Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
50 viewsFinal NCP
Final NCP
Uploaded by
BAGUIO CATSThis document provides an assessment and plan of care for a patient with severe COVID-19 and pneumonia. The patient has ineffective airway clearance due to secretions in the lungs. Short term goals include maintaining a clear airway through nursing interventions like assessing breath sounds, oxygen saturation, and teaching coughing and breathing exercises. Long term goals include the patient having normal vital signs, breath sounds, oxygen levels, and the ability to cough effectively to clear secretions after treatments.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- The Psychiatric Interview - Daniel CarlatDocument473 pagesThe Psychiatric Interview - Daniel CarlatAntonio L Yang94% (31)
- Lorma Colleges Patient Health History Related Learning ExperienceDocument2 pagesLorma Colleges Patient Health History Related Learning Experienceivy annNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For Activity IntoleranceDocument4 pagesNCP Risk For Activity IntoleranceBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- "My Breasts Are Sore and Tender But There Is No Milk Coming Out and Im Also in Pain Due To Uterine CrampingDocument3 pages"My Breasts Are Sore and Tender But There Is No Milk Coming Out and Im Also in Pain Due To Uterine CrampingBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- TONSILITIS AND ADENOIDITIS - Baldoza.E.Document9 pagesTONSILITIS AND ADENOIDITIS - Baldoza.E.Monette Abalos MendovaNo ratings yet
- How To Read A Medical ReportDocument3 pagesHow To Read A Medical ReportpinkuNo ratings yet
- Adams and Victor's Principles of Neurology, 9th EditionDocument171 pagesAdams and Victor's Principles of Neurology, 9th EditionAlvyna LaksitaNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance For PneumoniaDocument5 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance For PneumoniaKullin Rain100% (1)
- PRIORITY 2: Impaired Gas Exchange Related To Excessive or Thick Secretions Tree Secondary To PneumoniaDocument4 pagesPRIORITY 2: Impaired Gas Exchange Related To Excessive or Thick Secretions Tree Secondary To PneumoniaElay Pedroso100% (1)
- NCP Format 3 CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus NephropathyDocument4 pagesNCP Format 3 CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus NephropathySapna thakurNo ratings yet
- Problem: Viii. Planning (Nursing Cre Plan)Document10 pagesProblem: Viii. Planning (Nursing Cre Plan)Raidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- MCN NCPDocument4 pagesMCN NCPPEARL CHRISTINE CUDALNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument4 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing PatternSeika SouiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Analysis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Analysis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationElla EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Group 2 SOAPIE Case FinalDocument4 pagesGroup 2 SOAPIE Case FinalJames De VeraNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPRuth MontebonNo ratings yet
- NCP ProperDocument9 pagesNCP Properstephanie eduarteNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Proper CapcDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Proper CapcKit LaraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care Planjohn carlo aguillonNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjectivecammel ramos100% (1)
- Respi ElaborateDocument4 pagesRespi ElaborateBryant Riego IIINo ratings yet
- Name: Mr. M AGE: 62 Years Old SEX: Male CC: Persistent Cough Admitting/Working Diagnosis: PnuemoniaDocument3 pagesName: Mr. M AGE: 62 Years Old SEX: Male CC: Persistent Cough Admitting/Working Diagnosis: PnuemoniaMae Therese B. MAGNONo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Bronchitis Nursing Care PlansDocument10 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Bronchitis Nursing Care Planscy belNo ratings yet
- University of Cordilleras College of Nursing NCP: Mycobacterium TuberculosisDocument3 pagesUniversity of Cordilleras College of Nursing NCP: Mycobacterium TuberculosisLyn MhoreNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: IndependentDocument4 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: IndependentIrish Eunice FelixNo ratings yet
- Piguerra - Week 1 Activty Case Study - Ha Rle 2023to24Document5 pagesPiguerra - Week 1 Activty Case Study - Ha Rle 2023to24kc bpNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan AnemiaDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan AnemiaNat B. AntipoloNo ratings yet
- 1 Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument11 pages1 Impaired Gas ExchangeKristian Dave DivaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationTrisha SuazoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Congestive Heart Failure-Deep Vein ThrombosisDocument19 pagesNursing Care Plan: Congestive Heart Failure-Deep Vein ThrombosisRiza Angela BarazanNo ratings yet
- Loberiano NCPDocument2 pagesLoberiano NCPJoshua LoberianoNo ratings yet
- Materi Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageMateri Nursing Care PlanSiti nur Kholifatus samsiyahNo ratings yet
- Defining CharacteristicsDocument2 pagesDefining CharacteristicsAngel MayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Explanation of The Problem Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Explanation of The Problem Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationGuile RilleraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Tracheobronchial Secretions CAPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Tracheobronchial Secretions CAPLP Benoza100% (2)
- Bronchial Asthma (Parinas Rhoanne)Document10 pagesBronchial Asthma (Parinas Rhoanne)Carlojay IniegoNo ratings yet
- NCP Format 3 CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus NephropathyDocument3 pagesNCP Format 3 CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus NephropathyAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Explanation of The Problem Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Explanation of The Problem Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationGuile RilleraNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (Bronchitis) Nursing Care PlansDocument10 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (Bronchitis) Nursing Care PlansjamieboyRN100% (3)
- Nueva Ecija University of Science and Technology: Case 7Document7 pagesNueva Ecija University of Science and Technology: Case 7jomariNo ratings yet
