Professional Documents
Culture Documents
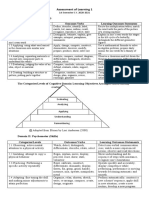
Lecture Bloom Taxonomy
Lecture Bloom Taxonomy
Uploaded by
Anne BautistaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture Bloom Taxonomy
Lecture Bloom Taxonomy
Uploaded by
Anne BautistaCopyright:
Available Formats
Bloom’s Taxonomy: The Behavior: Get involved in or participate
actively.
Affective Domain Verb: Respond, React, Clarify,
The affective domain (Krathwohl, Bloom, Contribute, Question, Cite, Perform, Write,
Masia, 1973) includes the manner in which we Assists, Aids, Recites, Presents, Answers,
deal with things emotionally, such as feelings, Reports, Discusses.
values, appreciation, enthusiasm, motivation and
attitude.
1. Receiving
The five major categories are listed from
the simplest behavior to the most complex. Behavior: Open to experience or idea,
willing to hear.
Receiving
Verb: Hear, Listen, Be Open To, Ask,
Responding Focus, Attend, Take Part In, Acknowledge,
Valuing Concentrate, Do, Feel, Follow, Read, Uses.
Organizing
Characterization Verbs suitable for Affective Domain
Receiving – Acknowledge, asks, attentive,
courteous, dutiful, follows, gives, listens, and
Bloom’s Taxonomy - Affective
understands.
5. Internalising
Responding – Answers, assists, aids,
Behavior: Adopt belief system or complies, conforms, discuss, performs, presents,
philosophy. and tells.
Verbs: Internalize, Acts, Displays, Valuing – appreciates, cherish, treasures,
Influence, Practice, Believe, Ingrain, Immerse, demonstrates, initiates, invites, joins, justifies,
Consistently, Incorporate, Acquire. proposes.
Organization – compares, relates,
4. Organising synthesizes.
Behavior: Reconcile disparate elements or Characterization – acts, discriminates,
conflicts, develop value system. displays, influences, modifies, performs, and
qualifies.
Verbs: Organise, Develop, Build, Relate,
Prioritise, Reconcile, Contrast, Compare, Arrange,
Integrate, Synthesize, Adhere, Alter, Modify,
Bloom’s Taxonomy: The Psychomotor
Formulate.
Domain
The psychomotor domain (Simpson, 1972)
3. Valuing includes physical movement, coordination, and
use of the motor-skill areas.
Behavior: Attach values and express
personal opinions. Psychomotor skills rage from manual
tasks. The Major levels of Psychomotor Domain
Verbs: Argue, Challenge, Debate, Refute, are:
Justify, Persuade, Critique, Explains, Invites,
Forms, Proposes, joins, Demonstrates. Perception (awareness through sensory
cues) – distinguish, hear, see, smell, taste, touch.
2. Responding
Set – adjust, approach, locate, place, Helps faculty to design and implement
position, prepare. appropriate assessment tasks, measures, and
instruments.
Guided Response – copy, determine,
discover, duplicate, imitate, inject, and repeat. Helps to ensure that instruction and
assessment are appropriately aligned with the
Mechanism (basic proficiency) – adjust,
intended outcomes.
build, illustrate, indicate, manipulate, mix, set up.
Complex Overt Response (Expert)
Adaptation – Adapt, build, change, Examples of Instructional
develop, and supply. Objectives – 3 Cognitive Levels
Organization – construct, create, design, After this presentation, the driver
and produce. education student will:
1. Recall the steps for starting an
automobile.
Verbs suitable for the Psychomotor 2. Explain the task of starting an
Domain automobile.
3. Create a protocol for starting an
Perception – chooses, describes, detects, automobile.
differentiates, distinguishes, identifies.
Set – proceeds, reacts, shows, states, volunteers.
Writing the Cognitive Objective
Guided Response – copies, traces, follows,
reacts, reproduce, and responds. Bloom’s Taxonomy (Revised)
Mechanism (basic proficiency) – It was later revised by Lorin Anderson and
assembles, calibrates, constructs, dismantles, David Krathwohl to reflect a more active form of
displays. thinking.
Complex overt Response (Expert) –
manipulates, measures, mends, mixes, and How to write a Cognitive Objective?
organizes, sketches.
2. Identify the cognitive level required for
Adaptation –adapts, alters, changes, the learning competency.
rearranges, reorganizes, and revises.
a. Remembering
Organization – constructs, creates, designs,
b. Understanding
initiate, and makes, originates.
c. Applying
d. Analyzing
Why to use Bloom’s Taxonomy?
e. Evaluating
Some of the reason for employing
Bloom’s Taxonomy include: f. Creating
Accurately measuring of Students’
abilities.
