Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 viewsReproductive System
Reproductive System
Uploaded by
Gelo AlonzoThis document contains exercises on the male and female reproductive systems for a nursing student named Alonzo Angelo F. For the male reproductive system exercise, the student is asked to draw and label diagrams of the sagittal section and internal structures of the penis. The student is also asked to define terms like circumcision and cryptorchidism. For the female reproductive system exercise, similar drawing and labeling of diagrams is requested along with enumerating the phases of the menstrual cycle and defining ectopic pregnancy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Reproductive - Systems - in - Vertebrates ss2Document12 pagesReproductive - Systems - in - Vertebrates ss2Ezeh Princess100% (1)
- WEEK 17 LAB EXERCISE - Reproductive System (Male & Female)Document6 pagesWEEK 17 LAB EXERCISE - Reproductive System (Male & Female)Lance KennethNo ratings yet
- Lab Act in Repro.Document4 pagesLab Act in Repro.Jhia TorreonNo ratings yet
- PP5. Human ReproductionDocument138 pagesPP5. Human ReproductionSamalaniNo ratings yet
- Please Discuss Your Answer BrieflyDocument4 pagesPlease Discuss Your Answer BrieflyAlexis John Hisula VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- Midterm 1Document18 pagesMidterm 1Jenelyn AbayatoNo ratings yet
- Manual Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesManual Reproductive Systemrayverjohnlayam073No ratings yet
- Lesson 11 - Human ReproductionDocument10 pagesLesson 11 - Human ReproductionkreativekerelleNo ratings yet
- Mod 2 7 For Students PDFDocument118 pagesMod 2 7 For Students PDFpetergomez0119No ratings yet
- Grade10 Lesson2 ReproductiveAnat - 1Document18 pagesGrade10 Lesson2 ReproductiveAnat - 1JaimeCrispino0% (1)
- Reproductive System Physiology NotesDocument5 pagesReproductive System Physiology NotesKaye Alyssa EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Promotive and Preventive Nursing Care ManagementDocument440 pagesPromotive and Preventive Nursing Care ManagementGrace Lladoc ChalmasNo ratings yet
- PPT1 BioDocument53 pagesPPT1 BioRalph NilloNo ratings yet
- WEEK 17 LAB EXERCISE Reproductive System Male Female 1Document6 pagesWEEK 17 LAB EXERCISE Reproductive System Male Female 1DELA CRUZ, JENISSE LOUISSENo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Life Science Human Reproduction NotesDocument138 pagesGrade 12 Life Science Human Reproduction NotesLulo NnenaNo ratings yet
- Uts Chapter 2 Lesson 1Document29 pagesUts Chapter 2 Lesson 1John Jerome GironellaNo ratings yet
- Week 6Document3 pagesWeek 6John JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Hr-Module 1-Lesson 1Document35 pagesHr-Module 1-Lesson 1Sevilla, Marpolo Joaquin Z.No ratings yet
- Unit Ii Biomedical Perspective in Gender and SexualityDocument46 pagesUnit Ii Biomedical Perspective in Gender and SexualityRowena Lanete ButaNo ratings yet
- Sci10-q3-Male and Female Repro SystemDocument71 pagesSci10-q3-Male and Female Repro SystemDani Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Topic12-Magcamit, Mark Vincent MaciasDocument8 pagesTopic12-Magcamit, Mark Vincent MaciasHermaphroditiusNo ratings yet
- SPEC I TASK 12 - Human Reproductive SystemDocument11 pagesSPEC I TASK 12 - Human Reproductive SystemJERIEL MARTIREZNo ratings yet
- Session #45 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab) (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Document6 pagesSession #45 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab) (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Nicole Ken AgdanaNo ratings yet
- q3 Science 10 w1Document5 pagesq3 Science 10 w1Kimi LegsonNo ratings yet
- Gned 10 - Biomedical Perspective of Gender and SexualityDocument6 pagesGned 10 - Biomedical Perspective of Gender and Sexualityjoanna.filosopoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System JblsDocument2 pagesReproductive System JblsLINDAS XEROXNo ratings yet
- Biology M13 Human Reproductive SystemDocument30 pagesBiology M13 Human Reproductive SystemEunice CorreaNo ratings yet
