Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Math9 Q2 Activity-2
Math9 Q2 Activity-2
Uploaded by
JAY AR ESPARTEROOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Math9 Q2 Activity-2
Math9 Q2 Activity-2
Uploaded by
JAY AR ESPARTEROCopyright:
Available Formats
CARMEN NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL
Carmen, Cotabato
Name: _________________________________ Score: _________________________
Section: _______________________________ Quarter/Subject: Q2-Mathematics 9
ACTIVITY SHEET (MODULE 2)
General Instruction: Read and understand each question. Write your answer on the space provided. Don’t use other
paper except this activity sheet. You may use the back page of this paper if necessary.
Test I. Directions: Identify each situation whether relationship illustrates direct or inverse variation. Write JV if it is Joint
Variation and CV if it is Combined Variation.
_____1. The area of a rectangle and its dimensions.
_____2. The volume of cylinder and its height and radius.
_____3. The speed of a car and its distance and covered.
_____4. The width of a rectangular prism, its volume, length and height.
_____5. The heat produced by an electric lamp, the resistance and current.
_____6. The electrical resistance of a wire, its length and diameter d.
_____7. The pressure of a gas, its temperature and volume.
_____8. The electrical voltage, the current and the resistance.
_____9. The force applied to an object, the mass and the acceleration.
_____10. The current, the electromotive force and the resistance.
Test II. Directions: Translate the following statements by means of an equation where k represents the constant of
variation. Please refer on the example provided.
Joint Variation Combined Variation
Equation Statement Equation Statement
kac Example. W varies jointly as the a and c and
P = kqr Example. P varies jointly as q and r W=
b inversely as b.
1. The pressure (P) of a gas varies directly as its
1. The area (A) of a parallelogram varies
temperature (t) and inversely as its
jointly as the base (b) and altitude (a).
volume (V).
2. The volume (V) of a cylinder varies 2. The electrical resistance (R) of a wire varies
jointly as its height (h) and the square of directly as its length (l) and inversely as the
the radius (r). square of its diameter (d).
3. The heat (H) produced by an electric lamp
3. The electrical voltage (V) varies jointly
varies jointly as the resistance (R) and the square
as the current (I) and the resistance (R).
of the current (C).
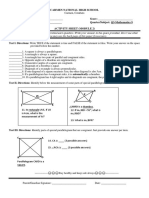
4. The appropriate length (s) of a 4. The kinetic energy (E) of a moving object
rectangular beam varies jointly as its width varies jointly as the mass (m) of the object and
(w) and its depth (d). the square of the velocity (v).
5. The acceleration (a) of an object varies directly
5. The area (A) of a square varies jointly
as the force (f) exerted and inversely as its mass
as its diagonals (d1) and (d2).
(m).
Test III. Directions: Answer the following problems. Use the back page of this paper for your solution.
1. “z varies jointly as x and y”. If z = 60 when x = 5 and y = 6. Find z when x = 7 and y = 6.
2. “w varies directly as x and y and inversely as v2” If w = 1200 when x = 4, y = 9 and v = 6. Find w when x = 3, y = 12,
and v = 9.
3. The area (A) of triangle varies jointly as the base (b) and the height (h). A triangle with a base of 8 cm and a height of 9
cm has an area of 36 square centimeters. Find the area when the base is 10 cm and the height is 7 cm.
4. The acceleration (a) of an object varies directly as the force (f) exerted and inversely as its mass (m). If the constant of
variation is 1, find the acceleration in meters/second2 of a 10 kg object exerting a force of 10 Newtons.
