Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topic 4 ME Levels of Evltn
Topic 4 ME Levels of Evltn
Uploaded by
Rodah MuchembiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic 4 ME Levels of Evltn
Topic 4 ME Levels of Evltn
Uploaded by
Rodah MuchembiCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic 4
LEVELS OF MONITORING AND EVALUATION
Internal evaluation
It involves the use of internal staff to evaluate programs or issues of direct relevance to an
organization. The use of internal evaluation has been growing rapidly during the last decade.
Nevertheless, there is a serious gap in knowledge about internal evaluation, especially for human
service and non‐governmental organizations. This paper begins by examining internal evaluation
within the discourse of a “new vision” of evaluation that links evaluation closely to management
and practice. The paper explores the unique characteristics of internal evaluation, its strengths
and weaknesses, the process of internal evaluation, steps in developing internal evaluation
capacity, strategies for effective internal evaluation, and positive and negative roles of internal
evaluators. It concludes with a look at some recent developments in the evolution of internal
evaluation.
External Evaluation
External evaluators are constructed from an outside agency or organization to conduct the
evaluation. They are found at Institutions, Consulting firms, Hospitals etc.
They may bring a different perspective to the evaluation because they are not directly affiliated
with your project, however this can also be a draw back. They are detached from the daily
operations of the organization, thus limited knowledge on the projects needs and goals.
CORE CONCERNS OF PROJECT EVALUATORS
These are aspects that evaluators need to be concerned with assessing the performance of a
project
1. Project Progress: This is continual development of the project towards the achievement
of the planned objectives
2. Project Adequacy: This means project objectives, inputs or activities are enough for the
purpose intended.
3. Project Relevance: This is related to how the projects objectives and activities respond
to the needs of intended beneficiaries.
4. Project Validity It assesses the extent to which the project design like;
Clear immediate objectives
Focuses on identified problems and needs
Describes main inputs, outputs and activities needed
States means of verification of achievements of objectives
5. Project Effectiveness: This is the extent to which a project produces the desired result.
6. Project efficiency: The extent to which the methods used by the project or activities are
the best in terms of cost, resources used, time required and appropriateness of the task.
7. Project Impact: Determines the overall effect of a project’s activities in terms of socio-
economic.
8. Project cost analysis: This evaluation on cost and their effect with regard to producing
an outcome.
9. Project Sustainability: It examines the extent to which project strategies and activities
are likely to continue to be implemented after termination of the project.
10. Project unintended outcomes: These are unforeseen negative or positive effects of a
project.
You might also like
- Case Study 3: Fountain Pens LimitedDocument3 pagesCase Study 3: Fountain Pens Limitedtanya singh100% (1)
- Inspection & Test Plan: PC ClientDocument9 pagesInspection & Test Plan: PC ClientMuhammed Abo-FandoodNo ratings yet
- Project - PPT 6 Monitoring and EvaluationDocument41 pagesProject - PPT 6 Monitoring and EvaluationWelday Gebremichael75% (4)
- CWTS Module 6 UpdatedDocument4 pagesCWTS Module 6 UpdatedAngela NavaltaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document15 pagesChapter 7Lowella May Tan ChengNo ratings yet
- Feasibility Study of A ProjectDocument13 pagesFeasibility Study of A ProjectScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- NSTP 2 - Lesson 10 - Participatory Monitoring and EvaluationDocument22 pagesNSTP 2 - Lesson 10 - Participatory Monitoring and EvaluationJanus FreudNo ratings yet
- What Are The Different Types of Monitoring and Evaluation M&EDocument148 pagesWhat Are The Different Types of Monitoring and Evaluation M&ESayed Burhan SohailNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Project EvaluationDocument5 pagesChapter 5 Project EvaluationkasuNo ratings yet
- 7 Monitoring and 10 Evaluation Types To Boost Your M&E StrategyDocument23 pages7 Monitoring and 10 Evaluation Types To Boost Your M&E StrategyreeNo ratings yet