- 24.3. Human Reproductive Anatomy and GametogenesiDocument2 pages24.3. Human Reproductive Anatomy and GametogenesijkhdgmbrvdNo ratings yet
- GENSOC M2 Lesson 4Document7 pagesGENSOC M2 Lesson 4cassy margaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document15 pagesLesson 4KR CoruñaNo ratings yet
- HARAMAY Reproductive Physiology and AI Course Handout Ashenafi andDocument72 pagesHARAMAY Reproductive Physiology and AI Course Handout Ashenafi andabrhamtafere700No ratings yet
- Lesson 4 To 7Document35 pagesLesson 4 To 7Macario estarjerasNo ratings yet
- Female Repro AssessmentDocument4 pagesFemale Repro AssessmentHu T. BunuanNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1FEMALE Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesMODULE 1FEMALE Reproductive SystemHoney Lou SemblanteNo ratings yet
- Gender and Society CompileDocument32 pagesGender and Society Compileクイーンクイーン ロペスNo ratings yet
- Science10 q3 Mod1 Reproductiveandendocrineeystems v5Document25 pagesScience10 q3 Mod1 Reproductiveandendocrineeystems v5cubillanjoshuajames12No ratings yet
- Human Reproduction: 3.1 T M R SDocument15 pagesHuman Reproduction: 3.1 T M R SSrajanNo ratings yet
- Ma'am Cantos Module 4Document5 pagesMa'am Cantos Module 4emmanuelNo ratings yet
- PP5. Human ReproductionDocument100 pagesPP5. Human ReproductionhellohlayisoNo ratings yet
- Urogenital SystemDocument5 pagesUrogenital Systemstudent10100No ratings yet
- PP5.Human Reproduction (Updated)Document65 pagesPP5.Human Reproduction (Updated)hellohlayisoNo ratings yet
- Repoductive SystemDocument14 pagesRepoductive SystemJhoanna Marie RebutNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE-5-Q2-WK 1 SHLT 1 OkDocument10 pagesSCIENCE-5-Q2-WK 1 SHLT 1 OkMaria Renita BelcinaNo ratings yet
- LAS 3rd Quarter FINALDocument58 pagesLAS 3rd Quarter FINALJustine Emilia100% (1)
- Unit 8 The Reproductive System Bilingual EducationDocument13 pagesUnit 8 The Reproductive System Bilingual EducationAntonio PrietoNo ratings yet
- Exemplar 3rdDocument5 pagesExemplar 3rdRAYMUND RODILLONo ratings yet
- Pre-Reading For Reproductive SystemDocument16 pagesPre-Reading For Reproductive SystemRill VasanthNo ratings yet
- Science: Third QuarterDocument10 pagesScience: Third Quarterrig guel100% (1)
- 2024 GRADE 12 Notes Term 1Document32 pages2024 GRADE 12 Notes Term 1simwingaelvis37No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of ReproductionAstorias Jayv B.No ratings yet
- Human Reproduction 2019Document138 pagesHuman Reproduction 2019daylinallie2007No ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument26 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemAlmario DacalcapNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health NursingDocument181 pagesMaternal and Child Health NursingKarina Jane Farnacio Purugganan100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology "Male and Female Reproductive System"Document12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology "Male and Female Reproductive System"tania scNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology CorrectedDocument15 pagesAnatomy and Physiology CorrectedSANCHAYEETANo ratings yet
- Q3-DLL Week 2Document5 pagesQ3-DLL Week 2Jun Dadiahon AlindayoNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Q3 - Module 1 For EditedDocument14 pagesScience 10 Q3 - Module 1 For Editedtaylorsheesh64No ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument130 pagesReproductive SystemReymark NovecioNo ratings yet
