Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP 3
NCP 3
Uploaded by
May Chelle ErazoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Gmail - The Acne Cure That No One Is Talking AboutDocument15 pagesGmail - The Acne Cure That No One Is Talking AboutbenmalisoffNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Risk For Skin BreakdownDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Risk For Skin BreakdownShelli Miller Pryor82% (11)
- Nursing Care Plan ConstipationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan ConstipationkazelleNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea (AGE)Document2 pagesDiarrhea (AGE)NursesLabs.com100% (1)
- Assessment Healt H Patte RN Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome (Edit) Intervention (Edit) Evaluation (EDIT) Rema RKSDocument3 pagesAssessment Healt H Patte RN Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome (Edit) Intervention (Edit) Evaluation (EDIT) Rema RKStflorenzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Outcome Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Outcome Intervention Rationale EvaluationMarivic Yuson MalagarNo ratings yet
- CONSTIPATIONDocument4 pagesCONSTIPATIONKarl Angelo MontanoNo ratings yet
- NCP Case 6Document1 pageNCP Case 6Eduard GarchitorenaNo ratings yet
- Nausea: Definition: A Subjective Unpleasant, Wavelike Sensation in The Back of The Throat, EpigastriumDocument14 pagesNausea: Definition: A Subjective Unpleasant, Wavelike Sensation in The Back of The Throat, EpigastriumK Jayakumar KandasamyNo ratings yet
- University of Eastern Philippines: University Town, Northern SamarDocument5 pagesUniversity of Eastern Philippines: University Town, Northern SamarJane MinNo ratings yet
- PeristalticDocument2 pagesPeristalticAllyzah Faith BernalesNo ratings yet
- Constipation: Patient Name: Shehzad Age: 45 Ward: Emergency BDocument2 pagesConstipation: Patient Name: Shehzad Age: 45 Ward: Emergency BShafiq Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- NCP Materna2 NutriDocument2 pagesNCP Materna2 Nutrigoodemonz15No ratings yet
- ConstipationDocument2 pagesConstipationBheru LalNo ratings yet
- DIARRHEADocument2 pagesDIARRHEADanielNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan 1Denise GabatoNo ratings yet
- NCP of Patient With GastritisDocument4 pagesNCP of Patient With GastritisBer AnneNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesDiarrhea Nursing Care PlanKrizha Angela NicolasNo ratings yet
- Defining Characteristics Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesDefining Characteristics Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationEduard GarchitorenaNo ratings yet
- NCP Nausea and VomitingDocument4 pagesNCP Nausea and VomitingKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan of IonDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan of IonvhentesixNo ratings yet
- NCP (Diarrhea)Document2 pagesNCP (Diarrhea)Rodj Bilang Jr.83% (30)
- A Nursing Care Plan On: Loose Bowel MovementDocument6 pagesA Nursing Care Plan On: Loose Bowel MovementakoitsmeNo ratings yet
- Activity On Care PlanningDocument4 pagesActivity On Care PlanningRichlle CortesNo ratings yet
- Age NCPDocument3 pagesAge NCPMartin Allen ClaudioNo ratings yet
- Patient'S Intials: A.M.B Age: 19 Sex: Male PATIENT'S DIAGNOSIS: AGE (Acute Gastroenteritis)Document1 pagePatient'S Intials: A.M.B Age: 19 Sex: Male PATIENT'S DIAGNOSIS: AGE (Acute Gastroenteritis)Markus Tobias CarreonNo ratings yet
- Activity 5 NCPDocument5 pagesActivity 5 NCPAl-Mujib TanogNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1BSN 14 Group 1Document8 pagesNursing Care Plan 1BSN 14 Group 1Mikaella GacostaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SorbitolDocument2 pagesDrug Study SorbitolみずNo ratings yet
- Ate Gabs Nyo Pagod NaDocument3 pagesAte Gabs Nyo Pagod NaGabrielle EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Bowel Incontinence ConstipationDocument3 pagesBowel Incontinence ConstipationMatty-b AskalaniNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - CancerDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan - CancerChristineAla0% (1)
- Activity On Care PlanningDocument4 pagesActivity On Care PlanningRichlle CortesNo ratings yet