- Assessment Health Pattern Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome Intervention (Edit) Evaluation Rema RKS General Objective: Independent InterventionDocument3 pagesAssessment Health Pattern Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome Intervention (Edit) Evaluation Rema RKS General Objective: Independent InterventiontflorenzNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPAmal MUTIANo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas Exchange PneumoniaDocument2 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange PneumoniaShanice BedecirNo ratings yet
- NCP (Ineffective Airway Clearance, URTI)Document6 pagesNCP (Ineffective Airway Clearance, URTI)Jenny AjocNo ratings yet
- Student NurseDocument2 pagesStudent NurseTAYABAN, KENNETH JAKE, Q.No ratings yet
- NCP PesebreDocument2 pagesNCP PesebreFrancoise Nicolette PesebreNo ratings yet
- Data NSG Diagnosis Goals & Outcomes NSG Interventions Rationale Evaluation O: StoDocument3 pagesData NSG Diagnosis Goals & Outcomes NSG Interventions Rationale Evaluation O: StoClaudineNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: Independent: IndependentDocument4 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: Independent: IndependentAlyssa Marie SantosNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance - PTBDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance - PTBIrish Eunice FelixNo ratings yet
- Goal:: Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Cumulation of SecretionDocument4 pagesGoal:: Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Cumulation of SecretionWyen CabatbatNo ratings yet
- Ncp3 CunananDocument2 pagesNcp3 CunananAbbyNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternPaolo Anthony GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Clustered Data Nursing Diagnosis (Diagnostic Label) PriorityDocument4 pagesClustered Data Nursing Diagnosis (Diagnostic Label) PriorityRoger ViloNo ratings yet
- Problem 3Document2 pagesProblem 3Janah PagayNo ratings yet
- Name: L.J.A AGE: 20 Years Old SEX: Male CC: Cough and DOB Admitting/Working Diagnosis: AsthmaDocument2 pagesName: L.J.A AGE: 20 Years Old SEX: Male CC: Cough and DOB Admitting/Working Diagnosis: AsthmaMae Therese B. MAGNONo ratings yet
- Group 1 Nursing Diagnosis FinalDocument59 pagesGroup 1 Nursing Diagnosis FinalChristian Angelo LeonorNo ratings yet
- NCP Difficulties in BreathingDocument4 pagesNCP Difficulties in BreathingKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- CopdDocument6 pagesCopdapi-3717941100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Client: N. D. Age: 39 Gender: Male Medical Diagnosis: Community Acquired Pneumonia, Moderate Risk, PTBDocument24 pagesNursing Care Plan Client: N. D. Age: 39 Gender: Male Medical Diagnosis: Community Acquired Pneumonia, Moderate Risk, PTBGertrude Araneta JavierNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective AirwayDocument1 pageNCP Ineffective AirwayRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- New Group A - NURSING CARE PLANDocument10 pagesNew Group A - NURSING CARE PLANVelmar De BelenNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute BrochitisDocument5 pagesNCP Acute BrochitisFrancine kimberlyNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument9 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationYzel Vasquez AdavanNo ratings yet
- Snoring, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandSnoring, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Journal 1Document7 pagesJournal 1BAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Journal 2Document4 pagesJournal 2BAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- June-Work at Home Arrangements - FormDocument2 pagesJune-Work at Home Arrangements - FormBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Setup of A Dedicated Coronavirus Intensive Care Unit: Logistical AspectsDocument3 pagesSetup of A Dedicated Coronavirus Intensive Care Unit: Logistical AspectsBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Goh2020 Article PreparingYourIntensiveCareUnitDocument19 pagesGoh2020 Article PreparingYourIntensiveCareUnitBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Covid 19 ProgramDocument12 pagesCovid 19 ProgramBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Declaration Form - Work From Home Attachment 2Document1 pageDeclaration Form - Work From Home Attachment 2BAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Minutes Meeting 4 21 2021Document5 pagesMinutes Meeting 4 21 2021BAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument1 pageNew Microsoft Word DocumentBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- All Is WellDocument1 pageAll Is WellBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- NURSING SERVICE WORK FROM HOME ACTIVITIES AND EXPECTED OUTPUTS - Implementing Guidelines - FinalDocument4 pagesNURSING SERVICE WORK FROM HOME ACTIVITIES AND EXPECTED OUTPUTS - Implementing Guidelines - FinalBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Work at Home Arrangements - FormDocument2 pagesWork at Home Arrangements - FormBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- AMDDDocument2 pagesAMDDBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Tarp 1Document1 pageTarp 1BAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Request To OpdDocument1 pageRequest To OpdBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- TraceDocument3 pagesTraceBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- BioterrorismDocument8 pagesBioterrorismBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Weekly Work Commitment and Accomplishment Report: Name of Staff: Position: Area of AssignmentDocument2 pagesWeekly Work Commitment and Accomplishment Report: Name of Staff: Position: Area of AssignmentBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Baguio General Hospital and Medical Center: Republic of The Philippines Department of HealthDocument2 pagesBaguio General Hospital and Medical Center: Republic of The Philippines Department of HealthBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Weekly Work Commitment and Accomplishment Report: Nursing Service OfficeDocument2 pagesWeekly Work Commitment and Accomplishment Report: Nursing Service OfficeBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Chart 1 FsdfgsgsdgsgsDocument1 pageChart 1 FsdfgsgsdgsgsBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Organizational Chart Tertiary LabDocument1 pageOrganizational Chart Tertiary LabBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Chart 1Document1 pageChart 1BAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- 10th BPS - JOINT NOTE 2015 PDFDocument49 pages10th BPS - JOINT NOTE 2015 PDFAnjaiah MandeNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal System Review QuestionsDocument10 pagesGastrointestinal System Review QuestionsSiena PlacinoNo ratings yet
- Suz 183Document29 pagesSuz 183Benny Chris TantoNo ratings yet
- 2-Preschool Parent QuestionnaireDocument3 pages2-Preschool Parent QuestionnaireION677No ratings yet
