Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 viewsScribed 3
Scribed 3
Uploaded by
zayed shbanA relay is a device that senses abnormal electrical conditions and closes its contacts. There are different types of relays including current, directional, and power relays. Maintenance testing of relays includes checking pickup values, dropout/reset values, and verifying proper contact function. Directional relays can be tested using an in-phase test to check minimum pickup without requiring a three-phase supply.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Eto Coc Oral Exam Prep QuestionsDocument29 pagesEto Coc Oral Exam Prep QuestionsHemraj Singh Rautela100% (4)
- WRT-100 - Winding Resistance TestDocument10 pagesWRT-100 - Winding Resistance TestVictor Jr Quijano100% (1)
- Condition Monitoring of RelaysDocument5 pagesCondition Monitoring of RelaysSaurabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Transformer Testing 8Document8 pagesTransformer Testing 8mp20ke1798No ratings yet
- Commissioning Numerical RelaysDocument24 pagesCommissioning Numerical RelaysVHMANOHARNo ratings yet
- Evaluate Relays For Automated Test StationsDocument5 pagesEvaluate Relays For Automated Test StationsKumar GauravNo ratings yet
- Scribed 4Document3 pagesScribed 4zayed shbanNo ratings yet
- Polarity / Vector Group TestDocument6 pagesPolarity / Vector Group TestHassan AbdoNo ratings yet
- Power Systems: Power Systems Undervoltage and Overvoltage Time Lag RelaysDocument4 pagesPower Systems: Power Systems Undervoltage and Overvoltage Time Lag RelaysHarkishen SinghNo ratings yet
- Testing of Power TransformersDocument7 pagesTesting of Power Transformerspctinformation100% (4)
- Transformer Winding Resistance Testing of Fundamental ImportanceDocument5 pagesTransformer Winding Resistance Testing of Fundamental Importancegeddam06108825No ratings yet
- Testing of Power TransformersDocument6 pagesTesting of Power TransformersSamsudin AhmadNo ratings yet
- Surge Test PDFDocument12 pagesSurge Test PDFPrashant PuriNo ratings yet
- Testing Electrical and Electronics: Component / Devices With MultimeterDocument17 pagesTesting Electrical and Electronics: Component / Devices With MultimeterIra CervoNo ratings yet
- Experiment Current RelayDocument6 pagesExperiment Current Relayকাওমিউজ্জামান কাব্যNo ratings yet
- Basic Electric Motor TestingDocument4 pagesBasic Electric Motor TestingHemendra JaniNo ratings yet
- General Guidelines 2 Test RelaysDocument3 pagesGeneral Guidelines 2 Test RelayssktorsiNo ratings yet
- Transformer Repairing Auto Saved)Document11 pagesTransformer Repairing Auto Saved)c0rr0deNo ratings yet
- IEEE 62 (Guide ForField Testing of Oil Filled TransforDocument1 pageIEEE 62 (Guide ForField Testing of Oil Filled TransforFaheem PP13No ratings yet
- Best Practice Manual-Transformers 44Document1 pageBest Practice Manual-Transformers 44sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
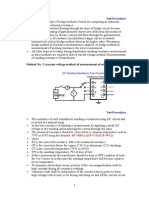
- Method No: 2 (Current Voltage Method of Measurement of Winding Resistance)Document6 pagesMethod No: 2 (Current Voltage Method of Measurement of Winding Resistance)Hassan AbdoNo ratings yet
- Testing NotesDocument12 pagesTesting NotesJigar TakoliaNo ratings yet
- Aprilia 3-Phase Recharging System DiagnosisDocument15 pagesAprilia 3-Phase Recharging System DiagnosisManuallesNo ratings yet
- Testing HVCB 2Document6 pagesTesting HVCB 2rmatspNo ratings yet
- Potentiometers Are Used in CircuitsDocument6 pagesPotentiometers Are Used in CircuitsNorAini MohamadNo ratings yet
- Piaggio 3 Phase Charging CheckingDocument15 pagesPiaggio 3 Phase Charging Checkingminekkell1No ratings yet
- Various Routine Test of Power Transformer - (Part-2)Document7 pagesVarious Routine Test of Power Transformer - (Part-2)supermannonNo ratings yet
- Commissioning of Electrical EquipmentDocument5 pagesCommissioning of Electrical Equipmentburaqtech49No ratings yet
- Setting The Pickup Point (CT & PT)Document3 pagesSetting The Pickup Point (CT & PT)jay shahNo ratings yet
