Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Wave Mechanics 8
Wave Mechanics 8
Uploaded by
DeanielCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Cooling TowerDocument23 pagesCooling TowerBevelyn L. Barreto HernandezNo ratings yet
- Experiment: The Properties of WaterDocument27 pagesExperiment: The Properties of WaterGideon IraborNo ratings yet
- P6 TonetDocument12 pagesP6 TonetAlyssa Fermin0% (1)
- 3.5 Archimedes' PrincipleDocument25 pages3.5 Archimedes' PrincipleShahrin Ahmad100% (2)
- FLUIDSDocument55 pagesFLUIDSMonville RedNo ratings yet
- IX. Waves, Sounds and FluidsDocument66 pagesIX. Waves, Sounds and FluidsMa Angelica Shane Navarro0% (1)
- Wave Mechanics 1Document8 pagesWave Mechanics 1DeanielNo ratings yet
- A. Wave Introduction: Waves InterferenceDocument13 pagesA. Wave Introduction: Waves InterferenceJeromeDelCastilloNo ratings yet
- Hibbeler 10e CH02Document46 pagesHibbeler 10e CH02Eugene ChandNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-Wave Properties of ParticleDocument29 pagesChapter 3-Wave Properties of ParticleI Gowtham ChandraNo ratings yet
- Practice Hookes and SHM SolutionsDocument10 pagesPractice Hookes and SHM SolutionsZhong Huang100% (1)
- Archimedes PrincipleDocument2 pagesArchimedes Principledemetri lanezNo ratings yet
- Basic Engineering Correlation Physics v4 001Document19 pagesBasic Engineering Correlation Physics v4 001Ska dooshNo ratings yet
- PHYS 81 - QuestionsDocument2 pagesPHYS 81 - QuestionsAlbertNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Deformable BodiesDocument2 pagesMechanics of Deformable BodiesJeff LaycoNo ratings yet
- Temperature and ExpansionDocument10 pagesTemperature and ExpansionH Aries OñaNo ratings yet
- PHY02 - Course Outcome 1Document50 pagesPHY02 - Course Outcome 1k marcusNo ratings yet
- BuoyancyDocument10 pagesBuoyancyYeddaMIlaganNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Earthquake DescriptorsDocument12 pagesLesson 5 Earthquake Descriptorspoliman2017No ratings yet
- Anastomosing Rivers PDFDocument48 pagesAnastomosing Rivers PDFMaría Alejandra BarajasNo ratings yet
- Electric Charge and CurrentDocument33 pagesElectric Charge and CurrenthasminNo ratings yet
- Internal Energy Solved ProblemsDocument1 pageInternal Energy Solved ProblemsKenneth OkoyeNo ratings yet
- Problem - 5A PDFDocument13 pagesProblem - 5A PDFMonicaNo ratings yet
- DisplacementDocument8 pagesDisplacementmilesNo ratings yet
- UNIT 11-PHY 131-Chapter 16-Electric Forces and FieldsDocument54 pagesUNIT 11-PHY 131-Chapter 16-Electric Forces and FieldscharlieNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2 2S AY2018-2019Document4 pagesProblem Set 2 2S AY2018-2019Allein Loisse EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Simple StressesDocument27 pagesChapter 1 Simple StressesLalaine RamosNo ratings yet
- Wave NotesDocument66 pagesWave NotesKwame Pee100% (1)
- Earthquake Engineering: Structural Prof Course 2Document10 pagesEarthquake Engineering: Structural Prof Course 2RAIZZNo ratings yet
- Syllabus in Fluid MechanicsDocument9 pagesSyllabus in Fluid MechanicsAlan BalilaNo ratings yet
- Work and EnergyDocument28 pagesWork and EnergyMir'atun Nissa QuinalendraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Electrical Energy and PowerDocument21 pagesLesson 1 - Electrical Energy and PowerMary Joy Llosa RedullaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Scalar and VectorDocument25 pagesLesson 3 - Scalar and VectorEji AlcorezaNo ratings yet
- Geology For Engineers Module 1 - IntroductionDocument31 pagesGeology For Engineers Module 1 - Introductiontaylor swiftNo ratings yet
