Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Secondary 4 Additional Mathematics Kinematics
Secondary 4 Additional Mathematics Kinematics
Uploaded by
Jonas Khoo TianyouCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Motion in A Straight LineDocument2 pagesMotion in A Straight LineSnehin PoddarNo ratings yet
- Phy 91171 MechanicshelpDocument4 pagesPhy 91171 MechanicshelpBenedick CruzNo ratings yet
- KINAMETICSDocument6 pagesKINAMETICSSaήjaγKsNo ratings yet
- DYNA - Rectilinear MotionDocument30 pagesDYNA - Rectilinear MotionFrancis Ko Badongen-Cawi Tabaniag Jr.No ratings yet
- Change in Position W.R.T. Time Speed: Change in Distance W.R.T Time Velocity Change in Displacement W.R.T Time Change in Velocity W.R.T TimeDocument2 pagesChange in Position W.R.T. Time Speed: Change in Distance W.R.T Time Velocity Change in Displacement W.R.T Time Change in Velocity W.R.T TimeNeetu JainNo ratings yet
- Motion Along A Straight Line: Chapter - 02Document15 pagesMotion Along A Straight Line: Chapter - 02Raichal P BijuNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Straight Line NotesDocument15 pagesMotion in A Straight Line NotesbetsyNo ratings yet
- Physics Types of MotionDocument4 pagesPhysics Types of Motiona01423336No ratings yet
- CH 3 & 5 & 6 Vectors, Newton's Laws, & Applications of Newton's LawsDocument4 pagesCH 3 & 5 & 6 Vectors, Newton's Laws, & Applications of Newton's LawsMelindaNo ratings yet
- Motion in 1DDocument1 pageMotion in 1DAtulyaNo ratings yet
- (H2 PHY) Chapter 2 - KinematicsDocument32 pages(H2 PHY) Chapter 2 - KinematicsMr TanNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of A ParticleDocument37 pagesKinematics of A ParticleHush PereraNo ratings yet
- Dynamics RectangularCoordinateDocument6 pagesDynamics RectangularCoordinateAubrey LanotNo ratings yet
- Physics NotesDocument2 pagesPhysics NotesDaniel KoNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of ParticleDocument94 pagesKinematics of ParticleFaiz IzzuddinNo ratings yet
- 4309 Topper 21 101 3 4 122 Motion in A Straight Line Up201611021148 1478067495 4997Document9 pages4309 Topper 21 101 3 4 122 Motion in A Straight Line Up201611021148 1478067495 4997sadhu associatesNo ratings yet
- 1870006580Document1 page1870006580rekhaNo ratings yet
- 01 - Motion in A Straight LineDocument34 pages01 - Motion in A Straight LineVivek KumarNo ratings yet
- NOTES - Motion - Diagrams and GraphsDocument40 pagesNOTES - Motion - Diagrams and GraphsAngelia SombreaNo ratings yet
- 1st Term Exam RevisionDocument20 pages1st Term Exam RevisionYammy IeongNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Introduction To Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: Learning ObjectivesDocument8 pagesModule 1: Introduction To Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: Learning Objectivesderping lemon100% (1)
- Revision-Map Chapter 7Document1 pageRevision-Map Chapter 7Megha BishtNo ratings yet
- Motion in Straight LineDocument16 pagesMotion in Straight LineSangamesh V ANo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics 2mohanad Engineering Mechanics DynamicDocument66 pagesEngineering Mechanics 2mohanad Engineering Mechanics DynamicNefer PitouNo ratings yet
- 11th PHYSICS NCERT SUMMARYDocument30 pages11th PHYSICS NCERT SUMMARYMithun RoyNo ratings yet