- Electromechanical Over Voltage RelayDocument6 pagesElectromechanical Over Voltage RelayJatin AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Relay Testing and Maintenance: GE Power Management Technical PublicationDocument8 pagesRelay Testing and Maintenance: GE Power Management Technical PublicationhariNo ratings yet
- Catalogo ProgrammaDocument132 pagesCatalogo Programmakammun007100% (1)
- Pickup Point (CT & PT)Document3 pagesPickup Point (CT & PT)jay shahNo ratings yet
- Pickup Point (CT & PT)Document3 pagesPickup Point (CT & PT)jay shahNo ratings yet
- Testing of Electrical EquipmentsDocument23 pagesTesting of Electrical EquipmentsPrashanth Reddy Gouni100% (5)
- Electrom Instruments IncDocument7 pagesElectrom Instruments Incgherswin requenaNo ratings yet
- Power Factor Testing of Power Distribution TransformersDocument8 pagesPower Factor Testing of Power Distribution TransformersfvicunaeNo ratings yet
- Lucas Generator and Control Box TestsDocument28 pagesLucas Generator and Control Box Testsruben_balea100% (1)
- Activity 2 Measurement DiscussionDocument5 pagesActivity 2 Measurement DiscussionJoel Kelly MabaoNo ratings yet
- Basic Battery TestingDocument5 pagesBasic Battery TestingkriziameiahnNo ratings yet
- Transformer Testing GuideDocument9 pagesTransformer Testing GuideShravan RawalNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Relay Definitions and TerminologyDocument19 pagesAn Introduction To Relay Definitions and Terminologyprashantsingh04No ratings yet
- The Principle of The Residual Current DeviceDocument6 pagesThe Principle of The Residual Current Devicestancu cosminNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of DistanceDocument18 pagesPerformance Analysis of DistanceFredrikNo ratings yet
- Method Statement Winding Resistance & TTRDocument7 pagesMethod Statement Winding Resistance & TTRsite.eng1No ratings yet
- Activity No. 1 Familiarization of Electrical Measuring Instruments and DevicesDocument7 pagesActivity No. 1 Familiarization of Electrical Measuring Instruments and DevicesVictoria U.No ratings yet
- Analog and Digital MultitesterDocument31 pagesAnalog and Digital MultitesterCedric Montiano100% (2)
- Pe Lab 8-200708Document21 pagesPe Lab 8-200708Omar JanjuaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power System ProtectionDocument8 pagesElectrical Power System ProtectionZain AbbasNo ratings yet
- 03 Directional OvercurrentDocument10 pages03 Directional OvercurrentM Kumar MarimuthuNo ratings yet
- Exp 6 Electrical CircuitsDocument15 pagesExp 6 Electrical Circuitsdegapudi prabhadityaNo ratings yet
- Boat Maintenance Companions: Electrics & Diesel Companions at SeaFrom EverandBoat Maintenance Companions: Electrics & Diesel Companions at SeaNo ratings yet
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Scribed 5Document1 pageScribed 5zayed shbanNo ratings yet
- Scribed 4Document3 pagesScribed 4zayed shbanNo ratings yet
- Scribed 1Document1 pageScribed 1zayed shbanNo ratings yet
- Scribed 2Document2 pagesScribed 2zayed shbanNo ratings yet
- Bearings and BushingsDocument11 pagesBearings and Bushingssaritha0003No ratings yet
- Mechanical Watch - WikipediaDocument11 pagesMechanical Watch - WikipediaEdson Alves dos Santos JuniorNo ratings yet
- 13 SlidingcontactbearingsDocument43 pages13 SlidingcontactbearingsMohammad AamirNo ratings yet
- Jewel BearingDocument3 pagesJewel Bearingslam12125No ratings yet
Scribed 3
Scribed 3
Uploaded by
zayed shban0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesA relay is a device that senses abnormal electrical conditions and closes its contacts. There are different types of relays including current, directional, and power relays. Maintenance testing of relays includes checking pickup values, dropout/reset values, and verifying proper contact function. Directional relays can be tested using an in-phase test to check minimum pickup without requiring a three-phase supply.
