Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Performance
Performance
Uploaded by
Amit Khadka0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesThis document discusses key performance, combustion, and emission terms for internal combustion engines. It defines terms related to engine performance parameters like indicated power, brake power, and thermal efficiencies. Combustion parameters like peak cylinder pressure, heat release rates, and ignition delay are also defined. Finally, it discusses engine emissions measurement tools like gas analyzers and opacity meters and outlines the first law of thermodynamics as it applies to a engine's thermal balance sheet.
Original Description:
perfomance of engine
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses key performance, combustion, and emission terms for internal combustion engines. It defines terms related to engine performance parameters like indicated power, brake power, and thermal efficiencies. Combustion parameters like peak cylinder pressure, heat release rates, and ignition delay are also defined. Finally, it discusses engine emissions measurement tools like gas analyzers and opacity meters and outlines the first law of thermodynamics as it applies to a engine's thermal balance sheet.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesPerformance
Performance
Uploaded by
Amit KhadkaThis document discusses key performance, combustion, and emission terms for internal combustion engines. It defines terms related to engine performance parameters like indicated power, brake power, and thermal efficiencies. Combustion parameters like peak cylinder pressure, heat release rates, and ignition delay are also defined. Finally, it discusses engine emissions measurement tools like gas analyzers and opacity meters and outlines the first law of thermodynamics as it applies to a engine's thermal balance sheet.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
PERFORMANCE, COMBUSTION AND EMISSION TERMS
1. Introduction
a. VCR engine
Explain along with CAD diagram
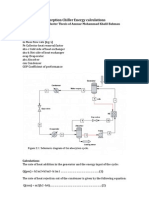
Where, F1 = Fuel consumption (kg/hr)
F2 = Air consumption (kg/hr)
F3 = Jacket cooling water (kg/hr)
F4 = Calorimeter water flow (kg/hr)
T1 = Jacket water inlet temp (°C)
T2 = Jacket water outlet temp (°C)
T3 = Calorimeter water inlet temp (°C)
T4 = Calorimeter water outlet temp (°C)
T5 = Exhaust gas to calorimeter inlet temp (°C)
T6 = Exhaust gas from calorimeter outlet temp (°C)
b. Eddy Current dynamometer
c. Injection Pressure
d. Compression ratio
e. Nozzle types
A. Performance Parameter
a. Indicated Power
b. Brake Power
c. Frictional Power
d. Indicated Thermal Efficiency
e. Brake Thermal Efficiency
f. Indicated mean effective pressure
g. Brake mean effective pressure
h. Mechanical Efficiency
i. Volumetric Efficiency
B. Combustion Parameters
a. Peak Cylinder Pressure
b. Cumulative Heat Release
c. Net Heat Release
d. Mean Gas Temperature
e. Exhaust Gas Temperature
f. Ignition Delay
g. Mass Fraction Burn
C. Thermal Balance Sheet
From the first law of thermodynamics, for a control volume, the steady flow equation will
be
Qs =Qbp + Qjw + Qex + Qmisc
Where,
Qs : Energy supplied by the fuel
Qbp : Output work delivered in the form of brake power
Qjw : Output work delivered in the form of heat to jacket cooling water
Qex : Output work delivered in the form of heat to exhaust
Qmisc : Output work delivered in the form of heat to miscellaneous loss
D. Emission Characteristics
a. 4 Gas Analyzer
b. 5 Gas Analyzer
c. 6 gas Analyzer
d. Opacity meter
e. Emission of CI and SI engine
You might also like
- Heat Balance Test On Diesel EngineDocument6 pagesHeat Balance Test On Diesel EngineMathew John0% (2)
- ICE Assign#2 May 18Document2 pagesICE Assign#2 May 18Isyraf FitriNo ratings yet
- Energy Lab Ful Manual-1Document6 pagesEnergy Lab Ful Manual-1dhanuc190No ratings yet
- Thermal Lab II Manual Cycle 1Document13 pagesThermal Lab II Manual Cycle 1Rony RkzNo ratings yet
