Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Protein Structures Table
Protein Structures Table
Uploaded by
Aiden O'GarroOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Protein Structures Table
Protein Structures Table
Uploaded by
Aiden O'GarroCopyright:
Available Formats
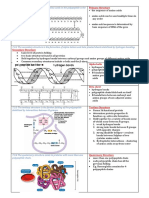
Level Types of Bonds Position of Bond Effect of Bond Formation
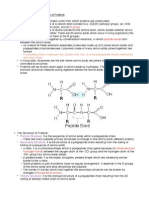
Primary Structure • Covalent Bonds • Between atoms in a single amino acid Forms straight chained polypeptide
• Peptide Bonds • Between the ionised carboxyl group and the
ionised amine group
Secondary • Hydrogen bonds • Alpha Helix- The hydrogen bonds are • Forms a helical structure.
Structure formed between the –CO of one amino acid
and the –NH of an amino acid.
• Forms a pleated fibrous
• Beta-Pleated Sheet- The hydrogen bonds structure.
are formed between the –CO of one amino
acid and the –NH of an amino acid in
adjacent anti-parallel chains of
polypeptides.
Tertiary Structure • Hydrogen bonds • Occurs when the –OH or –NH groups of All bonds cause folding of the structure
one –R group attracts the –O or –CO group which is essential for enzymes and
of another –R group antibodies.
Results in a 3-D structure
• Ionic bonds • Occurs between the amino and carboxyl
parts of some –R groups.
• Disulphide bonds • Occurs between the amino and carboxyl
parts of some –R groups.
Quaternary • Hydrogen bonds • Occurs when the –OH or –NH groups of Made up of many tertiary structures,
Structure one –R group attracts the –O or –CO group which all have folds as a result of their
of another –R group tertiary structures.
• Ionic bonds
Polypeptide chains are
• Occurs between the amino and carboxyl linked to a non-protein (prosthetic
parts of some –R groups. group) part of the
• Disulphide bonds molecule
• Occurs between the amino and carboxyl
parts of some –R groups.
You might also like
- Full Ebook of Inclusion Bodies Methods and Protocols 1St Edition Julian Kopp Online PDF All ChapterDocument67 pagesFull Ebook of Inclusion Bodies Methods and Protocols 1St Edition Julian Kopp Online PDF All Chapterjuanitahopkins608019100% (6)
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Fish Protein FingerprintingDocument23 pagesFish Protein Fingerprintingrahmi93No ratings yet
- Lec 6Document27 pagesLec 6Sreemanti DeyNo ratings yet
- ProteinsDocument38 pagesProteinsManan PatelNo ratings yet
- Intro To Proteins - ppt1 FixDocument52 pagesIntro To Proteins - ppt1 FixbrianNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15 - Covalent Bonding: Chem 103, Section F0F Unit VI - Compounds Part II: Covalent CompoundsDocument6 pagesLecture 15 - Covalent Bonding: Chem 103, Section F0F Unit VI - Compounds Part II: Covalent CompoundsHamza KhalidNo ratings yet
- Protein Structure ATEDocument31 pagesProtein Structure ATErollyNo ratings yet
- Proteins and Nucleic Acid 1Document58 pagesProteins and Nucleic Acid 1Jelly AceNo ratings yet
- Protien ASDocument25 pagesProtien ASRabia RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Primary Structure: Beta SheetDocument1 pagePrimary Structure: Beta Sheetthat/niggaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - The 3-D Structure of ProteinsDocument49 pagesChapter 4 - The 3-D Structure of Proteinsdaniel3676No ratings yet
- Protein StructureDocument43 pagesProtein StructureZeyNo ratings yet
- Protein: A Natural Polyamide Many Polypeptide Chains Together by Intermolecular ForcesDocument6 pagesProtein: A Natural Polyamide Many Polypeptide Chains Together by Intermolecular Forcesmuhdimran97No ratings yet
- Proteins HODocument11 pagesProteins HOJade PategaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules - Intro - Proteins1 PDFDocument31 pagesBiomolecules - Intro - Proteins1 PDFFake WalaNo ratings yet
- Proteins PDFDocument7 pagesProteins PDFAshley ArnoldNo ratings yet
- BasicDocument2 pagesBasicapi-296833859No ratings yet
- بروتين 2Document57 pagesبروتين 2MaNny BatawahNo ratings yet
- 2022.09.07 Protein Structure and Function PT 1 (Ch4)Document24 pages2022.09.07 Protein Structure and Function PT 1 (Ch4)Allison KwanNo ratings yet
- Protein StructureDocument41 pagesProtein Structureteklay100% (1)