3. Choose the correct action word in
Establishes intended learning outcomes in creating the cognitive objective.
professor/student interactions.
4. Examines the cognitive objective is complex of
SMAR. commitmen
t. This
Specific – clear behavior is
Measurable – tested in assessments based on the
phenomena
Attainable – applicable for grade level discussed.
Organization The learner Compares,
Result-oriented – learning is reflected in a organizes relates,
product. values into synthesizes.
priorities by
contrasting
Writing the Affective Domain different
values,
This includes the way we deal with things resolving
emotionally such as feelings, values, appreciation, conflicts
enthusiasms, motivations and attitudes. between
them and
creating a
unique
Five major categories of the Affective value
Domain system. The
learning
Category Description Action Words
outcome
Receiving Awareness Acknowledge
should
Phenomena to hear; s, asks,
focus on
does attentive,
comparing,
selected courteous,
relating and
attention. dutiful,
synthesizing
follows,
values.
gives, listens,
Internalization The learner Acts,
and
(Characterizatio has a value discriminates,
understand.
n) system that displays,
Responding Requires Answer,
controls the influences,
Phenomena active assists, aids,
behavior for modifies,
participatio complies,
every performs,
n of the conforms,
phenomena. qualifies,
learners and discusses,
questions,
reacts to a greets, helps, The values revises,
particular labels, were serves, solves,
situation. performs, compared, verifies.
presents, and given
tells. priorities
Valuing This Appreciates, and
involves the cherishes, practiced
value a treasures, consistency.
learner demonstrates,
attaches to a initiates,
particular invites, joins,
phenomeno justifies,
n. It could proposes, How to use the correct Affective
be seen respects, and Objective?
from the shares.
simplest 1. It depends on the teachers.
acceptance
2. It depends on the values integrated.
to the most
3. It depends on the degree of change a teacher a learner’s
wants the learners to experience. response to
different
situations.
Still we can decide if we want the learners Mechanism The practice Assembles,
to follow (receive), discuss (respond), give worth (basic becomes calibrates,
proficiency) habitual and constructs,
(value), compare (organize), or internalize a new
the learner dismantles,
learning. shows displays,
confidence fastens, fixes,
and grinds, heats,
The Psychomotor Domain proficiency in manipulates,
doing the measures,
Cognitive – Mental Skill skill. mends, mixes,
Affective – Attitude/Behavior and organizes,
sketches.
Psychomotor – Physical Movement Complex The learner Assembles,
(Motor Skill Areas) Overt shows a calibrates,
Response skilful constructs,
In order to develop the skill needed for the (Expert) performance dismantles,
learning competency, it should be measured in indicated by displays,
terms of speed, precision, procedures or Take note: the an accuracy fastens, fixes,
techniques in execution. keywords are and high grinds, heats,
the same with coordination manipulates,
The psychomotor skills can be seen from Mechanism. requiring measures,
manual tasks to more complex tasks. For COR, minimum mends, mixes,
adverbs or energy. and organizes,
adjectives will sketches.
MANUAL COMPLEX be used to
indicate
Answering a problem using a process deeper better
Creating a new process to solve a problem. performance.
Adaptation The learner’s Adapts, alters,
skills are changes,
Seven Categories of the Psychomotor well- rearranges,
developed and reorganizes,
Domain can modify and revises,
Category Description Action Words movements to varies.
Perception The learners’ Chooses, fit special
uses sensory describes, requirements.
sues to guide detects, Origination The learner
Arranges,
motor activity differentiates, creates new builds,
(the learner distinguishes, movement combines,
needs identifies, patterns to fit
composes,
stimulus to isolates, a particular
constructs,
perform task). relates, situation. creates,
selects. designs,
Set This refers to Begins, The learning initiate,
a learner’s displays, outcome makes,
readiness to explains, emphasizes originates
act. This moves, creativity.
includes the proceeds,
three mindsets reacts, shows, How to write your Psychomotor
that states,
predetermine volunteers. Objective?
It depends on the Cognitive Objective.
(The Cognitive objective contains the
mental skill needed.)
Do we have to use the Keywords
suggested?
No. You can use other action words to suit
the category used and become aligned with the
cognitive objective.
