Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Precipitation Noun
Precipitation Noun
Uploaded by
Àbïyãñ Sëlömõñ0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views3 pagesPrecipitation falls from the atmosphere in forms like rain, snow, and sleet. It is part of the water cycle along with evaporation and condensation. Runoff is the part of precipitation that flows over land as surface water instead of being absorbed or evaporating. Infiltration is the process by which precipitation soaks into subsurface soils through cracks and pores. The hydrologic cycle describes how water evaporates from the Earth's surface and condenses in the atmosphere before falling as precipitation and either running off or being absorbed again.
Original Description:
Original Title
precipitation noun
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPrecipitation falls from the atmosphere in forms like rain, snow, and sleet. It is part of the water cycle along with evaporation and condensation. Runoff is the part of precipitation that flows over land as surface water instead of being absorbed or evaporating. Infiltration is the process by which precipitation soaks into subsurface soils through cracks and pores. The hydrologic cycle describes how water evaporates from the Earth's surface and condenses in the atmosphere before falling as precipitation and either running off or being absorbed again.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views3 pagesPrecipitation Noun
Precipitation Noun
Uploaded by
Àbïyãñ SëlömõñPrecipitation falls from the atmosphere in forms like rain, snow, and sleet. It is part of the water cycle along with evaporation and condensation. Runoff is the part of precipitation that flows over land as surface water instead of being absorbed or evaporating. Infiltration is the process by which precipitation soaks into subsurface soils through cracks and pores. The hydrologic cycle describes how water evaporates from the Earth's surface and condenses in the atmosphere before falling as precipitation and either running off or being absorbed again.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
1
A, precipitation noun. Any or all of the forms of water particles, whether liquid
or solid, that fall from the atmosphere (e.g., rain, hail, snow or sleet). It is a
major class of hydrometeor, but it is distinguished from cloud, fog, dew, rime,
frost, etc., in that it must fall.
Precipitation is any liquid or frozen water that forms in the atmosphere and
falls back to the Earth. It comes in many forms, like rain, sleet, and snow.
Along with evaporation and condensation, precipitation is one of the three
major parts of the global water cycle.
B, Runoff. the occurrence of surplus liquid (as water) exceeding the limit or capacity.
Runoff can be described as the part of the water cycle that flows over land as
surface water instead of being absorbed into groundwater or
evaporating. Runoff is that part of the precipitation, snow melt, or
irrigation water that appears in uncontrolled surface streams, rivers, drains, or
sewers.
C, Infiltration is an indicator of the soil’s ability to allow water movement into
and through the soil profile.
Infiltration is the process by which precipitation or water soaks into subsurface
soils and moves into rocks through cracks and pore spaces.
D, Evaporation is simply the process by which liquid turns into a gas. Water (a
liquid) turns into vapor (a gas) when heat energy is applied to raise its
temperature to 100°C (212°F).
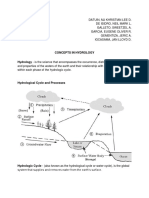
2 ,Hydro-logic Cycle The water, or hydrologic, cycle describes the pilgrimage
of water as water molecules make their way from the Earth’s surface to the
atmosphere and back again, in some cases to below the surface.
Hydro-logical cycle, also known as water cycle, is a continuous movement of water
between hydrosphere, atmosphere, and lithosphere in a cyclic manner
The hydro-logical cycle is the event of rotation of water from its source, then it becomes rain and
falls into groundwater again and some flows back into the sea.
Elements of hydro logical cycle
Precipitation,Evaporation,Infiltration and Surface Runoff.
3 a, major methods for calculating average-precipitation over a
watershed are:.
Arithmetic Mean
Theissen Polygon Method
ISO-Hyetal Method and
Inverse distance weighting method.
b, Theissen Polygon Method is the most accurate method because This
method assigns weight at each gauge station in proportion to the catchment
area that is closest to that gauge.
4A, Hydrology is an extremely important field of study, dealing
with one of the most valuable resources on Earth: water. All
aspects of the Earth’s available water are studied by experts
from many disciplines, from geologists to engineers, to obtain
the information needed to manage this vital resource.
B,
The field of hydrology consists not only of studying the natural distribution and
movement of water, it is also concerned with the impact of human activities on
water quality and with problems in water management. People use water for
many purposes. In their homes, people use water for drinking, cooking,
cleaning, and bathing.
5A, water balance A state of equilibrium in which the fluid intake from water
and other beverages, and foods equals fluid lost in the urine, GI tract, sweat,
and other secretions.
The meaning of WATER BALANCE is the ratio between the water assimilated into the
body and that lost from the bod
The law of water balance states that the inflows to any water system or area is equal to
its outflows plus change in storage during a time interval.