Original Description:
PROTECTION CURRENT
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA relay is a device that senses abnormal electrical conditions and closes its contacts. There are different types of relays including current, directional, and power relays. Maintenance testing of relays includes checking pickup values, dropout/reset values, and verifying proper contact function. Directional relays can be tested using an in-phase test to check minimum pickup without requiring a three-phase supply.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesScribed 3
Scribed 3
Uploaded by
zayed shbanA relay is a device that senses abnormal electrical conditions and closes its contacts. There are different types of relays including current, directional, and power relays. Maintenance testing of relays includes checking pickup values, dropout/reset values, and verifying proper contact function. Directional relays can be tested using an in-phase test to check minimum pickup without requiring a three-phase supply.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Relays
A relay is an automatic device which senses an abnormal condition of electrical circuit
and closes its contacts.
The first electrical test made on the relay should be a pickup test. Pickup is defined as
that value of current or voltage which will just close the relay contacts from the 0.5
time-dial position. Allowing for meter differences, interpretation of readings, etc., this
value should be within ±5% of previous data. Generally, one or two points on the time-
current curve are sufficient for maintenance purposes. Reset the relay to the original
time-dial setting and two points that could be checked and 3 and 5 times pickup. Of
course, other points could be used, but the important thing is to always use the same
point(s). The instantaneous unit should be checked for pickup using gradually applied
current for reasons previously discussed. Wherever possible, current should be applied
only to the instantaneous unit (to avoid over-heating the time unit).
There are different types of relays:
Current Relays
Relays can include phase overcurrent, current balance, negative sequence, zero
sequence, thermal, and ground fault.
This is the first generation oldest relaying system and they have been in use for many
years. They have earned a well-deserved reputation for accuracy, dependability, and
reliability.
Contact function – Manually close (or open) contacts and observe that they perform
their required function, i.e. trip, reclose, block, etc.
Pickup – Gradually apply current or voltage to see that pickup is within limits. Since
preventive maintenance is the guide post, gradually applied current or voltage will yield
data which can be compared with previous or future data and not be clouded by such
effects as transient overreach, etc.
Dropout or reset – Reduce the current until the relay drops out or fully resets. This test
will indicate excess friction. Should the relay be sluggish in resetting or fail to reset
completely, then the jewel bearing and pivot should be examined. A 4X eye loupe is
adequate for examining the pivot, and the jewel bearing can be examined with the aid of
a needle which will reveal any cracks in the jewel. Should dirt be the problem, the jewel
can be cleaned with an orange stick while the pivot can be wiped clean with a soft, lint
free cloth. No lubricant should be used on either the jewel or pivot.
Test should be made to check that the overcurrent unit operates only when the
directional unit contacts are closed.
Directional and Power Relays
Directional overcurrent relaying refers to relaying that can use the phase relationship of
voltage and current to determine direction to a fault.
Power Directional Relays provides protection against excess power flow in a
predetermined direction. And are used for anti-motoring protect on of AC generators.