You might also like
- Sample DLP 5 Organization and ManagementDocument5 pagesSample DLP 5 Organization and ManagementAileen I Reyes50% (2)
- Bloom's TaxonomyDocument3 pagesBloom's TaxonomyBerenice ChoongNo ratings yet
- Taxonomies of Learning 9feb2021Document11 pagesTaxonomies of Learning 9feb2021Fairusy Fitria HaryaniNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan. 222Document5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan. 222Realm Daffodil SuquibNo ratings yet
- ABM - BM11BS IIa 11Document6 pagesABM - BM11BS IIa 11Junard AsentistaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningBlessila LopezNo ratings yet
- OC 13 Identifies Strategies Used by Each Speaker To Convey Hisher Ideas EffectivelyDocument4 pagesOC 13 Identifies Strategies Used by Each Speaker To Convey Hisher Ideas EffectivelyZeen Dee100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningRed Zye UbayNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningJulia Maria LoviteNo ratings yet
- Instructional Planning (Iplan) : Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatDocument3 pagesInstructional Planning (Iplan) : Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatReynalyn HernandezNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Learning 1: Domain:1 Cognitive (Knowledge) Categories/Level Outcomes Verbs Learning Outcomes StatementsDocument3 pagesAssessment of Learning 1: Domain:1 Cognitive (Knowledge) Categories/Level Outcomes Verbs Learning Outcomes StatementsElpid Soleng BadongNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science DLP 13Document5 pagesEarth & Life Science DLP 13Bowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningRendyNo ratings yet
- 10.2.4 DLP GealonDocument4 pages10.2.4 DLP GealonGlad Norman LimoconNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningSuzetteBragaSamuela100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningJennibeth Garcia Dela RitaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Instructional PlanningJeraldine RepolloNo ratings yet
- Educ105 EportfolioDocument5 pagesEduc105 Eportfolioapi-569704745No ratings yet
- IPlan DLP Format v.02Document4 pagesIPlan DLP Format v.02Julie Anne MacuseNo ratings yet
- DLP WRB 10 1 DemoDocument5 pagesDLP WRB 10 1 DemoMakoy PadasasNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningRed Zye UbayNo ratings yet
- Final OutputDocument7 pagesFinal OutputCharlie Blauro BalisiNo ratings yet
- AL QuizDocument3 pagesAL QuizJohn Michael Porras HambreNo ratings yet
- DLP ELS 1Q Origin of The UniverseDocument7 pagesDLP ELS 1Q Origin of The Universekathleen b. cabacabaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningdanNo ratings yet
- OC 11.1 Ascertains The Verbal and Nonverbal Cues That Each Speaker Uses To Achieve His Her PurposeDocument4 pagesOC 11.1 Ascertains The Verbal and Nonverbal Cues That Each Speaker Uses To Achieve His Her PurposeZeen DeeNo ratings yet
- Session 4 Act. 3Document9 pagesSession 4 Act. 3Julia Maria LoviteNo ratings yet
- Category Examples Key Words (Verbs)Document5 pagesCategory Examples Key Words (Verbs)Christine Sheena Batican-BulalaNo ratings yet
- 10.1.4 DLP LanderoDocument4 pages10.1.4 DLP LanderoGlad Norman LimoconNo ratings yet
- OC 10 Watches and Listens To Sample Oral Communication ActivitiesDocument4 pagesOC 10 Watches and Listens To Sample Oral Communication ActivitiesZeen Dee86% (7)
- The Learner Can Put Elements Together To Form A Functional Whole, Create A New Product or Point of ViewDocument1 pageThe Learner Can Put Elements Together To Form A Functional Whole, Create A New Product or Point of ViewEmerson Mercado GalanoNo ratings yet
- Nail Care Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesNail Care Lesson PlanMa. Crissa Aboyme100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningZeen DeeNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningAnonymous HJlXukJrNo ratings yet
- 10.3.3 DLP RetuyaDocument4 pages10.3.3 DLP RetuyaGlad Norman LimoconNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningJesson AlbaranNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Feb 11Document3 pagesLesson 3 - Feb 11Desiree IsidroNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningRed Zye UbayNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningRed Zye UbayNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Revised Taxonomy: Cognitive, Affective, and PsychomotorDocument4 pagesBloom's Revised Taxonomy: Cognitive, Affective, and PsychomotorsumonNo ratings yet
- OC 12 The Learner Distinguishes The Types of SpeechDocument4 pagesOC 12 The Learner Distinguishes The Types of SpeechZeen DeeNo ratings yet