- Project Identification, Planning $ Scheduling Individual AssigmentDocument5 pagesProject Identification, Planning $ Scheduling Individual AssigmentAbata BageyuNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Cwts and LtsDocument11 pagesModule 7 Cwts and LtsJerico VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Module 7 - NSTP2 - Participatory Monitoring and EvaluationDocument9 pagesModule 7 - NSTP2 - Participatory Monitoring and EvaluationVenice Eve PelimaNo ratings yet
- Project Monitoring Evaluation SR 1223744598885201 9Document30 pagesProject Monitoring Evaluation SR 1223744598885201 9Vali KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document12 pagesChapter 4Wiz SantaNo ratings yet
- Undertaking A ProjectDocument14 pagesUndertaking A ProjectFrancis AppahNo ratings yet
- Post Project Evaluation: Waisuddin Sadry Sumit Sharma Mayank Babu Rohan BhardwajDocument18 pagesPost Project Evaluation: Waisuddin Sadry Sumit Sharma Mayank Babu Rohan Bhardwajmayank_b_usmsNo ratings yet
- Monitoring and EvaluationDocument19 pagesMonitoring and EvaluationnaqibullahshahabNo ratings yet
- Evaluation - Types of Evaluation - Presada BiancaDocument7 pagesEvaluation - Types of Evaluation - Presada BiancaBianca PresadaNo ratings yet
- Project - PPT 6 Monitoring and EvaluationDocument48 pagesProject - PPT 6 Monitoring and EvaluationBirhanu Abrha100% (1)
- Libs 837 Project Management 4Document5 pagesLibs 837 Project Management 4Ogechukwu Okeke100% (1)
- Feasibility StudyDocument16 pagesFeasibility StudyNabila Afrin RiyaNo ratings yet
- Project Evaluation and Auditing August2020Document24 pagesProject Evaluation and Auditing August2020Ram Prasad AwasthiNo ratings yet
- Types of Evaluation-ReviewedDocument23 pagesTypes of Evaluation-RevieweddmugalloyNo ratings yet
- Project Management SMU EDUDocument7 pagesProject Management SMU EDUVijayNo ratings yet
- 220 - Feasibility StudyDocument14 pages220 - Feasibility StudyNitin100% (1)
- PM Unit 1Document15 pagesPM Unit 1haashboi5100% (1)
- Infrastructure Financing Project 1Document19 pagesInfrastructure Financing Project 1Wajd NasserNo ratings yet
- Unit Introduction To Monitoring and EvaluationDocument3 pagesUnit Introduction To Monitoring and EvaluationKouame AdjepoleNo ratings yet
- Ep Unit 5Document6 pagesEp Unit 5Asif AliNo ratings yet
- 56 Eval and Impact AssessmentDocument37 pages56 Eval and Impact AssessmentSamoon Khan AhmadzaiNo ratings yet
- Project Closure SummaryDocument4 pagesProject Closure SummaryKenya CahyaNo ratings yet
- Studying For MCQDocument19 pagesStudying For MCQJames OuNo ratings yet
- 20170217110223lect3 Program Evaluation Approaches (Slide) (Nida)Document60 pages20170217110223lect3 Program Evaluation Approaches (Slide) (Nida)susilaramalingam100% (1)
- GROUP 4 - Project DesignDocument19 pagesGROUP 4 - Project Designodeke aronNo ratings yet
- Development Planning and Project Anlysis LLDocument18 pagesDevelopment Planning and Project Anlysis LLTeddy DerNo ratings yet
- Script For Project ControlDocument8 pagesScript For Project Controlsarahpatricia.vdlNo ratings yet
- 1 - 8617 - Autumn 2018 1552485421787Document16 pages1 - 8617 - Autumn 2018 1552485421787Ahtisham KhanNo ratings yet
- What Is MonitoringDocument14 pagesWhat Is MonitoringKipyegon ErickNo ratings yet
- Project Monitoring and EvaluationDocument29 pagesProject Monitoring and Evaluationjoy dungon100% (1)
- Project Audit: Phase 1 - Success Criteria and Questionnaire DevelopmentDocument4 pagesProject Audit: Phase 1 - Success Criteria and Questionnaire DevelopmentsjiipmNo ratings yet
- Cahp 14 Project Management JZDocument2 pagesCahp 14 Project Management JZFaisalAltafNo ratings yet
- Feasibility StudyDocument38 pagesFeasibility StudyKeerthi PremNo ratings yet
- Guide For The Development of A Project Evaluation PlanDocument17 pagesGuide For The Development of A Project Evaluation Planmou777100% (1)
- Project Management 1 EMBA JnUDocument12 pagesProject Management 1 EMBA JnUShamima AkterNo ratings yet
- Activity 7Document3 pagesActivity 7Nicole MalinaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 ReportDocument31 pagesChapter 6 ReportEloise Anne Tul-idNo ratings yet
- BUS 5611 Discussion Forum Unit 8Document4 pagesBUS 5611 Discussion Forum Unit 8David MukunzaNo ratings yet
- Faraw 1Document13 pagesFaraw 1melse firewNo ratings yet
- Guide To Project EvaluationDocument25 pagesGuide To Project EvaluationChristian Eduard de Dios100% (1)
- Project Closure Chapter OutlineDocument10 pagesProject Closure Chapter OutlineBasit KhanNo ratings yet
- Project InitiationDocument34 pagesProject InitiationJ. VinceNo ratings yet