The simplest pickup test for a directional unit is an in-phase test – i.e. current and
voltage in phase. This test will eliminate the need for a three-phase supply, phase
shifter, and phase-angle meter. However, it must be kept in mind that such a test is
usually far from the angle of maximum torque (usually 60° lag for ground relays) and
thus, small changes in components can yield large variations in in-phase pickup. As
long as this fact is recognized and the pickup value is within limits, an angle of
maximum torque check would not be necessary. Clutch pressure must always be
measured in the same manner. For example, some instruction books express clutch
settings in both grams and current/voltage levels. Portable pre-calibrated reactance-
resistance test boxes are available for many of these tests. The use of such equipment,
properly applied, will yield results which will exceed in accuracy those obtained with
conventional phase-angle meters, ammeters, voltmeters, etc. In addition to the tests
previously described for the overcurrent relay, the directional unit should be tested for
minimum pickup, angle of maximum torque, contact gap, and clutch pressure. Further, a
test should be made to check that the overcurrent unit operates only when the
directional unit contacts are closed. . Either test is valid, but to have comparative data,
the same method, either grams or electrical quantities should be employed each time
You might also like
- Eto Coc Oral Exam Prep QuestionsDocument29 pagesEto Coc Oral Exam Prep QuestionsHemraj Singh Rautela100% (4)
- WRT-100 - Winding Resistance TestDocument10 pagesWRT-100 - Winding Resistance TestVictor Jr Quijano100% (1)
- Condition Monitoring of RelaysDocument5 pagesCondition Monitoring of RelaysSaurabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Transformer Testing 8Document8 pagesTransformer Testing 8mp20ke1798No ratings yet
- Commissioning Numerical RelaysDocument24 pagesCommissioning Numerical RelaysVHMANOHARNo ratings yet
- Evaluate Relays For Automated Test StationsDocument5 pagesEvaluate Relays For Automated Test StationsKumar GauravNo ratings yet
- Scribed 4Document3 pagesScribed 4zayed shbanNo ratings yet
- Polarity / Vector Group TestDocument6 pagesPolarity / Vector Group TestHassan AbdoNo ratings yet
- Power Systems: Power Systems Undervoltage and Overvoltage Time Lag RelaysDocument4 pagesPower Systems: Power Systems Undervoltage and Overvoltage Time Lag RelaysHarkishen SinghNo ratings yet
- Testing of Power TransformersDocument7 pagesTesting of Power Transformerspctinformation100% (4)
- Transformer Winding Resistance Testing of Fundamental ImportanceDocument5 pagesTransformer Winding Resistance Testing of Fundamental Importancegeddam06108825No ratings yet
- Testing of Power TransformersDocument6 pagesTesting of Power TransformersSamsudin AhmadNo ratings yet
- Surge Test PDFDocument12 pagesSurge Test PDFPrashant PuriNo ratings yet
- Testing Electrical and Electronics: Component / Devices With MultimeterDocument17 pagesTesting Electrical and Electronics: Component / Devices With MultimeterIra CervoNo ratings yet
- Experiment Current RelayDocument6 pagesExperiment Current Relayকাওমিউজ্জামান কাব্যNo ratings yet
- Basic Electric Motor TestingDocument4 pagesBasic Electric Motor TestingHemendra JaniNo ratings yet
- General Guidelines 2 Test RelaysDocument3 pagesGeneral Guidelines 2 Test RelayssktorsiNo ratings yet
- Transformer Repairing Auto Saved)Document11 pagesTransformer Repairing Auto Saved)c0rr0deNo ratings yet
- IEEE 62 (Guide ForField Testing of Oil Filled TransforDocument1 pageIEEE 62 (Guide ForField Testing of Oil Filled TransforFaheem PP13No ratings yet
- Best Practice Manual-Transformers 44Document1 pageBest Practice Manual-Transformers 44sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Method No: 2 (Current Voltage Method of Measurement of Winding Resistance)Document6 pagesMethod No: 2 (Current Voltage Method of Measurement of Winding Resistance)Hassan AbdoNo ratings yet
- Testing NotesDocument12 pagesTesting NotesJigar TakoliaNo ratings yet