- 2 MEC32-1 REVIEW OF MEC30 (Robles)Document16 pages2 MEC32-1 REVIEW OF MEC30 (Robles)John BurnsideNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Exercices Enstab Cou SWDocument12 pagesFluid Mechanics Exercices Enstab Cou SWLourenze KigisNo ratings yet
- Spring - Axial Load Only: C AE/L and C EI/L Frame in Global Coordinate K (E/L) X (K) (K)Document4 pagesSpring - Axial Load Only: C AE/L and C EI/L Frame in Global Coordinate K (E/L) X (K) (K)Azmi Bin A MataliNo ratings yet
- 1 Simple StressDocument5 pages1 Simple StressKeane CortesNo ratings yet
- MODULE1Document11 pagesMODULE1streetranpuNo ratings yet
- Isu Module Subject: CE 223 and Dynamics of Rigid Bodies Continuation of Chapter 1 Topic 4 General Curvilinear MotionDocument22 pagesIsu Module Subject: CE 223 and Dynamics of Rigid Bodies Continuation of Chapter 1 Topic 4 General Curvilinear MotioneysNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarterly Physics 2 STEM Questions and AnswersDocument5 pages3rd Quarterly Physics 2 STEM Questions and Answersronaldo maanoNo ratings yet
- Hooke's Law Sample Problems With SolutionsDocument1 pageHooke's Law Sample Problems With SolutionsBasic PhysicsNo ratings yet
- C02 - Scalar and Vector QuantitiesDocument29 pagesC02 - Scalar and Vector QuantitiesWinjoe CapiliNo ratings yet
- Basic Wave MotionDocument42 pagesBasic Wave MotionDex JHNo ratings yet
- Module 3 EvaporationDocument22 pagesModule 3 EvaporationPrince VinceNo ratings yet
- 01 Thermodynamic Process 2Document20 pages01 Thermodynamic Process 2Ashok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 4 Waves Boundary BehaviorDocument2 pagesWorksheet 4 Waves Boundary BehaviorMary BakhoumNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1-3Document66 pagesLesson 1-3Andrich Rey CortesNo ratings yet
- Work and Energy Answer Key - HelpTeachingDocument2 pagesWork and Energy Answer Key - HelpTeachingDiona Bangga - ModestoNo ratings yet
- CMT Lab Report 8 FinalDocument5 pagesCMT Lab Report 8 FinalEngel De VillaNo ratings yet
- Cehdra 1 Obe Syllabus T2 2019 2020Document6 pagesCehdra 1 Obe Syllabus T2 2019 2020Jemina SamsonNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Pressure in LiquidsDocument15 pages3.2 Pressure in Liquidssaeed akhtar100% (1)
- GEAS Problems 2Document11 pagesGEAS Problems 2Jayson CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - Rectilinear MotionDocument54 pagesChapter 15 - Rectilinear MotionAbdallah KabalanNo ratings yet
- College of Engineering and Architecture Civil Engineering DepartmentDocument7 pagesCollege of Engineering and Architecture Civil Engineering DepartmentGenesis GendranoNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Momentum and COLLISIONDocument23 pagesConservation of Momentum and COLLISIONMarisa Jane RamelNo ratings yet
- Different Types of FaultsDocument13 pagesDifferent Types of FaultsDylene janeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3. Mechanics of Deformable BodiesDocument23 pagesChapter 3. Mechanics of Deformable BodiesEngrRyeTutorialsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Equilibrium of Particles: ObjectivesDocument6 pagesChapter 3 - Equilibrium of Particles: ObjectivesRhey LuceroNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 - Flight of Projectile - 2Document16 pagesTopic 6 - Flight of Projectile - 2Eugene GarbosaNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument9 pagesWavesakhilaappu16No ratings yet
- Introduction To Quantum Physics NotesDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Quantum Physics NotesViraj BukitagarNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Forces in COMSOLDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic Forces in COMSOLAlkalin100% (1)
- ch3 Mass Relationships in Chemical ReactionsDocument50 pagesch3 Mass Relationships in Chemical ReactionsPat RiciaNo ratings yet