- Week 11 - CD Course Task 4. PTB, Pneumonia, Diphtheria, Pertusis, MumpsDocument1 pageWeek 11 - CD Course Task 4. PTB, Pneumonia, Diphtheria, Pertusis, MumpsGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Week 15 - ONCO COURSE TASK - Breast Cancer DetectionDocument3 pagesWeek 15 - ONCO COURSE TASK - Breast Cancer DetectionGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Library Works - CD - Communicable Diseases Trends and IssuesDocument1 pageLibrary Works - CD - Communicable Diseases Trends and IssuesGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Exercise 6Document6 pagesExercise 6Gelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Exercise 8Document2 pagesExercise 8Gelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Exercise 7Document7 pagesExercise 7Gelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Week 5 ExerciseDocument7 pagesWeek 5 ExerciseGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- LABORATORY EXERCISE The Gastrointestinal System With Accessory GlandDocument5 pagesLABORATORY EXERCISE The Gastrointestinal System With Accessory GlandGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- WEEK 9 LABORATORY EXERCISE The Cardiovascular System, The Heart and The Blood VesselsDocument4 pagesWEEK 9 LABORATORY EXERCISE The Cardiovascular System, The Heart and The Blood VesselsGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- WEEK 15 LAB EXERCISE - Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesWEEK 15 LAB EXERCISE - Endocrine SystemGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- WEEK 16 LABORATORY EXERCISE Special SensesDocument7 pagesWEEK 16 LABORATORY EXERCISE Special SensesGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- WEEK 14 LABORATORY EXERCISE The Urinary SystemDocument2 pagesWEEK 14 LABORATORY EXERCISE The Urinary SystemGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Purc Transes PrelimDocument4 pagesPurc Transes PrelimGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Anph Transes PrelimDocument34 pagesAnph Transes PrelimGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Engl Transes PrelimDocument4 pagesEngl Transes PrelimGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- BSN1-YA-41 Princinple of Art 1. Balance 3. EmphasisDocument2 pagesBSN1-YA-41 Princinple of Art 1. Balance 3. EmphasisGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument56 pagesReproductive SystemRochelle Ann Cunanan100% (1)
- Activity 2 Finals Histo Lab - EDLAY2ADocument2 pagesActivity 2 Finals Histo Lab - EDLAY2ATom Anthony TonguiaNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument22 pagesAbstractnayayathNo ratings yet
- Male and Female Reproductive System and MenstruationDocument11 pagesMale and Female Reproductive System and MenstruationSav LiyanageNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Special Senses and Reproductive SystemDocument2 pagesCase Study - Special Senses and Reproductive SystemGlydenne Glaire Poncardas GayamNo ratings yet
- Kista Mammae IDKDocument4 pagesKista Mammae IDKNormanPrabowoNo ratings yet
- Observational Study of New Treatment Proposal For Severe Intrauterine AdhesionDocument14 pagesObservational Study of New Treatment Proposal For Severe Intrauterine AdhesionOpenaccess Research paperNo ratings yet
- Assisting in Papanicolaou SmearDocument13 pagesAssisting in Papanicolaou SmearRika Mae100% (1)
- Menstrual CycleDocument9 pagesMenstrual CycleZhen ObelidorNo ratings yet
- Lucija Kljaić Male Infertility: Course: Medical English 5Document11 pagesLucija Kljaić Male Infertility: Course: Medical English 5Lucija KljaićNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Hypomenorrhea-Amenorrhea (Asherman'S Syndrome) : R. Toaff, M, D, S, Ballas, M.DDocument9 pagesTraumatic Hypomenorrhea-Amenorrhea (Asherman'S Syndrome) : R. Toaff, M, D, S, Ballas, M.DfarahNo ratings yet
- Case Report: Epidermoid Inclusion Cyst of The Clitoris As A Long-Term Complication of Female Genital MutilationDocument4 pagesCase Report: Epidermoid Inclusion Cyst of The Clitoris As A Long-Term Complication of Female Genital MutilationAngelina BelaNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of The Adnexal Mass 2020Document38 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of The Adnexal Mass 2020Sonia MVNo ratings yet
- Menstrual DisordersDocument77 pagesMenstrual Disorders2012100% (3)
- Management of HypospadiasDocument34 pagesManagement of HypospadiasAdebisiNo ratings yet
- Medicult Case StudyDocument3 pagesMedicult Case Studyrandy ambogNo ratings yet
- Induction of LabourDocument4 pagesInduction of LabournavyakuthatiNo ratings yet
- Project - : Menstrual CycleDocument20 pagesProject - : Menstrual CycleJIBAN KUMAR DASNo ratings yet