- Diet in Benign Colonic Disorders: A Narrative ReviewDocument14 pagesDiet in Benign Colonic Disorders: A Narrative ReviewHouda LaatabiNo ratings yet
- INtususs Nursing DiagDocument5 pagesINtususs Nursing DiagVictoria EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term Goal: IndependentDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term Goal: IndependentEva Marielle CezaldoNo ratings yet
- NCP Con ConstipationDocument2 pagesNCP Con ConstipationChristine Marie Bucio OraizNo ratings yet
- DiarrheaDocument3 pagesDiarrheaBert GasalNo ratings yet
- NCP ConstipationDocument2 pagesNCP ConstipationFaith Bingan Remiscal67% (6)
- GROUP 2 - Class 1A - NCP of DiarrheaDocument4 pagesGROUP 2 - Class 1A - NCP of DiarrheaOrin Qadriatul NursyiNo ratings yet
- Constipation LeukemiaDocument1 pageConstipation LeukemiamawelNo ratings yet
- Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements Diabetes NCP PDFDocument5 pagesImbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements Diabetes NCP PDFashamy acolNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Subjective: Objective: General Objective: Independent IndependentDocument10 pagesCase Study: Subjective: Objective: General Objective: Independent IndependentChristine EmanNo ratings yet
- Afinidad, Jiezl A: Davao Doctors College Nursing ProgramDocument4 pagesAfinidad, Jiezl A: Davao Doctors College Nursing ProgramJiezl Abellano AfinidadNo ratings yet
- Final - Food PoisoningDocument10 pagesFinal - Food PoisoningCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit Related To Nausea and VomitDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Related To Nausea and VomitJakeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis and Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis and Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjay kusainNo ratings yet
- University of The East Ramon Magsaysay Memorial Medical Center, Inc. College of NursingDocument23 pagesUniversity of The East Ramon Magsaysay Memorial Medical Center, Inc. College of NursingReina RamonesNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Nursing Diagnoses & Care PlansDocument7 pagesDigestive System Nursing Diagnoses & Care PlansyormahdNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Bloating: Is It All in The Gas?Document6 pagesAbdominal Bloating: Is It All in The Gas?danny17phNo ratings yet
- NCP Acabo Hypokalemia 1Document2 pagesNCP Acabo Hypokalemia 1Doneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- NcpsDocument10 pagesNcpskotoirNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Objective Data: Short Term: Independent: Short Term: Goal Partially MetDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Objective Data: Short Term: Independent: Short Term: Goal Partially MetCess YNo ratings yet
- JVJV NCP Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesJVJV NCP Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitvicenteturasNo ratings yet
- Bioavailabilitas Per OralDocument16 pagesBioavailabilitas Per OralCathleya RestuNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document3 pagesNCP 1Mary Antonette Adriano EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Teaching Plan (Diet and Treatment)Document6 pagesTeaching Plan (Diet and Treatment)King Aldus ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea What To Look Out ForDocument15 pagesDiarrhea What To Look Out ForSiraf IldaNo ratings yet
- FiberCon (Polycarbophil)Document1 pageFiberCon (Polycarbophil)ENo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal System: Chapter EighteenDocument32 pagesGastrointestinal System: Chapter Eighteenhayascent hilarioNo ratings yet
- Need/Nursing Diagnosis/Cues Need: Physiologic Need Nursing Diagnosis: - Nutrition ImbalancedDocument1 pageNeed/Nursing Diagnosis/Cues Need: Physiologic Need Nursing Diagnosis: - Nutrition ImbalancedmawelNo ratings yet