- Complete Guide PDFDocument42 pagesComplete Guide PDFLeslie UyNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Handouts Vector and ScalarDocument3 pagesGrade 7 Handouts Vector and ScalarLovieAlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Mech 2 Module 1 Unit 3 (Position, Velocity and Acceleration)Document8 pagesMech 2 Module 1 Unit 3 (Position, Velocity and Acceleration)Zamantha DomingoNo ratings yet
- Forces and MotionDocument245 pagesForces and MotionNicole TNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Straight LineDocument9 pagesMotion in A Straight Linejayashriparida09No ratings yet
- 2 - Particle KinematicsDocument25 pages2 - Particle KinematicsAbdallah HassanNo ratings yet
- Kaela PhysicsDocument5 pagesKaela PhysicsJoan FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Force and Motion - Energy, Work and Power PDFDocument7 pagesForce and Motion - Energy, Work and Power PDFAnonymous ee5dOjNo ratings yet
- WEEK 2 - Lesson 1 - Position, Velocity, AccelerationDocument15 pagesWEEK 2 - Lesson 1 - Position, Velocity, AccelerationNoel Himolatan Bolair Jr.No ratings yet
- Vector Mechanics For Engineers: Dynamics: Kinematics of ParticlesDocument99 pagesVector Mechanics For Engineers: Dynamics: Kinematics of ParticlesMike Raphy T. VerdonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DynamicsDocument2 pagesIntroduction To DynamicsJulius CodiamatNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DynamicsDocument2 pagesIntroduction To DynamicsMark Joseph ValdezNo ratings yet
- Notes-OscillationsDocument9 pagesNotes-OscillationsMordecai ChimedzaNo ratings yet
- 3 Kinematics of A Particle Rectilinear MotionDocument13 pages3 Kinematics of A Particle Rectilinear MotionMichaella Corine GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Note, Fluid Dynamics, Force Motion and EnergyDocument77 pagesNote, Fluid Dynamics, Force Motion and EnergyyuyungeNo ratings yet
- ME 101-Lecture 22-25-Kinematics of A ParticleDocument66 pagesME 101-Lecture 22-25-Kinematics of A Particlesm737744No ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic Motion: Exambatofficial ExambatDocument33 pagesSimple Harmonic Motion: Exambatofficial Exambatemperor444ytNo ratings yet
- Class IX SCIENCE IITFoundation & Olympiad Study Package (PDFDrive)Document234 pagesClass IX SCIENCE IITFoundation & Olympiad Study Package (PDFDrive)Tawheed AlamNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of ParticlesDocument34 pagesKinematics of ParticlesRahel Yemane Embaye TeweldeNo ratings yet
- Selina Solutions For Class 9 Physics Chapter 2 Motion in One DimensionDocument39 pagesSelina Solutions For Class 9 Physics Chapter 2 Motion in One DimensionABHISHEK THAKURNo ratings yet
- 7.rotational MechanicsPROBLEM SOLVING TACTICSFormulae Sheet 2Document4 pages7.rotational MechanicsPROBLEM SOLVING TACTICSFormulae Sheet 2Gatbunton JethroeNo ratings yet
- Rohini 68059624624Document18 pagesRohini 68059624624PHANI RAJA RAONo ratings yet
- Ch.3 - RotationRigidBodyDocument9 pagesCh.3 - RotationRigidBodyPhương Trâm TrầnNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Kinematics Part 1Document21 pagesLesson 2 - Kinematics Part 1Jonathan VillapanaNo ratings yet
- Section 2.0 Newtonian MechanicsDocument52 pagesSection 2.0 Newtonian MechanicsIm rich lolNo ratings yet
- CH - 3 Physics Motion in A Straight LineDocument12 pagesCH - 3 Physics Motion in A Straight LineVENKATESH CHAKRABORTYNo ratings yet
- M1 - in A NutshellDocument9 pagesM1 - in A NutshelldaliatarekboushraNo ratings yet