- LG THerma V Catalogue 2021-2022 - ENGDocument74 pagesLG THerma V Catalogue 2021-2022 - ENGGyulovics NándorNo ratings yet
- ES 223 Statics and Strengh of Materials: Force System ResultantsDocument6 pagesES 223 Statics and Strengh of Materials: Force System ResultantsserhatNo ratings yet
- RED: Volume of Cubes and Cuboids Length X Width X Height ToDocument6 pagesRED: Volume of Cubes and Cuboids Length X Width X Height ToOliveenNo ratings yet
- Ripple Tank Lab ManualDocument4 pagesRipple Tank Lab ManualRaja Wajhi Ullah NisarNo ratings yet
- All Questions PhysicsDocument7 pagesAll Questions PhysicsChirag KundaliaNo ratings yet
- Easy Altivar 310 - ATV310H037N4EDocument6 pagesEasy Altivar 310 - ATV310H037N4ESundeep Bandi100% (1)
- JS120 Single Axis Fingertip Joystick: Features and Options Mobile Machine ManagementDocument2 pagesJS120 Single Axis Fingertip Joystick: Features and Options Mobile Machine ManagementStelian CrisanNo ratings yet
- 17thedition Mock Exam2Document11 pages17thedition Mock Exam2jackwpsoNo ratings yet
- Basics of VibrationsDocument45 pagesBasics of Vibrationsravimech_862750No ratings yet
- How To Execute SWYD Installation Works Substation ConstructionDocument6 pagesHow To Execute SWYD Installation Works Substation ConstructionOmarNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Field TheoryDocument77 pagesElectromagnetic Field TheoryashjunghareNo ratings yet
- Scholar Test Paper - PhysicsDocument12 pagesScholar Test Paper - PhysicsAashika DhareNo ratings yet
- Ship VibrationDocument242 pagesShip VibrationRahmat AnpsNo ratings yet
- Catalogue enDocument106 pagesCatalogue enANGELICANo ratings yet
- Hand Book Planning For Floor HeatingDocument8 pagesHand Book Planning For Floor HeatingChanelNo ratings yet
- Induccion Vs Combustion Por Gas NaturalDocument9 pagesInduccion Vs Combustion Por Gas NaturalMateo Pabón BarberyNo ratings yet
- Chp1 - MCQs (Answers)Document6 pagesChp1 - MCQs (Answers)Rushi PatilNo ratings yet
- MD1-0-E-505!06!00001 Generator Transformer Sizing CalculationDocument19 pagesMD1-0-E-505!06!00001 Generator Transformer Sizing Calculationtvpham12350% (2)
- En TCBB TCBTDocument18 pagesEn TCBB TCBTzaidNo ratings yet
- Ehv PaperDocument5 pagesEhv PaperVaibhav YadavNo ratings yet
- Material Balance 6.3.4 MEG Refining Column (Packed Column)Document29 pagesMaterial Balance 6.3.4 MEG Refining Column (Packed Column)noelNo ratings yet
- 514C DC Controller: Product ManualDocument44 pages514C DC Controller: Product ManualRIGID TYRESNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1Document3 pagesLab Report 1azarmechNo ratings yet
- Silicon NPN Triple Diffusion Mesa Type: Power TransistorsDocument3 pagesSilicon NPN Triple Diffusion Mesa Type: Power TransistorsVitorio LogoNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4 Vapour Power Cycles: H T L PDocument14 pagesUnit - 4 Vapour Power Cycles: H T L PMukesh MystNo ratings yet
- Xi Physics Practicals Class - 11 Term - 2 2022Document15 pagesXi Physics Practicals Class - 11 Term - 2 2022Sumeet MahapatraNo ratings yet
Wave Mechanics 8
Wave Mechanics 8
Uploaded by
DeanielOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Wave Mechanics 8
Wave Mechanics 8
Uploaded by
DeanielCopyright:
Available Formats
Wave Mechanics
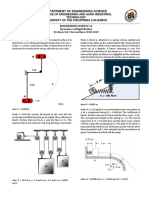
Identification. Write T if it is a Transverse wave and L if it is a Longitudinal wave. Write the letter on the space provided.
Phys222 | Yana Tapay
Wave Mechanics
The wave equation
Given the wave function 𝑦(𝑥,𝑡), we can obtain the expression of the transverse velocity of any
particle in a transverse wave by taking the partial derivative of the function with respect to 𝑡,
keeping 𝑥 constant.