- Boiler Efficiency Calculation:-: 2. Indirect MethodDocument8 pagesBoiler Efficiency Calculation:-: 2. Indirect MethodVISHAL GANGWARNo ratings yet
- 1-What Is The Different Between Heat Engine and Heat Pump?-Write An Equation For Each OneDocument11 pages1-What Is The Different Between Heat Engine and Heat Pump?-Write An Equation For Each OneZayn AhmedNo ratings yet
- Trial On Diesel EngineDocument4 pagesTrial On Diesel EngineAbhishek KhatavkarNo ratings yet
- 1.trial On Diesel Engine To Determine Variable Load Performance and Energy Balance PDFDocument16 pages1.trial On Diesel Engine To Determine Variable Load Performance and Energy Balance PDFPrasad varnekarNo ratings yet
- A. B. C. D. E.: Where R (D + D) /2 or (D + T) /2 M, and W (Load) (S - S) KGDocument5 pagesA. B. C. D. E.: Where R (D + D) /2 or (D + T) /2 M, and W (Load) (S - S) KGal hasan kanonNo ratings yet
- Heat Balance CalculationsDocument32 pagesHeat Balance CalculationsSamehibrahem100% (2)
- Heat Transfer Lab ManualDocument40 pagesHeat Transfer Lab ManualRachit_Goyal25_10No ratings yet
- Midterm Paper: Date: 20 August 2020 Name of Student: Roll NumberDocument2 pagesMidterm Paper: Date: 20 August 2020 Name of Student: Roll Numbertayyab khanNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics in Engine: Class WorkDocument2 pagesThermodynamics in Engine: Class WorkSnunkhaem EcharojNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Heat Transfer in EnginesDocument35 pagesChapter 10 - Heat Transfer in EnginesB NinhNo ratings yet
- شيت ٢Document4 pagesشيت ٢mohamedbaher180No ratings yet
- Pipe CNS 03Document59 pagesPipe CNS 03Matthew Dale BalisiNo ratings yet
- Pipe CNS 03Document59 pagesPipe CNS 03maria katherine pantojaNo ratings yet
- Heat Balance Diesel Rope Brake-6Document3 pagesHeat Balance Diesel Rope Brake-6Arup NaskarNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbines Tutorial Part 1 of 2Document4 pagesGas Turbines Tutorial Part 1 of 2Gulain Mayombo100% (1)
- Energy Optimization of Gasturbine Power Plant With Inlet Air Cooling SystemDocument16 pagesEnergy Optimization of Gasturbine Power Plant With Inlet Air Cooling SystemkorneluNo ratings yet
- Turbine Heat Rate and EfficiecyDocument48 pagesTurbine Heat Rate and EfficiecyPralay Raut100% (8)
- IC Engine - EC LabDocument7 pagesIC Engine - EC LabvedNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engine Lab/heat Engine Lab ExperimentsDocument19 pagesInternal Combustion Engine Lab/heat Engine Lab ExperimentsMathew John0% (2)
- Taller N1Document6 pagesTaller N1Isabella FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Engineering Thermodynamics Experiment: 04 Verification of First and Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocument5 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics Experiment: 04 Verification of First and Second Law of ThermodynamicsVishal DarjiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Equipment Sizing and CostingDocument21 pagesChapter 5 - Equipment Sizing and CostingHaiqal AzizNo ratings yet
- 4B. BOILER Efficency-D, ID Oil FiredDocument10 pages4B. BOILER Efficency-D, ID Oil Firedalokbdas100% (3)
- (Key Answer QUIZ 1) ME 421 FridayDocument13 pages(Key Answer QUIZ 1) ME 421 Fridaymichelangelo lemonNo ratings yet
- 4-Stroke, 4-Cylinder Petrol EngineDocument14 pages4-Stroke, 4-Cylinder Petrol Enginemanoj kumarNo ratings yet
- Heat Balance Sheet On Ic EngineDocument5 pagesHeat Balance Sheet On Ic Engineharisson31667% (6)
- Air Standard CycleDocument6 pagesAir Standard CycleBishOy NasrNo ratings yet
- Problem Set #2 - ChE 124 - Summer 2018Document3 pagesProblem Set #2 - ChE 124 - Summer 2018SkambalahardarNo ratings yet
- Revision Exam DisDocument9 pagesRevision Exam Dis2023471924No ratings yet
- 4 Stroke Single Cylinder Diesel EngineDocument4 pages4 Stroke Single Cylinder Diesel EngineDebadatta RathaNo ratings yet
- Power Plat EfficiencyDocument11 pagesPower Plat EfficiencyrezaNo ratings yet
- Heat BalanceDocument18 pagesHeat Balancehafidhrahadiyan2No ratings yet