- Kinema TicsDocument88 pagesKinema TicsdynamicranjanNo ratings yet
- Vectors, Distance and DisplacementDocument15 pagesVectors, Distance and DisplacementAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Motion-Chapter 8 Scalars and VectorsDocument5 pagesMotion-Chapter 8 Scalars and VectorsSandhya RoshanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document18 pagesChapter 2Taleb AbboudNo ratings yet
- I Important Rem Nders: Constant Velocity Is OK, Accelerated Observer Is NotDocument2 pagesI Important Rem Nders: Constant Velocity Is OK, Accelerated Observer Is NotJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- KinematicsDocument33 pagesKinematicsNordin fatihahNo ratings yet
- Kinematics: Two and Three Dimensional Motion: Intended Learning Outcomes (Ilo)Document4 pagesKinematics: Two and Three Dimensional Motion: Intended Learning Outcomes (Ilo)RALPH ANDREW ESPERONNo ratings yet
- How Is a Vector Used in Physics? Physics 8th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandHow Is a Vector Used in Physics? Physics 8th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Combined Chembio AnswersDocument13 pagesCombined Chembio AnswersJonas Khoo TianyouNo ratings yet
- C11 - The Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesC11 - The Nervous SystemJonas Khoo TianyouNo ratings yet
- Ciliac Green Secondary SchoolDocument3 pagesCiliac Green Secondary SchoolJonas Khoo TianyouNo ratings yet
- DateDocument3 pagesDateJonas Khoo TianyouNo ratings yet
- Higher LevelDocument2 pagesHigher LevelJonas Khoo TianyouNo ratings yet
- c10 Decimals 4 OperationsDocument23 pagesc10 Decimals 4 OperationsJonas Khoo TianyouNo ratings yet
Secondary 4 Additional Mathematics Kinematics
Secondary 4 Additional Mathematics Kinematics
Uploaded by
Jonas Khoo TianyouOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Secondary 4 Additional Mathematics Kinematics
Secondary 4 Additional Mathematics Kinematics
Uploaded by
Jonas Khoo TianyouCopyright:
Available Formats
Secondary 4 Additional Mathematics
Chapter 18: Kinematics
(NA)
Name: ______________________ Class: ____________ ( ) Date: _________________
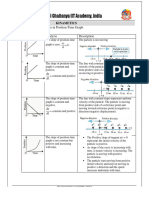
Displacement
The displacement of a particle is defined as the change in position of the particle with respect
to a fixed point, at a particular instant. It has both magnitude and direction. Displacement can
be positive, zero, or negative.
Positive Displacement
Direction (left → right)
Displacement
position
Original position
Magnitude
When a particle travels a straight distance with direction and magnitude fixed to one ending
point. The particle is in positive displacement motion.
Negative Displacement
+ve border
original
Direction (left → right)
Direction (right → left)
-ve
When a particle travels a straight distance with direction and magnitude fixed to one ending.
However, reverses due to bounce or wind affection, travels backwards. The particle is in
negative displacement motion.
Zero Displacement
When a particle is still or is moving at a constant speed from starting to ending position. The
particle is in zero displacement.
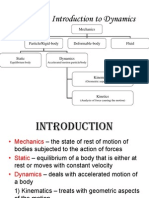
The Kinematical Analysis
There are 2 types of measure of motion, velocity, and acceleration.
Velocity – rate of change of displacement.
ds
v=
dt
Velocity
Velocity is the rate of change of displacement. If a particle is moving at x km/hr for y
minutes, its velocity is calculated to:
ds x km/ h
v= = .
