptoms are as follows:
a) The animal stops eating and becomes lethargic, looks exhausted, and remains
isolated as a result of the condition.
b) The animal shivers as its body temperature rises.
b) The animal produces an excessive amount of saliva, which hangs from its mouth
at times.
d) The animal excretes a mixture of loose dung and colourful urine.
e) The animal's mouth and ears droop.
Long Answer Type Questions 5 Marks
1. Explain any one method of crop production which ensures high yield.
Ans: Various cropping patterns can be very effective in ensuring good output. The
following cropping patterns should be mentioned:
1. a combination of crops
2. cropping in between
Class IX Science www.vedantu.com 17
3. Rotation of crops
Mixed cropping: is the practise of cultivating two or more crops on the same plot
of land at the same time, such as wheat + gramme, wheat + mustard, or groundnut
+ sunflower.
This lowers the risk and provides some protection in the event that one of
the crops fails.
Intercropping: is the practise of planting two or more crops on the same field in a
certain arrangement (as shown below).
The crops are chosen to have distinct nutrient requirements. This promotes
optimal nutrient use while also preventing pests and diseases from spreading
to all plants belonging to a single crop in a field, such as soya bean + maize
or finger millet.
Crop rotation: is the planting of various crops on a plot of land in a pre-
determined order succession.
Crop rotation is done for various crop combinations depending on the
period.
The crop to be planted after one harvest is determined by the availability of
moisture and irrigation infrastructure.
Two or three crops can be planted in a year with good harvests if crop
rotation is done appropriately.
2. What are the advantages of intercropping and crop rotation?
Ans: Advantages of inter -cropping and crop rotation:
This way,both crops can give better returns.Crop rotation, when done
correctly, allows for the replenishment of soil nutrients without the need of
fertilisers.
For example, growing leguminous plants following a non-leguminous crop
in the same field ensures nitrogen enrichment.
As a result, any decline in soil fertility is avoided.
Class IX Science www.vedantu.com 18
Intercropping makes the most use of the nutrients available. It also prevents
pests and illnesses from spreading to all plants of a single crop in a field.
3. What is genetic manipulation? How is it useful in agricultural practices?
Ans: Genetic manipulation is the introduction of a gene that confers a desired trait,
resulting in genetically engineered crops.
Agricultural methods benefit from genetic modification by creating varieties with
larger yields, better quality, shorter maturity periods, and more tolerance to
unfavourable environmental circumstances. Some of the other practices are:
High yielding pest resistant.
resistant to environmental stress don’t need fertilizers for good growth
All these features help not only to improve quality and quantity of products
but also reduce chances of environmental pollution.
4. How do good animal husbandry practices benefit farmers?
Ans: Animal husbandry refers to the scientific management of livestock animals. It
covers a wide range of topics.Feeding, breeding, and disease control are all factors
to consider.
The demand for milk, eggs, and meat is increasing as the population grows and
living standards rise. In addition, the increased awareness of the importance of
adequate animal treatment has imposed new restrictions on livestock production
.As a result, cattle output must be improved. Good animal husbandry practises,
such as providing good food and controlling infections in cattle, can contribute to
this progress, allowing farmers to receive higher quality and quantity goods.
5. How do you differentiate between capture fishing, mariculture and
aquaculture?
Ans: The difference between capture fishing, mariculture and aquaculture is as
follows:
Class IX Science www.vedantu.com 19
Capture fishing Mariculture Aquaculture
It's a technique for Marine culture fisheries are These cultural fisheries are
catching fish from culture fisheries that are kept in fresh or saltwater, and
natural sources. maintained in marine water they allow for the raising and
bodies only for the purpose production of a higher
of rearing and breeding number of aquatic creatures.
marine creatures such as fish
and prawns.
6. What is genetic manipulation? How is it useful in agricultural practices?
Ans: Genetic manipulation is a technique for improving the genetic make-up of
crop plants in order to achieve desired features.
Genetic manipulation's benefits
1) It creates high-yielding cultivars.
2) It creates disease-resistant strains.
3) It creates pest-resistant cultivars.
4) It creates cultivars with a quick maturation time and a consistent maturity.
5) creates higher-quality variations.
