Professional Documents
Culture Documents
STOICHIOMETRY
STOICHIOMETRY
Uploaded by
Kookiezy JeonCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- GENERAL CHEMISTRY 2 Module 1Document8 pagesGENERAL CHEMISTRY 2 Module 1Hassel AbayonNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry and Balancing ReactionsDocument12 pagesStoichiometry and Balancing Reactionsangeljin1207No ratings yet
- Moles and Chemical Reactions: StoichiometryDocument11 pagesMoles and Chemical Reactions: StoichiometryKezhia RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Moles and Chemical Reactions: StoichiometryDocument11 pagesMoles and Chemical Reactions: StoichiometryJessa Mae AguimbagNo ratings yet
- Module 4ADocument16 pagesModule 4Ashawnbatalla661No ratings yet
- 3general Chemistry 1 2nd Quarter Week 3 RUCDocument6 pages3general Chemistry 1 2nd Quarter Week 3 RUCKyleNo ratings yet
- How To Work Chemistry Problems - ExamplesDocument4 pagesHow To Work Chemistry Problems - ExamplesSteven CookeNo ratings yet
- Ideal Stoichiometric Calculations: Section 9.2Document10 pagesIdeal Stoichiometric Calculations: Section 9.2Kevin WeathersNo ratings yet
- CHEM 2 - Module 4 StoichiometryDocument11 pagesCHEM 2 - Module 4 StoichiometryMicah BlazaNo ratings yet
- ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY ReviewerDocument6 pagesANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY ReviewerJeff Nieva CardelNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem Reviewer FinalsDocument59 pagesGen Chem Reviewer FinalsAndrea ElcanoNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry 1Document23 pagesStoichiometry 1phygoNo ratings yet
- Chem Handout StoichDocument3 pagesChem Handout StoichAlexander DolinNo ratings yet
- Balancing Chemical EquationsDocument21 pagesBalancing Chemical EquationsHyacinth CaralipioNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionsDocument7 pagesChemical ReactionsShyla BantolinaoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document14 pagesLecture 7Md Al AminNo ratings yet
- StoichiometryDocument27 pagesStoichiometrymain.20002245No ratings yet
- Chemical Equation Notes - TeacherDocument18 pagesChemical Equation Notes - TeachersmedificationNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry & The Mole Concept - TeachifyMe PDFDocument5 pagesStoichiometry & The Mole Concept - TeachifyMe PDFMuhammad Tauseef100% (2)
- Grade 11 ChemistryDocument17 pagesGrade 11 ChemistryKevin George100% (1)
- General Chemistry 1: Self-Learning ModuleDocument12 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: Self-Learning ModuleMykhaela Louize GumbanNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionsDocument7 pagesChemical ReactionsShyla BantolinaoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1: Quarter 1 - Module 9: Calculations With Balanced EquationsDocument14 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: Quarter 1 - Module 9: Calculations With Balanced EquationsMark Allen Labasan100% (1)
- Grade 11 General Chemistry 1 Week 3 LASDocument17 pagesGrade 11 General Chemistry 1 Week 3 LASMaria Cristina TinioNo ratings yet
- Notes - Chapter 3 - Mole Concept Final Ver PDFDocument6 pagesNotes - Chapter 3 - Mole Concept Final Ver PDFRiza Mae Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- GENERAL CHEMISTRY 1 ReviewerDocument1 pageGENERAL CHEMISTRY 1 RevieweryvNo ratings yet
- I. Introductory Concept: SHS - Physical Science (Stoichiometry)Document8 pagesI. Introductory Concept: SHS - Physical Science (Stoichiometry)DYLAN100% (1)
- I. Introductory Concept: SHS - Physical Science (Stoichiometry)Document8 pagesI. Introductory Concept: SHS - Physical Science (Stoichiometry)DYLANNo ratings yet
- Balancing: Metron Means Measure, So StoichiometryDocument7 pagesBalancing: Metron Means Measure, So StoichiometryDora Naj100% (1)
- A Basic Introduction To StoichiometryDocument5 pagesA Basic Introduction To StoichiometrySara RaiNo ratings yet
- Molecules, Moles, and Chemical Equation: Chemistry For EngineersDocument46 pagesMolecules, Moles, and Chemical Equation: Chemistry For Engineersjoshuajoshua3913No ratings yet