dt y mins
You might also like
- Motion in A Straight LineDocument2 pagesMotion in A Straight LineSnehin PoddarNo ratings yet
- Phy 91171 MechanicshelpDocument4 pagesPhy 91171 MechanicshelpBenedick CruzNo ratings yet
- KINAMETICSDocument6 pagesKINAMETICSSaήjaγKsNo ratings yet
- DYNA - Rectilinear MotionDocument30 pagesDYNA - Rectilinear MotionFrancis Ko Badongen-Cawi Tabaniag Jr.No ratings yet
- Change in Position W.R.T. Time Speed: Change in Distance W.R.T Time Velocity Change in Displacement W.R.T Time Change in Velocity W.R.T TimeDocument2 pagesChange in Position W.R.T. Time Speed: Change in Distance W.R.T Time Velocity Change in Displacement W.R.T Time Change in Velocity W.R.T TimeNeetu JainNo ratings yet
- Motion Along A Straight Line: Chapter - 02Document15 pagesMotion Along A Straight Line: Chapter - 02Raichal P BijuNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Straight Line NotesDocument15 pagesMotion in A Straight Line NotesbetsyNo ratings yet
- Physics Types of MotionDocument4 pagesPhysics Types of Motiona01423336No ratings yet
- CH 3 & 5 & 6 Vectors, Newton's Laws, & Applications of Newton's LawsDocument4 pagesCH 3 & 5 & 6 Vectors, Newton's Laws, & Applications of Newton's LawsMelindaNo ratings yet
- Motion in 1DDocument1 pageMotion in 1DAtulyaNo ratings yet
- (H2 PHY) Chapter 2 - KinematicsDocument32 pages(H2 PHY) Chapter 2 - KinematicsMr TanNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of A ParticleDocument37 pagesKinematics of A ParticleHush PereraNo ratings yet
- Dynamics RectangularCoordinateDocument6 pagesDynamics RectangularCoordinateAubrey LanotNo ratings yet
- Physics NotesDocument2 pagesPhysics NotesDaniel KoNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of ParticleDocument94 pagesKinematics of ParticleFaiz IzzuddinNo ratings yet
- 4309 Topper 21 101 3 4 122 Motion in A Straight Line Up201611021148 1478067495 4997Document9 pages4309 Topper 21 101 3 4 122 Motion in A Straight Line Up201611021148 1478067495 4997sadhu associatesNo ratings yet
- 1870006580Document1 page1870006580rekhaNo ratings yet
- 01 - Motion in A Straight LineDocument34 pages01 - Motion in A Straight LineVivek KumarNo ratings yet
- NOTES - Motion - Diagrams and GraphsDocument40 pagesNOTES - Motion - Diagrams and GraphsAngelia SombreaNo ratings yet
- 1st Term Exam RevisionDocument20 pages1st Term Exam RevisionYammy IeongNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Introduction To Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: Learning ObjectivesDocument8 pagesModule 1: Introduction To Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: Learning Objectivesderping lemon100% (1)
- Revision-Map Chapter 7Document1 pageRevision-Map Chapter 7Megha BishtNo ratings yet
- Motion in Straight LineDocument16 pagesMotion in Straight LineSangamesh V ANo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics 2mohanad Engineering Mechanics DynamicDocument66 pagesEngineering Mechanics 2mohanad Engineering Mechanics DynamicNefer PitouNo ratings yet
- 11th PHYSICS NCERT SUMMARYDocument30 pages11th PHYSICS NCERT SUMMARYMithun RoyNo ratings yet
- Complete Guide PDFDocument42 pagesComplete Guide PDFLeslie UyNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Handouts Vector and ScalarDocument3 pagesGrade 7 Handouts Vector and ScalarLovieAlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Mech 2 Module 1 Unit 3 (Position, Velocity and Acceleration)Document8 pagesMech 2 Module 1 Unit 3 (Position, Velocity and Acceleration)Zamantha DomingoNo ratings yet
- Forces and MotionDocument245 pagesForces and MotionNicole TNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Straight LineDocument9 pagesMotion in A Straight Linejayashriparida09No ratings yet
- 2 - Particle KinematicsDocument25 pages2 - Particle KinematicsAbdallah HassanNo ratings yet
- Kaela PhysicsDocument5 pagesKaela PhysicsJoan FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Force and Motion - Energy, Work and Power PDFDocument7 pagesForce and Motion - Energy, Work and Power PDFAnonymous ee5dOjNo ratings yet
- WEEK 2 - Lesson 1 - Position, Velocity, AccelerationDocument15 pagesWEEK 2 - Lesson 1 - Position, Velocity, AccelerationNoel Himolatan Bolair Jr.No ratings yet