- NICU Drug StudyDocument2 pagesNICU Drug StudyMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- The Measurement of Quality of Life ConceptualizatiDocument61 pagesThe Measurement of Quality of Life ConceptualizatiMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Cover Page CHNDocument1 pageCover Page CHNMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- COA Problem IdentifiedDocument1 pageCOA Problem IdentifiedMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- COA LEVEL III NutritionsollyDocument6 pagesCOA LEVEL III NutritionsollyMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- School Nurse InterviewDocument3 pagesSchool Nurse InterviewMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Fluid Therapy For 2nd Year ConceptDocument83 pagesIntravenous Fluid Therapy For 2nd Year ConceptMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Family Case PresentationDocument32 pagesFamily Case PresentationMay Chelle Erazo0% (2)
- QUINTANO CHN Home Visit Plan-3Document2 pagesQUINTANO CHN Home Visit Plan-3May Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Diet Recommendation GelocaguiralDocument1 pageDiet Recommendation GelocaguiralMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Isolation Precautions (CD Tech)Document7 pagesIsolation Precautions (CD Tech)May Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Coping Index FCPDocument1 pageCoping Index FCPMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Disorders Assessment Methods 2Document27 pagesEndocrine Disorders Assessment Methods 2May Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Father Saturnino Urios University: Nursing ProgramDocument5 pagesFather Saturnino Urios University: Nursing ProgramMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Family Case PresentationDocument61 pagesFamily Case PresentationMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Case KitDocument6 pagesGeriatric Case KitMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Individual Case Study GDDocument9 pagesIndividual Case Study GDMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- CMCR Rle Bse UeDocument8 pagesCMCR Rle Bse UeMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Father Saturnino Urios University Nursing Program Urian Health Center Individual Treatment RecordDocument5 pagesFather Saturnino Urios University Nursing Program Urian Health Center Individual Treatment RecordMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System Review MSDocument39 pagesThe Endocrine System Review MSMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- G8 - Watchers Class NutritionDocument10 pagesG8 - Watchers Class NutritionMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Evidence-Based ReportDocument1 pageEvidence-Based ReportMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Diets 2Document17 pagesTherapeutic Diets 2May Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Diets 1Document19 pagesTherapeutic Diets 1May Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Dermatologic Agents Integumentary System FunctionsDocument3 pagesDermatologic Agents Integumentary System FunctionsMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Quiz Drug Approval ProcessDocument4 pagesQuiz Drug Approval ProcessMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Infant Tub BathDocument47 pagesInfant Tub BathMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Theology 110: Prof. Arniel M. Iway, PH.DDocument31 pagesTheology 110: Prof. Arniel M. Iway, PH.DMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Postmortem CareDocument2 pagesPostmortem CareMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Theology 110: Prof. Arniel M. Iway, PH.DDocument20 pagesTheology 110: Prof. Arniel M. Iway, PH.DMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Gordon'S Pattern of Functioning Before Hospitalization During Hospitalization Health PerceptionDocument3 pagesGordon'S Pattern of Functioning Before Hospitalization During Hospitalization Health PerceptionTintin TagupaNo ratings yet
- New Eat Healthy Stay HealthyDocument48 pagesNew Eat Healthy Stay HealthyArun Mathew RajuNo ratings yet
- The Components of School Health ProgramDocument2 pagesThe Components of School Health ProgramTRINA FATNo ratings yet
- Nutrition After Severe Burn Injury.7Document6 pagesNutrition After Severe Burn Injury.7Carlos GomesNo ratings yet
- ResultsDocument13 pagesResultsAgnes MilomNo ratings yet
- 2011 Guideline On Xylitol Use in Caries Prevention.Document3 pages2011 Guideline On Xylitol Use in Caries Prevention.Jinx Pro AmandaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Lesson 2 - Group 9Document23 pagesChapter 3 Lesson 2 - Group 9LalicanTeresa 1BTLEDANo ratings yet