- Balancing Chemical EquationsDocument5 pagesBalancing Chemical Equationsseung mooNo ratings yet
- What Is Stoichiometry?: by Prof Devender Singh Roorkee Notes and Examples ChemistryDocument8 pagesWhat Is Stoichiometry?: by Prof Devender Singh Roorkee Notes and Examples Chemistrydevender singhNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry SL and HLDocument108 pagesIB Chemistry SL and HLVed JoshiNo ratings yet
- BalancingDocument6 pagesBalancingJan Paul GalopeNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry and Balancing ReactionsDocument11 pagesStoichiometry and Balancing ReactionsEdizon De Andres JaoNo ratings yet
- 6 - Chemical Reactions and Foundation of StoichiometryDocument13 pages6 - Chemical Reactions and Foundation of StoichiometryAngelocker RenaciaNo ratings yet
- Chem12 C120Document4 pagesChem12 C120MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 StoichiometryDocument10 pagesUnit 1 StoichiometryGhenwa DimachkiNo ratings yet
- Steps in Balancing EquationDocument4 pagesSteps in Balancing EquationJanelyn GarinNo ratings yet
- General Guidelines For Balancing Simple Equations: StoichiometryDocument6 pagesGeneral Guidelines For Balancing Simple Equations: StoichiometryJonel Mark CarandangNo ratings yet
- basics of chemistry 4Document13 pagesbasics of chemistry 4chaitanya.palutlaNo ratings yet
- STEM General Chemistry1 Q1 M3Document16 pagesSTEM General Chemistry1 Q1 M3GINA BAYTANo ratings yet
- Summary of Units Chemistry Class XI.2022-23Document73 pagesSummary of Units Chemistry Class XI.2022-23shilpa07.nairNo ratings yet
- Chemical Stoichiometric EquationDocument5 pagesChemical Stoichiometric EquationNeharika PuriNo ratings yet
- Balancing Chemical EquationDocument34 pagesBalancing Chemical EquationKingNo ratings yet
- Chem Calculation, FlashcardDocument14 pagesChem Calculation, FlashcardRayyan KhalidNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem Module 3 L3 &4Document10 pagesGen Chem Module 3 L3 &4Hazel Cosep RicoNo ratings yet
- Chemical CalculationsDocument32 pagesChemical CalculationssamNo ratings yet
- GENERAL CHEMISTRY - Q1 - Mod9 - Calculations With Balanced EquationDocument14 pagesGENERAL CHEMISTRY - Q1 - Mod9 - Calculations With Balanced EquationMichelle GuinanaoNo ratings yet
- GC06 - Mass Relationships in Chemical ReactionsDocument21 pagesGC06 - Mass Relationships in Chemical ReactionsVince DulayNo ratings yet
- Cream and Green Illustrative Science Project PresentationDocument22 pagesCream and Green Illustrative Science Project Presentationralphvallespin8No ratings yet
- Amatac Report in ChemDocument58 pagesAmatac Report in ChemNica Rose GrozenNo ratings yet
- Balancing Chemical Equation2Document39 pagesBalancing Chemical Equation2KingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 2023 Part 2Document14 pagesChapter 3 2023 Part 2johnnfjayNo ratings yet
- Mole ConceptDocument24 pagesMole ConceptRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Mole ProtocolDocument1 pageMole ProtocolMarin PesicNo ratings yet
- Chem11 Module 4bDocument18 pagesChem11 Module 4bJhon Phillip CostoNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Dynamic in Engineering by Akbari-Ganji’S MethodFrom EverandNonlinear Dynamic in Engineering by Akbari-Ganji’S MethodNo ratings yet
STOICHIOMETRY
STOICHIOMETRY
Uploaded by
Kookiezy JeonOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
STOICHIOMETRY
STOICHIOMETRY
Uploaded by
Kookiezy JeonCopyright:
Available Formats
STOICHIOMETRY
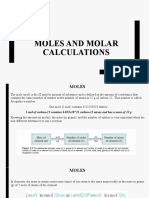
The branch of Chemistry that deals with quantities of substances in chemical reactions
is known as stoichiometry.
A balanced chemical reaction can show how much of a certain product is made, given a
certain amount of reactant, since coefficients represent number of particles.
Coefficients in a balanced equation represent the numbers of particles for each
substance in a reaction, but in a practical sense, they represent moles.