B,The simplest form of water balance equation is as follows:
P = Q + E ± ∆S.
Where, P is precipitation, Q is runoff, E is evaporation and ∆S is the storage
in the soil, aquifers or reservoirs.
6A,Precipitation is measured from space using a combination of
active and passive remote-sensing techniques, improving the
spatial and temporal coverage of global precipitation observations.
Precipitation is measured by using a rain gauge.
B, Types of rain gauges:
1) Non-recording: Symon’sgauge
Non-recording rain gauges only show how much rain has fallen.
2) Recording
recording rain gauge An instrument that automatically records the amount of
precipitation collected as a function of time.
:this types rain gauge also classify in to:
- Tipping-bucket type
- Weighing-bucket type
- Natural-syphon type
C,Non-recording rain gauges only collect rain. It do not simultaneously
measure or record rainfall.But recording rain gauge is An instrument that
automatically records the amount of precipitation collected as a function of time.
7,
Rain gauge measuring principle (rain gauge type) determines the general
accuracy, reliability and maintenance requirements of the rain gauge.
Graduated cylinder rain gauge (also called a standard rain gauge or a
manual rain gauge) is highly reliable but one must get wet in the rain to read
off rain information in real-time.
8A, Environmental data, particularly, rainfall data are highly vulnerable to be
missed, which is due to several reasons, such as malfunction instrument,
incorrect measurements, and relocation of stations. Rainfall data are also
affected by the presence of outliers due to the temporal and spatial variability
of rainfall measurements.
1. B,
Simple Arithmetic Method
Normal Ratio Method
Modified normal ratio method
Inverse distance method
Linear programming method
You might also like
- Report of IETSDocument33 pagesReport of IETSFarhans Ahmad100% (4)
- Malaysia Sewerage Industry Guideline Volume 5Document65 pagesMalaysia Sewerage Industry Guideline Volume 5Asiff Razif100% (4)
- GK Today EcologyDocument96 pagesGK Today EcologyRitesh Singh100% (1)
- The Seven Environmental PrinciplesDocument2 pagesThe Seven Environmental PrinciplesGM Alisangco Jarabejo50% (2)
- Cefc 513 Lecture 6Document13 pagesCefc 513 Lecture 6Amihan De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 HydrologyDocument26 pagesChapter 1 HydrologyAsyraf Malik80% (5)
- Ch.1 IntroductionDocument35 pagesCh.1 IntroductionhamzaNo ratings yet
- War 2103 IntroductionDocument36 pagesWar 2103 IntroductionEgana IsaacNo ratings yet
- SWC 201 - Watershed Hydrology - All Lectures 2 4Document3 pagesSWC 201 - Watershed Hydrology - All Lectures 2 4CAVEMAN MUSCLENo ratings yet
- Module 7: Recharge and Groundwater Flow PatternsDocument11 pagesModule 7: Recharge and Groundwater Flow PatternsDaniela Villacres MezaNo ratings yet
- Faculty of EngineeringDocument41 pagesFaculty of EngineeringAhmed Abdi IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Hydrology and Irrigation Engineering 10CV55: UNIT-1Document20 pagesHydrology and Irrigation Engineering 10CV55: UNIT-1yusuf anwerNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 - Hydrolgic CycleDocument37 pagesChap 2 - Hydrolgic CycleRezaul KarimNo ratings yet
- Assignment - IDocument15 pagesAssignment - IAniket PrakashNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Introduction To HydrometeorologyDocument13 pagesModule 1 - Introduction To HydrometeorologyApril Bumanglag100% (2)
- Notes On Introduction To Hydrology and PrecipiationDocument57 pagesNotes On Introduction To Hydrology and Precipiationroshan PaudelNo ratings yet
- Hyd Cyc and Water BalanceDocument40 pagesHyd Cyc and Water BalanceAyush KishoreNo ratings yet
- Tutorial@Principles of HydroDocument86 pagesTutorial@Principles of HydroGeleta SafeNo ratings yet
- Environmental Hydrology (Ensc253)Document19 pagesEnvironmental Hydrology (Ensc253)kelifa799No ratings yet
- Wk1 Hydrological CycleDocument6 pagesWk1 Hydrological CycleJessie Jade Sestina Duroja - MainNo ratings yet
- Module - 1 Introduction To Hydrology and Precipitation (Module 1 Full Notes)Document68 pagesModule - 1 Introduction To Hydrology and Precipitation (Module 1 Full Notes)rohitNo ratings yet