Class IX Science www.vedantu.com 20
You might also like
- Lorna Freeman - Borderlands 01 - CovenantsDocument325 pagesLorna Freeman - Borderlands 01 - CovenantsAnokshii100% (3)
- Cultural Management PracticesDocument13 pagesCultural Management PracticesFebz Canutab67% (12)
- Science UT 1Document99 pagesScience UT 1chitra sabarinathanNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food Resources... Chapter .. Home Work QuestionsDocument6 pagesImprovement in Food Resources... Chapter .. Home Work Questionsthe pantherNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food Resources Concept WS For Class 9 KeyDocument9 pagesImprovement in Food Resources Concept WS For Class 9 Key1210442No ratings yet
- Question Bank BioDocument19 pagesQuestion Bank BioMr Sony MathewNo ratings yet
- Ypvpgwl15ypvpgwl15-Study Material-202005110828pm028364-Science 1-1Document5 pagesYpvpgwl15ypvpgwl15-Study Material-202005110828pm028364-Science 1-1AnantNo ratings yet
- 9 Science Imp Ch15 3Document10 pages9 Science Imp Ch15 3deepakNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food Resources Q & AnsDocument6 pagesImprovement in Food Resources Q & AnsMohammed AadilNo ratings yet
- QB Science Improvement in Food Resources Class IX 2023Document5 pagesQB Science Improvement in Food Resources Class IX 2023dhannu2204No ratings yet
- Ch1 Crop Production: Short Q/A: Answer in A Sentence or Two - (Type I)Document9 pagesCh1 Crop Production: Short Q/A: Answer in A Sentence or Two - (Type I)KRISHNA STANGELNo ratings yet
- Test Paper 2Document4 pagesTest Paper 2masaaza001No ratings yet
- Ch-15 Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument9 pagesCh-15 Improvement in Food ResourcesAakankshaNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food IxDocument6 pagesImprovement in Food IxGOPAL SINo ratings yet
- NCERT Questions - Improvement in Food Resources - Everonn - CBSE Class-9thDocument6 pagesNCERT Questions - Improvement in Food Resources - Everonn - CBSE Class-9thViren PatelNo ratings yet
- RAM-TVL11 Organic AgricultureDocument13 pagesRAM-TVL11 Organic AgricultureHazel JusosNo ratings yet
- 8th Food Production and Management Cordova Mastering Science-8 SolutionDocument4 pages8th Food Production and Management Cordova Mastering Science-8 Solution【Yᴀᴋꜱʜ Gᴀᴜᴛᴀᴍ】No ratings yet
- IX SC - CH 15 - Q & A - Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument6 pagesIX SC - CH 15 - Q & A - Improvement in Food Resourcesgbshse.techNo ratings yet
- Page No: 204: Chapter 15 - Improvement in Food Resources in Text QuestionsDocument7 pagesPage No: 204: Chapter 15 - Improvement in Food Resources in Text Questionsmadhurreet jaiswalNo ratings yet
- Crop Production AnswersDocument5 pagesCrop Production AnswersdfefeeeeeNo ratings yet
- Biology 20240120151639Document17 pagesBiology 20240120151639muskangoswami212No ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - Intext QuesionsDocument5 pagesChapter 15 - Intext QuesionsShailaja MestryNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter-1 Crop Production and Management ModuleDocument3 pagesBiology Chapter-1 Crop Production and Management ModuleNEIL GAROONo ratings yet
- Textbook ExercisesDocument4 pagesTextbook ExercisesBheeyahh Marie AvilaNo ratings yet
- Class 8 - Science - Crop Production and ManagementDocument7 pagesClass 8 - Science - Crop Production and ManagementAyaan KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Food Production and ManagementDocument6 pagesFood Production and ManagementAamirNo ratings yet
- RAM-TLE10 Organic AgricultureDocument13 pagesRAM-TLE10 Organic AgricultureHazel JusosNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food Resources NotesDocument20 pagesImprovement in Food Resources Notesprusty.nishant.09No ratings yet
- Working of InstitutionsDocument11 pagesWorking of InstitutionsShiv KotadiyaNo ratings yet
- CH 13 Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument3 pagesCH 13 Improvement in Food ResourcesPRAVEEN KUMARNo ratings yet
- Wa0139.Document5 pagesWa0139.Learn with Saransh & Tanishq manglaNo ratings yet