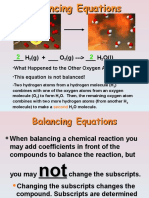
2H2 + 1O2 2H2O
Mole Ratio
In stoichiometry problems, the mole ratio (obtained from the coefficients in a balanced
equation) lets you convert from moles of a known substance to moles of an unknown
substance.
The mole ratio is obtained by first balancing the equation. Using coefficients from the
balanced equation, set up the mole ratio with the known substance on the bottom (mole
units with chemical, and the unknown substance on top (mole units and chemical)).
Mole numbers are from the coefficients.
The Mole ratio is setup in fraction form just like any other conversion factor, except now
it converts given chemicals to unknown or asked for chemicals.
For the balanced equation:
N2 + 3H2 2NH3
How many moles of hydrogen are needed to prepare 312 moles ammonia?
NH3 = ammonia
Steps in Stoichiometry
1. Balance equation
2. Write what is given (#, unit, and chemical)
3. Convert to moles of the chemical given if not already in moles
4. Calculate mole ratio and setup as a conversion factor to convert to unknown
chemical
5. Convert out of moles if problem asks for unknown chemical in different unit.
You might also like
- GENERAL CHEMISTRY 2 Module 1Document8 pagesGENERAL CHEMISTRY 2 Module 1Hassel AbayonNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry and Balancing ReactionsDocument12 pagesStoichiometry and Balancing Reactionsangeljin1207No ratings yet
- Moles and Chemical Reactions: StoichiometryDocument11 pagesMoles and Chemical Reactions: StoichiometryKezhia RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Moles and Chemical Reactions: StoichiometryDocument11 pagesMoles and Chemical Reactions: StoichiometryJessa Mae AguimbagNo ratings yet
- Module 4ADocument16 pagesModule 4Ashawnbatalla661No ratings yet
- 3general Chemistry 1 2nd Quarter Week 3 RUCDocument6 pages3general Chemistry 1 2nd Quarter Week 3 RUCKyleNo ratings yet
- How To Work Chemistry Problems - ExamplesDocument4 pagesHow To Work Chemistry Problems - ExamplesSteven CookeNo ratings yet
- Ideal Stoichiometric Calculations: Section 9.2Document10 pagesIdeal Stoichiometric Calculations: Section 9.2Kevin WeathersNo ratings yet
- CHEM 2 - Module 4 StoichiometryDocument11 pagesCHEM 2 - Module 4 StoichiometryMicah BlazaNo ratings yet
- ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY ReviewerDocument6 pagesANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY ReviewerJeff Nieva CardelNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem Reviewer FinalsDocument59 pagesGen Chem Reviewer FinalsAndrea ElcanoNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry 1Document23 pagesStoichiometry 1phygoNo ratings yet
- Chem Handout StoichDocument3 pagesChem Handout StoichAlexander DolinNo ratings yet
- Balancing Chemical EquationsDocument21 pagesBalancing Chemical EquationsHyacinth CaralipioNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionsDocument7 pagesChemical ReactionsShyla BantolinaoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document14 pagesLecture 7Md Al AminNo ratings yet
- StoichiometryDocument27 pagesStoichiometrymain.20002245No ratings yet
- Chemical Equation Notes - TeacherDocument18 pagesChemical Equation Notes - TeachersmedificationNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry & The Mole Concept - TeachifyMe PDFDocument5 pagesStoichiometry & The Mole Concept - TeachifyMe PDFMuhammad Tauseef100% (2)
- Grade 11 ChemistryDocument17 pagesGrade 11 ChemistryKevin George100% (1)
- General Chemistry 1: Self-Learning ModuleDocument12 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: Self-Learning ModuleMykhaela Louize GumbanNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionsDocument7 pagesChemical ReactionsShyla BantolinaoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1: Quarter 1 - Module 9: Calculations With Balanced EquationsDocument14 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: Quarter 1 - Module 9: Calculations With Balanced EquationsMark Allen Labasan100% (1)
- Grade 11 General Chemistry 1 Week 3 LASDocument17 pagesGrade 11 General Chemistry 1 Week 3 LASMaria Cristina TinioNo ratings yet