- Types of PhobiaDocument24 pagesTypes of PhobiaAman KalraNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Aspen Healthcare BrochureDocument8 pagesA Guide To Aspen Healthcare BrochureAntonio LoscialeNo ratings yet
- B SRAVANI-Female16 Years-2090Document1 pageB SRAVANI-Female16 Years-2090vijaykumarNo ratings yet
- Clinical Teaching ON Geriatric AssessmentDocument9 pagesClinical Teaching ON Geriatric AssessmentANITTA SNo ratings yet
- VheeeeDocument50 pagesVheeeeKathlene GamitNo ratings yet
- Aisyah HPTDocument10 pagesAisyah HPTBesari Md DaudNo ratings yet
- CEA Pilgastrim Vs FilgastrimDocument13 pagesCEA Pilgastrim Vs FilgastrimMaya Aulia MulakhaillaNo ratings yet
- Mental Retardation 1Document4 pagesMental Retardation 1Aizah Lazo LuzonNo ratings yet
- Star Fho One Page Feb 2020Document2 pagesStar Fho One Page Feb 2020suryaNo ratings yet
- Systemic VPT-Lecture NotesDocument34 pagesSystemic VPT-Lecture NotesshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 - Blood VesselsDocument40 pagesChapter 19 - Blood VesselsZuleyha ZuleyhaNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis C Education Class - 2009Document64 pagesHepatitis C Education Class - 2009BENNo ratings yet
- Panduan Perkhidmatan Makmal JPMD HCTM Versi 2020 2 CompressedDocument151 pagesPanduan Perkhidmatan Makmal JPMD HCTM Versi 2020 2 Compressed23-Chong Kar KinNo ratings yet
- Pathology: Fajar L. Gultom Departemen Patologi Anatomik FK UKI April 2019Document39 pagesPathology: Fajar L. Gultom Departemen Patologi Anatomik FK UKI April 2019ErniNo ratings yet
- A Manual On Clinical Surgery by Das S: 8.lee Mcgregor'S Synopsis of Surgical Anatomy 500Document1 pageA Manual On Clinical Surgery by Das S: 8.lee Mcgregor'S Synopsis of Surgical Anatomy 500prabhakarNo ratings yet
- Nonconvulsive Status Epilepticus: Validating The Salzburg Criteria Against An Expert EEG ExaminerDocument5 pagesNonconvulsive Status Epilepticus: Validating The Salzburg Criteria Against An Expert EEG ExaminerNathaly LapoNo ratings yet
- List of Medical and Nursing Abbreviations, Acronyms, Terms 1 - NurseslabsDocument25 pagesList of Medical and Nursing Abbreviations, Acronyms, Terms 1 - NurseslabsbeingfiredNo ratings yet
- Trindade 2018Document10 pagesTrindade 2018Tales FernandoNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Guidance School Case Contact and Outbreak Management 2021-08-11 FINAL AODA enDocument27 pagesCOVID-19 Guidance School Case Contact and Outbreak Management 2021-08-11 FINAL AODA enCityNewsTorontoNo ratings yet
- Buku Kedokteran Keluarga 1Document5 pagesBuku Kedokteran Keluarga 1Intan Alwaystry TobehappyNo ratings yet
- Intussusception: Afua A.J. Hesse Francis A. Abantanga Kokila LakhooDocument8 pagesIntussusception: Afua A.J. Hesse Francis A. Abantanga Kokila LakhooFATIN NAJIHAHNo ratings yet
- Eosinophilic Ulcer of The Oral MucosaDocument4 pagesEosinophilic Ulcer of The Oral MucosaKhairunnisa Indah NurfaizahNo ratings yet
Final NCP
Final NCP
Uploaded by
BAGUIO CATS0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
50 views13 pagesThis document provides an assessment and plan of care for a patient with severe COVID-19 and pneumonia. The patient has ineffective airway clearance due to secretions in the lungs. Short term goals include maintaining a clear airway through nursing interventions like assessing breath sounds, oxygen saturation, and teaching coughing and breathing exercises. Long term goals include the patient having normal vital signs, breath sounds, oxygen levels, and the ability to cough effectively to clear secretions after treatments.
Original Description:
Original Title
FINAL NCP
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an assessment and plan of care for a patient with severe COVID-19 and pneumonia. The patient has ineffective airway clearance due to secretions in the lungs. Short term goals include maintaining a clear airway through nursing interventions like assessing breath sounds, oxygen saturation, and teaching coughing and breathing exercises. Long term goals include the patient having normal vital signs, breath sounds, oxygen levels, and the ability to cough effectively to clear secretions after treatments.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
50 views13 pagesFinal NCP
Final NCP
Uploaded by
BAGUIO CATSThis document provides an assessment and plan of care for a patient with severe COVID-19 and pneumonia. The patient has ineffective airway clearance due to secretions in the lungs. Short term goals include maintaining a clear airway through nursing interventions like assessing breath sounds, oxygen saturation, and teaching coughing and breathing exercises. Long term goals include the patient having normal vital signs, breath sounds, oxygen levels, and the ability to cough effectively to clear secretions after treatments.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 13
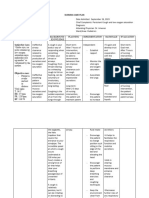
DIAGNOSIS:
SEVERE COVID 19 POSITIVE
Ineffective Airway Clearance Related to Presence of secretions in the tracheobronchial tree secondary to pneumonia
ASSESSMENT EXPLANATION OF OBJECTIVES INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE CRITERIA ACTUAL
THE PROBLEM EVALUATION
Subjective: Ineffective Airway Short term goal: >Assess airway for >Maintaining patent Short term goal: Partially met
> Mayat met Clearance: Inability >After 12 hour of patency. airway is always the Fully met if after because patient Z
bassit, Ngem, to clear secretions nursing Auscultate lungs for first priority, 12 hours of still has crackles
marigatan nak pay or obstructions from interventions the presence of normal especially in cases nursing upon auscultation on
the lung fields but
lang aganges. the respiratory tract client will be able or adventitious like trauma, acute interventions the has been lessened
to maintain a clear to maintain airway breath sounds, as in neurological client will have compared to the first
Objective airway. >Breathing patency by having the following: decompensation, or clear breath day
> Inhalation via comes naturally and clear breath >Decreased or cardiac arrest. sounds Fully met patient Z
high flow venturi effortlessly to sounds absent breath Abnormal breath Partially meet if identified 3 danger
mask attached to everyone. But there After 5 minutes of sounds sounds can be there are still signs
mechanical are some who are nursing >Wheezing heard as fluid and adventitious Fully met patient Z
ventilator incapable of interventions >Coarse Crackles mucus accumulate. breath sounds but identified 3
keeping their patient would >Assess This may indicate has been alterations in lifestyle
>RR of 29, shallow and daily activities
>tachypnea airways clear and identify the respirations. airway is lessened Partially met, patient