- Hydrology Module 101Document18 pagesHydrology Module 101juncos0729No ratings yet
- Hydrological CycleDocument28 pagesHydrological Cyclesilverking300100% (1)
- HydrologyDocument38 pagesHydrologyMelannie ArgenteraNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - HydroDocument55 pagesLecture Notes - HydroAlvin Deliro100% (5)
- Hydrologic CycleDocument7 pagesHydrologic CycleJane EspañolaNo ratings yet
- Hydropowerchapter 2Document31 pagesHydropowerchapter 2Sagar patelNo ratings yet
- LectureSeries2 PrecipitationDocument20 pagesLectureSeries2 Precipitationashwinagrawal198231100% (1)
- CE 425 - Engineering HydrologyDocument32 pagesCE 425 - Engineering HydrologyCiel RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Hydrology PPT 02Document18 pagesHydrology PPT 02Got7No ratings yet
- Module 1 - Hydrological CycleDocument13 pagesModule 1 - Hydrological CycleJudy Ann CacutNo ratings yet
- Engineering Hydrology (ECIV 4323) : Instructor: Dr. Said GhabayenDocument16 pagesEngineering Hydrology (ECIV 4323) : Instructor: Dr. Said Ghabayenrizwan ghafoorNo ratings yet
- Hydro TemplateDocument13 pagesHydro TemplateGwyneth SantosNo ratings yet
- Global GeomorphologyDocument13 pagesGlobal GeomorphologyAlexantia Ardi MustofaNo ratings yet
- Hydrology Is The Scientific Study of The Movement, Distribution, and Quality of Water On Earth andDocument5 pagesHydrology Is The Scientific Study of The Movement, Distribution, and Quality of Water On Earth andMonika KshetriNo ratings yet
- 1-Introduction To HydrologyDocument25 pages1-Introduction To HydrologyYao SsengssNo ratings yet
- Civil-V-hydrology and Irrigation Engineering (10cv55) - SolutionDocument99 pagesCivil-V-hydrology and Irrigation Engineering (10cv55) - SolutionRavi Kumar C NNo ratings yet
- The Hydrologic CycleDocument3 pagesThe Hydrologic CycleMark Anthony TajonNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Applications: Introduction To Autocad 2010 ForDocument14 pagesCivil Engineering Applications: Introduction To Autocad 2010 ForPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Hydrology: Instructor: Mahmoud Mahmoud (MASCE) Assistant Professor Cihan UniversityDocument16 pagesHydrology: Instructor: Mahmoud Mahmoud (MASCE) Assistant Professor Cihan UniversityMahmoud I. MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Hydrology Final TranscriptDocument30 pagesConcepts of Hydrology Final TranscriptJeric GementizaNo ratings yet
- Hyrdo-Point Rainfall MeasurementDocument40 pagesHyrdo-Point Rainfall MeasurementAishlly Crystal OrtizNo ratings yet
- Hydrologic CycleDocument7 pagesHydrologic CycleNaveed NawazNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Hydrology StudyDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Hydrology Studyelnaqa176No ratings yet
- Lect. No. 1: Hydrology: Engineering Hydrology Deals With All Hydrology Aspects Which Are Related To PlanningDocument8 pagesLect. No. 1: Hydrology: Engineering Hydrology Deals With All Hydrology Aspects Which Are Related To PlanningSaad ShauketNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Basic HydrologyDocument32 pagesChapter 1 - Basic Hydrologyhayati morsidiNo ratings yet
- Topic 1Document33 pagesTopic 1Adron LimNo ratings yet
- Power Plant AssignmentDocument17 pagesPower Plant AssignmentViswanath Babu RNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Hydrology: Introduction. Hydrologic Cycle, World Water Budget. Precipitation-Forms, TypesDocument44 pagesUnit IV Hydrology: Introduction. Hydrologic Cycle, World Water Budget. Precipitation-Forms, TypesKushaal RajNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HydrometeorologyDocument21 pagesIntroduction To HydrometeorologyApril JulianoNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument15 pagesIntroductionKATE SARAH MARANANNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Hydrology PDFDocument16 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Hydrology PDFKimmieNo ratings yet
- Hydrology: Prepared byDocument36 pagesHydrology: Prepared byMithun100% (1)
- BCE 3102 Hydrology and Hydraulics - Lecture 2 (The Hydrologic and Carbon Cycle)Document29 pagesBCE 3102 Hydrology and Hydraulics - Lecture 2 (The Hydrologic and Carbon Cycle)Philip TibenderanaNo ratings yet