---------------😊😊😊Stay healthy and keep safe always😊😊😊---------------
Parent/Guardian Signature: __________________________ Date: ___________________
You might also like
- Joint Variation Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesJoint Variation Lesson PlanErnie Estrera92% (12)
- Variation Test QuestionsDocument5 pagesVariation Test QuestionsMellicent U. Daigdigan100% (3)
- Math 9 Summative Test Joint VariationDocument1 pageMath 9 Summative Test Joint VariationMaricris Dizon-Miguel100% (2)
- Second Quarterly Examination Math 9Document2 pagesSecond Quarterly Examination Math 9Mark Kiven Martinez94% (16)
- Current LogDocument48 pagesCurrent LogBadia Charef Bent MohammedNo ratings yet
- A. - 3. P Varies Directly As L and Inversely As The Square Root of GDocument2 pagesA. - 3. P Varies Directly As L and Inversely As The Square Root of GNeo VillarealNo ratings yet
- SLHT Math9 Q2 Wk1Document4 pagesSLHT Math9 Q2 Wk1Zeus Romero100% (1)
- W1 - Direct Variation Set ADocument1 pageW1 - Direct Variation Set ATeacher AngelicaNo ratings yet
- Moreh Academy: - Quarter - 2 - Week - 1Document10 pagesMoreh Academy: - Quarter - 2 - Week - 1Bernadeth PlanasNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet in Math 9 Q2Document5 pagesLearning Activity Sheet in Math 9 Q2Charmae Ann CañeteNo ratings yet
- Module in Mathematics 9Document5 pagesModule in Mathematics 9Lady MaeNo ratings yet
- 1st Summative Test-Math 9 - Q2Document2 pages1st Summative Test-Math 9 - Q2Jhonrey GetioNo ratings yet
- VARIATIONDocument1 pageVARIATIONdonna grace supnadNo ratings yet
- Week 1. Direct and Inverse Variation. Learning Activity SheetDocument4 pagesWeek 1. Direct and Inverse Variation. Learning Activity SheetBea Lyn OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Direct VariationDocument4 pagesDirect VariationPrinceMarkoNo ratings yet
- DLL Math9 2ndquarter Week1Document4 pagesDLL Math9 2ndquarter Week1Lichelle Calicdan AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- S-DLP Inverse VariationDocument5 pagesS-DLP Inverse VariationChessa Mae PelongcoNo ratings yet
- MELC 1bDocument31 pagesMELC 1bNorlie LamisNo ratings yet
- Q2 Mathematics 9 - Module 1Document24 pagesQ2 Mathematics 9 - Module 1Eden Pearl LumaynoNo ratings yet
- Translating Into Variation Statement Relationship Between Two Given QuantitiesDocument35 pagesTranslating Into Variation Statement Relationship Between Two Given QuantitiesJenilyn Espejo100% (1)
- 92-320 F05 G. Rankin (Midterm)Document6 pages92-320 F05 G. Rankin (Midterm)CKNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 - Long Test (3rd Quarter)Document2 pagesGrade 9 - Long Test (3rd Quarter)Daneca100% (2)
- Y X X K BC A: and K Xy Joint Variation A KBC and KDocument1 pageY X X K BC A: and K Xy Joint Variation A KBC and KRosemarie Sumao-i BugaoanNo ratings yet
- G9MATH Q2 M2 FeDocument15 pagesG9MATH Q2 M2 FeRalph NilloNo ratings yet
- Y9 Variations Proportions Handout 2022Document5 pagesY9 Variations Proportions Handout 2022Ahron SenNo ratings yet
- 2nd QRT Exam MathDocument7 pages2nd QRT Exam MathGehg MalaqueNo ratings yet
- Q2W2 - Inverse Variation AutosavedDocument33 pagesQ2W2 - Inverse Variation AutosavedAstig GamingNo ratings yet
- Joint VarianceDocument8 pagesJoint VarianceRivette A.No ratings yet
- Abstract:: τ = μ (du/dy)Document7 pagesAbstract:: τ = μ (du/dy)Yahya IsiedNo ratings yet
- Q2M1 VariationsDocument56 pagesQ2M1 VariationsIvanka VillaramaNo ratings yet
- Joint and Combined VariationDocument19 pagesJoint and Combined Variationcharis04No ratings yet
- Mathematics 9 VariationDocument21 pagesMathematics 9 VariationRichelle Piedad EncioNo ratings yet
- MELC 1 ADocument33 pagesMELC 1 ANorlie LamisNo ratings yet