- Management of Asherman's SyndromeDocument14 pagesManagement of Asherman's SyndromeEquipmed VenezuelaNo ratings yet
- In-Vitro Fertilisation (Ivf) in Singapore: Charges and Success RatesDocument4 pagesIn-Vitro Fertilisation (Ivf) in Singapore: Charges and Success RatesLászló ÉvaNo ratings yet
- Third Assignment (Forensic)Document2 pagesThird Assignment (Forensic)Dean Mark AnacioNo ratings yet
- The Gynaecological History Taking and Physical Examination: Associate Professor DR - Yin Moe HanDocument50 pagesThe Gynaecological History Taking and Physical Examination: Associate Professor DR - Yin Moe HanAimethevanNo ratings yet
- DLL SCIENCE (MELCs) W1Document7 pagesDLL SCIENCE (MELCs) W1MYLEEN P. GONZALESNo ratings yet
- Hubungan Nyeri Haid (Dismenore) Dengan Aktivitas Belajar Sehari-Hari Pada Remaja Putri Kelas VII Di SMPN 3 PulungDocument8 pagesHubungan Nyeri Haid (Dismenore) Dengan Aktivitas Belajar Sehari-Hari Pada Remaja Putri Kelas VII Di SMPN 3 PulungTitaniaafni TasyabilaNo ratings yet
- Munce y 2021Document11 pagesMunce y 2021Your Imaginary StarNo ratings yet
- VaginitisDocument4 pagesVaginitisBinita ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Endometriosis PresentationDocument58 pagesEndometriosis PresentationBRI KU100% (1)
- Yeny Elfiyanti - 1910070100082 - Tugas Praktikum Anatomi 2Document5 pagesYeny Elfiyanti - 1910070100082 - Tugas Praktikum Anatomi 2Yeny ElfiyantiNo ratings yet
- Infertilidad MasculinaDocument22 pagesInfertilidad MasculinaAnaNo ratings yet
- DR Nadine Rev All (Samra's Edition)Document313 pagesDR Nadine Rev All (Samra's Edition)Cyril I.Makar100% (1)
Reproductive System
Reproductive System
Uploaded by
Gelo Alonzo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views5 pagesThis document contains exercises on the male and female reproductive systems for a nursing student named Alonzo Angelo F. For the male reproductive system exercise, the student is asked to draw and label diagrams of the sagittal section and internal structures of the penis. The student is also asked to define terms like circumcision and cryptorchidism. For the female reproductive system exercise, similar drawing and labeling of diagrams is requested along with enumerating the phases of the menstrual cycle and defining ectopic pregnancy.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains exercises on the male and female reproductive systems for a nursing student named Alonzo Angelo F. For the male reproductive system exercise, the student is asked to draw and label diagrams of the sagittal section and internal structures of the penis. The student is also asked to define terms like circumcision and cryptorchidism. For the female reproductive system exercise, similar drawing and labeling of diagrams is requested along with enumerating the phases of the menstrual cycle and defining ectopic pregnancy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views5 pagesReproductive System
Reproductive System
Uploaded by
Gelo AlonzoThis document contains exercises on the male and female reproductive systems for a nursing student named Alonzo Angelo F. For the male reproductive system exercise, the student is asked to draw and label diagrams of the sagittal section and internal structures of the penis. The student is also asked to define terms like circumcision and cryptorchidism. For the female reproductive system exercise, similar drawing and labeling of diagrams is requested along with enumerating the phases of the menstrual cycle and defining ectopic pregnancy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
Name: Alonzo Angelo F. Teacher: Dra.
Dorlyn Billones
Course: BSN1-YA-41 Date: December 22,2021
EXERCISE
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
OBJECTIVE; To study the anatomic and physiologic function of the male
reproductive
system.
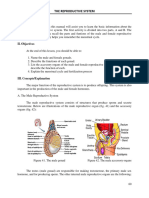
1. Draw and label sagittal section of male reproductive system.
2. List the male accessory reproductive organs and their functions.
Vas deferens: Transports mature sperm to the urethra in preparation for
ejaculation.