>SPo2: 87% their lungs healthy. importance of DBE Note quality, rate obstructed. Not met if the Z’s
>Has episodes of Maintaining a and coughing pattern, depth, >These may adventitious oxygen saturation is
productive patent airway has exercises and flaring of indicate presence of breath sounds are now lingering at 88-
Cough and always been vital to perform DBE and nostrils, dyspnea on a mucous plug or the same or 89%
Dyspnea life. When problem atleast 2-3 exertion, evidence other major worsened Partially met patient
concerning the coughing of obstruction. STO: Z still has abnormal
airway happens, exercises splinting, use of >This may indicate Criteria breath sounds
coughing takes >After 5 minutes of accessory muscles, partial airway Fully met if after 5 (crackles), and
irregular respiration
place, which is the nursing and obstruction or minutes the but is able to cough
main mechanism interventions the position for resistance. patients identifies effectively and
for clearing it. patient will breathing. >This may indicate 3 danger signs expectorate
However, coughing verbalize presence of Partially met if the secretions after
may not always be understanding of 3 >Note for changes secretions along patients identifies treatments and deep
easy to everyone danger signs of in HR, BP, and larger airways. 2-3 danger signs breaths
especially to those pneumonia temperature. >A change in the Not met if the Partially met
patients with >After 5 minutes of >Note cough for usual respiration patient did not because the patient
incisions, trauma, health teaching the may mean identify anything still has abnormal
efficacy and Spo2, and RR but is
respiratory muscle patient will identify productivity respiratory STO 2 able to expectorate
fatigue, or 3 necessary >Note presence of compromise. An Fully met if after 5 secretions
neuromuscular alterations in sputum; evaluate its increase in minutes of health
weakness. lifestyle and daily quality, color, respiratory rate and teaching the
activities to amount, rhythm may be a patient will
chronic cough or manage odor, and compensatory perform DBE and
sputum production. pneumonia consistency. response to airway identify 3
>There is a wide >after 2days of >Use pulse oximetry obstruction. coughing
range of airway nursing to monitor oxygen exercises
clearance interventions the saturation; assess >Increased work of Partially met if the
interventions that patient will have arterial blood gases breathing can lead patient will
nurses can choose normal ranges in (ABGs) to tachycardia and perform DBE and
from when they are her oxygen hypertension. identify 1-2
teaching the saturation (93% >Teach the patient Retained secretions coughing
patients and family and above) the proper ways of or atelectasis may exercises
members the coughing and be a sign of an Not met if the
strategies of LTO: breathing. (e.g., take existing infection or patient does not
secretion removal. >After 3 days of a deep breath, hold inflammatory do DBE and not
In general, these nursing for 2 seconds, and process manifested identify any
interventions are interventions cough two or three by a fever or coughing exercise
done to maintain a Patient will times in increased STO 3
patent airway, maintain clear, succession). temperature Fully met if after 5
improve comfort open airways as >Educate the >Coughing is a minutes
and ease of evidence by patient in the mechanism for The patient
breathing, improve normal breath following: clearing secretions. identifies 3
pulmonary sounds, normal Optimal positioning An ineffective alterations in
ventilation and rate and depth of (sitting position) cough compromises lifestlyle and daily
oxygenation, and to respirations, and Use of pillow or airway clearance activities
prevent risks ability to effectively hand splints when and prevents Partially met if the
associated with cough up coughing mucus from being patient identies 1-
oxygenation secretions after Use of abdominal expelled. 2 alterations
problems. treatments and muscles for more Respiratory muscle Not met if the
>Pneumonia is an deep breaths. forceful cough fatigue, severe patient does not
infection in one or >After 3 day of Use of quad and bronchospasm, or identify anything
both lungs. It can nursing huff techniques thick and tenacious STO 4
be caused by intervention ,the Use of incentive secretions are Fully met if After 2
bacteria, viruses, or client will be able spirometry possible causes of days of nursing
fungi. Bacterial to expectorate Importance of ineffective cough. intervention the
pneumonia is the retained secretions ambulation and >Unusual patient will have
most common type and maintain frequent position appearance of normal range in
in adults. normal breathing changes secretions may be a Oxygen saturation
>Pneumonia measured by >Position the patient result of infection, (93% and above)
causes SPo2, RR, depth upright if tolerated. bronchitis, chronic Partially met if the
inflammation in the and rhythm Regularly check the smoking, or other patients oxygen
air sacs in your patient’s position to condition. A saturation
lungs, which are prevent sliding down discolored sputum increases to 90%
called alveoli. The in bed. remove most is a sign of to 92% or
alveoli fill with fluid secretions is infection; an odor increases from
or pus, making it coughing. So it is may be present. any range higher
difficult to breathe. necessary to assist Dehydration may be than former SPo2
>Normally the lungs the patient during present if patient Not met if the
are free from this activity. Deep has labored patients SPo2
secretions. breathing, on the breathing with thick, decreased or
Pneumonia bacteria other hand, tenacious remained the
are invading the promotes secretions that same
lung oxygenation before increase airway LTO:
parenchymathus, controlled coughing. resistance. Criteria:
producing >The proper sitting >Pulse oximetry is Fully met if after 3
inflammatory position and used to detect days of nursing
process. And these splinting of the changes in interventions
responses leading abdomen promote oxygenation. Patient will
to filling of the effective coughing Oxygen saturation maintain clear,
alveolar sacs with by increasing should be open airways as
exudates leading to abdominal pressure maintained at 90% evidence by
consolidation. The and upward or greater. normal breath
airway is narrowed diaphragmatic Alteration in ABGS sounds, normal
thus wheezes is movement. may result in rate and depth of
being heard. DOB Controlled coughing increased respirations, and
in some cases methods help pulmonary ability to
mobilize secretions secretions and effectively cough
from smaller airways respiratory fatigue. up secretions
to larger airways >The most after treatments
because the convenient way to and deep
coughing is done at remove most breaths.