- Aprilia 3-Phase Recharging System DiagnosisDocument15 pagesAprilia 3-Phase Recharging System DiagnosisManuallesNo ratings yet
- Testing HVCB 2Document6 pagesTesting HVCB 2rmatspNo ratings yet
- Potentiometers Are Used in CircuitsDocument6 pagesPotentiometers Are Used in CircuitsNorAini MohamadNo ratings yet
- Piaggio 3 Phase Charging CheckingDocument15 pagesPiaggio 3 Phase Charging Checkingminekkell1No ratings yet
- Various Routine Test of Power Transformer - (Part-2)Document7 pagesVarious Routine Test of Power Transformer - (Part-2)supermannonNo ratings yet
- Commissioning of Electrical EquipmentDocument5 pagesCommissioning of Electrical Equipmentburaqtech49No ratings yet
- Setting The Pickup Point (CT & PT)Document3 pagesSetting The Pickup Point (CT & PT)jay shahNo ratings yet
- Electromechanical Over Voltage RelayDocument6 pagesElectromechanical Over Voltage RelayJatin AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Relay Testing and Maintenance: GE Power Management Technical PublicationDocument8 pagesRelay Testing and Maintenance: GE Power Management Technical PublicationhariNo ratings yet
- Catalogo ProgrammaDocument132 pagesCatalogo Programmakammun007100% (1)
- Pickup Point (CT & PT)Document3 pagesPickup Point (CT & PT)jay shahNo ratings yet
- Pickup Point (CT & PT)Document3 pagesPickup Point (CT & PT)jay shahNo ratings yet
- Testing of Electrical EquipmentsDocument23 pagesTesting of Electrical EquipmentsPrashanth Reddy Gouni100% (5)
- Electrom Instruments IncDocument7 pagesElectrom Instruments Incgherswin requenaNo ratings yet
- Power Factor Testing of Power Distribution TransformersDocument8 pagesPower Factor Testing of Power Distribution TransformersfvicunaeNo ratings yet
- Lucas Generator and Control Box TestsDocument28 pagesLucas Generator and Control Box Testsruben_balea100% (1)
- Activity 2 Measurement DiscussionDocument5 pagesActivity 2 Measurement DiscussionJoel Kelly MabaoNo ratings yet
- Basic Battery TestingDocument5 pagesBasic Battery TestingkriziameiahnNo ratings yet
- Transformer Testing GuideDocument9 pagesTransformer Testing GuideShravan RawalNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Relay Definitions and TerminologyDocument19 pagesAn Introduction To Relay Definitions and Terminologyprashantsingh04No ratings yet
- The Principle of The Residual Current DeviceDocument6 pagesThe Principle of The Residual Current Devicestancu cosminNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of DistanceDocument18 pagesPerformance Analysis of DistanceFredrikNo ratings yet
- Method Statement Winding Resistance & TTRDocument7 pagesMethod Statement Winding Resistance & TTRsite.eng1No ratings yet
- Activity No. 1 Familiarization of Electrical Measuring Instruments and DevicesDocument7 pagesActivity No. 1 Familiarization of Electrical Measuring Instruments and DevicesVictoria U.No ratings yet
- Analog and Digital MultitesterDocument31 pagesAnalog and Digital MultitesterCedric Montiano100% (2)
- Pe Lab 8-200708Document21 pagesPe Lab 8-200708Omar JanjuaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power System ProtectionDocument8 pagesElectrical Power System ProtectionZain AbbasNo ratings yet
- 03 Directional OvercurrentDocument10 pages03 Directional OvercurrentM Kumar MarimuthuNo ratings yet
- Exp 6 Electrical CircuitsDocument15 pagesExp 6 Electrical Circuitsdegapudi prabhadityaNo ratings yet
- Boat Maintenance Companions: Electrics & Diesel Companions at SeaFrom EverandBoat Maintenance Companions: Electrics & Diesel Companions at SeaNo ratings yet
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Scribed 5Document1 pageScribed 5zayed shbanNo ratings yet
- Scribed 4Document3 pagesScribed 4zayed shbanNo ratings yet
- Scribed 1Document1 pageScribed 1zayed shbanNo ratings yet
- Scribed 2Document2 pagesScribed 2zayed shbanNo ratings yet
- Bearings and BushingsDocument11 pagesBearings and Bushingssaritha0003No ratings yet
- Mechanical Watch - WikipediaDocument11 pagesMechanical Watch - WikipediaEdson Alves dos Santos JuniorNo ratings yet
- 13 SlidingcontactbearingsDocument43 pages13 SlidingcontactbearingsMohammad AamirNo ratings yet
- Jewel BearingDocument3 pagesJewel Bearingslam12125No ratings yet