For wave function 𝑦(𝑥,𝑡)=𝐴𝑠𝑖𝑛(𝜔𝑡−𝑘𝑥), the transverse velocity is given by
For the transverse acceleration, take its second partial derivative to obtain
Manipulating equations above and using 𝜔=𝑣𝑘 we can derive the wave equation as:
Phys222 | Yana Tapay
Wave Mechanics
Speed of a transverse wave
Weather: Thunder and lightning strike as warm humid air moves over New Zealand 29/10/2022
https://www.newshub.co.nz/
In this section we’ll see what determines the speed of propagation of one
particular kind of wave: transverse waves on a string.
The physical quantities that determine the speed of transverse waves on a string are the
tension in the string and its mass per unit length (also called linear mass density).
Increasing the tension should increase the restoring forces that tend to straighten the
string when it is disturbed, thus increasing the wave speed.
Increasing the mass of the string should make the motion more sluggish and decrease the speed.
Phys222 | Yana Tapay
Wave Mechanics
Speed of a transverse wave
Speed of a transverse wave in a vibrating string is given by
where 𝑭 is the tensional force in the string and 𝝁 is the mass per unit length (𝜇=𝑚/𝐿).
Speed of a longitudinal wave in a solid bar is given by
where 𝒀 is the Young’s modulus (𝑌=𝑠𝑡𝑟𝑒𝑠𝑠/𝑠𝑡𝑟𝑎𝑖𝑛=(𝐹/𝐴)/(Δ𝐿/𝐿)) in unit Pascal (Pa) and 𝝆 is the
density of the solid.
Speed of a longitudinal wave in a vibrating fluid is given by
where 𝑩𝒂𝒅 is the adiabatic bulk modulus and 𝝆 is the density of the fluid.
Sound waves in gases
For an ideal gas, 𝑩_𝒂𝒅=𝜸𝒑 where 𝜸=𝑪_𝒑/𝑪_𝒗 is the dimensionless ratio of molar heat
capacities and 𝒑 is the absolute pressure.
At sea level, the absolute pressure at standard temperature and pressure is 1.013×10^5 𝑃𝑎.
Therefore, speed of sound in an ideal gas is given by
where 𝝆=𝒑𝑴/𝑹𝑻, 𝑹=𝟖.𝟑𝟏𝟒𝟓 𝑱/(𝒎𝒐𝒍.𝑲) is the universal gas constant, 𝑴=𝟐𝟖.𝟖 𝒈/𝒎𝒐𝒍 is the
molecular mass, 𝑻 is the absolute temperature, and 𝜸=𝟏.𝟒𝟎.
Phys222 | Yana Tapay
Wave Mechanics
Speed of a transverse wave
A guitar string that is 2m long has a mass of
10g and is attached in such way that there's a
tension of 400N on it how fast will the wave
move as the player strung the guitar
Phys222 | Yana Tapay
Wave Mechanics
Speed of a transverse wave
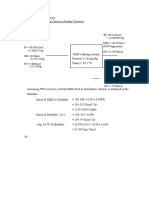
One end of a 2.00-kg rope is tied to a support
at the top of a mine shaft 80.0 m deep (see
figure at the side). The rope is stretched taut by
a 20.0-kg box of rocks attached at the bottom.
(a) The geologist at the bottom of the shaft
signals to a colleague at the top by jerking the
rope sideways. What is the speed of a
transverse wave on the rope? (b) If a point on
the rope is in transverse SHM with ƒ = 2.00
Hz, how many cycles of the wave are there in
the rope’s length?
Phys222 | Yana Tapay
Wave Mechanics
Speed of a transverse wave
Calculate the speed of sound in air at (a) 0*C and (b) 27*C
Phys222 | Yana Tapay
Wave Mechanics
Energy in Wave Motion
The energy we receive from sunlight and
the destructive effects of ocean surf and
earthquakes bear this out.