- CH 15 QPDocument10 pagesCH 15 QPzoomNo ratings yet
- CH-1 Exercise Q-ADocument6 pagesCH-1 Exercise Q-Aanandsuryavanshi08No ratings yet
- WWW - CBSE123.CO - CC: Chapter 1 - Class Viii Crop Production and ManagementDocument5 pagesWWW - CBSE123.CO - CC: Chapter 1 - Class Viii Crop Production and ManagementgunjantiggaNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food Resource - Mat PDFDocument13 pagesImprovement in Food Resource - Mat PDFAyushman TripathyNo ratings yet
- Aanswer Key Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument4 pagesAanswer Key Improvement in Food ResourcesJeffrish Doni EzhilNo ratings yet
- Biology - Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources: Intext QuestionsDocument3 pagesBiology - Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources: Intext QuestionsShailaja MestryNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food Resources-NotesDocument6 pagesImprovement in Food Resources-Notesyatharthdange131No ratings yet
- Improvement in Food Resources-1Document4 pagesImprovement in Food Resources-1haadiya aliNo ratings yet
- Answer: Page No: 205Document6 pagesAnswer: Page No: 205apoorv saxenaNo ratings yet
- Bio Questions Answers CropDocument3 pagesBio Questions Answers Cropharshpreet kaurNo ratings yet
- CBSE NCERT Solutions For Class 8 Science Chapter 1: Back of Chapter QuestionsDocument7 pagesCBSE NCERT Solutions For Class 8 Science Chapter 1: Back of Chapter Questionsprem singhNo ratings yet
- Worksheet-IX - Ch.15-Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument9 pagesWorksheet-IX - Ch.15-Improvement in Food ResourcesPallavi MantriNo ratings yet
- Crop Production and Management NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Chapter 1Document10 pagesCrop Production and Management NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Chapter 1Shaurya ManiktalaNo ratings yet
- Cl-8 Crop ProductionDocument4 pagesCl-8 Crop ProductionTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Lakhmir Singh Sol Class 8 Science Chapter 1Document12 pagesLakhmir Singh Sol Class 8 Science Chapter 1shantijoshi152011No ratings yet
- Crop Production and Management ExamplerDocument12 pagesCrop Production and Management ExamplerSubham ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- CROP PRODUCTION AND MANAGEMNT Answer KeyDocument3 pagesCROP PRODUCTION AND MANAGEMNT Answer KeyVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- AGRI 32 Lecture Fourth ExamDocument2 pagesAGRI 32 Lecture Fourth ExamAria MoonNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Crop Production Eureka Plus Science Exercise AnswerDocument5 pagesClass 8 Crop Production Eureka Plus Science Exercise AnswerabhimanusksNo ratings yet
- Module - 1/4 Class IX Prepared By-Punam Jyoti Lakra School - AECS TuramdihDocument16 pagesModule - 1/4 Class IX Prepared By-Punam Jyoti Lakra School - AECS TuramdihDanica S.JNo ratings yet
- 8 Science NCERT Solutions Chapter 1Document5 pages8 Science NCERT Solutions Chapter 1Suyash100% (1)
- Crop Production Class 8Document4 pagesCrop Production Class 8Tanya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Master Copy Science Class 8Document76 pagesMaster Copy Science Class 8Phani Kumar AllamrajuNo ratings yet
- Science 8th English Medium ch1Document6 pagesScience 8th English Medium ch1Shashank GokaviNo ratings yet
- CH 15Document12 pagesCH 15sneha2701choudharyNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food Resources-NotesDocument9 pagesImprovement in Food Resources-Notesapi-285274293No ratings yet
- ISFO Science+Grade+8 2022Document73 pagesISFO Science+Grade+8 2022Aerospace Briefcase100% (2)
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 8Document8 pagesMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 8Shubham YadavNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions For Class 9 March 29 Science Chapter 15 Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument12 pagesNcert Solutions For Class 9 March 29 Science Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resourceshiten00008No ratings yet