varying times. secretions is Partially met if
Ambulation coughing. So it is she has normal
promotes lung necessary to assist breath sounds,
expansion, the patient during rate and depth of
mobilizes this activity. Deep respirations but is
secretions, and breathing, on the not able to
lessens atelectasis. other hand, effectively cough
>Upright position promotes up secretions
limits abdominal oxygenation before after treatments
contents from controlled coughing. and deep breath
pushing upward and >The proper sitting Not met if the
inhibiting lung position and patient does not
expansion. This splinting of the improve at all
position promotes abdomen promote LTO:
better lung effective coughing Fully met if after 3
expansion and by increasing days of nursing
improved air abdominal pressure interventions the
exchange. and upward patient will be
diaphragmatic able to
movement. expectorate
Controlled coughing retained
methods help secretions and
mobilize secretions maintain normal
from smaller breathing
airways to larger measured by
airways because SPo2, RR, depth
the coughing is and rhythm
done at varying Partially met if the
times. Ambulation patient is able to
promotes lung expectorate the
expansion, phlegm but
mobilizes breathing
secretions, and Not met if the
lessens atelectasis. patient does not
>Upright position improve at any
limits abdominal factor all till has
contents from abnormal
pushing upward
and inhibiting lung
expansion. This
position promotes
better lung
expansion and
improved air
exchange.
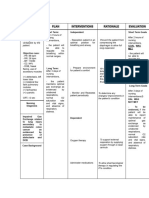
Impaired gas exchange related to ventilation perfusion imbalance.
ASSESSMENT EXPLANATION OBJECTIVES INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE CRITERIA ACTUAL
OF THE EVALUATION
PROBLEM
Subjective- Impaired gas After 12 hours of Independent: After 12 hours of Goal – met when
“marigatan nak exchange r/t nursing nursing intervention patient was able
makaanges” ventilation intervention the 1. Elevated head of 1. To maintain the patient will be to demonstrate
As verbalized by perfusion patient will be able bed/ position client airway able to: improved
the patient imbalance to: appropriately, ventilation and
provide airway 1.Patient maintains adequate
1.Demonstrate adjuncts and optimal gas oxygenation of
improved suction as exchange as tissues by HBGs
ventilation and indicated. evidenced by usual within clients
adequate mental status, normal limits
Objective- Patient oxygenation of 2.Encouraged unlabored
is restless. Rate, tissues by HBGs frequent deep respiration at 12-20
2. Promotes
rhythm and depth within clients breathing/ coughing per minute, oximetry
optimal chest
of breathing is normal limits exercises. results within normal
expansion and
abnormal. Nasal range, blood gases
drainage of
flaring was noted. 2.Participate in within normal range,
secretions.
Inhalation via high treatment and baseline Heart
flow venturi mask regimen(e.g, 3. auscultated Rate for patient.
attached to breathing breath sounds
mechanical exercises, noting crakles, 2.Patient participates
effective coughing, 3. Reveals in procedures to
ventilator wheezes presence of
use of oxygen) optimize
within level of pulmonary oxygenation and in
V/S: congestion/
BP: 140/100 ability/situation. management
collection of regimen within level
mmHg secretion,
T: 36.6 ˚C 3.Verbalize of
indicating need for capability/condition.
P: 160 bpm understanding of
Collaborative: further intervention.
R: 32 cpm causative factors
SpO2- 89% and appropriate
intervention 1. Assisted with
procedures as 1. to improve
individually respiratory function/
indicated ( e.g., oxygen-carrying
transfusion, capacity
phlebotomy,
bronchoscopy
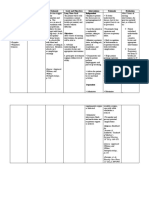
Hyperthermia related to the infectious process.
ASSESSMENT EXPLANATION OBJECTIVES INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE CRITERIA ACTUAL
OF THE EVALUATION
PROBLEM
Subjective: Hyperthermia After 12 hours of INDEPENDENT: After 12 hours of Goal – met when
“Napudot pay lang related to the comprehensive Provide tepid Enhances heat comprehensive patient was able
bagi na”, as infectious process nursing sponge bath. loss by nursing to demonstrate
verbalized by the or cerebral edema intervention, the evaporation & intervention, the improved
significant other patient Assess fluid loss conduction. patient will: ventilation and
temperature will & facilitate oral Increases Maintain adequate
Objective: lower down to intake. metabolic rate & normal oxygenation of
Skin warm to Scientific Basis: normal levels: T: Promote bed diaphoresis. temperature of tissues by HBGs
touch with a Pyrogens cause a 36.5°C – 37.5°C rest. Reduces body 37.5°C within clients
temperature of rise in body heat production. Be free of normal limits
38.3-39.1°C temperature, it Provide cool Dissipates heat dehydration
↑RR: 32cpm also acts as an circulating air by convection. Maintain vital
↑HR: 102bpm antigen triggering using a fan. Increases signs at
Weakness immune system Assist patient in comfort. normal levels
observed responses. The changing into dry Be alert and
Dry mucous hypothalamus clothing. Prevents herpetic responsive
membranes reacts to raise the Provide oral lesions of the Be
Flushed Skin set point and the hygiene. mouth. comfortable in
body respond by Notes progress & bed.
producing heat. Monitor vital changes of
signs. condition.