- IplanDocument4 pagesIplanJeraldine RepolloNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Instructional PlanningJeraldine RepolloNo ratings yet
- C1 - Joey Jabonet-W4-Dlp1-3Document5 pagesC1 - Joey Jabonet-W4-Dlp1-3ludabelle19No ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Various Models of CommunicationDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Various Models of CommunicationZeen DeeNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningJoel MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- DLP 2Document5 pagesDLP 2Baby YanyanNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science DLP 12Document4 pagesEarth & Life Science DLP 12Bowina KhoNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningRed Zye UbayNo ratings yet
- IPlan DLP Format English-VersionDocument5 pagesIPlan DLP Format English-VersionDina ArcenalNo ratings yet
- ABM - BM11FO-Ia-1 GSAYDDLPQTR1-DAY 2Document4 pagesABM - BM11FO-Ia-1 GSAYDDLPQTR1-DAY 2Junard AsentistaNo ratings yet
- M11 GM-Ic-1Document5 pagesM11 GM-Ic-1Dan Albert AbesNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Principles and Techniques of Measuring Vital SignsDocument9 pagesDiscuss The Principles and Techniques of Measuring Vital SignsMarielle ContaNo ratings yet
- DLP Observation EntrepDocument4 pagesDLP Observation EntrepAnne HathawayNo ratings yet
- OC 11 The Learner Distinguishes The Types of SpeechDocument4 pagesOC 11 The Learner Distinguishes The Types of SpeechZeen DeeNo ratings yet
- Blooms Taxo Ran2022Document4 pagesBlooms Taxo Ran2022Ramon Lord A. NerierNo ratings yet
- MontedeRamos Diagnostic Test For N 229Document2 pagesMontedeRamos Diagnostic Test For N 229Uri Perez MontedeRamosNo ratings yet
- Bae, Jacqueline Nichole D. - 3A7 - Midterm ProjectDocument4 pagesBae, Jacqueline Nichole D. - 3A7 - Midterm Projectjacqueline baeNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningReynalyn HernandezNo ratings yet
- Leading with Purpose The Guide to Becoming a Remarkable ChiefFrom EverandLeading with Purpose The Guide to Becoming a Remarkable ChiefNo ratings yet
- Lecture Test Construction and EvaluationDocument7 pagesLecture Test Construction and EvaluationAnne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 12 Principles High Quality Classroom AssessmentsDocument2 pagesLecture - 12 Principles High Quality Classroom AssessmentsAnne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lecture in AstronomyDocument6 pagesLecture in AstronomyAnne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 MeteorologyDocument4 pagesLecture 5 MeteorologyAnne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 MotionDocument4 pagesLecture 2 MotionAnne BautistaNo ratings yet
- LectureDocument1 pageLectureAnne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Elements of ArtDocument2 pagesLecture 2 - Elements of ArtAnne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lecture GeologyDocument4 pagesLecture GeologyAnne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lecture in Foundations of ArtDocument1 pageLecture in Foundations of ArtAnne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Basic Concepts in Classroom AssessmentDocument3 pagesLecture 1 - Basic Concepts in Classroom AssessmentAnne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lecture in Educ 206 - Sir Khristian - The Four Role of AssessmentDocument4 pagesLecture in Educ 206 - Sir Khristian - The Four Role of AssessmentAnne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Motion in One DimensionDocument5 pagesLecture Motion in One DimensionAnne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Instructional ObjectivesDocument4 pagesLecture - Instructional ObjectivesAnne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lecture in GEd 201 - Lesson 4 Language Planning and Language PolicyDocument2 pagesLecture in GEd 201 - Lesson 4 Language Planning and Language PolicyAnne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Lesson PlanningDocument4 pagesLecture Lesson PlanningAnne Bautista100% (1)
- Lecture in GEd 202 - Module 09Document6 pagesLecture in GEd 202 - Module 09Anne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Factors Affecting Success of MultilingualismDocument2 pagesLecture 5 - Factors Affecting Success of MultilingualismAnne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lecture in GEd 202 - Module 05Document7 pagesLecture in GEd 202 - Module 05Anne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lecture in GEd 202 - Module 08Document12 pagesLecture in GEd 202 - Module 08Anne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lecture in GEd 202 - Module 3 and 4Document8 pagesLecture in GEd 202 - Module 3 and 4Anne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lecture