Seminal vesicles: Sac-like pouches that attach to the vas deferens near the
base of the bladder. The vesicles produce molecules such as fructose that
serve as energy sources for sperm. The seminal vesicle fluid makes up most of
the volume of a man’s ejaculate.
Prostate gland: A walnut-sized structure located below the urinary bladder in
front of the rectum. It contributes additional fluid to the ejaculate that serves
as nourishment for sperm.
Bulbourethral (Cowper’s) glands: Pea-sized structures located on the sides
of the urethra just below the prostate gland. These glands produce a clear,
slippery fluid that empties directly into the urethra. Fluid produced by these
glands lubricates the urethra and neutralizes acidity associated with residual
urine.
3. Draw & label a spermatozoa.
4. Draw and label frontal section of penis showing internal structure of penis.
5. Discuss the mechanisms involved in the process of erection and ejaculation.
- An erection is caused by blood trapped under high pressure. Ejaculation is a
reflex action that the central nervous system regulates
6. Define circumcision.
- The removal of the foreskin from the human penis is known as circumcision.
7 Define cryptorchidism.
- Cryptorchidism is a condition in which one or both testicles do not migrate
down into the scrotum from the belly, where they form before birth.
Name: Alonzo Angelo F. Teacher: Dra. Dorlyn Billones
Course: BSN1-YA-41 Date: December 22,2021
EXERCISE
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
OBJECTIVE: To study the anatomic and physiologic functions of the female
reproductive
System
1. Draw and label sagittal section of the female reproductive system.
2. Draw and label the vulva
3. Enumerate the structures found within the vestibule.
- UTRICLE
- SACCULE
4. Draw and label the sagittal section of the female breast.
5. Enumerate the phases of the female reproductive cycle.
- MENSTRUATION
- FOLLICULAR PHASE
- OVULATION
- LUTEAL PHASE
6. Enumerate the hormones and their function in female reproduction.
A. FOLLICLE -STIMUAATING HORMONE
- helps control the menstrual cycle and stimulates the growth of eggs in the
ovaries.
B. LUTEINIZING HORMONE
- helps control the menstrual cycle
C. ESTROGEN
- it helps develop and maintain both the reproductive system and female
characteristics,
D. PROGESTERONE
- prepares the endometrium for the potential of pregnancy after ovulation.
7. Define ectopic pregnancy.
- When a fertilized egg implants and grows outside the main cavity of the
uterus, it is called an ectopic pregnancy. The most common site of an ectopic
pregnancy is the fallopian tube, which transports eggs from the ovaries to the
uterus. Tubal pregnancy is the name for this form of ectopic pregnancy.
You might also like
- Reproductive - Systems - in - Vertebrates ss2Document12 pagesReproductive - Systems - in - Vertebrates ss2Ezeh Princess100% (1)
- WEEK 17 LAB EXERCISE - Reproductive System (Male & Female)Document6 pagesWEEK 17 LAB EXERCISE - Reproductive System (Male & Female)Lance KennethNo ratings yet
- Lab Act in Repro.Document4 pagesLab Act in Repro.Jhia TorreonNo ratings yet
- PP5. Human ReproductionDocument138 pagesPP5. Human ReproductionSamalaniNo ratings yet
- Please Discuss Your Answer BrieflyDocument4 pagesPlease Discuss Your Answer BrieflyAlexis John Hisula VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- Midterm 1Document18 pagesMidterm 1Jenelyn AbayatoNo ratings yet
- Manual Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesManual Reproductive Systemrayverjohnlayam073No ratings yet
- Lesson 11 - Human ReproductionDocument10 pagesLesson 11 - Human ReproductionkreativekerelleNo ratings yet
- Mod 2 7 For Students PDFDocument118 pagesMod 2 7 For Students PDFpetergomez0119No ratings yet
- Grade10 Lesson2 ReproductiveAnat - 1Document18 pagesGrade10 Lesson2 ReproductiveAnat - 1JaimeCrispino0% (1)