Reference:
Fundamentals of DEPENDENT: Prevents
Nursing Maintain IV fluids dehydration.
-Harry & Perry as ordered by
physician. Reduces fever.
Administer anti-
pyretic as Treats underlying
ordered. cause.
Administer
antibiotic as
ordered.
Indicates
COLLABORATIVE: presence of
Monitor infection &
hematologic test dehydration.
& other pertinent
lab records. Ensures continuous
Discuss condition of intervention.
the patient with other
members of the
health care team.
Imbalanced nutrition less than body requirements related to loss of appetite as evidenced by partial loss of taste.
ASSESSMENT EXPLANATION OF OBJECTIVES INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE CRITERIA ACTUAL
THE PROBLEM EVALUATION
Independent:
Subjective: Imbalanced nutrition After 12 hours of After 12 hours of Goal partially met
“Awan pinangraman less than body nursing intervention 1.identify if the client at -to assess causative/ nursing intervention
ko pay lang.” requirements related the patient will be risk for malnutrition Contributing factors the patient will be The client was able
Verbalized by the to loss of appetite as able to: 2.Encourage the client -to evaluate degree of able to: to eat 50% of meal
patient. evidenced by parital to eat and discuss the deficit. served and
loss of taste. Patient presents importance of well Partially met if weakness is lessen.
understanding of balanced nutrition. patient presents
significance of 3.evaluate total daily understanding of
-to establish a
Definition: nutrition to healing food intake significance of
Objective: nutritional plan that
Intake of nutrients process and general nutrition to healing
Weight: 49.5kgs meets individual
insufficient to meet health. process and general
Body weakness needs.
metabolic needs. health.
Consumed 10% of
the meal served. Patient takes
Dependent
Source: adequate amount of Partially met if
1. Give
Nurse’s Pocket Guide calories or nutrients patient takes
omeprazole 40 mg.
-An antisecretory adequate amount of
IVTTonce a day
compound that is a calories or nutrients.
Author: Marilynn E.
gastric acid pump
Doenges et al. Collaborative inhibitor. Suppresses Fully met if patient
Gastric acid secretion. displays nutritional
ingestion sufficient
2. Diet as -to sustain nutritional to meet metabolic
tolerated avoid dark demands. needs as
colored foods. manifested by
stable weight,
3. Assisted on food - to ensure the food is positive nitrogen
distribution and health given to the said balance, tissue
teaching patient and to discuss regeneration and
the benefits of exhibits improved
consuming the right energy level.
amount of food for
faster recovery.
You might also like
- The Psychiatric Interview - Daniel CarlatDocument473 pagesThe Psychiatric Interview - Daniel CarlatAntonio L Yang94% (31)
- Lorma Colleges Patient Health History Related Learning ExperienceDocument2 pagesLorma Colleges Patient Health History Related Learning Experienceivy annNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For Activity IntoleranceDocument4 pagesNCP Risk For Activity IntoleranceBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- "My Breasts Are Sore and Tender But There Is No Milk Coming Out and Im Also in Pain Due To Uterine CrampingDocument3 pages"My Breasts Are Sore and Tender But There Is No Milk Coming Out and Im Also in Pain Due To Uterine CrampingBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- TONSILITIS AND ADENOIDITIS - Baldoza.E.Document9 pagesTONSILITIS AND ADENOIDITIS - Baldoza.E.Monette Abalos MendovaNo ratings yet
- How To Read A Medical ReportDocument3 pagesHow To Read A Medical ReportpinkuNo ratings yet
- Adams and Victor's Principles of Neurology, 9th EditionDocument171 pagesAdams and Victor's Principles of Neurology, 9th EditionAlvyna LaksitaNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance For PneumoniaDocument5 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance For PneumoniaKullin Rain100% (1)
- PRIORITY 2: Impaired Gas Exchange Related To Excessive or Thick Secretions Tree Secondary To PneumoniaDocument4 pagesPRIORITY 2: Impaired Gas Exchange Related To Excessive or Thick Secretions Tree Secondary To PneumoniaElay Pedroso100% (1)
- NCP Format 3 CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus NephropathyDocument4 pagesNCP Format 3 CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus NephropathySapna thakurNo ratings yet
- Problem: Viii. Planning (Nursing Cre Plan)Document10 pagesProblem: Viii. Planning (Nursing Cre Plan)Raidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- MCN NCPDocument4 pagesMCN NCPPEARL CHRISTINE CUDALNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument4 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing PatternSeika SouiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Analysis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Analysis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationElla EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Group 2 SOAPIE Case FinalDocument4 pagesGroup 2 SOAPIE Case FinalJames De VeraNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPRuth MontebonNo ratings yet
- NCP ProperDocument9 pagesNCP Properstephanie eduarteNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Proper CapcDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Proper CapcKit LaraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care Planjohn carlo aguillonNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjectivecammel ramos100% (1)
- Respi ElaborateDocument4 pagesRespi ElaborateBryant Riego IIINo ratings yet
- Name: Mr. M AGE: 62 Years Old SEX: Male CC: Persistent Cough Admitting/Working Diagnosis: PnuemoniaDocument3 pagesName: Mr. M AGE: 62 Years Old SEX: Male CC: Persistent Cough Admitting/Working Diagnosis: PnuemoniaMae Therese B. MAGNONo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Bronchitis Nursing Care PlansDocument10 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Bronchitis Nursing Care Planscy belNo ratings yet
- University of Cordilleras College of Nursing NCP: Mycobacterium TuberculosisDocument3 pagesUniversity of Cordilleras College of Nursing NCP: Mycobacterium TuberculosisLyn MhoreNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: IndependentDocument4 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: IndependentIrish Eunice FelixNo ratings yet