- Notes - Chapter 3 - Mole Concept Final Ver PDFDocument6 pagesNotes - Chapter 3 - Mole Concept Final Ver PDFRiza Mae Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- GENERAL CHEMISTRY 1 ReviewerDocument1 pageGENERAL CHEMISTRY 1 RevieweryvNo ratings yet
- I. Introductory Concept: SHS - Physical Science (Stoichiometry)Document8 pagesI. Introductory Concept: SHS - Physical Science (Stoichiometry)DYLAN100% (1)
- I. Introductory Concept: SHS - Physical Science (Stoichiometry)Document8 pagesI. Introductory Concept: SHS - Physical Science (Stoichiometry)DYLANNo ratings yet
- Balancing: Metron Means Measure, So StoichiometryDocument7 pagesBalancing: Metron Means Measure, So StoichiometryDora Naj100% (1)
- A Basic Introduction To StoichiometryDocument5 pagesA Basic Introduction To StoichiometrySara RaiNo ratings yet
- Molecules, Moles, and Chemical Equation: Chemistry For EngineersDocument46 pagesMolecules, Moles, and Chemical Equation: Chemistry For Engineersjoshuajoshua3913No ratings yet
- Balancing Chemical EquationsDocument5 pagesBalancing Chemical Equationsseung mooNo ratings yet
- What Is Stoichiometry?: by Prof Devender Singh Roorkee Notes and Examples ChemistryDocument8 pagesWhat Is Stoichiometry?: by Prof Devender Singh Roorkee Notes and Examples Chemistrydevender singhNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry SL and HLDocument108 pagesIB Chemistry SL and HLVed JoshiNo ratings yet
- BalancingDocument6 pagesBalancingJan Paul GalopeNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry and Balancing ReactionsDocument11 pagesStoichiometry and Balancing ReactionsEdizon De Andres JaoNo ratings yet
- 6 - Chemical Reactions and Foundation of StoichiometryDocument13 pages6 - Chemical Reactions and Foundation of StoichiometryAngelocker RenaciaNo ratings yet
- Chem12 C120Document4 pagesChem12 C120MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 StoichiometryDocument10 pagesUnit 1 StoichiometryGhenwa DimachkiNo ratings yet
- Steps in Balancing EquationDocument4 pagesSteps in Balancing EquationJanelyn GarinNo ratings yet
- General Guidelines For Balancing Simple Equations: StoichiometryDocument6 pagesGeneral Guidelines For Balancing Simple Equations: StoichiometryJonel Mark CarandangNo ratings yet
- basics of chemistry 4Document13 pagesbasics of chemistry 4chaitanya.palutlaNo ratings yet
- STEM General Chemistry1 Q1 M3Document16 pagesSTEM General Chemistry1 Q1 M3GINA BAYTANo ratings yet
- Summary of Units Chemistry Class XI.2022-23Document73 pagesSummary of Units Chemistry Class XI.2022-23shilpa07.nairNo ratings yet
- Chemical Stoichiometric EquationDocument5 pagesChemical Stoichiometric EquationNeharika PuriNo ratings yet
- Balancing Chemical EquationDocument34 pagesBalancing Chemical EquationKingNo ratings yet
- Chem Calculation, FlashcardDocument14 pagesChem Calculation, FlashcardRayyan KhalidNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem Module 3 L3 &4Document10 pagesGen Chem Module 3 L3 &4Hazel Cosep RicoNo ratings yet
- Chemical CalculationsDocument32 pagesChemical CalculationssamNo ratings yet
- GENERAL CHEMISTRY - Q1 - Mod9 - Calculations With Balanced EquationDocument14 pagesGENERAL CHEMISTRY - Q1 - Mod9 - Calculations With Balanced EquationMichelle GuinanaoNo ratings yet
- GC06 - Mass Relationships in Chemical ReactionsDocument21 pagesGC06 - Mass Relationships in Chemical ReactionsVince DulayNo ratings yet
- Cream and Green Illustrative Science Project PresentationDocument22 pagesCream and Green Illustrative Science Project Presentationralphvallespin8No ratings yet
- Amatac Report in ChemDocument58 pagesAmatac Report in ChemNica Rose GrozenNo ratings yet
- Balancing Chemical Equation2Document39 pagesBalancing Chemical Equation2KingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 2023 Part 2Document14 pagesChapter 3 2023 Part 2johnnfjayNo ratings yet
- Mole ConceptDocument24 pagesMole ConceptRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Mole ProtocolDocument1 pageMole ProtocolMarin PesicNo ratings yet
- Chem11 Module 4bDocument18 pagesChem11 Module 4bJhon Phillip CostoNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Dynamic in Engineering by Akbari-Ganji’S MethodFrom EverandNonlinear Dynamic in Engineering by Akbari-Ganji’S MethodNo ratings yet