- Reproductive System Physiology NotesDocument5 pagesReproductive System Physiology NotesKaye Alyssa EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Promotive and Preventive Nursing Care ManagementDocument440 pagesPromotive and Preventive Nursing Care ManagementGrace Lladoc ChalmasNo ratings yet
- PPT1 BioDocument53 pagesPPT1 BioRalph NilloNo ratings yet
- WEEK 17 LAB EXERCISE Reproductive System Male Female 1Document6 pagesWEEK 17 LAB EXERCISE Reproductive System Male Female 1DELA CRUZ, JENISSE LOUISSENo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Life Science Human Reproduction NotesDocument138 pagesGrade 12 Life Science Human Reproduction NotesLulo NnenaNo ratings yet
- Uts Chapter 2 Lesson 1Document29 pagesUts Chapter 2 Lesson 1John Jerome GironellaNo ratings yet
- Week 6Document3 pagesWeek 6John JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Hr-Module 1-Lesson 1Document35 pagesHr-Module 1-Lesson 1Sevilla, Marpolo Joaquin Z.No ratings yet
- Unit Ii Biomedical Perspective in Gender and SexualityDocument46 pagesUnit Ii Biomedical Perspective in Gender and SexualityRowena Lanete ButaNo ratings yet
- Sci10-q3-Male and Female Repro SystemDocument71 pagesSci10-q3-Male and Female Repro SystemDani Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Topic12-Magcamit, Mark Vincent MaciasDocument8 pagesTopic12-Magcamit, Mark Vincent MaciasHermaphroditiusNo ratings yet
- SPEC I TASK 12 - Human Reproductive SystemDocument11 pagesSPEC I TASK 12 - Human Reproductive SystemJERIEL MARTIREZNo ratings yet
- Session #45 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab) (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Document6 pagesSession #45 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab) (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Nicole Ken AgdanaNo ratings yet
- q3 Science 10 w1Document5 pagesq3 Science 10 w1Kimi LegsonNo ratings yet
- Gned 10 - Biomedical Perspective of Gender and SexualityDocument6 pagesGned 10 - Biomedical Perspective of Gender and Sexualityjoanna.filosopoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System JblsDocument2 pagesReproductive System JblsLINDAS XEROXNo ratings yet
- Biology M13 Human Reproductive SystemDocument30 pagesBiology M13 Human Reproductive SystemEunice CorreaNo ratings yet
- 24.3. Human Reproductive Anatomy and GametogenesiDocument2 pages24.3. Human Reproductive Anatomy and GametogenesijkhdgmbrvdNo ratings yet
- GENSOC M2 Lesson 4Document7 pagesGENSOC M2 Lesson 4cassy margaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document15 pagesLesson 4KR CoruñaNo ratings yet
- HARAMAY Reproductive Physiology and AI Course Handout Ashenafi andDocument72 pagesHARAMAY Reproductive Physiology and AI Course Handout Ashenafi andabrhamtafere700No ratings yet
- Lesson 4 To 7Document35 pagesLesson 4 To 7Macario estarjerasNo ratings yet
- Female Repro AssessmentDocument4 pagesFemale Repro AssessmentHu T. BunuanNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1FEMALE Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesMODULE 1FEMALE Reproductive SystemHoney Lou SemblanteNo ratings yet
- Gender and Society CompileDocument32 pagesGender and Society Compileクイーンクイーン ロペスNo ratings yet
- Science10 q3 Mod1 Reproductiveandendocrineeystems v5Document25 pagesScience10 q3 Mod1 Reproductiveandendocrineeystems v5cubillanjoshuajames12No ratings yet
- Human Reproduction: 3.1 T M R SDocument15 pagesHuman Reproduction: 3.1 T M R SSrajanNo ratings yet
- Ma'am Cantos Module 4Document5 pagesMa'am Cantos Module 4emmanuelNo ratings yet
- PP5. Human ReproductionDocument100 pagesPP5. Human ReproductionhellohlayisoNo ratings yet
- Urogenital SystemDocument5 pagesUrogenital Systemstudent10100No ratings yet
- PP5.Human Reproduction (Updated)Document65 pagesPP5.Human Reproduction (Updated)hellohlayisoNo ratings yet
- Repoductive SystemDocument14 pagesRepoductive SystemJhoanna Marie RebutNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE-5-Q2-WK 1 SHLT 1 OkDocument10 pagesSCIENCE-5-Q2-WK 1 SHLT 1 OkMaria Renita BelcinaNo ratings yet
- LAS 3rd Quarter FINALDocument58 pagesLAS 3rd Quarter FINALJustine Emilia100% (1)