- VariationsDocument3 pagesVariationsSherchen Antonio-CortesNo ratings yet
- Activities For Dec. 12-16, 2022Document2 pagesActivities For Dec. 12-16, 2022shirley dalangNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 - VariationDocument13 pagesGrade 9 - VariationLyndon B. PaguntalanNo ratings yet
- Q2 1st Summative TestDocument2 pagesQ2 1st Summative Testmarnelli binanNo ratings yet
- 318283535-LONG-TEST-Variation - For MergeDocument3 pages318283535-LONG-TEST-Variation - For MergeeleonoraNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 M1 - W1 Mathematics 9Document50 pagesQuarter 2 M1 - W1 Mathematics 9cutiegab57No ratings yet
- Q2 Mathematics 9 - Module 2Document21 pagesQ2 Mathematics 9 - Module 2Eden Pearl LumaynoNo ratings yet
- VARIATION Word Problems DV - IV Joint - CombinedDocument24 pagesVARIATION Word Problems DV - IV Joint - CombinedPrince Andrew Catacutan MangahasNo ratings yet
- Math 9 - Q2 - Week 2 - Module 2 - Variations Joint and Combined Variations - For ReproductionDocument18 pagesMath 9 - Q2 - Week 2 - Module 2 - Variations Joint and Combined Variations - For ReproductionJubilo , Daniella Mae S.100% (1)
- JME 3700 Midterm Exam: March 4, 2020 NameDocument4 pagesJME 3700 Midterm Exam: March 4, 2020 NameMichael WendlNo ratings yet
- G9 Math - Term 2 - Short Test #1 ReviewerDocument12 pagesG9 Math - Term 2 - Short Test #1 Reviewerzmhnz2rgfcNo ratings yet
- Lab Ex (Center of Presure)Document5 pagesLab Ex (Center of Presure)Jhay jhay AlcorconNo ratings yet
- Joint Variation PowerpointDocument23 pagesJoint Variation Powerpointangelica galulanNo ratings yet
- 2324 8CCS - Math - Study Guide For 2nd Endterm Test (2324)Document8 pages2324 8CCS - Math - Study Guide For 2nd Endterm Test (2324)kienkienNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2Document3 pagesQuiz 2Erich Joy Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Activity 9Document3 pagesActivity 9Rizza Mae ReponteNo ratings yet
- S-DLP Direct VariationDocument4 pagesS-DLP Direct VariationChessa Mae PelongcoNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity SheetDocument10 pagesLearning Activity SheetJasmin Move-RamirezNo ratings yet
- Tasas de Cambio Relacionadas: Related RatesDocument4 pagesTasas de Cambio Relacionadas: Related RatesRaul Humberto Mora VillamizarNo ratings yet
- LAS-LESACA Math9 Wk2 Checked by Dela CruzDocument15 pagesLAS-LESACA Math9 Wk2 Checked by Dela CruzJoan SilvaNo ratings yet
- NVS - Physics - Class XI - 2020-21aDocument5 pagesNVS - Physics - Class XI - 2020-21aKartik PatilNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Illustrating Variation 1Document42 pagesMath 9 Illustrating Variation 1Ken-Ken BormateNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Illustrating VariationDocument31 pagesMath 9 Illustrating VariationKen-Ken Bormate100% (1)
- Alg2 1.5-1.6 PracticeDocument4 pagesAlg2 1.5-1.6 PracticeRupal HessNo ratings yet
- PT For Grade 9Document2 pagesPT For Grade 9John SalaanNo ratings yet
- Math9 Q2 Activity-5Document1 pageMath9 Q2 Activity-5JAY AR ESPARTERONo ratings yet
- Math9 Q3 ActivitySheet Mod5Document1 pageMath9 Q3 ActivitySheet Mod5JAY AR ESPARTERONo ratings yet
- Math9 Q3 ActivitySheet Mod2Document1 pageMath9 Q3 ActivitySheet Mod2JAY AR ESPARTERONo ratings yet
- Math9 Q3 ActivitySheet Mod4Document1 pageMath9 Q3 ActivitySheet Mod4JAY AR ESPARTERONo ratings yet
- Math9 Q3 ActivitySheet Mod3Document1 pageMath9 Q3 ActivitySheet Mod3JAY AR ESPARTERONo ratings yet
- Math9 Q3 ActivitySheet Mod1Document1 pageMath9 Q3 ActivitySheet Mod1JAY AR ESPARTERO100% (1)
- CCNA 1 v7 Examen Final de Habilidades ITN (PTSA) RespuestasDocument10 pagesCCNA 1 v7 Examen Final de Habilidades ITN (PTSA) Respuestasandresgo123No ratings yet