From the property of a mechanical wave, energy is transported along the length of the vibrating
string and this instantaneous rate at which energy is transferred is referred to as Power and its
value is dependent on both position 𝑥 and time 𝑡 by
The maximum value of the instantaneous power 𝑃(𝑥,𝑡) occurs when the cos^2𝑓𝑢𝑛𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 has the
value unity:
To obtain the average power from Eq. (1-12), we note that the average value of the cos^2
function, averaged over any whole number of cycles, is 1/2. Hence the average power is
The average rate of energy transfer is proportional to the square of the amplitude and to the
square of the frequency.
Phys222 | Yana Tapay
Wave Mechanics
Energy in Wave Motion
Waves of wavelength 35 cm and amplitude 1.2 cm move along a 15-m string that has a mass of 80 g
and a tension of 12 N. Find the average power transmitted past a given point on the string.
Phys222 | Yana Tapay
You might also like
- Cooling TowerDocument23 pagesCooling TowerBevelyn L. Barreto HernandezNo ratings yet
- Experiment: The Properties of WaterDocument27 pagesExperiment: The Properties of WaterGideon IraborNo ratings yet
- P6 TonetDocument12 pagesP6 TonetAlyssa Fermin0% (1)
- 3.5 Archimedes' PrincipleDocument25 pages3.5 Archimedes' PrincipleShahrin Ahmad100% (2)
- FLUIDSDocument55 pagesFLUIDSMonville RedNo ratings yet
- IX. Waves, Sounds and FluidsDocument66 pagesIX. Waves, Sounds and FluidsMa Angelica Shane Navarro0% (1)
- Wave Mechanics 1Document8 pagesWave Mechanics 1DeanielNo ratings yet
- A. Wave Introduction: Waves InterferenceDocument13 pagesA. Wave Introduction: Waves InterferenceJeromeDelCastilloNo ratings yet
- Hibbeler 10e CH02Document46 pagesHibbeler 10e CH02Eugene ChandNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-Wave Properties of ParticleDocument29 pagesChapter 3-Wave Properties of ParticleI Gowtham ChandraNo ratings yet
- Practice Hookes and SHM SolutionsDocument10 pagesPractice Hookes and SHM SolutionsZhong Huang100% (1)
- Archimedes PrincipleDocument2 pagesArchimedes Principledemetri lanezNo ratings yet
- Basic Engineering Correlation Physics v4 001Document19 pagesBasic Engineering Correlation Physics v4 001Ska dooshNo ratings yet
- PHYS 81 - QuestionsDocument2 pagesPHYS 81 - QuestionsAlbertNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Deformable BodiesDocument2 pagesMechanics of Deformable BodiesJeff LaycoNo ratings yet
- Temperature and ExpansionDocument10 pagesTemperature and ExpansionH Aries OñaNo ratings yet
- PHY02 - Course Outcome 1Document50 pagesPHY02 - Course Outcome 1k marcusNo ratings yet
- BuoyancyDocument10 pagesBuoyancyYeddaMIlaganNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Earthquake DescriptorsDocument12 pagesLesson 5 Earthquake Descriptorspoliman2017No ratings yet
- Anastomosing Rivers PDFDocument48 pagesAnastomosing Rivers PDFMaría Alejandra BarajasNo ratings yet
- Electric Charge and CurrentDocument33 pagesElectric Charge and CurrenthasminNo ratings yet
- Internal Energy Solved ProblemsDocument1 pageInternal Energy Solved ProblemsKenneth OkoyeNo ratings yet
- Problem - 5A PDFDocument13 pagesProblem - 5A PDFMonicaNo ratings yet
- DisplacementDocument8 pagesDisplacementmilesNo ratings yet
- UNIT 11-PHY 131-Chapter 16-Electric Forces and FieldsDocument54 pagesUNIT 11-PHY 131-Chapter 16-Electric Forces and FieldscharlieNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2 2S AY2018-2019Document4 pagesProblem Set 2 2S AY2018-2019Allein Loisse EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Simple StressesDocument27 pagesChapter 1 Simple StressesLalaine RamosNo ratings yet
- Wave NotesDocument66 pagesWave NotesKwame Pee100% (1)
- Earthquake Engineering: Structural Prof Course 2Document10 pagesEarthquake Engineering: Structural Prof Course 2RAIZZNo ratings yet