- Protein 3Document32 pagesProtein 3Miran El-MaghrabiNo ratings yet
- Protein Structure Discussion. AleksandrovaDocument1 pageProtein Structure Discussion. AleksandrovaАнастасия АлександроваNo ratings yet
- 2 1moleculestometabolismpptxDocument30 pages2 1moleculestometabolismpptxKhin (Darin) Hnin PhyuNo ratings yet
- Protein Engineering Yves Rival VF2Document195 pagesProtein Engineering Yves Rival VF2Kilian DuchesneNo ratings yet
- 05 - Amino Acid, Protein and Protein MetabolismDocument63 pages05 - Amino Acid, Protein and Protein MetabolismAzzarina AzreenNo ratings yet
- Molecules To MetabolismDocument16 pagesMolecules To MetabolismEmaNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Organic ChemistryDocument15 pages1.3 Organic Chemistryアリ ハイナNo ratings yet
- NMAT-Org-Chem - Biochem Lecture (1-JDDocument77 pagesNMAT-Org-Chem - Biochem Lecture (1-JDBose LogoNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 4Document4 pagesBiochemistry 4Lykisha Larraine CosmianoNo ratings yet
- Summary of Proteins (Biochemistry)Document12 pagesSummary of Proteins (Biochemistry)Xie LianNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Proteins-1Document54 pages1.4 Proteins-1Ng Kei CheongNo ratings yet
- Bio 1.proteinsDocument88 pagesBio 1.proteinsAnish PandeyNo ratings yet
- CH 4Document7 pagesCH 4Marybelle VencioNo ratings yet
- ProteinsDocument20 pagesProteinsGrishma RanaNo ratings yet
- Macromolecules of The Cells PDFDocument30 pagesMacromolecules of The Cells PDFAgzar RidhoNo ratings yet
- Proteins: Presented By: Deepika Kaithal M.Sc. Semester Iv Department of Applied PhysicsDocument23 pagesProteins: Presented By: Deepika Kaithal M.Sc. Semester Iv Department of Applied PhysicsasifNo ratings yet
- Func Tional Groups: Heteroatoms-Atoms Other Than Carbon or Hydrogen. Common Heteroatoms Are NitroDocument3 pagesFunc Tional Groups: Heteroatoms-Atoms Other Than Carbon or Hydrogen. Common Heteroatoms Are NitrokalloliNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and ProteinsDocument5 pagesAmino Acids and ProteinsGrace FernandoNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 and 3 NotesDocument15 pagesTopic 2 and 3 NotesvDraqNo ratings yet
- Intro To BiochemDocument12 pagesIntro To BiochemDanielle AguilaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry - C5 Proteins Higher Orders of StructureDocument5 pagesBiochemistry - C5 Proteins Higher Orders of StructureKim LlamasNo ratings yet
- Proteins: - Aminoacid Is Composed ofDocument3 pagesProteins: - Aminoacid Is Composed ofmax2711No ratings yet
- The 3D Structure of ProteinsDocument38 pagesThe 3D Structure of ProteinsZakiyah ShahabuddinNo ratings yet
- PDF DocumentDocument52 pagesPDF DocumentJulio DuncanNo ratings yet
- Fst613 1 ProteinsDocument78 pagesFst613 1 ProteinsmohamadbarsyikNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Organic Chemistry:: The Saturated HydrocarbonsDocument73 pagesAn Introduction To Organic Chemistry:: The Saturated HydrocarbonsGabz Gabby0% (1)
- Lecture 3 - RNA & ProteinDocument69 pagesLecture 3 - RNA & ProteinConstance WongNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Proteins - Tagged 2Document88 pagesLecture 5 - Proteins - Tagged 2hashm.f.alamerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Unit 1Document12 pagesChapter 2 Unit 1harshit khareNo ratings yet
- BIO122 Chapter 4Document174 pagesBIO122 Chapter 4Miss KillerNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - 3Document29 pagesUnit 2 - 3Sunita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Protein Structure Students (1563)Document32 pagesProtein Structure Students (1563)ΜΑΡΙΑ ΣΟΛΑΚΙΔΟΥNo ratings yet
- AAs and ProteinsDocument67 pagesAAs and ProteinsChitrasen GuptaNo ratings yet
- L4.1 Protein StructureDocument23 pagesL4.1 Protein StructureAzamu Shahiullah ProttoyNo ratings yet
- Final PDF For Grade 9 PDFDocument5 pagesFinal PDF For Grade 9 PDFmadhuri pawarNo ratings yet
- Electrophoresis (Chapter 27) :: Electrophoresis: The Separation of Charged Particles by Their Different Rates of MovementDocument12 pagesElectrophoresis (Chapter 27) :: Electrophoresis: The Separation of Charged Particles by Their Different Rates of MovementIrfan Syahmi ZulkipliNo ratings yet