- Piguerra - Week 1 Activty Case Study - Ha Rle 2023to24Document5 pagesPiguerra - Week 1 Activty Case Study - Ha Rle 2023to24kc bpNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan AnemiaDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan AnemiaNat B. AntipoloNo ratings yet
- 1 Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument11 pages1 Impaired Gas ExchangeKristian Dave DivaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationTrisha SuazoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Congestive Heart Failure-Deep Vein ThrombosisDocument19 pagesNursing Care Plan: Congestive Heart Failure-Deep Vein ThrombosisRiza Angela BarazanNo ratings yet
- Loberiano NCPDocument2 pagesLoberiano NCPJoshua LoberianoNo ratings yet
- Materi Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageMateri Nursing Care PlanSiti nur Kholifatus samsiyahNo ratings yet
- Defining CharacteristicsDocument2 pagesDefining CharacteristicsAngel MayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Explanation of The Problem Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Explanation of The Problem Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationGuile RilleraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Tracheobronchial Secretions CAPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Tracheobronchial Secretions CAPLP Benoza100% (2)
- Bronchial Asthma (Parinas Rhoanne)Document10 pagesBronchial Asthma (Parinas Rhoanne)Carlojay IniegoNo ratings yet
- NCP Format 3 CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus NephropathyDocument3 pagesNCP Format 3 CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus NephropathyAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Explanation of The Problem Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Explanation of The Problem Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationGuile RilleraNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (Bronchitis) Nursing Care PlansDocument10 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (Bronchitis) Nursing Care PlansjamieboyRN100% (3)
- Nueva Ecija University of Science and Technology: Case 7Document7 pagesNueva Ecija University of Science and Technology: Case 7jomariNo ratings yet
- Assessment Health Pattern Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome Intervention (Edit) Evaluation Rema RKS General Objective: Independent InterventionDocument3 pagesAssessment Health Pattern Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome Intervention (Edit) Evaluation Rema RKS General Objective: Independent InterventiontflorenzNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPAmal MUTIANo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas Exchange PneumoniaDocument2 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange PneumoniaShanice BedecirNo ratings yet
- NCP (Ineffective Airway Clearance, URTI)Document6 pagesNCP (Ineffective Airway Clearance, URTI)Jenny AjocNo ratings yet
- Student NurseDocument2 pagesStudent NurseTAYABAN, KENNETH JAKE, Q.No ratings yet
- NCP PesebreDocument2 pagesNCP PesebreFrancoise Nicolette PesebreNo ratings yet
- Data NSG Diagnosis Goals & Outcomes NSG Interventions Rationale Evaluation O: StoDocument3 pagesData NSG Diagnosis Goals & Outcomes NSG Interventions Rationale Evaluation O: StoClaudineNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: Independent: IndependentDocument4 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: Independent: IndependentAlyssa Marie SantosNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance - PTBDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance - PTBIrish Eunice FelixNo ratings yet
- Goal:: Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Cumulation of SecretionDocument4 pagesGoal:: Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Cumulation of SecretionWyen CabatbatNo ratings yet
- Ncp3 CunananDocument2 pagesNcp3 CunananAbbyNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternPaolo Anthony GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Clustered Data Nursing Diagnosis (Diagnostic Label) PriorityDocument4 pagesClustered Data Nursing Diagnosis (Diagnostic Label) PriorityRoger ViloNo ratings yet
- Problem 3Document2 pagesProblem 3Janah PagayNo ratings yet
- Name: L.J.A AGE: 20 Years Old SEX: Male CC: Cough and DOB Admitting/Working Diagnosis: AsthmaDocument2 pagesName: L.J.A AGE: 20 Years Old SEX: Male CC: Cough and DOB Admitting/Working Diagnosis: AsthmaMae Therese B. MAGNONo ratings yet
- Group 1 Nursing Diagnosis FinalDocument59 pagesGroup 1 Nursing Diagnosis FinalChristian Angelo LeonorNo ratings yet
- NCP Difficulties in BreathingDocument4 pagesNCP Difficulties in BreathingKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- CopdDocument6 pagesCopdapi-3717941100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Client: N. D. Age: 39 Gender: Male Medical Diagnosis: Community Acquired Pneumonia, Moderate Risk, PTBDocument24 pagesNursing Care Plan Client: N. D. Age: 39 Gender: Male Medical Diagnosis: Community Acquired Pneumonia, Moderate Risk, PTBGertrude Araneta JavierNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective AirwayDocument1 pageNCP Ineffective AirwayRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- New Group A - NURSING CARE PLANDocument10 pagesNew Group A - NURSING CARE PLANVelmar De BelenNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute BrochitisDocument5 pagesNCP Acute BrochitisFrancine kimberlyNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument9 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationYzel Vasquez AdavanNo ratings yet