- Vector Mechanics For Engineers: Dynamics: Kinematics of ParticlesDocument99 pagesVector Mechanics For Engineers: Dynamics: Kinematics of ParticlesMike Raphy T. VerdonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DynamicsDocument2 pagesIntroduction To DynamicsJulius CodiamatNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DynamicsDocument2 pagesIntroduction To DynamicsMark Joseph ValdezNo ratings yet
- Notes-OscillationsDocument9 pagesNotes-OscillationsMordecai ChimedzaNo ratings yet
- 3 Kinematics of A Particle Rectilinear MotionDocument13 pages3 Kinematics of A Particle Rectilinear MotionMichaella Corine GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Note, Fluid Dynamics, Force Motion and EnergyDocument77 pagesNote, Fluid Dynamics, Force Motion and EnergyyuyungeNo ratings yet
- ME 101-Lecture 22-25-Kinematics of A ParticleDocument66 pagesME 101-Lecture 22-25-Kinematics of A Particlesm737744No ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic Motion: Exambatofficial ExambatDocument33 pagesSimple Harmonic Motion: Exambatofficial Exambatemperor444ytNo ratings yet
- Class IX SCIENCE IITFoundation & Olympiad Study Package (PDFDrive)Document234 pagesClass IX SCIENCE IITFoundation & Olympiad Study Package (PDFDrive)Tawheed AlamNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of ParticlesDocument34 pagesKinematics of ParticlesRahel Yemane Embaye TeweldeNo ratings yet
- Selina Solutions For Class 9 Physics Chapter 2 Motion in One DimensionDocument39 pagesSelina Solutions For Class 9 Physics Chapter 2 Motion in One DimensionABHISHEK THAKURNo ratings yet
- 7.rotational MechanicsPROBLEM SOLVING TACTICSFormulae Sheet 2Document4 pages7.rotational MechanicsPROBLEM SOLVING TACTICSFormulae Sheet 2Gatbunton JethroeNo ratings yet
- Rohini 68059624624Document18 pagesRohini 68059624624PHANI RAJA RAONo ratings yet
- Ch.3 - RotationRigidBodyDocument9 pagesCh.3 - RotationRigidBodyPhương Trâm TrầnNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Kinematics Part 1Document21 pagesLesson 2 - Kinematics Part 1Jonathan VillapanaNo ratings yet
- Section 2.0 Newtonian MechanicsDocument52 pagesSection 2.0 Newtonian MechanicsIm rich lolNo ratings yet
- CH - 3 Physics Motion in A Straight LineDocument12 pagesCH - 3 Physics Motion in A Straight LineVENKATESH CHAKRABORTYNo ratings yet
- M1 - in A NutshellDocument9 pagesM1 - in A NutshelldaliatarekboushraNo ratings yet
- Kinema TicsDocument88 pagesKinema TicsdynamicranjanNo ratings yet
- Vectors, Distance and DisplacementDocument15 pagesVectors, Distance and DisplacementAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Motion-Chapter 8 Scalars and VectorsDocument5 pagesMotion-Chapter 8 Scalars and VectorsSandhya RoshanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document18 pagesChapter 2Taleb AbboudNo ratings yet
- I Important Rem Nders: Constant Velocity Is OK, Accelerated Observer Is NotDocument2 pagesI Important Rem Nders: Constant Velocity Is OK, Accelerated Observer Is NotJoØrsh Ênrique Tu Xikytø NînîØflowNo ratings yet
- KinematicsDocument33 pagesKinematicsNordin fatihahNo ratings yet
- Kinematics: Two and Three Dimensional Motion: Intended Learning Outcomes (Ilo)Document4 pagesKinematics: Two and Three Dimensional Motion: Intended Learning Outcomes (Ilo)RALPH ANDREW ESPERONNo ratings yet
- How Is a Vector Used in Physics? Physics 8th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandHow Is a Vector Used in Physics? Physics 8th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Combined Chembio AnswersDocument13 pagesCombined Chembio AnswersJonas Khoo TianyouNo ratings yet
- C11 - The Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesC11 - The Nervous SystemJonas Khoo TianyouNo ratings yet
- Ciliac Green Secondary SchoolDocument3 pagesCiliac Green Secondary SchoolJonas Khoo TianyouNo ratings yet
- DateDocument3 pagesDateJonas Khoo TianyouNo ratings yet
- Higher LevelDocument2 pagesHigher LevelJonas Khoo TianyouNo ratings yet
- c10 Decimals 4 OperationsDocument23 pagesc10 Decimals 4 OperationsJonas Khoo TianyouNo ratings yet