- Topic 2.4: PROTEINS: Peptide Bonds Amino AcidsDocument1 pageTopic 2.4: PROTEINS: Peptide Bonds Amino AcidsYasser Khairy AbdelghaniNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lec Trans - Module 1 Unit 1Document8 pagesBiochem Lec Trans - Module 1 Unit 156bmkkn2rnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ProteinsDocument45 pagesChapter 3 ProteinsAcyuta RajNo ratings yet
- MT3239 Polimer Hayati (3 SKS) : Dr. Lia Asri & Steven, ST., MTDocument68 pagesMT3239 Polimer Hayati (3 SKS) : Dr. Lia Asri & Steven, ST., MTimeldaNo ratings yet
- Intro To Protein StructureDocument31 pagesIntro To Protein StructureNehemia ManucducNo ratings yet
- Mcqs and Seqs of BiochemistryDocument6 pagesMcqs and Seqs of BiochemistrymisbahnazNo ratings yet
- ProteinsDocument13 pagesProteinsDevendra Yadav100% (1)
- Bengt Nolting Protein Folding Kinetics Biophysic PDFDocument228 pagesBengt Nolting Protein Folding Kinetics Biophysic PDFAnonymous qo9HWQ100% (1)
- Copy of Protein Folding ActivityDocument5 pagesCopy of Protein Folding ActivityIsrael Jimenez FelixNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Notes AP BiologyDocument11 pagesChapter 5 Notes AP BiologyAndrew AltenNo ratings yet
- Protein As MicromoleculesDocument7 pagesProtein As MicromoleculesPrincess JacintoNo ratings yet
- Towards A Digital Bioprocess Replica Computational Approac - 2020 - Trends in BDocument13 pagesTowards A Digital Bioprocess Replica Computational Approac - 2020 - Trends in BJUAN C. OVIEDO LOPERANo ratings yet
- Methods in Molecular Biology Volume Vol. 857Document432 pagesMethods in Molecular Biology Volume Vol. 857Roniele MonteiroNo ratings yet
- WheyDocument91 pagesWheyEviTrianaNo ratings yet
- ProteinsDocument25 pagesProteinsapi-260674021No ratings yet
- Denaturation of ProteinsDocument42 pagesDenaturation of ProteinsArchana MadpathiNo ratings yet
- Next-Step MCAT OutlineDocument24 pagesNext-Step MCAT OutlineSage NorrieNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry - Biomolecules AssignmentDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry - Biomolecules Assignmentsyed0% (1)
- Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Protein FoldingDocument21 pagesKinetics and Thermodynamics of Protein FoldingEduardo OtalvaroNo ratings yet
- Reflection PaperDocument11 pagesReflection PaperDaisy C. LabradaNo ratings yet
- ProteinsDocument11 pagesProteinsCed HernandezNo ratings yet
- BIO307 Lecture (Protein Structure and Function)Document18 pagesBIO307 Lecture (Protein Structure and Function)Kerstin MarobelaNo ratings yet
- Protein FoldingDocument21 pagesProtein FoldingRONAK LASHKARINo ratings yet
- Intro 2 Molecular Modelling & Molecular MechanicsDocument35 pagesIntro 2 Molecular Modelling & Molecular Mechanicsachsanuddin50% (2)
- Lecture 10 in ClassDocument8 pagesLecture 10 in ClassAyodejiES1No ratings yet
- (Poly, Many Mer, Unit) Monomers (Mono, One) : Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O) and Nitrogen (N) PolymersDocument5 pages(Poly, Many Mer, Unit) Monomers (Mono, One) : Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O) and Nitrogen (N) PolymersDaneth Julia TuberaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Cell Biology 7th Edition Lodish Test BankDocument8 pagesMolecular Cell Biology 7th Edition Lodish Test BankLaurenThompsonfpniz100% (15)
- FST3107-INTRODUCTION TO FOOD CHEMISTRY - ProteinDocument67 pagesFST3107-INTRODUCTION TO FOOD CHEMISTRY - ProteinZHOU TIANLENo ratings yet
- MEDF1012A Amino Acids and ProteinsDocument48 pagesMEDF1012A Amino Acids and ProteinsminhyunxiiiiNo ratings yet
- LSM2106-SII-Amino Acid-Proteins (2023-2024-Sem I)Document116 pagesLSM2106-SII-Amino Acid-Proteins (2023-2024-Sem I)Jojo LomoNo ratings yet
- Full Lab Report On: Exercise No. 4 Protein DenaturationDocument8 pagesFull Lab Report On: Exercise No. 4 Protein DenaturationElaine FaloNo ratings yet
- Nurture Their Nature: Helping Those With A Neurodiversity Enjoy Learning AgainDocument136 pagesNurture Their Nature: Helping Those With A Neurodiversity Enjoy Learning AgainTricia CookNo ratings yet
- 2d 3d StructureDocument38 pages2d 3d Structureth_kiranNo ratings yet