- Syllabus in Fluid MechanicsDocument9 pagesSyllabus in Fluid MechanicsAlan BalilaNo ratings yet
- Work and EnergyDocument28 pagesWork and EnergyMir'atun Nissa QuinalendraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Electrical Energy and PowerDocument21 pagesLesson 1 - Electrical Energy and PowerMary Joy Llosa RedullaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Scalar and VectorDocument25 pagesLesson 3 - Scalar and VectorEji AlcorezaNo ratings yet
- Geology For Engineers Module 1 - IntroductionDocument31 pagesGeology For Engineers Module 1 - Introductiontaylor swiftNo ratings yet
- 2 MEC32-1 REVIEW OF MEC30 (Robles)Document16 pages2 MEC32-1 REVIEW OF MEC30 (Robles)John BurnsideNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Exercices Enstab Cou SWDocument12 pagesFluid Mechanics Exercices Enstab Cou SWLourenze KigisNo ratings yet
- Spring - Axial Load Only: C AE/L and C EI/L Frame in Global Coordinate K (E/L) X (K) (K)Document4 pagesSpring - Axial Load Only: C AE/L and C EI/L Frame in Global Coordinate K (E/L) X (K) (K)Azmi Bin A MataliNo ratings yet
- 1 Simple StressDocument5 pages1 Simple StressKeane CortesNo ratings yet
- MODULE1Document11 pagesMODULE1streetranpuNo ratings yet
- Isu Module Subject: CE 223 and Dynamics of Rigid Bodies Continuation of Chapter 1 Topic 4 General Curvilinear MotionDocument22 pagesIsu Module Subject: CE 223 and Dynamics of Rigid Bodies Continuation of Chapter 1 Topic 4 General Curvilinear MotioneysNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarterly Physics 2 STEM Questions and AnswersDocument5 pages3rd Quarterly Physics 2 STEM Questions and Answersronaldo maanoNo ratings yet
- Hooke's Law Sample Problems With SolutionsDocument1 pageHooke's Law Sample Problems With SolutionsBasic PhysicsNo ratings yet
- C02 - Scalar and Vector QuantitiesDocument29 pagesC02 - Scalar and Vector QuantitiesWinjoe CapiliNo ratings yet
- Basic Wave MotionDocument42 pagesBasic Wave MotionDex JHNo ratings yet
- Module 3 EvaporationDocument22 pagesModule 3 EvaporationPrince VinceNo ratings yet
- 01 Thermodynamic Process 2Document20 pages01 Thermodynamic Process 2Ashok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 4 Waves Boundary BehaviorDocument2 pagesWorksheet 4 Waves Boundary BehaviorMary BakhoumNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1-3Document66 pagesLesson 1-3Andrich Rey CortesNo ratings yet
- Work and Energy Answer Key - HelpTeachingDocument2 pagesWork and Energy Answer Key - HelpTeachingDiona Bangga - ModestoNo ratings yet
- CMT Lab Report 8 FinalDocument5 pagesCMT Lab Report 8 FinalEngel De VillaNo ratings yet
- Cehdra 1 Obe Syllabus T2 2019 2020Document6 pagesCehdra 1 Obe Syllabus T2 2019 2020Jemina SamsonNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Pressure in LiquidsDocument15 pages3.2 Pressure in Liquidssaeed akhtar100% (1)
- GEAS Problems 2Document11 pagesGEAS Problems 2Jayson CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - Rectilinear MotionDocument54 pagesChapter 15 - Rectilinear MotionAbdallah KabalanNo ratings yet
- College of Engineering and Architecture Civil Engineering DepartmentDocument7 pagesCollege of Engineering and Architecture Civil Engineering DepartmentGenesis GendranoNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Momentum and COLLISIONDocument23 pagesConservation of Momentum and COLLISIONMarisa Jane RamelNo ratings yet
- Different Types of FaultsDocument13 pagesDifferent Types of FaultsDylene janeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3. Mechanics of Deformable BodiesDocument23 pagesChapter 3. Mechanics of Deformable BodiesEngrRyeTutorialsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Equilibrium of Particles: ObjectivesDocument6 pagesChapter 3 - Equilibrium of Particles: ObjectivesRhey LuceroNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 - Flight of Projectile - 2Document16 pagesTopic 6 - Flight of Projectile - 2Eugene GarbosaNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument9 pagesWavesakhilaappu16No ratings yet