- Cooling Tower 6MWDocument6 pagesCooling Tower 6MWtedfdfeNo ratings yet
- Tata Chemical LTD., Babrala: Efficiency of GTGDocument32 pagesTata Chemical LTD., Babrala: Efficiency of GTGRishabh KumarNo ratings yet
- Fuel and CombustionDocument6 pagesFuel and Combustion123genrev100% (1)
- Mid SemDocument2 pagesMid SemVivekananda NandamNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Dynamic Control Simulation of Unitary Gas Engine Heat PumpDocument8 pagesModeling and Dynamic Control Simulation of Unitary Gas Engine Heat PumpabareqisinaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics QuestionsDocument3 pagesFluid Mechanics QuestionsWaleed UsmanNo ratings yet
- Vapor-Compression Refrigeration CycleDocument23 pagesVapor-Compression Refrigeration CycleJamshidNo ratings yet
- Furnace Heater DesignDocument7 pagesFurnace Heater DesignSamNo ratings yet
- Boiler Efficiency Calculation:-: 2. Indirect MethodDocument3 pagesBoiler Efficiency Calculation:-: 2. Indirect MethodVISHAL GANGWARNo ratings yet
- ProblemsDocument35 pagesProblemsAhmed Adel IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Boiler EfficiencyDocument14 pagesCalculation of Boiler EfficiencyBharat Choksi100% (1)
- Furnace Heater DesignDocument7 pagesFurnace Heater Designhassanzohaib7823No ratings yet
- HVAC Calculation Engine Room Airflow CapacityDocument2 pagesHVAC Calculation Engine Room Airflow Capacityiqbal_syawalNo ratings yet
- (235795183) Heat Balance Sheet On Ic EngineDocument5 pages(235795183) Heat Balance Sheet On Ic EngineSivi NallamothuNo ratings yet
- IGCC Power Plant Second Report (Repaired)Document9 pagesIGCC Power Plant Second Report (Repaired)Annas FauzyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9,10,11Document50 pagesChapter 9,10,11myra091100% (1)
- 4.10.4 Performance Evaluation of BoilersDocument7 pages4.10.4 Performance Evaluation of BoilersGanti AsegarNo ratings yet
- Boiler Eff SolutionsDocument11 pagesBoiler Eff SolutionsnpNo ratings yet
- Absorption Chiller Energy CalculationsDocument2 pagesAbsorption Chiller Energy CalculationsSarah SamuelNo ratings yet
- Process Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersFrom EverandProcess Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Energy Conversion for Electricity and Coproducts: Principles, Technologies, and EquipmentFrom EverandSustainable Energy Conversion for Electricity and Coproducts: Principles, Technologies, and EquipmentNo ratings yet
- CamscannerDocument17 pagesCamscannerAmit KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Process PlanningDocument4 pagesProcess PlanningAmit KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Inventory Control 1Document16 pagesInventory Control 1Amit KhadkaNo ratings yet
- New - vc0 ReportDocument9 pagesNew - vc0 ReportAmit KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document74 pagesChapter 1Amit KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Compounding of Steam TurbineDocument8 pagesCompounding of Steam TurbineAmit KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Pump Part 2Document35 pagesPump Part 2Amit KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Pump Part 1Document82 pagesPump Part 1Amit KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument77 pagesSteam TurbineAmit Khadka100% (2)
- Water Turbines Part 1Document42 pagesWater Turbines Part 1Amit KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Water Turbines Part 2Document39 pagesWater Turbines Part 2Amit KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Hydroelectric PowerplantDocument47 pagesHydroelectric PowerplantAmit KhadkaNo ratings yet
- SOM Tutorial3Document18 pagesSOM Tutorial3Amit KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Numerical Related To Correlation and RegressionDocument16 pagesNumerical Related To Correlation and RegressionAmit KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Old-Question For Mechanical Engineering 2nd Year 4th SemDocument123 pagesOld-Question For Mechanical Engineering 2nd Year 4th SemAmit KhadkaNo ratings yet