- Interview ChecklistDocument4 pagesInterview ChecklistGreizen John ViloriaNo ratings yet
- 12 Health Benefits of BeetrootDocument2 pages12 Health Benefits of BeetrootjosdanasNo ratings yet
- 3 NRH Operational Guideline-Final 2070Document20 pages3 NRH Operational Guideline-Final 2070Pradip kumar yadavNo ratings yet
- Samantaray 1997Document9 pagesSamantaray 1997Chimo PissangNo ratings yet
- Impact of GMO's ContributionDocument31 pagesImpact of GMO's ContributionVanessa NicolNo ratings yet
- Government PoliciesDocument2 pagesGovernment PoliciesShaira Santito Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Sustainability Report CompleteDocument51 pagesSustainability Report CompleteTrang ĐỗNo ratings yet
- RPT DLP T3Document26 pagesRPT DLP T3ANDRIANNo ratings yet
- Full Download Human Nutrition Science For Healthy Living 1st Edition Stephenson Solutions ManualDocument31 pagesFull Download Human Nutrition Science For Healthy Living 1st Edition Stephenson Solutions Manualnobbilytiverj5s7100% (36)
- Weightloss TricksDocument13 pagesWeightloss TricksCHIMDIUTO OKOLINo ratings yet
- Module 1 - ReviewerDocument12 pagesModule 1 - ReviewerClaire GargaritaNo ratings yet
- Project PlanDocument2 pagesProject PlanCHAI XIAO LING MoeNo ratings yet
- My ReportDocument80 pagesMy ReportSujith StephenNo ratings yet
- Corn Coffee FinalDocument85 pagesCorn Coffee FinalNhelia Santos Bañaga100% (1)
- COLLABORATION AND NETWORKING - PPTXC K SIMANGO-1Document56 pagesCOLLABORATION AND NETWORKING - PPTXC K SIMANGO-1LeahNo ratings yet
- Dr. Catherine W. Kisavi-Atatah (PH.D.), Dr. Park E. Atatah (PH.D.), Dr. Angela Branch-Vital (PH.D.)Document20 pagesDr. Catherine W. Kisavi-Atatah (PH.D.), Dr. Park E. Atatah (PH.D.), Dr. Angela Branch-Vital (PH.D.)Ijahss JournalNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Influence of Advertisement On Food Habits of Children in Moga CityDocument54 pagesProject Report On Influence of Advertisement On Food Habits of Children in Moga CityKanwar Vishawjeet100% (1)
- Bus 5910 Written Assignment Unit 6Document10 pagesBus 5910 Written Assignment Unit 6Sheu BasharuNo ratings yet
- Healthy Living: A Teacher's Guide To PKU (Phenylketonuria)Document2 pagesHealthy Living: A Teacher's Guide To PKU (Phenylketonuria)Ana ĐorđijevskiNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal NutritionDocument37 pagesPlant and Animal Nutritionglaiza abucayNo ratings yet
- Nutrients: Food Timing, Circadian Rhythm and Chrononutrition: A Systematic Review of Time-Restricted Eating's EDocument15 pagesNutrients: Food Timing, Circadian Rhythm and Chrononutrition: A Systematic Review of Time-Restricted Eating's EvicenteNo ratings yet
NCP 3
NCP 3
Uploaded by
May Chelle ErazoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCP 3
NCP 3
Uploaded by
May Chelle ErazoCopyright:
Available Formats
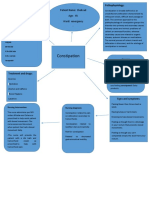
NURSING CARE PLAN NO.
Cues Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Subjective: Dysfunctional Within 4 hours of Independent interventions: Within 4 hours of
Patient verbalizes gastrointestinal nursing 1. Note the presence of 1. These conditions nursing
feeling full and motility r/t intervention, the long-term disorders are associated with intervention, the
tight, and gastroenteritis patient will be able such as GERD, hiatal increased, patient was be
intermittent pain in to reestablish and hernia, inflammatory decreased, or able to reestablish
her abdomen maintain normal bowel, and ineffective and maintain
pattern of bowel malabsorption. peristaltic activity. normal pattern of
Objective: functioning bowel functioning
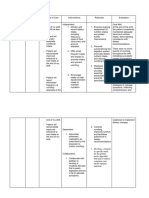
- Abdominal 2. Note lifestyle such as 2. To identify issues
pain travelling to areas with that can affect GI
- Abdominal contaminated food or functioning and
bloating water, poor sanitary health.
- Nausea and living conditions,
vomiting overeating, or intake of
- Hyperthermic foods associated with
- Pale looking gastric diseases.
3. Inspect, auscultate, 3. To identify
percuss, and palpate distension of
abdomen. bowel, distinguish
bowel sounds, and
note any presence
of masses or
enlarged organs.