- Cover Crops : Improving Soil Structure and Reducing ErosionFrom EverandCover Crops : Improving Soil Structure and Reducing ErosionNo ratings yet
- NECO 2024 PRACTICAL AGRIC Study Guide by The EXAM LANDLORDS 07011946086Document20 pagesNECO 2024 PRACTICAL AGRIC Study Guide by The EXAM LANDLORDS 07011946086divinemaxwell2001No ratings yet
- Biodiversity Book English PDFDocument90 pagesBiodiversity Book English PDFsarora_usNo ratings yet
- Climate Change and Food SecurityDocument11 pagesClimate Change and Food SecuritySNEHA SENGUPTANo ratings yet
- PROBLEM SET Ab ProductsDocument1 pagePROBLEM SET Ab ProductsXari FayeNo ratings yet
- Ext QB SIE BComABCD SemVI ZehanDocument2 pagesExt QB SIE BComABCD SemVI ZehanRoguewolfx VFXNo ratings yet
- Learning Area Grade Level Quarter Date: Tvl-Afa-Landscape Installation and Maintenance Eleven FourDocument4 pagesLearning Area Grade Level Quarter Date: Tvl-Afa-Landscape Installation and Maintenance Eleven FourAngel TeumeNo ratings yet
- English II. Directions: Read Each Question Carefully Then Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerDocument4 pagesEnglish II. Directions: Read Each Question Carefully Then Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerAaron Broglie CondeNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Irrigation ShadufDocument10 pagesChapter Two: Irrigation ShadufvectorNo ratings yet
- The Trophy Cow - A Mooing Story 1Document9 pagesThe Trophy Cow - A Mooing Story 1Manjunath UBNo ratings yet
- Scales of Corn Stages ArvalisDocument2 pagesScales of Corn Stages ArvalisNecula CristianaNo ratings yet
- HLURB CLUP Guidebook Vol 3 07312015Document101 pagesHLURB CLUP Guidebook Vol 3 07312015tineosiervo23No ratings yet
- Coffee Tea and Spice Handout EndestDocument128 pagesCoffee Tea and Spice Handout EndestHailu Hameso100% (5)
- Inception ReportDocument43 pagesInception ReportsurendramaharjanNo ratings yet
- Alkalinity Management in Shrimp PondDocument3 pagesAlkalinity Management in Shrimp Pondly minh quanNo ratings yet
- Sifat Keterawetan Dan Keawetan Kayu Durian, Limus, Dan Duku Terhadap Rayap Kayu Kering, Rayap Tanah, Dan Jamur PelapukDocument69 pagesSifat Keterawetan Dan Keawetan Kayu Durian, Limus, Dan Duku Terhadap Rayap Kayu Kering, Rayap Tanah, Dan Jamur PelapukEnoNo ratings yet
- SudokuDocument32 pagesSudokuYeeyee Aung100% (3)
- FMP211 Practical Manual - B.sc. (Horti) - 2023Document94 pagesFMP211 Practical Manual - B.sc. (Horti) - 2023Bharathi ShankarNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument6 pagesThesisRomeo Mariano100% (1)
- A Letter To EditorDocument9 pagesA Letter To EditorPooja SainiNo ratings yet
- Wbi13 01 Que 20220526Document20 pagesWbi13 01 Que 20220526Mysterio OfficiallyNo ratings yet
- Effect of Fruit Load On Dry Matter Partitioning in TomatoDocument9 pagesEffect of Fruit Load On Dry Matter Partitioning in TomatofirdatunNo ratings yet
- Amit Card DPM Basudeo Banerjee Chiraag - ChhattisgarhDocument2 pagesAmit Card DPM Basudeo Banerjee Chiraag - ChhattisgarhRavi S. SharmaNo ratings yet
- Company Profile PT Bintang Agro Sentosa English Standard Version PDFDocument24 pagesCompany Profile PT Bintang Agro Sentosa English Standard Version PDFSkandinavia ApartmentNo ratings yet
- Biological AssetsDocument22 pagesBiological AssetsSaeym Segovia100% (2)
- National Agricultural Setup in IndiaDocument10 pagesNational Agricultural Setup in IndiaVivek PatelNo ratings yet
- ODOP AbhijatDocument34 pagesODOP AbhijatAbhijat MittalNo ratings yet
- "Maharashtra Educationaltour": Prajval Gopalrao Deshmukh Ss-1303Document54 pages"Maharashtra Educationaltour": Prajval Gopalrao Deshmukh Ss-1303Prajval Gopalrao DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal Form: Sorsogon State UniversityDocument4 pagesResearch Proposal Form: Sorsogon State UniversityMichael BongalontaNo ratings yet
- 2017 - Dohong Et Al - Review of Drivers of Tropical Degradaton in ASEAN PDFDocument12 pages2017 - Dohong Et Al - Review of Drivers of Tropical Degradaton in ASEAN PDFnesijaycoNo ratings yet