- Snoring, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandSnoring, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Journal 1Document7 pagesJournal 1BAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Journal 2Document4 pagesJournal 2BAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- June-Work at Home Arrangements - FormDocument2 pagesJune-Work at Home Arrangements - FormBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Setup of A Dedicated Coronavirus Intensive Care Unit: Logistical AspectsDocument3 pagesSetup of A Dedicated Coronavirus Intensive Care Unit: Logistical AspectsBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Goh2020 Article PreparingYourIntensiveCareUnitDocument19 pagesGoh2020 Article PreparingYourIntensiveCareUnitBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Covid 19 ProgramDocument12 pagesCovid 19 ProgramBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Declaration Form - Work From Home Attachment 2Document1 pageDeclaration Form - Work From Home Attachment 2BAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Minutes Meeting 4 21 2021Document5 pagesMinutes Meeting 4 21 2021BAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument1 pageNew Microsoft Word DocumentBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- All Is WellDocument1 pageAll Is WellBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- NURSING SERVICE WORK FROM HOME ACTIVITIES AND EXPECTED OUTPUTS - Implementing Guidelines - FinalDocument4 pagesNURSING SERVICE WORK FROM HOME ACTIVITIES AND EXPECTED OUTPUTS - Implementing Guidelines - FinalBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Work at Home Arrangements - FormDocument2 pagesWork at Home Arrangements - FormBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- AMDDDocument2 pagesAMDDBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Tarp 1Document1 pageTarp 1BAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Request To OpdDocument1 pageRequest To OpdBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- TraceDocument3 pagesTraceBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- BioterrorismDocument8 pagesBioterrorismBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Weekly Work Commitment and Accomplishment Report: Name of Staff: Position: Area of AssignmentDocument2 pagesWeekly Work Commitment and Accomplishment Report: Name of Staff: Position: Area of AssignmentBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Baguio General Hospital and Medical Center: Republic of The Philippines Department of HealthDocument2 pagesBaguio General Hospital and Medical Center: Republic of The Philippines Department of HealthBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Weekly Work Commitment and Accomplishment Report: Nursing Service OfficeDocument2 pagesWeekly Work Commitment and Accomplishment Report: Nursing Service OfficeBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Chart 1 FsdfgsgsdgsgsDocument1 pageChart 1 FsdfgsgsdgsgsBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Organizational Chart Tertiary LabDocument1 pageOrganizational Chart Tertiary LabBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Chart 1Document1 pageChart 1BAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- 10th BPS - JOINT NOTE 2015 PDFDocument49 pages10th BPS - JOINT NOTE 2015 PDFAnjaiah MandeNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal System Review QuestionsDocument10 pagesGastrointestinal System Review QuestionsSiena PlacinoNo ratings yet
- Suz 183Document29 pagesSuz 183Benny Chris TantoNo ratings yet
- 2-Preschool Parent QuestionnaireDocument3 pages2-Preschool Parent QuestionnaireION677No ratings yet
- Types of PhobiaDocument24 pagesTypes of PhobiaAman KalraNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Aspen Healthcare BrochureDocument8 pagesA Guide To Aspen Healthcare BrochureAntonio LoscialeNo ratings yet
- B SRAVANI-Female16 Years-2090Document1 pageB SRAVANI-Female16 Years-2090vijaykumarNo ratings yet
- Clinical Teaching ON Geriatric AssessmentDocument9 pagesClinical Teaching ON Geriatric AssessmentANITTA SNo ratings yet
- VheeeeDocument50 pagesVheeeeKathlene GamitNo ratings yet
- Aisyah HPTDocument10 pagesAisyah HPTBesari Md DaudNo ratings yet
- CEA Pilgastrim Vs FilgastrimDocument13 pagesCEA Pilgastrim Vs FilgastrimMaya Aulia MulakhaillaNo ratings yet
- Mental Retardation 1Document4 pagesMental Retardation 1Aizah Lazo LuzonNo ratings yet
- Star Fho One Page Feb 2020Document2 pagesStar Fho One Page Feb 2020suryaNo ratings yet
- Systemic VPT-Lecture NotesDocument34 pagesSystemic VPT-Lecture NotesshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 - Blood VesselsDocument40 pagesChapter 19 - Blood VesselsZuleyha ZuleyhaNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis C Education Class - 2009Document64 pagesHepatitis C Education Class - 2009BENNo ratings yet
- Panduan Perkhidmatan Makmal JPMD HCTM Versi 2020 2 CompressedDocument151 pagesPanduan Perkhidmatan Makmal JPMD HCTM Versi 2020 2 Compressed23-Chong Kar KinNo ratings yet
- Pathology: Fajar L. Gultom Departemen Patologi Anatomik FK UKI April 2019Document39 pagesPathology: Fajar L. Gultom Departemen Patologi Anatomik FK UKI April 2019ErniNo ratings yet
- A Manual On Clinical Surgery by Das S: 8.lee Mcgregor'S Synopsis of Surgical Anatomy 500Document1 pageA Manual On Clinical Surgery by Das S: 8.lee Mcgregor'S Synopsis of Surgical Anatomy 500prabhakarNo ratings yet
- Nonconvulsive Status Epilepticus: Validating The Salzburg Criteria Against An Expert EEG ExaminerDocument5 pagesNonconvulsive Status Epilepticus: Validating The Salzburg Criteria Against An Expert EEG ExaminerNathaly LapoNo ratings yet
- List of Medical and Nursing Abbreviations, Acronyms, Terms 1 - NurseslabsDocument25 pagesList of Medical and Nursing Abbreviations, Acronyms, Terms 1 - NurseslabsbeingfiredNo ratings yet
- Trindade 2018Document10 pagesTrindade 2018Tales FernandoNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Guidance School Case Contact and Outbreak Management 2021-08-11 FINAL AODA enDocument27 pagesCOVID-19 Guidance School Case Contact and Outbreak Management 2021-08-11 FINAL AODA enCityNewsTorontoNo ratings yet
- Buku Kedokteran Keluarga 1Document5 pagesBuku Kedokteran Keluarga 1Intan Alwaystry TobehappyNo ratings yet
- Intussusception: Afua A.J. Hesse Francis A. Abantanga Kokila LakhooDocument8 pagesIntussusception: Afua A.J. Hesse Francis A. Abantanga Kokila LakhooFATIN NAJIHAHNo ratings yet
- Eosinophilic Ulcer of The Oral MucosaDocument4 pagesEosinophilic Ulcer of The Oral MucosaKhairunnisa Indah NurfaizahNo ratings yet