- Unit 8 The Reproductive System Bilingual EducationDocument13 pagesUnit 8 The Reproductive System Bilingual EducationAntonio PrietoNo ratings yet
- Exemplar 3rdDocument5 pagesExemplar 3rdRAYMUND RODILLONo ratings yet
- Pre-Reading For Reproductive SystemDocument16 pagesPre-Reading For Reproductive SystemRill VasanthNo ratings yet
- Science: Third QuarterDocument10 pagesScience: Third Quarterrig guel100% (1)
- 2024 GRADE 12 Notes Term 1Document32 pages2024 GRADE 12 Notes Term 1simwingaelvis37No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of ReproductionAstorias Jayv B.No ratings yet
- Human Reproduction 2019Document138 pagesHuman Reproduction 2019daylinallie2007No ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument26 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemAlmario DacalcapNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health NursingDocument181 pagesMaternal and Child Health NursingKarina Jane Farnacio Purugganan100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology "Male and Female Reproductive System"Document12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology "Male and Female Reproductive System"tania scNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology CorrectedDocument15 pagesAnatomy and Physiology CorrectedSANCHAYEETANo ratings yet
- Q3-DLL Week 2Document5 pagesQ3-DLL Week 2Jun Dadiahon AlindayoNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Q3 - Module 1 For EditedDocument14 pagesScience 10 Q3 - Module 1 For Editedtaylorsheesh64No ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument130 pagesReproductive SystemReymark NovecioNo ratings yet
- Week 11 - CD Course Task 4. PTB, Pneumonia, Diphtheria, Pertusis, MumpsDocument1 pageWeek 11 - CD Course Task 4. PTB, Pneumonia, Diphtheria, Pertusis, MumpsGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Week 15 - ONCO COURSE TASK - Breast Cancer DetectionDocument3 pagesWeek 15 - ONCO COURSE TASK - Breast Cancer DetectionGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Library Works - CD - Communicable Diseases Trends and IssuesDocument1 pageLibrary Works - CD - Communicable Diseases Trends and IssuesGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Exercise 6Document6 pagesExercise 6Gelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Exercise 8Document2 pagesExercise 8Gelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Exercise 7Document7 pagesExercise 7Gelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Week 5 ExerciseDocument7 pagesWeek 5 ExerciseGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- LABORATORY EXERCISE The Gastrointestinal System With Accessory GlandDocument5 pagesLABORATORY EXERCISE The Gastrointestinal System With Accessory GlandGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- WEEK 9 LABORATORY EXERCISE The Cardiovascular System, The Heart and The Blood VesselsDocument4 pagesWEEK 9 LABORATORY EXERCISE The Cardiovascular System, The Heart and The Blood VesselsGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- WEEK 15 LAB EXERCISE - Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesWEEK 15 LAB EXERCISE - Endocrine SystemGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- WEEK 16 LABORATORY EXERCISE Special SensesDocument7 pagesWEEK 16 LABORATORY EXERCISE Special SensesGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- WEEK 14 LABORATORY EXERCISE The Urinary SystemDocument2 pagesWEEK 14 LABORATORY EXERCISE The Urinary SystemGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Purc Transes PrelimDocument4 pagesPurc Transes PrelimGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Anph Transes PrelimDocument34 pagesAnph Transes PrelimGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Engl Transes PrelimDocument4 pagesEngl Transes PrelimGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- BSN1-YA-41 Princinple of Art 1. Balance 3. EmphasisDocument2 pagesBSN1-YA-41 Princinple of Art 1. Balance 3. EmphasisGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument56 pagesReproductive SystemRochelle Ann Cunanan100% (1)