- Hydrology AssignmentDocument20 pagesHydrology AssignmentMannat DhaliwalNo ratings yet
- List of Majors That Hydrology Study AboutDocument17 pagesList of Majors That Hydrology Study Aboutomed muhammadNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 01 Hydrological MeasurementsDocument59 pagesChapter - 01 Hydrological Measurementsabdullah fatehNo ratings yet
- Streammflow - WikipediaDocument28 pagesStreammflow - WikipediaNimanNo ratings yet
- Hydrological Fluvial Coastal Limestone EnvironmentsDocument52 pagesHydrological Fluvial Coastal Limestone EnvironmentsDharam Jagroop100% (1)
- Lesson 4 - Run-Off AnalysisDocument13 pagesLesson 4 - Run-Off AnalysisJoshua EsquerdoNo ratings yet
- The ImportanceDocument4 pagesThe ImportanceÀbïyãñ SëlömõñNo ratings yet
- Chapter5-Slope StabilityDocument14 pagesChapter5-Slope StabilityÀbïyãñ SëlömõñNo ratings yet
- Engineering Hydrology Group AssignmentDocument3 pagesEngineering Hydrology Group AssignmentÀbïyãñ SëlömõñNo ratings yet
- Engineering Hydrology Assignment OneDocument2 pagesEngineering Hydrology Assignment OneÀbïyãñ SëlömõñNo ratings yet
- Ppt2 Quantity Ch2Document24 pagesPpt2 Quantity Ch2Àbïyãñ SëlömõñNo ratings yet
- Xe-Pian Xe-Namnoy ProjectDocument61 pagesXe-Pian Xe-Namnoy ProjectLovewater RainingNo ratings yet
- 13ee704 Renewable Energy Sources Set 1Document2 pages13ee704 Renewable Energy Sources Set 1Prathap VuyyuruNo ratings yet
- Low Level Phosphorus Pilot With Sorex100Document55 pagesLow Level Phosphorus Pilot With Sorex100jiawen dingNo ratings yet
- Mid Exam Solution by EsayasDocument20 pagesMid Exam Solution by EsayasChanako DaneNo ratings yet
- Argumentative EssayDocument3 pagesArgumentative EssayHariz Akmal0% (1)
- Manure PresentationDocument8 pagesManure PresentationSagar PantNo ratings yet
- Green BuildingDocument35 pagesGreen BuildingMakna SuarNo ratings yet
- Week 1: Natural ResourcesDocument1 pageWeek 1: Natural ResourcesEdli Ane AnchetaNo ratings yet
- Solar Wind Desal Arab PDFDocument11 pagesSolar Wind Desal Arab PDFali alasdyNo ratings yet
- And Domkundawar, S., A Course in Power Plant Engineering, Dhanpatrai (2002)Document2 pagesAnd Domkundawar, S., A Course in Power Plant Engineering, Dhanpatrai (2002)Dr. Gollapalli NareshNo ratings yet
- Lec - 1-Week (1) (Introduction To Environmental Engineering) PDFDocument22 pagesLec - 1-Week (1) (Introduction To Environmental Engineering) PDFKhanNo ratings yet
- Irena Remap DHC Report 2017Document112 pagesIrena Remap DHC Report 2017Dewanjee AshrafNo ratings yet
- Ijresm V2 I6 35Document5 pagesIjresm V2 I6 35surya reddyNo ratings yet
- Tendernotice 1Document1 pageTendernotice 1Vijaykumar JaganiaNo ratings yet
- 1 SMDocument10 pages1 SMAlvionita ManukranteNo ratings yet
- Combined & Separate Sewer SystemsDocument9 pagesCombined & Separate Sewer SystemsKhairylle JuanNo ratings yet
- For "A Student Practicing Conservation of Natural Resources" (g3)Document10 pagesFor "A Student Practicing Conservation of Natural Resources" (g3)Sandra Louise CamarinesNo ratings yet
- A Review of Constructed Wetland On Type, Treatment andDocument23 pagesA Review of Constructed Wetland On Type, Treatment andLaura YustiNo ratings yet
- chp7 DO Sag Curves StreamsDocument40 pageschp7 DO Sag Curves StreamsMarlon Gomez Casicote100% (1)
- Pond Ecology and Conservation Research PrioritiesDocument22 pagesPond Ecology and Conservation Research PrioritiesCalessNo ratings yet
- Pa291 Payatas DisasterDocument6 pagesPa291 Payatas DisasterthepolicyanalystNo ratings yet
- Evaluasi Kinerja Kompor UB-03-1 Berbahan Bakar Limbah Industri Kayu Olahan, Tempurung Kelapa, Pelepah Sawit, Dan Ranting Kayu AkasiaDocument9 pagesEvaluasi Kinerja Kompor UB-03-1 Berbahan Bakar Limbah Industri Kayu Olahan, Tempurung Kelapa, Pelepah Sawit, Dan Ranting Kayu Akasiamuhamad ainul yakinNo ratings yet
- Technical Guidance Document Quality MonitoringDocument27 pagesTechnical Guidance Document Quality MonitoringtalhaNo ratings yet
- Topics of Water PollutionDocument7 pagesTopics of Water PollutionsabaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 PDFDocument154 pagesUnit 5 PDFKhalilNo ratings yet