- Introduction To Quantum Physics NotesDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Quantum Physics NotesViraj BukitagarNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Forces in COMSOLDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic Forces in COMSOLAlkalin100% (1)
- ch3 Mass Relationships in Chemical ReactionsDocument50 pagesch3 Mass Relationships in Chemical ReactionsPat RiciaNo ratings yet
- LG THerma V Catalogue 2021-2022 - ENGDocument74 pagesLG THerma V Catalogue 2021-2022 - ENGGyulovics NándorNo ratings yet
- ES 223 Statics and Strengh of Materials: Force System ResultantsDocument6 pagesES 223 Statics and Strengh of Materials: Force System ResultantsserhatNo ratings yet
- RED: Volume of Cubes and Cuboids Length X Width X Height ToDocument6 pagesRED: Volume of Cubes and Cuboids Length X Width X Height ToOliveenNo ratings yet
- Ripple Tank Lab ManualDocument4 pagesRipple Tank Lab ManualRaja Wajhi Ullah NisarNo ratings yet
- All Questions PhysicsDocument7 pagesAll Questions PhysicsChirag KundaliaNo ratings yet
- Easy Altivar 310 - ATV310H037N4EDocument6 pagesEasy Altivar 310 - ATV310H037N4ESundeep Bandi100% (1)
- JS120 Single Axis Fingertip Joystick: Features and Options Mobile Machine ManagementDocument2 pagesJS120 Single Axis Fingertip Joystick: Features and Options Mobile Machine ManagementStelian CrisanNo ratings yet
- 17thedition Mock Exam2Document11 pages17thedition Mock Exam2jackwpsoNo ratings yet
- Basics of VibrationsDocument45 pagesBasics of Vibrationsravimech_862750No ratings yet
- How To Execute SWYD Installation Works Substation ConstructionDocument6 pagesHow To Execute SWYD Installation Works Substation ConstructionOmarNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Field TheoryDocument77 pagesElectromagnetic Field TheoryashjunghareNo ratings yet
- Scholar Test Paper - PhysicsDocument12 pagesScholar Test Paper - PhysicsAashika DhareNo ratings yet
- Ship VibrationDocument242 pagesShip VibrationRahmat AnpsNo ratings yet
- Catalogue enDocument106 pagesCatalogue enANGELICANo ratings yet
- Hand Book Planning For Floor HeatingDocument8 pagesHand Book Planning For Floor HeatingChanelNo ratings yet
- Induccion Vs Combustion Por Gas NaturalDocument9 pagesInduccion Vs Combustion Por Gas NaturalMateo Pabón BarberyNo ratings yet
- Chp1 - MCQs (Answers)Document6 pagesChp1 - MCQs (Answers)Rushi PatilNo ratings yet
- MD1-0-E-505!06!00001 Generator Transformer Sizing CalculationDocument19 pagesMD1-0-E-505!06!00001 Generator Transformer Sizing Calculationtvpham12350% (2)
- En TCBB TCBTDocument18 pagesEn TCBB TCBTzaidNo ratings yet
- Ehv PaperDocument5 pagesEhv PaperVaibhav YadavNo ratings yet
- Material Balance 6.3.4 MEG Refining Column (Packed Column)Document29 pagesMaterial Balance 6.3.4 MEG Refining Column (Packed Column)noelNo ratings yet
- 514C DC Controller: Product ManualDocument44 pages514C DC Controller: Product ManualRIGID TYRESNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1Document3 pagesLab Report 1azarmechNo ratings yet
- Silicon NPN Triple Diffusion Mesa Type: Power TransistorsDocument3 pagesSilicon NPN Triple Diffusion Mesa Type: Power TransistorsVitorio LogoNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4 Vapour Power Cycles: H T L PDocument14 pagesUnit - 4 Vapour Power Cycles: H T L PMukesh MystNo ratings yet
- Xi Physics Practicals Class - 11 Term - 2 2022Document15 pagesXi Physics Practicals Class - 11 Term - 2 2022Sumeet MahapatraNo ratings yet