- Activity 2 Finals Histo Lab - EDLAY2ADocument2 pagesActivity 2 Finals Histo Lab - EDLAY2ATom Anthony TonguiaNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument22 pagesAbstractnayayathNo ratings yet
- Male and Female Reproductive System and MenstruationDocument11 pagesMale and Female Reproductive System and MenstruationSav LiyanageNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Special Senses and Reproductive SystemDocument2 pagesCase Study - Special Senses and Reproductive SystemGlydenne Glaire Poncardas GayamNo ratings yet
- Kista Mammae IDKDocument4 pagesKista Mammae IDKNormanPrabowoNo ratings yet
- Observational Study of New Treatment Proposal For Severe Intrauterine AdhesionDocument14 pagesObservational Study of New Treatment Proposal For Severe Intrauterine AdhesionOpenaccess Research paperNo ratings yet
- Assisting in Papanicolaou SmearDocument13 pagesAssisting in Papanicolaou SmearRika Mae100% (1)
- Menstrual CycleDocument9 pagesMenstrual CycleZhen ObelidorNo ratings yet
- Lucija Kljaić Male Infertility: Course: Medical English 5Document11 pagesLucija Kljaić Male Infertility: Course: Medical English 5Lucija KljaićNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Hypomenorrhea-Amenorrhea (Asherman'S Syndrome) : R. Toaff, M, D, S, Ballas, M.DDocument9 pagesTraumatic Hypomenorrhea-Amenorrhea (Asherman'S Syndrome) : R. Toaff, M, D, S, Ballas, M.DfarahNo ratings yet
- Case Report: Epidermoid Inclusion Cyst of The Clitoris As A Long-Term Complication of Female Genital MutilationDocument4 pagesCase Report: Epidermoid Inclusion Cyst of The Clitoris As A Long-Term Complication of Female Genital MutilationAngelina BelaNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of The Adnexal Mass 2020Document38 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of The Adnexal Mass 2020Sonia MVNo ratings yet
- Menstrual DisordersDocument77 pagesMenstrual Disorders2012100% (3)
- Management of HypospadiasDocument34 pagesManagement of HypospadiasAdebisiNo ratings yet
- Medicult Case StudyDocument3 pagesMedicult Case Studyrandy ambogNo ratings yet
- Induction of LabourDocument4 pagesInduction of LabournavyakuthatiNo ratings yet
- Project - : Menstrual CycleDocument20 pagesProject - : Menstrual CycleJIBAN KUMAR DASNo ratings yet
- Management of Asherman's SyndromeDocument14 pagesManagement of Asherman's SyndromeEquipmed VenezuelaNo ratings yet
- In-Vitro Fertilisation (Ivf) in Singapore: Charges and Success RatesDocument4 pagesIn-Vitro Fertilisation (Ivf) in Singapore: Charges and Success RatesLászló ÉvaNo ratings yet
- Third Assignment (Forensic)Document2 pagesThird Assignment (Forensic)Dean Mark AnacioNo ratings yet
- The Gynaecological History Taking and Physical Examination: Associate Professor DR - Yin Moe HanDocument50 pagesThe Gynaecological History Taking and Physical Examination: Associate Professor DR - Yin Moe HanAimethevanNo ratings yet
- DLL SCIENCE (MELCs) W1Document7 pagesDLL SCIENCE (MELCs) W1MYLEEN P. GONZALESNo ratings yet
- Hubungan Nyeri Haid (Dismenore) Dengan Aktivitas Belajar Sehari-Hari Pada Remaja Putri Kelas VII Di SMPN 3 PulungDocument8 pagesHubungan Nyeri Haid (Dismenore) Dengan Aktivitas Belajar Sehari-Hari Pada Remaja Putri Kelas VII Di SMPN 3 PulungTitaniaafni TasyabilaNo ratings yet
- Munce y 2021Document11 pagesMunce y 2021Your Imaginary StarNo ratings yet
- VaginitisDocument4 pagesVaginitisBinita ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Endometriosis PresentationDocument58 pagesEndometriosis PresentationBRI KU100% (1)
- Yeny Elfiyanti - 1910070100082 - Tugas Praktikum Anatomi 2Document5 pagesYeny Elfiyanti - 1910070100082 - Tugas Praktikum Anatomi 2Yeny ElfiyantiNo ratings yet
- Infertilidad MasculinaDocument22 pagesInfertilidad MasculinaAnaNo ratings yet
- DR Nadine Rev All (Samra's Edition)Document313 pagesDR Nadine Rev All (Samra's Edition)Cyril I.Makar100% (1)