- Digital Filters Digital Filters Digital Filters Digital Filters Digital Filters 55555Document54 pagesDigital Filters Digital Filters Digital Filters Digital Filters Digital Filters 55555Beroxi MihaiNo ratings yet
- 2g Audit TrakerDocument24 pages2g Audit TrakerPankaj KumarNo ratings yet
- CommsDocument3 pagesCommsBeauMattyNo ratings yet
- Windows CMD CommandsDocument19 pagesWindows CMD Commandsiaas labs100% (1)
- Larrondo. 2003. A Novel Extracellular Multicopper Oxidase From Phanerochaete Chrysosporium With Ferroxidase ActivityDocument7 pagesLarrondo. 2003. A Novel Extracellular Multicopper Oxidase From Phanerochaete Chrysosporium With Ferroxidase ActivityAnahí TbpNo ratings yet
- FQ5-2012-019 FS-2575 FS-5075 Ver.01.06 Remedy For LAN CommunicationDocument4 pagesFQ5-2012-019 FS-2575 FS-5075 Ver.01.06 Remedy For LAN CommunicationAndrew NazarovNo ratings yet
- HP Laserjet Enterprise MFP M630 SeriesDocument4 pagesHP Laserjet Enterprise MFP M630 SeriesonttNo ratings yet
- Tesis Flipped ClassroomDocument63 pagesTesis Flipped ClassroomEdward David Caté100% (1)
- Capitol 10 CorectDocument50 pagesCapitol 10 CorectRatiu SilviuNo ratings yet
- Remedial Measures Incorporating Jet Grouting and Micropiles For The Construction of A New Back Ow PreventerDocument10 pagesRemedial Measures Incorporating Jet Grouting and Micropiles For The Construction of A New Back Ow Preventerrigaz6366No ratings yet
- Credit Card Fraud Detection Using Enhanced Random Forest Classifier For Imbalanced DataDocument11 pagesCredit Card Fraud Detection Using Enhanced Random Forest Classifier For Imbalanced Datanarendramatta18No ratings yet
- Simple Musical LEDs Circuit DiagramDocument22 pagesSimple Musical LEDs Circuit Diagrambluesky_1976No ratings yet
- Soft-Soil Const ModelDocument6 pagesSoft-Soil Const ModelicabullangueroNo ratings yet
- Be Civil-Engineering Semester-4 2022 December Structural-Analysisrev-2019-CDocument3 pagesBe Civil-Engineering Semester-4 2022 December Structural-Analysisrev-2019-Csapna.chaudhary171096No ratings yet
- Module Week 5Document13 pagesModule Week 5DM BartolayNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of Skin and Its ApplicationsDocument94 pagesPhysical Properties of Skin and Its ApplicationsdrshilpibhadaniNo ratings yet
- Selenium IntroductionDocument64 pagesSelenium IntroductionDeveloper 4No ratings yet
- Fiber Optics: Prof. R.K. ShevgaonkarDocument6 pagesFiber Optics: Prof. R.K. ShevgaonkarVivek UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Game Theory: Part 1: Introduction and Types of GamesDocument13 pagesGame Theory: Part 1: Introduction and Types of Gameszwer0122No ratings yet
- B.tech (IT)Document57 pagesB.tech (IT)coolvar90No ratings yet
- Straight Wire PIODocument16 pagesStraight Wire PIOZaid DewachiNo ratings yet
- 2.2.3 Enzymes WorksheetDocument8 pages2.2.3 Enzymes WorksheetGrace Ann Matanguihan RentoriaNo ratings yet
- Paper Sludge PDFDocument13 pagesPaper Sludge PDFDanie RoyNo ratings yet
- Research TechniquesDocument8 pagesResearch TechniquesSomhita DasNo ratings yet
- An Experimental Study of The Recrystallization Mechanism During Hot Deformation of AluminiumDocument15 pagesAn Experimental Study of The Recrystallization Mechanism During Hot Deformation of AluminiumManolo GipielaNo ratings yet
- Dry Dial Single Jet Water Meter: Application Main CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesDry Dial Single Jet Water Meter: Application Main CharacteristicsDavid NeiraNo ratings yet
- Internetworking or Network LayerDocument94 pagesInternetworking or Network LayerWaleed MallickNo ratings yet
- Column HP10 To Base Plate Connection Report PDFDocument7 pagesColumn HP10 To Base Plate Connection Report PDFAhmed AlmayaliNo ratings yet