- 5 6075868613338727912 PDFDocument40 pages5 6075868613338727912 PDFPrabhatNo ratings yet
- Project M and E NewDocument183 pagesProject M and E Newtesfayeme14No ratings yet
- 4 Project EvaluationDocument18 pages4 Project EvaluationMansoor HafeezNo ratings yet
- 3.5.7. What Are The Steps in Implementing An Impact Assessment?Document2 pages3.5.7. What Are The Steps in Implementing An Impact Assessment?Erika PetersonNo ratings yet
- NSTP Mod2Document3 pagesNSTP Mod2cshenNo ratings yet
- Reena Sekhon 2Document14 pagesReena Sekhon 2randhawarobinNo ratings yet
- Porposal WritingDocument102 pagesPorposal WritingMoustapha AlexNo ratings yet
- NSTP Unit 10Document18 pagesNSTP Unit 10sinichiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Project ManagementDocument7 pagesAssignment 1 Project ManagementRihame Khodor HdedeNo ratings yet
- Camera Topic 6Document7 pagesCamera Topic 6Rodah MuchembiNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 5-Online AdvertisingDocument2 pagesTOPIC 5-Online AdvertisingRodah MuchembiNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 MEDocument3 pagesTopic 2 MERodah MuchembiNo ratings yet
- ME Topic 3Document2 pagesME Topic 3Rodah MuchembiNo ratings yet
- Production Crew TOPIC 3 CinematographyDocument8 pagesProduction Crew TOPIC 3 CinematographyRodah MuchembiNo ratings yet
- MA Mock Exam 2021 SolutionsDocument17 pagesMA Mock Exam 2021 Solutionsnissa.dawson18No ratings yet
- Facilities ManagementDocument3 pagesFacilities ManagementAlvin AloysiusNo ratings yet
- Final Draft - Mainstreaming ManualDocument42 pagesFinal Draft - Mainstreaming ManualRamilNo ratings yet
- 051.30 Trade Officer Position SBH-SpainDocument2 pages051.30 Trade Officer Position SBH-SpainMiguel Angel Lahera RiveroNo ratings yet
- 1.axis - Copper Pod Drawing - 26.06.23Document7 pages1.axis - Copper Pod Drawing - 26.06.23Tamanna ShenoyNo ratings yet
- PIA SWOT MATRIX Group AssignmentDocument4 pagesPIA SWOT MATRIX Group AssignmentMahnoor baqaiNo ratings yet
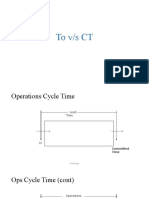
- To Vs CTDocument24 pagesTo Vs CTIMRAN MASUDNo ratings yet
- A Study On Inventory Management at Anantha PVC Pipes PVT LTD, AnanthapurDocument8 pagesA Study On Inventory Management at Anantha PVC Pipes PVT LTD, AnanthapurEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- ALL GOLD OFFERS June 2021-1-1Document15 pagesALL GOLD OFFERS June 2021-1-1Lin Chris100% (1)
- Instalment Payment Plan FormDocument1 pageInstalment Payment Plan Formckeat_2No ratings yet
- ArtikelShobikin 8Document17 pagesArtikelShobikin 8Dandi HermawanNo ratings yet
- Sub Topic 1-Frameworks - Roles of QsDocument21 pagesSub Topic 1-Frameworks - Roles of QsaqmarhazimeNo ratings yet
- CV Business Adm Mgr-S.DridiDocument2 pagesCV Business Adm Mgr-S.DridiMoaatazz NouisriNo ratings yet
- S19-1510u30-1 WJEC A Level Business - Unit 3 MS S19Document17 pagesS19-1510u30-1 WJEC A Level Business - Unit 3 MS S19Ameen BaigNo ratings yet
- Value Chain AnalysisDocument7 pagesValue Chain AnalysisVivek Singh TomarNo ratings yet
- Determination of Optimal Portfolio by Using Tangency Portfolio and Sharpe RatioDocument7 pagesDetermination of Optimal Portfolio by Using Tangency Portfolio and Sharpe RatiowoelfertNo ratings yet
- SITXHRM010 Recruitment Report TemplateDocument2 pagesSITXHRM010 Recruitment Report TemplateSmile Reacts0% (1)
- Legal Focus Dec 2023Document3 pagesLegal Focus Dec 2023jianNo ratings yet
- Resume - CA Tarun Khandelwal - pdf-1Document2 pagesResume - CA Tarun Khandelwal - pdf-1OM JARWALNo ratings yet
- Annex D - SOP For Warehouse and Inventory Management in IvsDocument41 pagesAnnex D - SOP For Warehouse and Inventory Management in IvsSelvamuthukumara AsohanNo ratings yet
- Process Discovery Part 2Document32 pagesProcess Discovery Part 2Rahul AryanNo ratings yet
- Compro 2022 - PT OBSESI MASA DEPAN SUKSES - CompressedDocument44 pagesCompro 2022 - PT OBSESI MASA DEPAN SUKSES - CompressedOtak Kanan TattooNo ratings yet
- Kf16ce49 - Assignment #1Document9 pagesKf16ce49 - Assignment #1Aslam LaghariNo ratings yet
- At MCQ Salogsacol Auditing Theory Multiple ChoiceDocument32 pagesAt MCQ Salogsacol Auditing Theory Multiple Choicealmira garciaNo ratings yet
- Termeni Contabili EnglezaDocument2 pagesTermeni Contabili EnglezaAdrianaNo ratings yet
- Abdulrahman Hashem Assignment 1Document6 pagesAbdulrahman Hashem Assignment 1TarekYehiaNo ratings yet
- Newspaper - Advert - 20072023 - Other - VacanciesDocument3 pagesNewspaper - Advert - 20072023 - Other - Vacanciespeterkimani24138255No ratings yet
- Weekly Report Augest 23 Up To 28Document7 pagesWeekly Report Augest 23 Up To 28FIREW GETACHEWNo ratings yet