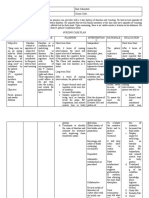
4. Measure GI input and 4. Manage fluid
output and note losses and
characteristics of replacement needs
drainage. and electrolyte
balances.
5. Help indicates
5. Encourage patient to worsening of
report changes in nature condition,
or intensity of pain. requiring more
intensive
interventions.
6. To enhance muscle
6. Encourage relaxation and
nonpharmacological reduce discomfort.
interventions such as
positioning, back rub, or
heating pad.
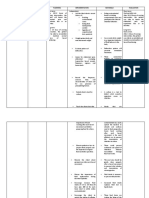
7. The patient may
7. Discuss dietary elect to make
recommendations with adaptations in food
patient and significant choices and eating
others. habits to avoid GI
complications.
Dependent interventions: 8. To relieve pain.
8. Manage pain with
medications as ordered.
9. To replace losses
9. Administer fluid and and to improve GI
electrolytes as circulation and
indicated. function.
10. To reduce the
10. Administer prescribed potential for GI
prophylactic complications such
medications as ordered. as bleeding,
ulcerations of
stomach mucosa,
and viral diarrheas.
Collaborative interventions: 11. To provide diet
11. Collaborate with sufficient in
dietitian or nutritionist. nutrients by best
possible route –
oral, enteral, or
parenteral.
12. To correct or treat
12. Collaborate in treatment disorders
of underlying conditions. associated with
patient’s current GI
dysfunction.
You might also like
- Gmail - The Acne Cure That No One Is Talking AboutDocument15 pagesGmail - The Acne Cure That No One Is Talking AboutbenmalisoffNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Risk For Skin BreakdownDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Risk For Skin BreakdownShelli Miller Pryor82% (11)
- Nursing Care Plan ConstipationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan ConstipationkazelleNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea (AGE)Document2 pagesDiarrhea (AGE)NursesLabs.com100% (1)
- Assessment Healt H Patte RN Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome (Edit) Intervention (Edit) Evaluation (EDIT) Rema RKSDocument3 pagesAssessment Healt H Patte RN Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome (Edit) Intervention (Edit) Evaluation (EDIT) Rema RKStflorenzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Outcome Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Outcome Intervention Rationale EvaluationMarivic Yuson MalagarNo ratings yet
- CONSTIPATIONDocument4 pagesCONSTIPATIONKarl Angelo MontanoNo ratings yet
- NCP Case 6Document1 pageNCP Case 6Eduard GarchitorenaNo ratings yet
- Nausea: Definition: A Subjective Unpleasant, Wavelike Sensation in The Back of The Throat, EpigastriumDocument14 pagesNausea: Definition: A Subjective Unpleasant, Wavelike Sensation in The Back of The Throat, EpigastriumK Jayakumar KandasamyNo ratings yet
- University of Eastern Philippines: University Town, Northern SamarDocument5 pagesUniversity of Eastern Philippines: University Town, Northern SamarJane MinNo ratings yet
- PeristalticDocument2 pagesPeristalticAllyzah Faith BernalesNo ratings yet
- Constipation: Patient Name: Shehzad Age: 45 Ward: Emergency BDocument2 pagesConstipation: Patient Name: Shehzad Age: 45 Ward: Emergency BShafiq Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- NCP Materna2 NutriDocument2 pagesNCP Materna2 Nutrigoodemonz15No ratings yet
- ConstipationDocument2 pagesConstipationBheru LalNo ratings yet
- DIARRHEADocument2 pagesDIARRHEADanielNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan 1Denise GabatoNo ratings yet
- NCP of Patient With GastritisDocument4 pagesNCP of Patient With GastritisBer AnneNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesDiarrhea Nursing Care PlanKrizha Angela NicolasNo ratings yet
- Defining Characteristics Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesDefining Characteristics Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationEduard GarchitorenaNo ratings yet
- NCP Nausea and VomitingDocument4 pagesNCP Nausea and VomitingKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan of IonDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan of IonvhentesixNo ratings yet
- NCP (Diarrhea)Document2 pagesNCP (Diarrhea)Rodj Bilang Jr.83% (30)
- A Nursing Care Plan On: Loose Bowel MovementDocument6 pagesA Nursing Care Plan On: Loose Bowel MovementakoitsmeNo ratings yet
- Activity On Care PlanningDocument4 pagesActivity On Care PlanningRichlle CortesNo ratings yet
- Age NCPDocument3 pagesAge NCPMartin Allen ClaudioNo ratings yet
- Patient'S Intials: A.M.B Age: 19 Sex: Male PATIENT'S DIAGNOSIS: AGE (Acute Gastroenteritis)Document1 pagePatient'S Intials: A.M.B Age: 19 Sex: Male PATIENT'S DIAGNOSIS: AGE (Acute Gastroenteritis)Markus Tobias CarreonNo ratings yet
- Activity 5 NCPDocument5 pagesActivity 5 NCPAl-Mujib TanogNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1BSN 14 Group 1Document8 pagesNursing Care Plan 1BSN 14 Group 1Mikaella GacostaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SorbitolDocument2 pagesDrug Study SorbitolみずNo ratings yet
- Ate Gabs Nyo Pagod NaDocument3 pagesAte Gabs Nyo Pagod NaGabrielle EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Bowel Incontinence ConstipationDocument3 pagesBowel Incontinence ConstipationMatty-b AskalaniNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - CancerDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan - CancerChristineAla0% (1)
- Activity On Care PlanningDocument4 pagesActivity On Care PlanningRichlle CortesNo ratings yet
- Diet in Benign Colonic Disorders: A Narrative ReviewDocument14 pagesDiet in Benign Colonic Disorders: A Narrative ReviewHouda LaatabiNo ratings yet
- INtususs Nursing DiagDocument5 pagesINtususs Nursing DiagVictoria EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term Goal: IndependentDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term Goal: IndependentEva Marielle CezaldoNo ratings yet
- NCP Con ConstipationDocument2 pagesNCP Con ConstipationChristine Marie Bucio OraizNo ratings yet
- DiarrheaDocument3 pagesDiarrheaBert GasalNo ratings yet
- NCP ConstipationDocument2 pagesNCP ConstipationFaith Bingan Remiscal67% (6)
- GROUP 2 - Class 1A - NCP of DiarrheaDocument4 pagesGROUP 2 - Class 1A - NCP of DiarrheaOrin Qadriatul NursyiNo ratings yet
- Constipation LeukemiaDocument1 pageConstipation LeukemiamawelNo ratings yet
- Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements Diabetes NCP PDFDocument5 pagesImbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements Diabetes NCP PDFashamy acolNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Subjective: Objective: General Objective: Independent IndependentDocument10 pagesCase Study: Subjective: Objective: General Objective: Independent IndependentChristine EmanNo ratings yet
- Afinidad, Jiezl A: Davao Doctors College Nursing ProgramDocument4 pagesAfinidad, Jiezl A: Davao Doctors College Nursing ProgramJiezl Abellano AfinidadNo ratings yet
- Final - Food PoisoningDocument10 pagesFinal - Food PoisoningCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit Related To Nausea and VomitDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Related To Nausea and VomitJakeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis and Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis and Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjay kusainNo ratings yet
- University of The East Ramon Magsaysay Memorial Medical Center, Inc. College of NursingDocument23 pagesUniversity of The East Ramon Magsaysay Memorial Medical Center, Inc. College of NursingReina RamonesNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Nursing Diagnoses & Care PlansDocument7 pagesDigestive System Nursing Diagnoses & Care PlansyormahdNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Bloating: Is It All in The Gas?Document6 pagesAbdominal Bloating: Is It All in The Gas?danny17phNo ratings yet
- NCP Acabo Hypokalemia 1Document2 pagesNCP Acabo Hypokalemia 1Doneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- NcpsDocument10 pagesNcpskotoirNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Objective Data: Short Term: Independent: Short Term: Goal Partially MetDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Objective Data: Short Term: Independent: Short Term: Goal Partially MetCess YNo ratings yet
- JVJV NCP Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesJVJV NCP Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitvicenteturasNo ratings yet
- Bioavailabilitas Per OralDocument16 pagesBioavailabilitas Per OralCathleya RestuNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document3 pagesNCP 1Mary Antonette Adriano EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Teaching Plan (Diet and Treatment)Document6 pagesTeaching Plan (Diet and Treatment)King Aldus ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea What To Look Out ForDocument15 pagesDiarrhea What To Look Out ForSiraf IldaNo ratings yet
- FiberCon (Polycarbophil)Document1 pageFiberCon (Polycarbophil)ENo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal System: Chapter EighteenDocument32 pagesGastrointestinal System: Chapter Eighteenhayascent hilarioNo ratings yet
- Need/Nursing Diagnosis/Cues Need: Physiologic Need Nursing Diagnosis: - Nutrition ImbalancedDocument1 pageNeed/Nursing Diagnosis/Cues Need: Physiologic Need Nursing Diagnosis: - Nutrition ImbalancedmawelNo ratings yet
- NICU Drug StudyDocument2 pagesNICU Drug StudyMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- The Measurement of Quality of Life ConceptualizatiDocument61 pagesThe Measurement of Quality of Life ConceptualizatiMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Cover Page CHNDocument1 pageCover Page CHNMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- COA Problem IdentifiedDocument1 pageCOA Problem IdentifiedMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- COA LEVEL III NutritionsollyDocument6 pagesCOA LEVEL III NutritionsollyMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- School Nurse InterviewDocument3 pagesSchool Nurse InterviewMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Fluid Therapy For 2nd Year ConceptDocument83 pagesIntravenous Fluid Therapy For 2nd Year ConceptMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Family Case PresentationDocument32 pagesFamily Case PresentationMay Chelle Erazo0% (2)
- QUINTANO CHN Home Visit Plan-3Document2 pagesQUINTANO CHN Home Visit Plan-3May Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Diet Recommendation GelocaguiralDocument1 pageDiet Recommendation GelocaguiralMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Isolation Precautions (CD Tech)Document7 pagesIsolation Precautions (CD Tech)May Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Coping Index FCPDocument1 pageCoping Index FCPMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Disorders Assessment Methods 2Document27 pagesEndocrine Disorders Assessment Methods 2May Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Father Saturnino Urios University: Nursing ProgramDocument5 pagesFather Saturnino Urios University: Nursing ProgramMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Family Case PresentationDocument61 pagesFamily Case PresentationMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Case KitDocument6 pagesGeriatric Case KitMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Individual Case Study GDDocument9 pagesIndividual Case Study GDMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- CMCR Rle Bse UeDocument8 pagesCMCR Rle Bse UeMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Father Saturnino Urios University Nursing Program Urian Health Center Individual Treatment RecordDocument5 pagesFather Saturnino Urios University Nursing Program Urian Health Center Individual Treatment RecordMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System Review MSDocument39 pagesThe Endocrine System Review MSMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- G8 - Watchers Class NutritionDocument10 pagesG8 - Watchers Class NutritionMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Evidence-Based ReportDocument1 pageEvidence-Based ReportMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Diets 2Document17 pagesTherapeutic Diets 2May Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Diets 1Document19 pagesTherapeutic Diets 1May Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Dermatologic Agents Integumentary System FunctionsDocument3 pagesDermatologic Agents Integumentary System FunctionsMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Quiz Drug Approval ProcessDocument4 pagesQuiz Drug Approval ProcessMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Infant Tub BathDocument47 pagesInfant Tub BathMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Theology 110: Prof. Arniel M. Iway, PH.DDocument31 pagesTheology 110: Prof. Arniel M. Iway, PH.DMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Postmortem CareDocument2 pagesPostmortem CareMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Theology 110: Prof. Arniel M. Iway, PH.DDocument20 pagesTheology 110: Prof. Arniel M. Iway, PH.DMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Gordon'S Pattern of Functioning Before Hospitalization During Hospitalization Health PerceptionDocument3 pagesGordon'S Pattern of Functioning Before Hospitalization During Hospitalization Health PerceptionTintin TagupaNo ratings yet
- New Eat Healthy Stay HealthyDocument48 pagesNew Eat Healthy Stay HealthyArun Mathew RajuNo ratings yet
- The Components of School Health ProgramDocument2 pagesThe Components of School Health ProgramTRINA FATNo ratings yet
- Nutrition After Severe Burn Injury.7Document6 pagesNutrition After Severe Burn Injury.7Carlos GomesNo ratings yet
- ResultsDocument13 pagesResultsAgnes MilomNo ratings yet
- 2011 Guideline On Xylitol Use in Caries Prevention.Document3 pages2011 Guideline On Xylitol Use in Caries Prevention.Jinx Pro AmandaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Lesson 2 - Group 9Document23 pagesChapter 3 Lesson 2 - Group 9LalicanTeresa 1BTLEDANo ratings yet
- Interview ChecklistDocument4 pagesInterview ChecklistGreizen John ViloriaNo ratings yet
- 12 Health Benefits of BeetrootDocument2 pages12 Health Benefits of BeetrootjosdanasNo ratings yet
- 3 NRH Operational Guideline-Final 2070Document20 pages3 NRH Operational Guideline-Final 2070Pradip kumar yadavNo ratings yet
- Samantaray 1997Document9 pagesSamantaray 1997Chimo PissangNo ratings yet
- Impact of GMO's ContributionDocument31 pagesImpact of GMO's ContributionVanessa NicolNo ratings yet
- Government PoliciesDocument2 pagesGovernment PoliciesShaira Santito Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Sustainability Report CompleteDocument51 pagesSustainability Report CompleteTrang ĐỗNo ratings yet
- RPT DLP T3Document26 pagesRPT DLP T3ANDRIANNo ratings yet
- Full Download Human Nutrition Science For Healthy Living 1st Edition Stephenson Solutions ManualDocument31 pagesFull Download Human Nutrition Science For Healthy Living 1st Edition Stephenson Solutions Manualnobbilytiverj5s7100% (36)
- Weightloss TricksDocument13 pagesWeightloss TricksCHIMDIUTO OKOLINo ratings yet
- Module 1 - ReviewerDocument12 pagesModule 1 - ReviewerClaire GargaritaNo ratings yet
- Project PlanDocument2 pagesProject PlanCHAI XIAO LING MoeNo ratings yet
- My ReportDocument80 pagesMy ReportSujith StephenNo ratings yet
- Corn Coffee FinalDocument85 pagesCorn Coffee FinalNhelia Santos Bañaga100% (1)
- COLLABORATION AND NETWORKING - PPTXC K SIMANGO-1Document56 pagesCOLLABORATION AND NETWORKING - PPTXC K SIMANGO-1LeahNo ratings yet
- Dr. Catherine W. Kisavi-Atatah (PH.D.), Dr. Park E. Atatah (PH.D.), Dr. Angela Branch-Vital (PH.D.)Document20 pagesDr. Catherine W. Kisavi-Atatah (PH.D.), Dr. Park E. Atatah (PH.D.), Dr. Angela Branch-Vital (PH.D.)Ijahss JournalNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Influence of Advertisement On Food Habits of Children in Moga CityDocument54 pagesProject Report On Influence of Advertisement On Food Habits of Children in Moga CityKanwar Vishawjeet100% (1)
- Bus 5910 Written Assignment Unit 6Document10 pagesBus 5910 Written Assignment Unit 6Sheu BasharuNo ratings yet
- Healthy Living: A Teacher's Guide To PKU (Phenylketonuria)Document2 pagesHealthy Living: A Teacher's Guide To PKU (Phenylketonuria)Ana ĐorđijevskiNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal NutritionDocument37 pagesPlant and Animal Nutritionglaiza abucayNo ratings yet
- Nutrients: Food Timing, Circadian Rhythm and Chrononutrition: A Systematic Review of Time-Restricted Eating's EDocument15 pagesNutrients: Food Timing, Circadian Rhythm and Chrononutrition: A Systematic Review of Time-Restricted Eating's EvicenteNo ratings yet