in GEd 202 - Module 6&7Document8 pagesLecture in GEd 202 - Module 6&7Anne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lecture in Ethics - Filipino As A Moral AgentDocument16 pagesLecture in Ethics - Filipino As A Moral AgentAnne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lecture in GEd 201 Legal Bases and Benefits of Teaching and Learning Mother TongueDocument2 pagesLecture in GEd 201 Legal Bases and Benefits of Teaching and Learning Mother TongueAnne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Theories and Principles of MTB-MLEDocument3 pagesLecture 2 Theories and Principles of MTB-MLEAnne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lecture in GEd 201 - MTB-MLE)Document2 pagesLecture in GEd 201 - MTB-MLE)Anne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lecture in Ethics Filipino Values and Moral DevelopmentDocument4 pagesLecture in Ethics Filipino Values and Moral DevelopmentAnne BautistaNo ratings yet
- 4 Innovation Decision ProcessDocument41 pages4 Innovation Decision Processmalsha gunarathneNo ratings yet
- EIPGDocument103 pagesEIPGBrijlal MallikNo ratings yet
- Happy Classroom - MCQDocument7 pagesHappy Classroom - MCQmahamood md100% (2)
- Promotion and TransferDocument8 pagesPromotion and Transfermdimransram95No ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument8 pagesPurposive CommunicationBorgonia, Khryzlin May C.No ratings yet
- Test Bank For The Social Animal, 12e Elliot Aronson, Joshua Aronson Test BankDocument9 pagesTest Bank For The Social Animal, 12e Elliot Aronson, Joshua Aronson Test BankNail BaskoNo ratings yet
- Ebook PDF The Interpersonal Communication Book 14th Edition PDFDocument41 pagesEbook PDF The Interpersonal Communication Book 14th Edition PDFscott.stokley449100% (42)
- Organizational Socialization Outcomes: Now and Into The FutureDocument25 pagesOrganizational Socialization Outcomes: Now and Into The FutureMarko GalićNo ratings yet
- Document OriginalDocument4 pagesDocument OriginalCrisia ConstantineNo ratings yet
- 6 Pillars of Talent MangementDocument3 pages6 Pillars of Talent MangementTouseef RizviNo ratings yet
- Teaching-Guide-Catchup-Science Values Grade 7Document3 pagesTeaching-Guide-Catchup-Science Values Grade 7Lea Andria100% (1)
- Lab A15-4 Gender Communication QuizDocument1 pageLab A15-4 Gender Communication QuizRadhika SinghalNo ratings yet
- The Mental Health Problems of African Americans Who Attend Predominately White InstitutionsDocument8 pagesThe Mental Health Problems of African Americans Who Attend Predominately White Institutionsapi-665386311No ratings yet
- Business CommunicationDocument2 pagesBusiness CommunicationSraban Ahmed MasumNo ratings yet
- NCM 102 Prelim NotesDocument12 pagesNCM 102 Prelim NotesCABAÑAS, Azenyth Ken A.No ratings yet
- Mental Health Is All About How People ThinkDocument5 pagesMental Health Is All About How People ThinkresyaniNo ratings yet
- Learner Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument36 pagesLearner Centered Psychological PrinciplesMariel D. BelandoNo ratings yet
- Preventing Perfectionism Among ChildrenDocument14 pagesPreventing Perfectionism Among ChildrenHobi's Important BusinesseuNo ratings yet
- Đề ôn HVTC (Trắc nghiệm)Document10 pagesĐề ôn HVTC (Trắc nghiệm)Bùi Thị Vân Anh 06No ratings yet
- Reflection-Communicating About Mental HealthDocument6 pagesReflection-Communicating About Mental HealthAshley KiddNo ratings yet
- The Happiness Trap Extra Bits - Russ HarrisDocument3 pagesThe Happiness Trap Extra Bits - Russ HarrisThabo Seane0% (1)
- Nurhaya912, Artikel 11886Document10 pagesNurhaya912, Artikel 11886Axel YoelNo ratings yet
- PDF 20230211 110338 0000 PDFDocument19 pagesPDF 20230211 110338 0000 PDFIris FayNo ratings yet
- Managerial Negotiations - Spring 2024 - Bidding Syllabus2Document7 pagesManagerial Negotiations - Spring 2024 - Bidding Syllabus2pradyut.agrawal18No ratings yet
- DLL Gifted and DisabilitiesDocument6 pagesDLL Gifted and DisabilitiesPropsero Luke Godfrey CaberteNo ratings yet
- CBT Formulation GuideDocument13 pagesCBT Formulation GuidevaleriaNo ratings yet
- Anti-Bullying Policy FlyerDocument2 pagesAnti-Bullying Policy FlyerBim de LeonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Self ConceptDocument29 pagesLesson 1 Self Conceptpenales.andrei.oNo ratings yet
- The Role of Teacher in ELT - Raxmonov ParvizbekDocument23 pagesThe Role of Teacher in ELT - Raxmonov ParvizbekMakhmud MukumovNo ratings yet
- Exploring The Relationship Between Sexual Desires, Fulfilment and Relationship SatisfactionDocument8 pagesExploring The Relationship Between Sexual Desires, Fulfilment and Relationship SatisfactionIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet