Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Finals Reviewer
Finals Reviewer
Uploaded by
Aira ArabitCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Media and Information Literacy ReviewerDocument3 pagesMedia and Information Literacy ReviewerJeffsiccion100% (4)
- LV5-1510-20-UL-SLR 1MW/ GFDI/6input/Insul - Monitor: Verdrahtungshinweise Wiring InstructionsDocument113 pagesLV5-1510-20-UL-SLR 1MW/ GFDI/6input/Insul - Monitor: Verdrahtungshinweise Wiring Instructionsedvaldo alves pintoNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 - Module 3: Evolution of Media: I. Multiple ChoiceDocument5 pagesQuarter 1 - Module 3: Evolution of Media: I. Multiple ChoicekarylleNo ratings yet
- STS Module 5-6Document3 pagesSTS Module 5-6なるNo ratings yet
- Module 5communication and TechnologylovelyDocument9 pagesModule 5communication and TechnologylovelyLyca jean PascuaNo ratings yet
- Knowing Your Media at Different AgesDocument2 pagesKnowing Your Media at Different AgesWanwanNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 MIL Week4Document11 pagesGrade 12 MIL Week4rambo tanNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 - MIL - Q1 - Week4 Final EditDocument12 pagesGrade 12 - MIL - Q1 - Week4 Final EditJomari BandilloNo ratings yet
- WEEK 3 - ULOhDocument2 pagesWEEK 3 - ULOhNOLIMAR CAMPOSANONo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy Week 3Document5 pagesMedia and Information Literacy Week 3Nicole LealNo ratings yet
- PCOM M8 Communication TechnologyDocument10 pagesPCOM M8 Communication TechnologyjazzieballadoNo ratings yet
- Day 1 AnswersDocument3 pagesDay 1 AnswersRairaiNo ratings yet
- STS ReviewerDocument14 pagesSTS Reviewerdavid.oballasNo ratings yet
- Media and GlobalizationDocument15 pagesMedia and GlobalizationCadim'z Kyelloied0% (1)
- Notes For MITL (Lesson 1)Document2 pagesNotes For MITL (Lesson 1)Nicolette Dream GreenNo ratings yet
- Mod 4Document3 pagesMod 4Zeth Angelo Fernandez BacaocoNo ratings yet
- Nathalie Grace Getino Grade 12-ABM ExecutiveDocument5 pagesNathalie Grace Getino Grade 12-ABM ExecutiveYsai GeverNo ratings yet
- Tugas CL 2Document4 pagesTugas CL 2desiyanitanewNo ratings yet
- Uses of Social Media 1Document2 pagesUses of Social Media 1Niñanne Nicole Baring BalbuenaNo ratings yet
- Media Lit For Print FinalDocument5 pagesMedia Lit For Print FinalJinalyn B. AlvizoNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document11 pagesModule 4Jolly Vee Marie CastilloNo ratings yet
- 5.0 Intended Learning Outcomes and TopicsDocument10 pages5.0 Intended Learning Outcomes and TopicsMon RamNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Media and Its Function UPDATEDDocument10 pagesGroup 4 Media and Its Function UPDATEDRicaJeanLagawanNo ratings yet
- Media Information Literacy Reviewer Introduction To M.I.L. The Influence of Media and Information To CommunicationDocument3 pagesMedia Information Literacy Reviewer Introduction To M.I.L. The Influence of Media and Information To CommunicationMa ChelynNo ratings yet
- Block 2Document94 pagesBlock 2Prabhanshu MishraNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2 Communication in A Changing WorldDocument29 pagesLESSON 2 Communication in A Changing WorldJohnRowenPerjeDianaNo ratings yet
- New Political Media Fake NewsDocument7 pagesNew Political Media Fake NewsLyn BeautyNo ratings yet
- Social Media and Changing RelationshipsDocument1 pageSocial Media and Changing RelationshipsZeeshan Maqbool DanishNo ratings yet
- Globalization in Media Culture ReportDocument16 pagesGlobalization in Media Culture ReportApril Angel Mae ObeñaNo ratings yet
- Mil Reviewer 1Document5 pagesMil Reviewer 1Ali HarrietaNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education: Region VII, Central VisayasDocument5 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education: Region VII, Central VisayasCecille HernandoNo ratings yet
- Module Answers - TrinidadDocument4 pagesModule Answers - TrinidadSamuel Miguel TrinidadNo ratings yet
- The Information AgeDocument15 pagesThe Information AgeCylc Clarence CalubingNo ratings yet
- MIL Reviewer Lesson 1: Lesson 2Document4 pagesMIL Reviewer Lesson 1: Lesson 2jhna mggyNo ratings yet
- MIL Class: Dia Divina B. TabadaDocument38 pagesMIL Class: Dia Divina B. TabadaDia Divina TabadaNo ratings yet
- MIL ReviewerDocument7 pagesMIL ReviewerJuliana Shane OrapNo ratings yet
- Ebook Digital Politics and Culture in Contemporary India The Making of An Info Nation Routledge Advances in Internationalizing Media Studies 1St Edition Biswarup Sen Online PDF All ChapterDocument70 pagesEbook Digital Politics and Culture in Contemporary India The Making of An Info Nation Routledge Advances in Internationalizing Media Studies 1St Edition Biswarup Sen Online PDF All Chaptermichael.long858100% (7)
- SLK 3 Media and Information Literacy 1 PDFDocument19 pagesSLK 3 Media and Information Literacy 1 PDFEmarkzkie Mosra OrecrebNo ratings yet
- Handout For Media LiteracyDocument1 pageHandout For Media LiteracyChristian Joy Elandag JacobeNo ratings yet
- MIL q3-w3-4Document4 pagesMIL q3-w3-4Cyril FaithNo ratings yet
- Has Social Media Helped or Hurt Indonesian Society ?: A. Zulfahmi Eri SusantoDocument7 pagesHas Social Media Helped or Hurt Indonesian Society ?: A. Zulfahmi Eri SusantoAlfi DilaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - Information Age and Social MediaDocument2 pagesLesson 6 - Information Age and Social MediaRaquelMagtalasNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 Week 4: Media and Information LiteracyDocument6 pagesQuarter 1 Week 4: Media and Information LiteracyClar De JesusNo ratings yet
- DLP - COT 2022 - Media & Information Literacy For ScribeDocument5 pagesDLP - COT 2022 - Media & Information Literacy For ScribeAnna Marie ManluluNo ratings yet
- Quarter 01 Act 2Document4 pagesQuarter 01 Act 2franceloiseNo ratings yet
- Meil 1Document59 pagesMeil 1Yssa SayconNo ratings yet
- GE3 - Contemporary-World-Finals-ReviewerDocument8 pagesGE3 - Contemporary-World-Finals-ReviewerKim Klevin MarasiganNo ratings yet
- MidtermhandoutsDocument6 pagesMidtermhandoutsCarlo MontejoNo ratings yet
- Method of Research TPDocument3 pagesMethod of Research TPCallen ManaoatNo ratings yet
- Colegio de La Purisima Concepcion: Intended Learning OutcomesDocument4 pagesColegio de La Purisima Concepcion: Intended Learning OutcomesReyy ArbolerasNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document16 pagesUnit 5pankaj.shukla5432No ratings yet
- Summative Assessment: Answer Key For The Exercises in The LessonDocument3 pagesSummative Assessment: Answer Key For The Exercises in The LessonPrem KukrejaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8: Contemporary WorldDocument5 pagesLesson 8: Contemporary Worldkenchan smithNo ratings yet
- Mil - l2 - Evolution of MediaDocument5 pagesMil - l2 - Evolution of MediaKchieffer Lainell ArcangelNo ratings yet
- Stso Final ReviewerDocument4 pagesStso Final ReviewerHaru ScarfyNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 - MIL - Q1 - Week4 FinalDocument18 pagesGrade 12 - MIL - Q1 - Week4 FinalRaniel John Avila SampianoNo ratings yet
- Stas Final ReviewerDocument8 pagesStas Final ReviewerShane SaynoNo ratings yet
- Meil 2122Document102 pagesMeil 2122Heather GomezNo ratings yet
- Meil 1Document6 pagesMeil 1nhixoleNo ratings yet
- Fin ManDocument2 pagesFin ManAira ArabitNo ratings yet
- SCMDocument4 pagesSCMAira ArabitNo ratings yet
- MIDTERM FinMar 1Document11 pagesMIDTERM FinMar 1Aira ArabitNo ratings yet
- Strama AssessmentDocument4 pagesStrama AssessmentAira ArabitNo ratings yet
- SummationDocument5 pagesSummationAira ArabitNo ratings yet
- Strama AssessmentDocument3 pagesStrama AssessmentAira ArabitNo ratings yet
- Auditing in A Cis Environment-Part 1Document17 pagesAuditing in A Cis Environment-Part 1Aira ArabitNo ratings yet
- Mechanism Mobility and A Local Dimension TestDocument26 pagesMechanism Mobility and A Local Dimension TestSURESH KUMAR APNo ratings yet
- Type-Iv Staff Quarters: SpecificationsDocument3 pagesType-Iv Staff Quarters: SpecificationsLokeswaraRaoNo ratings yet
- F-760-001 HACCP PlanDocument3 pagesF-760-001 HACCP PlanglennysNo ratings yet
- SP Bti CP658 V2.2Document4 pagesSP Bti CP658 V2.2Ry GiNo ratings yet
- Published Article 2Document17 pagesPublished Article 2Bharathi RajaNo ratings yet
- 8066 TOEFL AllDocument42 pages8066 TOEFL AllJimmy_Jambul100% (1)
- Beating The Bonk QuestionsDocument1 pageBeating The Bonk Questionst3xxaNo ratings yet
- Kala-2000 LedDocument2 pagesKala-2000 LedJohnNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study Based On Thermal Efficiency of Solar Air HeatersDocument6 pagesComparative Study Based On Thermal Efficiency of Solar Air Heatershicham El FeroualiNo ratings yet
- Page15 CoscoDocument16 pagesPage15 Coscoaeroamir1No ratings yet
- Design Elements PDFDocument132 pagesDesign Elements PDFestherNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Art HistoryDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 Art HistoryFarhanNo ratings yet
- Verbs List SoundDocument16 pagesVerbs List SoundEliana Zapata RuedaNo ratings yet
- 2bhk Sell in Casa Rio Palava City 909sqf PDFDocument54 pages2bhk Sell in Casa Rio Palava City 909sqf PDFDailydiegestNo ratings yet
- Factsheet - REPowerEU PDFDocument2 pagesFactsheet - REPowerEU PDFconor farrellNo ratings yet
- The Yoga Sutras of PatanjaliDocument23 pagesThe Yoga Sutras of Patanjaliapi-3736105No ratings yet
- Abdel-Salam-2014-Citric Acid Effects On BrainDocument11 pagesAbdel-Salam-2014-Citric Acid Effects On BrainEduard-Marius LungulescuNo ratings yet
- Enventory 1Document11 pagesEnventory 1Albert Jay Oring TuicoNo ratings yet
- IOL Calculation in Complex Corneal ConditionsDocument8 pagesIOL Calculation in Complex Corneal ConditionsShimaa MersalNo ratings yet
- A Legend of The Northland StuffDocument4 pagesA Legend of The Northland StuffAngel B.No ratings yet
- ASTM C 566 Kadar AirDocument2 pagesASTM C 566 Kadar AirBengkulu BetonNo ratings yet
- Site Installation Standard - Ver 20200706Document179 pagesSite Installation Standard - Ver 20200706Kyaw Kyaw WinNo ratings yet
- Q-PCF-12-30-PN 6Document1 pageQ-PCF-12-30-PN 6Camilo Maya PodestaNo ratings yet
- Orthogonally Stiffened Plates Hoppman W.H. 1953Document46 pagesOrthogonally Stiffened Plates Hoppman W.H. 1953Iliyah87No ratings yet
- CSJ HydraulicDocument43 pagesCSJ HydraulicВаня БойкоNo ratings yet
- Saint Gobainseals Omniseal Ses Handbook EuDocument60 pagesSaint Gobainseals Omniseal Ses Handbook EuMuhamed RafficNo ratings yet
- MQB 09 WS 2Document4 pagesMQB 09 WS 2Nasmer BembiNo ratings yet
- s7220b inDocument74 pagess7220b inAndry WayNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Diaphragm WallDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Diaphragm WallSanthosh BabuNo ratings yet
Finals Reviewer
Finals Reviewer
Uploaded by
Aira ArabitOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Finals Reviewer
Finals Reviewer
Uploaded by
Aira ArabitCopyright:
Available Formats
Science Technology and Society Melted mixture of lead, tin, and
antimony at low temp and carved lower
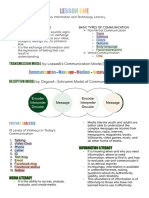
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION AGE
and upper case letters and punctuation
Introduction marks
the transfer of ink from movable type to
How many handwritten books could an
paper was automatic
author produce in a year?
characters were rearrange and reused
Where will these "few" books go now?
during printing
Who can read them?
Overall the printing accommodated 42
How many people can have access to lines per page.
the information written in those books?
What if the contents of a book are so The Information Age
important that without the knowledge it
An individual has the urge to understand
brings, life could be awful?
his commonalities with any other people
The Gutenberg Revolution and the society where he belong
This is a basic need to maintain sanity
Johannes Gutenberg – February 3, and self-worth
1468 (Mainz Germany)
Communication - "commun" (common)
Democratizing Information through his "ication" (understanding) - is a common
printing press understanding of something
The Gutenberg Principle - refers to the The information age Also called
establishment of mass communication Computer Age, Cyber Age or Digital
Age
Gutenberg’s Way of Printing
Information can be effortlessly be
use of wooden block to press ink into obtained or accessed through to
the paper massive publications.
All written materials were produced by Has greatly influenced the life of a
hand. person and the life of a society.
expensive Info easily and quickly shared computer
painstaking task became so powerful
produced a very minimal number of escalated the way of communication,
pages a day transportation, entertainment, culture
Gutenberg's Bible 0.6 % 49 copies - $35 Amplified economy of a society,
million industries, and environment.
Utilized movable text that could produce People are now burdened with
thousands of pages per day. complicated experiences and
confusions
Ten Truth of the Information Age 2. Life dissatisfaction, Negative psychological
effects including envy, materialism, and theft-
1. Media space must eat
tendency.
2. Information must compete
3. The early word gets the perm 3. Lead to personal isolation and severe
4. The frame makes the painting depression
5. selection of viewpoint
4. UK study 62% feelings of inadequacy, 60%
6. newer is equated with ruler
felt jealous.
7. The media cells what the cultures buy
8. You are what you eat and so is your
brain
9. All ideas are seen as controversial
10. anything in great demand will be
OTHER NEGATIVE EFFECTS OF SOCIAL
counterfeited
MEDIA
1. FOMO (Fear of Missing Out)
2. Unrealistic Expectations
3. Unhealthy sleep patterns
The Era of Social Media 4. Cyber bullying
SOCIAL - refers to the interactions OTHER NEGATIVE EFFECTS OF SOCIAL
among people with different levels of MEDIA
communications
1. Efficient channel of communication
MEDIA - instrument that aid
2. Promotion of collaboration via reviews
communication, such as TV, internet,
and opinions
radio, newspaper etc.
3. Business promotion via reviews and
Study shows that people check out their
opinions
phone about 80 times a day. That is at
4. convenient shopping and selling
least every 12 mins.
5. entertainment
NoMoPhobia - No Mobile Phone
6. media sharing and expression of talents
Phobia
and passion
"Facebook Addiction Disorder" - neglect
7. Political activity and news reporting
personal life, social obligations,
8. Streaming of free tutorial for personal
academic duties.
and skill enhancement
RESEARCH FINDINGS ON FACEBOOK USE: 9. artificial intelligence and machine
learning and
1. Researcher from University of Missouri
10. Personal life-story keeping and
Facebook - Symptoms of Depression platforms for blogging.
CHAPTER 2: BIODIVERSITY health problems. These local upheavals
can be causally linked to the changes in
INTRODUCTION
the global ecosystem, and the
The human population has doubled to increasing rate of loss of biodiversity is
7.4 billion since 1960. The population another result.
explosion has a great impact on nature People are experiencing these changes
because of increasing demands for raw over the span of just one lifetime;
materials. Raw materials are used for significant changes and loss of
the production of science and biodiversity are in some places
technological inventions. Also, they are observed and experienced not in terms
used for human consumption to live. of millenniums or centuries but rather
Since the last century, in just a few over decades or years.
decades, concerns about the increasing
WHAT IS BIODIVERSITY?
rate of loss of biodiversity have become
widespread among the public. They The term biodiversity is made up of two
have ceased to be the exclusive roots: Biology, which means "life" in
concern of well-informed person’s Greek and diversity or “variations”.
ecology or biology scientists and Number of species of animals, plants,
experts. and microorganisms, like bacteria and
Indeed, these losses have been other Protista in the ecosystem.
examined in the media, and it is Visible part of biodiversity – There are
becoming common knowledge that the about 1.7 million species that have been
loss of biodiversity is intimately linked to counted by taxonomists.
ecosystem changes, some of which are Not very accessible for study -
already visible and tangible. Microorganisms, like bacteria, are hard
In many places, ordinary people are to identify in their natural habitat
already directly or indirectly coping and A large part of inaccessible marine
adapting to the global atmosphere's biodiversity remains unknown - 95 % of
warming, which is a major change in the oceans are still unexplored.
global ecosystem. In some places, Recent studies estimate the total
people are facing historically number of species between three and
unpredictable flooding of formerly ten million.
inhabited lands or islands; in several Living beings adapt to different
other places, people are facing severe environments everywhere: on land
droughts, the spreading of deserts and deserts, rainforests, or underground
the consequent famine, shortage of galleries; in water, oceans, lakes,
clean drinking water, or unexpected ponds, or some other watercourses.
It is in these environments, also called - Each ecosystem consists of various
ecosystems that living populations types of organisms. They are living
interact with one another and all that are together in a region connected by the
around. So, ecosystems draw on flow of energy and nutrients. The
biological diversity. ultimate source of energy for all types of
ecosystems is the sun.
TYPES OF BIODIVERSITY
The energy from the sun is converted into a
1. GENETIC DIVERSITY
chemical energy by plants through the process
- Genetic diversity pertains to the
of photosynthesis; this energy is used not only
variation of organisms based on their
by plants but by all organisms within the
genetic makeup. The genetic
ecosystem. Plants are eaten by the animals,
constitution of plants is different from the
which are also eaten by some other animals.
genetic designs of animals, protests,
Fungi and bacteria, on the other hand, obtain
bacteria, and fungi. Within each
their energy requirements from the decomposing
kingdom, genetic make-up is also
dead organisms. In turn, they release nutrients
different from one species to another.
back into the soil, which is another requirement
The genetic makeup or codes of
of the plant to live and to continuously
organisms give them specific
manufacture food through photosynthesis. The
characters. The genetic variability is
richness of the ecosystem defines the richness
formed because of the infinite number of
of the organisms living in it. The nonliving
possible combinations of genes within
components of an ecosystem, like temperature,
the DNA.
soil, water system, etc., determine what types of
2. SPECIES DIVERSITY
organisms can survive and thrive. Thus, there
- Species is the basic unit of organisms.
are more organisms in a rainforest where there
Species diversity refers to biodiversity at
are abundant food sources than in Tundra which
the most basic level. It implies variety
is largely composed of ice sheets.
and richness of different types of
organisms at the species level in a given STATUS OF PHILIPPINE BIODIVERSITY
area. It includes all the species on earth
The Philippines is considered a mega
ranging from cyanobacteria, fungi,
diverse country because of its very rich
gymnosperms, angiosperms, different
variety of ecosystems, species, and
type of algae, bryophytes, to simple and
genetic makeup within species.
complex animals and all the accessible
It is driven by being an archipelago,
species including all prokaryotes and
which produces assortments of
eukaryotes.
resources for the organisms.
Many of the islands in the Philippines
3. ECOLOGICAL/ ECOSYSTEM DIVERSITY
are believed to have a great number of
endemic organisms both on land and in ranges, support gene-level and species-
water. level diversity.
In fact, 50% of the 52,177 species found 4. Elevation has an influence on
in the Philippines cannot be found in any biodiversity. Productivity stressors, such
other parts of the world (Philippine as heat and atmospheric pressure,
Biodiversity) Conservation Priorities: A decrease while the other more life-
second iteration of the National supporting factors, such as humidity and
Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan, rainfall increase as elevation increases.
2002). Therefore, in the Philippines' rugged
This makes the Philippines one of the topography, one may find a generous
richest countries in terms of biodiversity offering of biological diversity, especially
compared to any other country on the in the highlands.
planet. Despite being known for rich biodiversity,
There are several geographic and the Philippines is also considered a
ecological characteristics that enable biodiversity hotspot. Being a biodiversity
the Philippines to be rich in biodiversity, hotspot implies the occurrence of threats
supporting 70-80% of the species on the or an alarming rate of destruction of
entire planet. Here are some of the these important resources. Based on the
reasons for a well-distributed diversity of report of the Foundation for the Philippine
species of wild fauna and flora in the Environment, a number of species from
country: different groups are being threatened
through the years.
1. The Philippines is found in the tropics. Some of the causes of this malady
Where the climate supports a high level include, but are not limited to, the
of organic productivity to provide the following:
resources needed by interdependent 1. Urbanization and industrialization. As a
organisms to survive. country that is undergoing modernization,
2. The Philippines has a highly forests and some other wild ecosystems
heterogeneous and complex are being converted into industrialized
topography. Philippine ecological spots.
locations vary from mountain ranges to 2. Overexploitation. The wild animals are in
coral reefs - and everything in between, demand to foreign consumers. This
providing multitudes of plant and animal motivates some people in the country to
species more than adequate space to catch these animals up to the point of
occupy. exploiting them.
3. The isolation created by separate 3. Deforestation. As part of the
islands, as well as peaks of mountain industrialization and urbanization in the
country, a need to cut down trees natural habitats is called Beetle Com. Will
becomes a necessity. It also includes land Burrard-Lucas, a conservation
degradation photographer, has produced a high-tech
4. Climate change and Pollution. See solution in capturing images.
separate lesson for climate change and 3. REMOTE MEASUREMENT TOOLS.- A
pollution in this chapter. stereo-camera system was developed to
get up close, observe, and take precise
TECHNOLOGICAL ADVANCEMENT THAT
measurements among some species such
SUPPORTS BIODIVERSITY
as sharks and crocodiles, for conservation
The innovation and creativity of the people and research efforts. This is a high-tech
is used, together with technological tool that gives measurements with great
advances, in coming up with solutions for accuracy without actually being in contact
preserving biodiversity on earth. It helps with an animal at all.
meeting the end-goal of preventing 4. CONSERVATION DRONES.- Drones are
organisms from becoming endangered, or very helpful for the military in warships.
even extinct. They are also currently used for exposing
1. BETTER MAPPING AND VISUALIZATION. the top view of scenic spots for visual
- Google Earth has been very instrumental entertainment. Recently, an ecologist and a
in locating organisms in inaccessible biologist have created a conservation drone
regions of the earth. It has proven that it is complete with cameras, sensors, and GPS
not just a map to get directions but it is also to map deforestation. Moreover, it was
a real tool that helps conserve and used to count orangutans and some other
preserve species and habitats. This endangered species in Northern Sumatra.
software is powerful in mapping and This is now used as a tool in various
visualizing threats to the survival of those environmental researches.
organisms. 5. GENE SEQUENCING. - Understanding the
2. REMOTE CONTROL PHOTOGRAPHY nature of pathogens or cause of diseases
AND VIDEO. - Getting up close and among animals is important for the right
recording the details and behavior of treatment. Gene sequencing is used to
wildlife in their natural habitat are essential identify pathogens. Scientists are now
to learn about the needs and risks of using high-tech gene-sequencing machines
endangered species. This undertaking was to understand the biology of organisms. It is
very hard to achieve with a blurred likewise used to confirm the grouping of
exposure when remote control photography organisms in a species level.
and video was not yet developed. An
example of technology that has made
possible the viewing of wild animals in their
CHAPTER 3: GENETICALLY MODIFIED 2. Herbicidal Resistance
ORGANISM
3. Fortification
Interesting GMO’s
1. Glow in the dark cat, mice, dogs, pigs, fish, 4. Growth Increase
etc.
2. Super mouse 5. Environmental Resistance
3. Sudden death mosquitoes
4. Featherless chicken 6. Flower Production
5. Web-spinning goats
6. Test tube babies 7. Cosmetic Preservation
Genetically Modified Organisms or widely
Claims of Companies Producing GMO’s
known as GMO – are organisms that have
been altered genetically through genetic
1. There is no known harm in
engineering.
consuming genetically modified foods
Genetic Engineering - Changes the
organism’s phenotypes by using technique that 2. GM foods are developed source of food
will alter genetic make up
Genetic Recombination - Is the exchange of 3. GMOs are easily marketed because of their
genetic material between different organisms improved qualities
which leads to production of offspring with
combinations of traits that differ from those 4. GMOs usually have a lower price, higher
found in either parent durability, and better nutritional value.
5. GM foods have passed risk assessments
Simple Mating – Animals and plants
Genetic Modification - can be done to a wide 6. GMOs are not likely to present risks
range of organisms from microorganisms like for human health
bacteria, to insects, fish, plants, mammals,
among others. Risk of genetic modifies organisms
GM CROPS – new attribute of food products
1. Possible ecological damage –
Purposes: implication for the flow of life in the
environment
1. Pest Resistance
2. Difficult damage control – difficult and
sometimes even impossible to eliminate
3. Adverse effects on the health of people
– possible creation of a new disease.
4. Unpredictable and unintended effects –
unidentified organisms that may cause
wide diseases burden
5. Ethical concerns – ethical issues
adulteration of the concept of natural
order.
You might also like
- Media and Information Literacy ReviewerDocument3 pagesMedia and Information Literacy ReviewerJeffsiccion100% (4)
- LV5-1510-20-UL-SLR 1MW/ GFDI/6input/Insul - Monitor: Verdrahtungshinweise Wiring InstructionsDocument113 pagesLV5-1510-20-UL-SLR 1MW/ GFDI/6input/Insul - Monitor: Verdrahtungshinweise Wiring Instructionsedvaldo alves pintoNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 - Module 3: Evolution of Media: I. Multiple ChoiceDocument5 pagesQuarter 1 - Module 3: Evolution of Media: I. Multiple ChoicekarylleNo ratings yet
- STS Module 5-6Document3 pagesSTS Module 5-6なるNo ratings yet
- Module 5communication and TechnologylovelyDocument9 pagesModule 5communication and TechnologylovelyLyca jean PascuaNo ratings yet
- Knowing Your Media at Different AgesDocument2 pagesKnowing Your Media at Different AgesWanwanNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 MIL Week4Document11 pagesGrade 12 MIL Week4rambo tanNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 - MIL - Q1 - Week4 Final EditDocument12 pagesGrade 12 - MIL - Q1 - Week4 Final EditJomari BandilloNo ratings yet
- WEEK 3 - ULOhDocument2 pagesWEEK 3 - ULOhNOLIMAR CAMPOSANONo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy Week 3Document5 pagesMedia and Information Literacy Week 3Nicole LealNo ratings yet
- PCOM M8 Communication TechnologyDocument10 pagesPCOM M8 Communication TechnologyjazzieballadoNo ratings yet
- Day 1 AnswersDocument3 pagesDay 1 AnswersRairaiNo ratings yet
- STS ReviewerDocument14 pagesSTS Reviewerdavid.oballasNo ratings yet
- Media and GlobalizationDocument15 pagesMedia and GlobalizationCadim'z Kyelloied0% (1)
- Notes For MITL (Lesson 1)Document2 pagesNotes For MITL (Lesson 1)Nicolette Dream GreenNo ratings yet
- Mod 4Document3 pagesMod 4Zeth Angelo Fernandez BacaocoNo ratings yet
- Nathalie Grace Getino Grade 12-ABM ExecutiveDocument5 pagesNathalie Grace Getino Grade 12-ABM ExecutiveYsai GeverNo ratings yet
- Tugas CL 2Document4 pagesTugas CL 2desiyanitanewNo ratings yet
- Uses of Social Media 1Document2 pagesUses of Social Media 1Niñanne Nicole Baring BalbuenaNo ratings yet
- Media Lit For Print FinalDocument5 pagesMedia Lit For Print FinalJinalyn B. AlvizoNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document11 pagesModule 4Jolly Vee Marie CastilloNo ratings yet
- 5.0 Intended Learning Outcomes and TopicsDocument10 pages5.0 Intended Learning Outcomes and TopicsMon RamNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Media and Its Function UPDATEDDocument10 pagesGroup 4 Media and Its Function UPDATEDRicaJeanLagawanNo ratings yet
- Media Information Literacy Reviewer Introduction To M.I.L. The Influence of Media and Information To CommunicationDocument3 pagesMedia Information Literacy Reviewer Introduction To M.I.L. The Influence of Media and Information To CommunicationMa ChelynNo ratings yet
- Block 2Document94 pagesBlock 2Prabhanshu MishraNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2 Communication in A Changing WorldDocument29 pagesLESSON 2 Communication in A Changing WorldJohnRowenPerjeDianaNo ratings yet
- New Political Media Fake NewsDocument7 pagesNew Political Media Fake NewsLyn BeautyNo ratings yet
- Social Media and Changing RelationshipsDocument1 pageSocial Media and Changing RelationshipsZeeshan Maqbool DanishNo ratings yet
- Globalization in Media Culture ReportDocument16 pagesGlobalization in Media Culture ReportApril Angel Mae ObeñaNo ratings yet
- Mil Reviewer 1Document5 pagesMil Reviewer 1Ali HarrietaNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education: Region VII, Central VisayasDocument5 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education: Region VII, Central VisayasCecille HernandoNo ratings yet
- Module Answers - TrinidadDocument4 pagesModule Answers - TrinidadSamuel Miguel TrinidadNo ratings yet
- The Information AgeDocument15 pagesThe Information AgeCylc Clarence CalubingNo ratings yet
- MIL Reviewer Lesson 1: Lesson 2Document4 pagesMIL Reviewer Lesson 1: Lesson 2jhna mggyNo ratings yet
- MIL Class: Dia Divina B. TabadaDocument38 pagesMIL Class: Dia Divina B. TabadaDia Divina TabadaNo ratings yet
- MIL ReviewerDocument7 pagesMIL ReviewerJuliana Shane OrapNo ratings yet
- Ebook Digital Politics and Culture in Contemporary India The Making of An Info Nation Routledge Advances in Internationalizing Media Studies 1St Edition Biswarup Sen Online PDF All ChapterDocument70 pagesEbook Digital Politics and Culture in Contemporary India The Making of An Info Nation Routledge Advances in Internationalizing Media Studies 1St Edition Biswarup Sen Online PDF All Chaptermichael.long858100% (7)
- SLK 3 Media and Information Literacy 1 PDFDocument19 pagesSLK 3 Media and Information Literacy 1 PDFEmarkzkie Mosra OrecrebNo ratings yet
- Handout For Media LiteracyDocument1 pageHandout For Media LiteracyChristian Joy Elandag JacobeNo ratings yet
- MIL q3-w3-4Document4 pagesMIL q3-w3-4Cyril FaithNo ratings yet
- Has Social Media Helped or Hurt Indonesian Society ?: A. Zulfahmi Eri SusantoDocument7 pagesHas Social Media Helped or Hurt Indonesian Society ?: A. Zulfahmi Eri SusantoAlfi DilaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - Information Age and Social MediaDocument2 pagesLesson 6 - Information Age and Social MediaRaquelMagtalasNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 Week 4: Media and Information LiteracyDocument6 pagesQuarter 1 Week 4: Media and Information LiteracyClar De JesusNo ratings yet
- DLP - COT 2022 - Media & Information Literacy For ScribeDocument5 pagesDLP - COT 2022 - Media & Information Literacy For ScribeAnna Marie ManluluNo ratings yet
- Quarter 01 Act 2Document4 pagesQuarter 01 Act 2franceloiseNo ratings yet
- Meil 1Document59 pagesMeil 1Yssa SayconNo ratings yet
- GE3 - Contemporary-World-Finals-ReviewerDocument8 pagesGE3 - Contemporary-World-Finals-ReviewerKim Klevin MarasiganNo ratings yet
- MidtermhandoutsDocument6 pagesMidtermhandoutsCarlo MontejoNo ratings yet
- Method of Research TPDocument3 pagesMethod of Research TPCallen ManaoatNo ratings yet
- Colegio de La Purisima Concepcion: Intended Learning OutcomesDocument4 pagesColegio de La Purisima Concepcion: Intended Learning OutcomesReyy ArbolerasNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document16 pagesUnit 5pankaj.shukla5432No ratings yet
- Summative Assessment: Answer Key For The Exercises in The LessonDocument3 pagesSummative Assessment: Answer Key For The Exercises in The LessonPrem KukrejaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8: Contemporary WorldDocument5 pagesLesson 8: Contemporary Worldkenchan smithNo ratings yet
- Mil - l2 - Evolution of MediaDocument5 pagesMil - l2 - Evolution of MediaKchieffer Lainell ArcangelNo ratings yet
- Stso Final ReviewerDocument4 pagesStso Final ReviewerHaru ScarfyNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 - MIL - Q1 - Week4 FinalDocument18 pagesGrade 12 - MIL - Q1 - Week4 FinalRaniel John Avila SampianoNo ratings yet
- Stas Final ReviewerDocument8 pagesStas Final ReviewerShane SaynoNo ratings yet
- Meil 2122Document102 pagesMeil 2122Heather GomezNo ratings yet
- Meil 1Document6 pagesMeil 1nhixoleNo ratings yet
- Fin ManDocument2 pagesFin ManAira ArabitNo ratings yet
- SCMDocument4 pagesSCMAira ArabitNo ratings yet
- MIDTERM FinMar 1Document11 pagesMIDTERM FinMar 1Aira ArabitNo ratings yet
- Strama AssessmentDocument4 pagesStrama AssessmentAira ArabitNo ratings yet
- SummationDocument5 pagesSummationAira ArabitNo ratings yet
- Strama AssessmentDocument3 pagesStrama AssessmentAira ArabitNo ratings yet
- Auditing in A Cis Environment-Part 1Document17 pagesAuditing in A Cis Environment-Part 1Aira ArabitNo ratings yet
- Mechanism Mobility and A Local Dimension TestDocument26 pagesMechanism Mobility and A Local Dimension TestSURESH KUMAR APNo ratings yet
- Type-Iv Staff Quarters: SpecificationsDocument3 pagesType-Iv Staff Quarters: SpecificationsLokeswaraRaoNo ratings yet
- F-760-001 HACCP PlanDocument3 pagesF-760-001 HACCP PlanglennysNo ratings yet
- SP Bti CP658 V2.2Document4 pagesSP Bti CP658 V2.2Ry GiNo ratings yet
- Published Article 2Document17 pagesPublished Article 2Bharathi RajaNo ratings yet
- 8066 TOEFL AllDocument42 pages8066 TOEFL AllJimmy_Jambul100% (1)
- Beating The Bonk QuestionsDocument1 pageBeating The Bonk Questionst3xxaNo ratings yet
- Kala-2000 LedDocument2 pagesKala-2000 LedJohnNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study Based On Thermal Efficiency of Solar Air HeatersDocument6 pagesComparative Study Based On Thermal Efficiency of Solar Air Heatershicham El FeroualiNo ratings yet
- Page15 CoscoDocument16 pagesPage15 Coscoaeroamir1No ratings yet
- Design Elements PDFDocument132 pagesDesign Elements PDFestherNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Art HistoryDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 Art HistoryFarhanNo ratings yet
- Verbs List SoundDocument16 pagesVerbs List SoundEliana Zapata RuedaNo ratings yet
- 2bhk Sell in Casa Rio Palava City 909sqf PDFDocument54 pages2bhk Sell in Casa Rio Palava City 909sqf PDFDailydiegestNo ratings yet
- Factsheet - REPowerEU PDFDocument2 pagesFactsheet - REPowerEU PDFconor farrellNo ratings yet
- The Yoga Sutras of PatanjaliDocument23 pagesThe Yoga Sutras of Patanjaliapi-3736105No ratings yet
- Abdel-Salam-2014-Citric Acid Effects On BrainDocument11 pagesAbdel-Salam-2014-Citric Acid Effects On BrainEduard-Marius LungulescuNo ratings yet
- Enventory 1Document11 pagesEnventory 1Albert Jay Oring TuicoNo ratings yet
- IOL Calculation in Complex Corneal ConditionsDocument8 pagesIOL Calculation in Complex Corneal ConditionsShimaa MersalNo ratings yet
- A Legend of The Northland StuffDocument4 pagesA Legend of The Northland StuffAngel B.No ratings yet
- ASTM C 566 Kadar AirDocument2 pagesASTM C 566 Kadar AirBengkulu BetonNo ratings yet
- Site Installation Standard - Ver 20200706Document179 pagesSite Installation Standard - Ver 20200706Kyaw Kyaw WinNo ratings yet
- Q-PCF-12-30-PN 6Document1 pageQ-PCF-12-30-PN 6Camilo Maya PodestaNo ratings yet
- Orthogonally Stiffened Plates Hoppman W.H. 1953Document46 pagesOrthogonally Stiffened Plates Hoppman W.H. 1953Iliyah87No ratings yet
- CSJ HydraulicDocument43 pagesCSJ HydraulicВаня БойкоNo ratings yet
- Saint Gobainseals Omniseal Ses Handbook EuDocument60 pagesSaint Gobainseals Omniseal Ses Handbook EuMuhamed RafficNo ratings yet
- MQB 09 WS 2Document4 pagesMQB 09 WS 2Nasmer BembiNo ratings yet
- s7220b inDocument74 pagess7220b inAndry WayNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Diaphragm WallDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Diaphragm WallSanthosh BabuNo ratings yet